Do viruses prolong life?
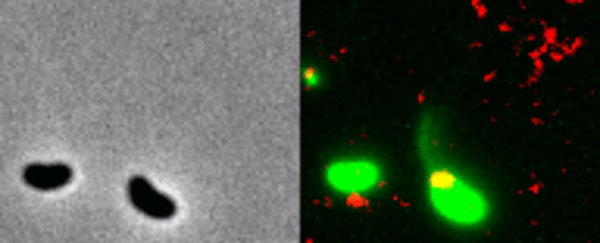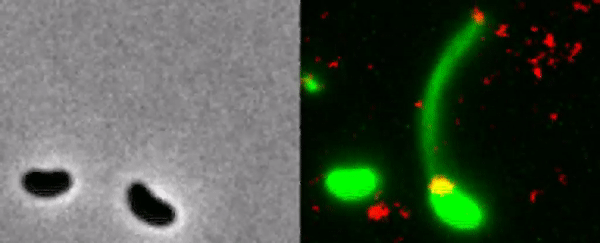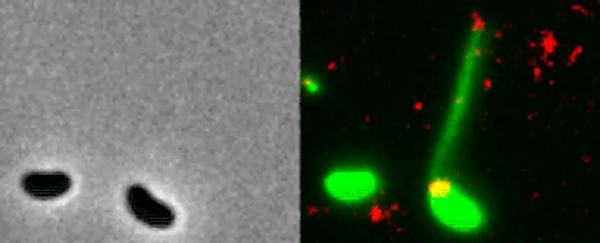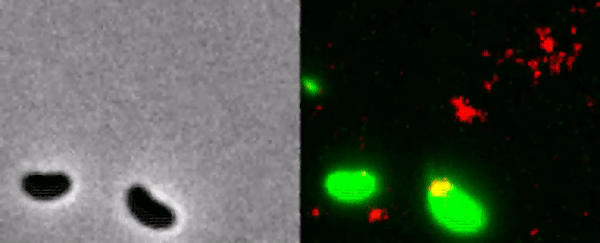
The bacterium catches the DNA of a neighbor.
Viruses are known for their destructive role in biology. However, bacterial DNA viruses may possibly prolong life.
Further, the vitamin theory of aging will be described, in which viruses that are not specific to us and our microbiota are an absolutely necessary source of ATCG (A is adenine; T is thymine; C is cytosine; G is guanine) of nucleotides for DNA repair.
Also, daily dosages of all other mineral ( iron, magnesium, molybdenum, calcium, sodium ...), amino acid ( glutamic acid, lysine ...) and directly vitamins ( ascorbic acid, retinol, nicotinic acid ...) are given and given
Heterotrophic organisms (for example, animals) should receive organic matter in finished form and extract energy from their decay processes (respiration, fermentation). Autotrophic organisms, such as plants, are able to build all the necessary organic substances from simple inorganic precursors (carbon dioxide, water, and mineral salts) and receive energy usually in the form of light (photosynthesis). At the same time, an additional source of energy-expensive molecules for synthesizing is useful for mammals.
Perhaps it is precisely the delivery of nucleotides that explain the beneficial effects of honey (pollen of plants) and yogurt (live bacteria) (they are good at the same time as a source of trace elements, for example, selenium).
Description of the DNA repair system
DNA encodes information about all the components and functions of a cell. Each cell contains only two copies of each chromosome, and if the sequence is once lost, its replacement is impossible. The indispensability of DNA distinguishes it from other cell macromolecules and makes it a key target for age-related wear.
The theory linking aging, DNA damage and somatic mutations has a wide range of evidence:
- Mutations of the Ercc2 (Xpd), Xrcc5 (Ku86) and Wrn DNA repair enzymes lead to premature aging syndromes, so-called partial progeria.
- High-dose ionizing radiation and chemical mutagens, for example, 5-bromodeoxyuridine, accelerate the aging process of experimental animals.
- The frequency of various cytogenetic, mutational and molecular genetic disorders increases with age.
