Space scale feil
The idea to launch a balloon into space came up with one of the employees of the Magway web studio (it seems they were programmers) back in January. Inspired by the examples of predecessors ( launch 1 , launch 2 ), we decided to do this. The ball should rise to a height of 20-30 km., Then burst and land on a parachute. During the flight from two cameras, continuous photo and video shooting is conducted.
May 14, we went to launch the ball.
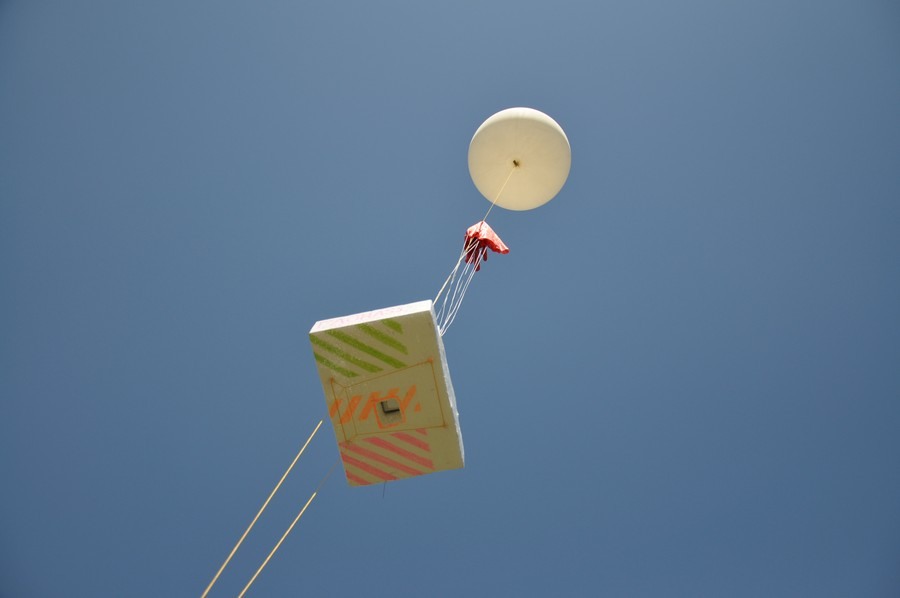

Equipment that will fly:
Spot 2 GPS tracker, with it we will track the movement of the ball. The spot works via satellite, location data is sent to Google maps every 10 minutes.
Old Premier camera for video recording.
New Panasonic Lumix with 16G card for photos.
An adrenaline clock that tracks temperature, altitude (up to 7km.) And pressure (to calculate maximum altitude).
Two chemical hot-water bottles Hot hands 2. At altitudes the temperature reaches -60, we decided to warm up a bit.
Under the cut photo and video report about the launch.

Starting place: Gornaya Polyana (a village near Volgograd).
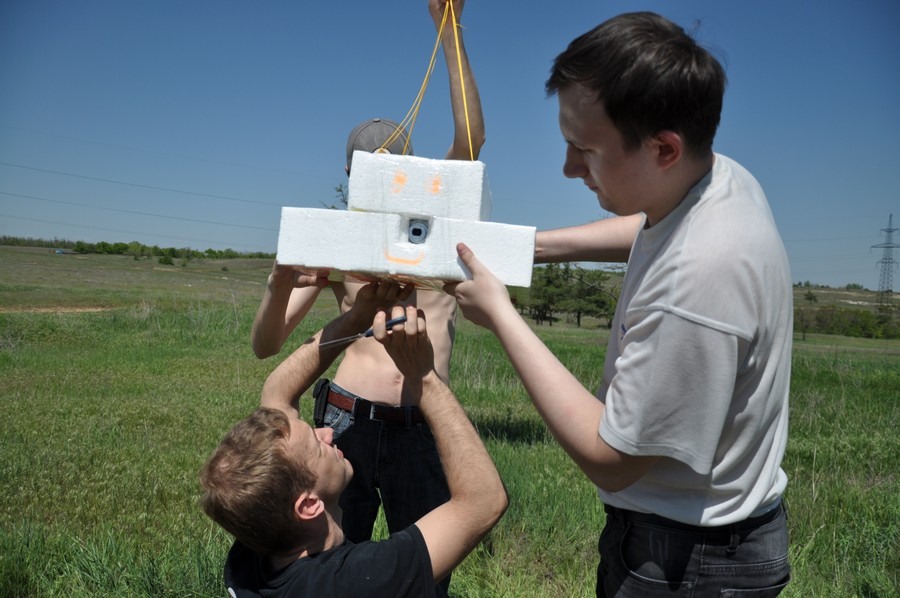
Check the parachute. Our probe will fall at a very high speed or just simply big) the

equipment will fly in a box. The video is taken by the camera below, the photo from the side.