- The level of repair of various types of DNA damage decreases with age.
Somatic mutations are also not harmless - because of them, out of sync occurs in a multicellular organism.
Nuclear DNA is susceptible to various types of damage, such as hydrolysis, oxidation and alkylation. Nucleotides can be deleted, a reading frame shift, base replacement, cross-linking with other bases and proteins can occur, DNA strands and chromosomal aberrations can occur, and sister chromatid exchanges can occur.
The DNA of a typical cell spontaneously undergoes about 10,000 depurinizations every day (loss of adenine or guanine bases), 500 depyrimidinations (loss of cytosine or thymine bases) and 160 cytidine deamination (conversion of 5-methylcytosine to thymine). As a result of the action of endogenous mutagens in the eukaryotic genome of each cell of the organism, 10 ^ 4-10 ^ 5 damaged nucleotides are present in the steady state.

Сrispr [Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats] breaks DNA DNA
repair genes are expressed much more often in the human genome and the naked digger, in comparison with the mouse. Including 5 of 11 DNA glycosylases, which find and remove damaged nucleotides.
Symbol The full name of the gene
MBD4 methyl-CpG binding domain protein 4
MSH3 mutS homolog 3 (E. coli)
MUTYH mutY homolog (E. coli)
NEIL1 nei endonuclease VIII-like 1 (E. coli)
NEIL2 nei like 2 (E. coli)
NHEJ1 nonhomologous end-joining factor 1
POLK polymerase (directed ) kappa
POLL polymerase (DNA directed), lambda
TDG thymine-DNA glycosylase
TP53 tumor protein p53
UBE2N ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2N (UBC13 homolog, yeast)
XRCC6 X-ray repair; 70 kDa subunit, Ku70
Active forms of oxygen lead to the formation of modified (oxidized) nitrogenous bases.
When the damaged bases are removed with DNA glycosylases, AP sites arise, in the absence of further repair, leading to substitutions of the bases for the AP site → T or single- and double-stranded DNA breaks.
Although DNA and RNA polymerases recognize damaged and modified bases, this recognition is not absolute and they can embed damaged nucleotides into nucleic acid.
The area devoid of base is further processed by AP endonuclease (APE1), which leaves a single-weighted gap. The gap is filled with DNA polymerase β and stitched with DNA ligase.
A decrease in the activity of NER [nucleotide excision repair, NER]] with age in fibroblasts has been shown. Apparently, this is partly due to a decrease in the synthesis of nucleotides, since treatment with nucleotides corrects the activity.
Why do you lack own nucleotides synthesized by the cell?
Nucleotides belong to the most complex metabolites. Their biosynthesis requires a lot of time and high energy costs. Therefore, it is clear that nucleotides are not completely destroyed, but for the most part are again involved in the synthesis. First of all, this refers to the purine bases of adenine and guanine. In higher animals, about 90% of the purine bases are again converted to nucleoside monophosphates, binding to phosphoribosyl diphosphate (PRPP). The participation of pyrimidine bases (thymine and cytosine) in resynthesis is very small.
synthesis of purinenucleotides are derived from inosine monophosphate [IMP (IMP)]. Its base hypoxanthine is converted in two stages, respectively, to adenine or guanine. The resulting nucleoside monophosphates AMP (AMP) and GMP (GMP) are transferred to the diphosphates of ADP (ADP) and GDF (GDP) under the action of nucleoside phosphate kinase, and finally phosphorylated nucleoside diphosphate kinases to ATP triphosphates (ATP) and GTP (GTP).
Synthesis of 5'-phosphoribosylamine

Inosine Monophosphate Synthesis
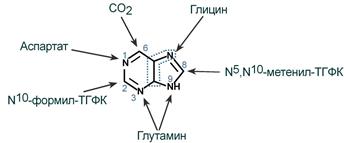
Guanosine monophosphate (HMP) is formed in two reactions: first, it is oxidized by IMP-dehydrogenase to xanthosyl monophosphate, water is the source of oxygen, NAD is a hydrogen acceptor. After that, GMP synthetase works, it uses the universal cellular donor of NH2-groups - glutamine, ATP is the source of energy for the reaction.
Adenosine monophosphate (AMP) also forms in two reactions, but aspartic acid acts as a donor of the NH2 group. In the first, adenylosuccinate-synthetase, the reaction to the addition of aspartate, GTP decomposition energy is used; in the second reaction, adenylosuccinate lyase removes part of the aspartic acid as fumarate. Pyrimidine
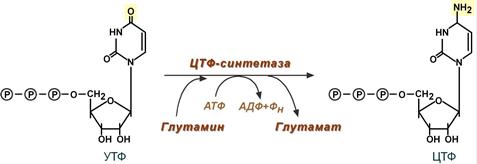
biosynthesis pathwaysnucleotides are more complicated than pathways for the synthesis of purine nucleotides. First of all, the original UMP (UMP) is phosphorylated to UTP di-, and then UTP triphosphate (UTP). UTP converts cytidine triphosphate synthase (CTP synthase) to CTF (CTP). Since the reduction of pyrimidine nucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides occurs at the stage of diphosphates, CTP must be hydrolyzed by phosphatase to CDP (CDP), after which dCDP (dCDP) and dCTP (dCTP) can be formed.
Synthesis of pyrimidine bases occurs in all cells of the body. Aspartic acid, glutamine, CO2 is involved in the synthesis reactions, 2 ATP molecules are consumed. In contrast to the branched synthesis of purines, this synthesis occurs linearly, i.e. pyrimidine nucleotides are formed sequentially, one after another.
Synthesis of orotidin monophosphate and uridine monophosphoric acid
In the reaction with phosphoribosyldiphosphate (FRDF), ribose-5-phosphate is attached to orotic acid and orotidyl monophosphate is formed, which is converted to uridine monophosphate (UMP) during decarboxylation.
The source of phosphoribosyl diphosphate is the first of two reactions of phosphoribosylamine synthesis during the formation of purines.

Synthesis of uridine triphosphate
Synthesis of UTP is carried out from MFIs in 2 stages through the transfer of high-energy phosphate groups from ATP.

Synthesis of cytidine triphosphate The
formation of cytidine triphosphate (CTP) occurs from the UTP with the energy of ATP with the participation of glutamine, which is a donor of the NH2-group.
It is worth noting that despite the fact that glutamic acid belongs to the group of replaceable amino acids, its supplement prolonged the life of mice by 25% in the experience of screening 1000 dosage forms on 15000 mice for 4 years. That is, even when synthesized inside the body, an additional source of vitamin is good for health.
It can be assumed that nucleotides are synthesized by a growing organism in abundance up to 27 years. And after cessation of growth, the concentration of nucleotides in the cell nucleus decreases.
Viruses
The number of bacteriophages is estimated at 10 ^ 31 viruses on our planet.
Viruses are single-stranded and double-stranded, RNA and DNA. In appearance: spindle-shaped, rod-shaped, filiform, icosahedral and spherical. The structure is linear, circular, fragmented, unfragmented with repeating and inverted sequences. Dimensions - from 15 to 2000 nm.
We are interested in bacteriophages: the genome of viruses vary greatly from 10 thousand nucleotides to 2.5 million nucleotides in length. The largest bacteriophage - Klebsiella Phage vB_KleM-RaK2 346 thousand nucleotides.
Viruses can infect bacteria, archaea, insects, algae, protozoa single-celled organisms, vertebrates, plants, fungi, crustaceans, dinofortilla algae, strerenopila (ratiophobia organisms), fish and other large viruses (satellite viruses).