10 liter helium cylinder.

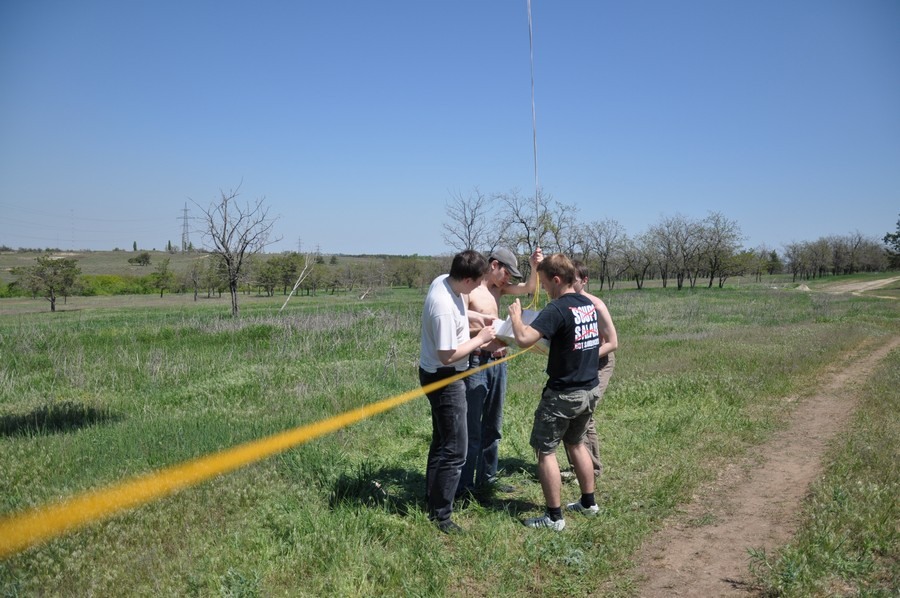
We begin to inflate the meteorological ball.


Fooled!
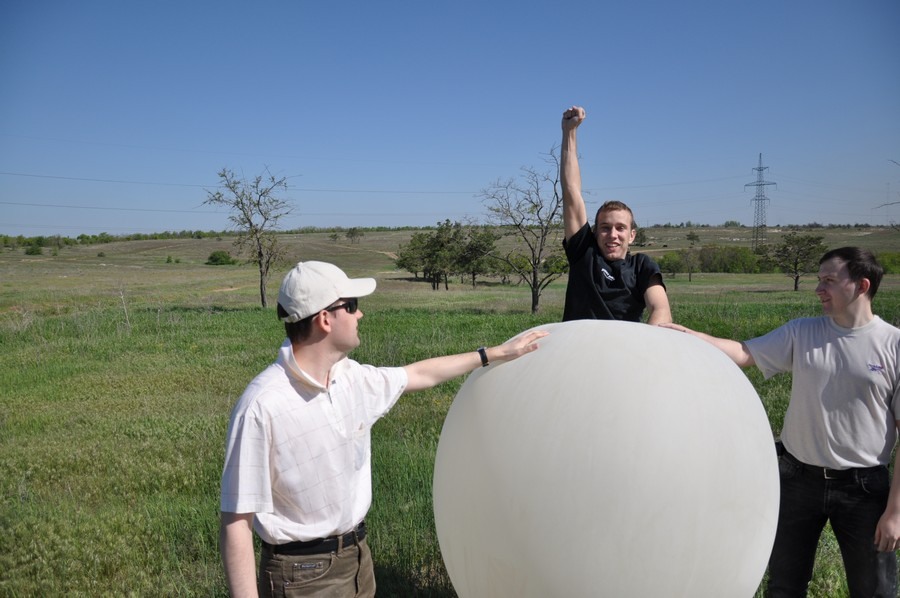

A ball does not fly! Barely rising from the ground. Either the balloon was not completely filled for us, or the load was too heavy. Such a cylinder should be enough to lift 1.1 kg.