RNA viruses are
the arenaviruses fragmented, single-stranded viruses 50-300nm Lassa, Machupo
Bunyaviridae fragmented, single-stranded, circular 90-100nm Viruses encephalitis and hemorrhagic fevers
Caliciviruses single stranded 20-30nm Hepatitis E virus, caliciviruses human
Coronaviruses a single-stranded RNA 80-130nm human Coronaviruses
orthomyxo- viruses single-stranded , fragmented 80-120nm RNA Influenza viruses
Paramikso- viruses are single-stranded, linear 150-300nm parainfluenza virus, measles, mumps, RS-virus
picornavirus 20-30nm single-stranded polio virus, Coxsackie, ECHO, hepatitis A, rhinoviruses,
reovirus reovirus double-stranded 60-80nm
Retroviruses single-stranded 80-100nm cancer viruses leukemia, sarcoma, HIV
Togaviridae 30-90nm single-stranded equine encephalitis viruses, rubella et al.
Flaviviruses single stranded 30-90nm tick-borne encephalitis viruses, yellow fever, dengue, Japanese encephalitis, hepatitis C, G
rhabdovirus 30-90nm single-stranded virus beshens Islands, vesicular stomatitis virus
Filoviruses single-stranded 200-4000nm fever virus Ebola, Marburg
, but for the purpose of prolonging life, we need only DNA viruses!
DNA viruses
Iridovirusy double-stranded 125-300 nm Iridovirus, Chloriridovirus, Lymphocystivirus and Ranavirus fish and lizards
adenoviruses is linear, double-stranded 70-90nm mammals and birds Adenovirus
Gepadnavirusy double-stranded, circular single-stranded portion with 45-50nm Hepatitis B virus
Herpesviridae linear, double-stranded viruses Herpes simplex, cytomegaly, chicken pox, infectious mononucleosis
Papovaviruses are double-stranded, circular 45-55nm Papilloma viruses, polyomas
Poxviruses are double-stranded with closed ends 130-250nm Vaccine virus, variola virus
Parvovirus ling Single, single-stranded 18-26nm Adeno-associated virus
Bacteriophages
Since 1959, ~ 6300 prokaryotes (cell without a nucleus) of viruses have been described morphologically, including ~ 6200 bacterial ~ 100 archaeal viruses. Most of these viruses — with tails — come from the early Pre-Cambrian pЄ period. One of the most dense sources of bacteriophages is sea water, where on the surface of microbial mats there are up to 9 × 10 ^ 8 virions per milliliter. It should be noted that it is absolutely safe to drink these viruses, as they have been used for more than 90 years as an alternative to antibiotics in the Soviet Union and France.

Lytic cycle takes about 30 minutes (at 37 ° C)
- Penetration into the cell (starts immediately when the tail clings to the cell membrane)
- Arrest of host gene expression (starts immediately)
- Enzyme synthesis (starts after 5 minutes)
- DNA replication (starts after 10 minutes)
- Formation of new 100-150 viral particles per cell (starts after 12 minutes)
Perhaps you should pay attention to viruses infecting archaea, as safer than bacteriophages of Escherichia coli or Staphylococcus [which in non-pathogenic form are natural for the intestines and mucous membranes]. But the experience in mice can be set now.
Vitamins
Here I include directly vitamins (13 pieces), as well as trace elements and essential amino acids that are not synthesized in the body. In brackets daily daily need is indicated.
Trace elements
sodium (1500 mg)
potassium (4700 mg)
chlorine (2300 mg)
calcium (1200 mg)
iron (18 mg)
phosphorus (700 mg),
iodine (0.15 mg);
magnesium (420 mg);
zinc (11 mg);
selenium (0.05 mg);
copper (0.9 mg);
manganese (2.3 mg);
chromium (0.035 mg);
molybdenum (0.045 mg);
Vitamins
vitamin A (1 mg);
Vitamin B6 (2 mg);
Vitamin B12 (0.003 mg)
Vitamin C (90 mg);
Vitamin D (0.015 mg);
vitamin E (15 mg);
vitamin K (0.11 mg);
thiamine B1 (1.2 mg);
Riboflavin B2 (1.1 mg);
Niacin B3 nicotinic acid (14 mg);
Pantothenic acid B5 (5 mg);
folic acid B9 (0.4 mg);
Biotin B7 (0.05 mg);
Two DNA metabolites have been reclassified as non-vitamins
Vitamin B4 - nucleotide Adenine (Adenine)
Vitamin B8 - Adenosine monophosphate (AMP) (Adenylic acid)
Amino Acids
Contains a daily dose of essential amino acid (the one that is not synthesized in the body) per 1 kg of weight
histidine 10mg
Isoleucine 20 mg
Leucine 39mg
Lysine 30 mg
Methionine + Cysteine 15mg
Phenylalanine + Tyrosine 25mg
Threonine 15 mg
Tryptophan 4mg
Valine 26mg
order to replenish the vitamin supply of the body is recommended every day, drink beverages with a daily dose of all necessary substances.
In the aforementioned experience of screening pharmacological preparations on long-lived mice, revolutionary results were obtained : life is prolonged by a combination of 3 components
- Inulin (available in Jerusalem artichoke, extended the life of mice by 18%)
- one of these substances (more than 10% increase in the extension of the maximum lifespan)
[Lemon or lime extract, DTPA, EDTA, St. John's wort extract, Hyperforin, Ginkgo bilogoba extract, Ginkgolide A or B, vitamin C, Ascorbic acid 6-palmitate, Pantothenic acid (vitamin B-5), Niacinamide, Allicin (garlic), Lactobionate, Melatonin, Metformin, L-Dopa, extract Mucuna beans (Mucuna Dopa), L-Histidine, Quercetin, Curcumin, L-Glutamic acid, succinic acid, N-Acetil Cysteine, Green tea extract, Epigallocatechin-3-gallaye, Glutathione, Aspirin, Salicylate, Glycine, Resveratrol, Glutathione , Garnosine, Rapamycin, Lipoic acid, or Taurine]
L-Glutamic acid is a replaceable amino acid, but nevertheless it extended the life of the mice! - and Magnesium (+ 25%) [magnesium is a necessary substance for DNA replication]
estrogen 17-estradiol, reduced the average lifespan of a mouse by 21%.
When the first viruses appeared on Earth, science cannot say for sure. Today there are several hypotheses about the origin of viruses. One of the most respected virus scientists, academician of RAMS V.M. Zhdanov, highlights three of them. According to the first, viruses can be descendants of bacteria or other unicellular organisms that have undergone degenerative evolution. That is, bacteria or unicellular for some reason, instead of the usual development towards complication, have lost some of the structures and “simplified” to viruses.
According to the second hypothesis, viruses appeared before the formation of the first living cells and are descendants of ancient precellular forms of life. Perhaps at first they possessed autonomy, but then moved to the parasitic way of life, using other forms for their reproduction. According to the third hypothesis, viruses evolved from cellular genetic structures - retrotransposons - capable of moving in the genomes.

An experience scheme that can confirm or disprove the hypothesis of the vitamin theory of aging [excessive supply of the body with vitamins and individual ATCG nucleotides (for example, in the form of viruses) is also in excess - this is all that is required for a significant extension of life (and methods like epigenetic recoil, combinations of geroprotectors, repair of damage, lose by the maximum extension of life years)]:
15-20 year old mice for at least 2 years should be given water with densely diluted bacterial viruses, or the same with bacteria (as suppliers of mineral elements in abundance). If the mice do not grow old after 3 years, the hypothesis can be considered confirmed.
It is also well possible to predict the course of the experiment.Open Longevity aging biomarkers (C-reactive protein [<1 mg / l], blood albumin [43-46 g / l], blood glucose [4.1-5.3 mmol / l], cholesterol [<5.18 mmol / l] , glycated hemoglobin [not higher than 5.7%], ALT [20-41 units / l], insulin [240 pmol / l)], Vitamin B12 [not less than 600 pg / ml], homocysteine [not higher than 7 µmol / l], ...)