If you put the cameras, it rises, but also with insufficient speed.

I had to go to refuel the cylinder.
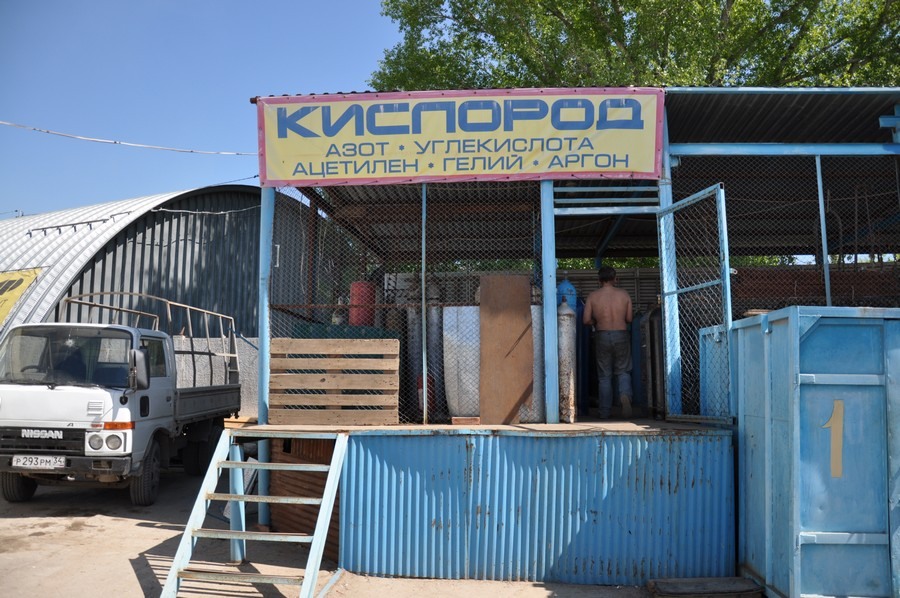

While team A refills the cylinder with helium, team B fries kebab.

After a snack, we pump the ball again.
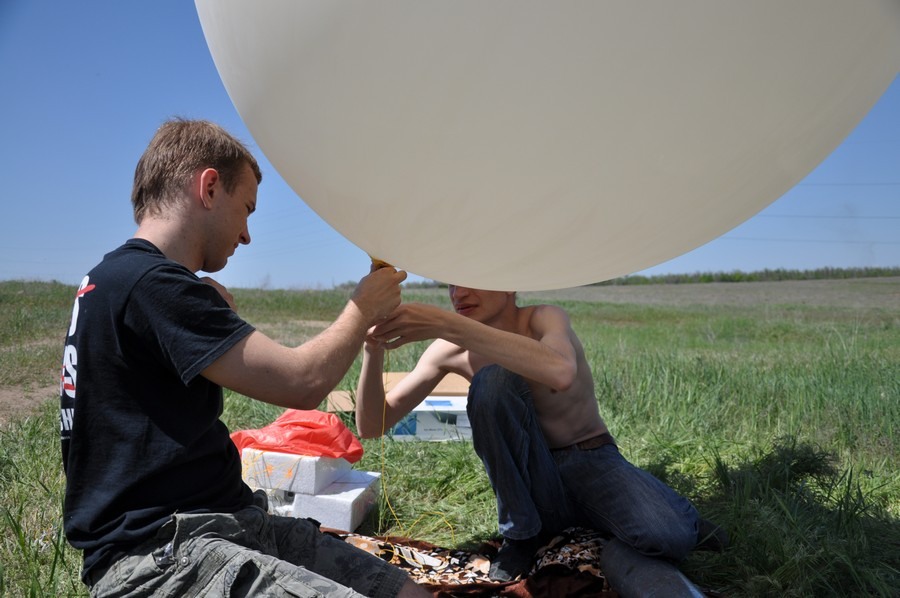

Test run with insurance. Again, the lifting force is insufficient, the ball gains height slowly. As a result, we had to download it twice more. You don’t pump enough - the ball will not rise high with the load, if it is pumped, it will burst faster (at heights, due to the pressure drop, the ball inflates).
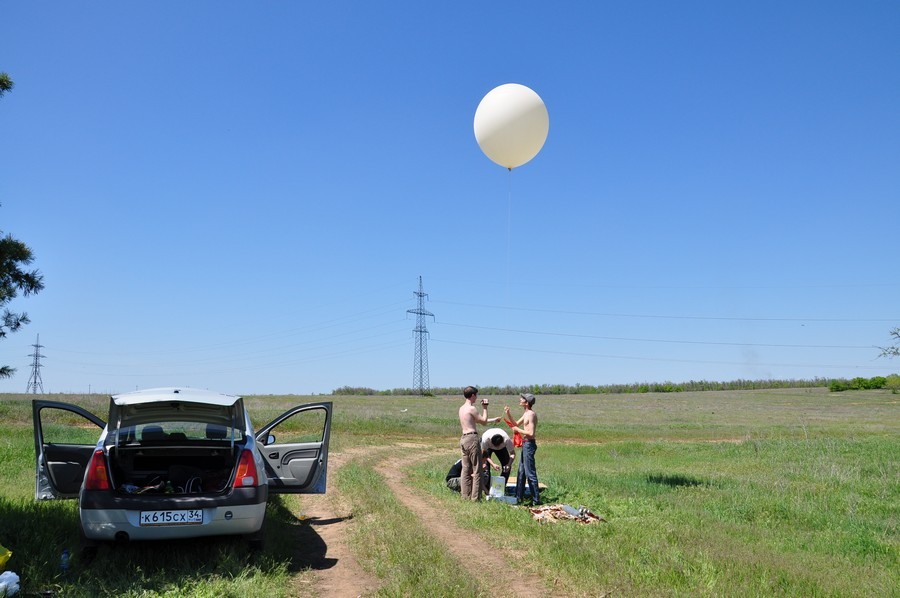





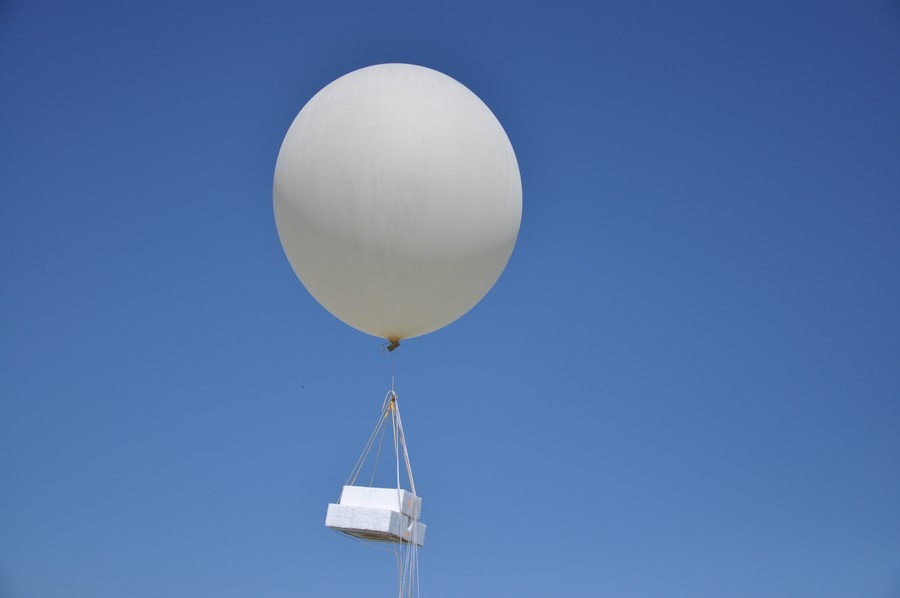
24. Ready to go!
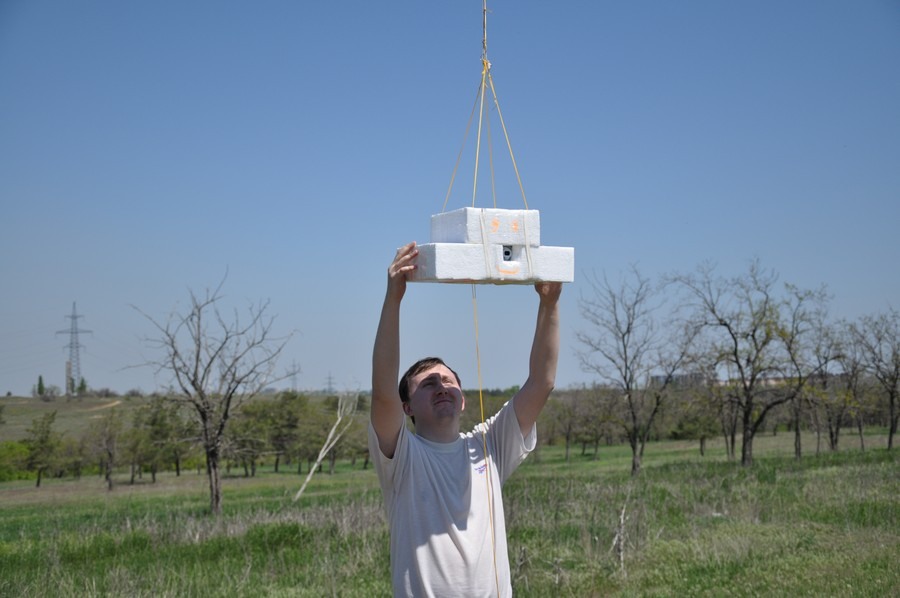

25. Flew! The launch took place at 12-57.
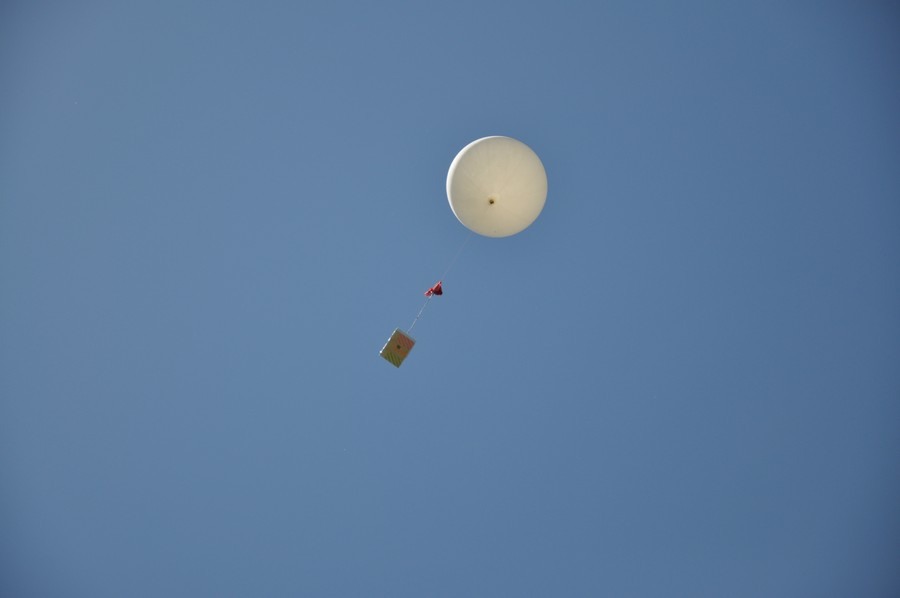

26. Flies! There is no wind, the ball rises almost vertically.
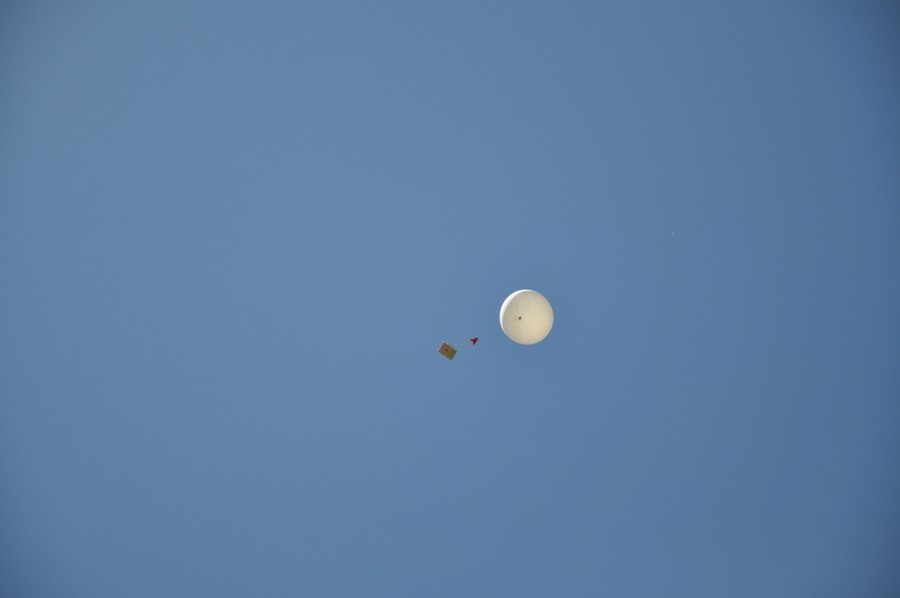

The first coordinates are received. The ball moves southwest. We are going to the Krasnoarmeysky district of Volgograd and further out of town. If the wind does not change, then the ball will cross the Volga-Don canal and fly towards Kalmykia.

The last point on the map was received on 14-06. Perhaps the ball has left the signal sending zone, the tracker works up to 8 km. in height. We are waiting, but the last coordinates do not change. The flight of the ball cannot last more than 3 hours (according to the experience of the people who launched them earlier), during this time it must reach its maximum height and burst. We are going to the last known point.

37. Check the coordinates. We are in the direction of the village of Ivanovka. We tracked the flight of the ball using a netbook, iPhone and iPad. The iPad with a SIM card from MTS turned out to be the most inhibitory for some reason, while the iPhone and MTS worked more quickly. He most accurately showed our location.
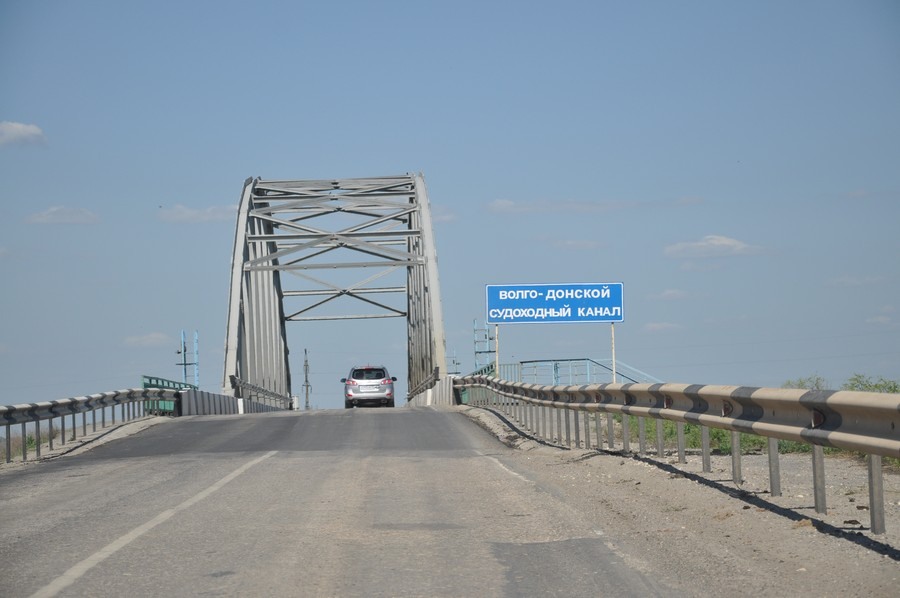


41. An unpaved road of excellent quality leaves from Ivanovka towards the fields (this is better than holey asphalt in the region).

Already close, but how to get closer to the expected point of fall?

The primer rests against the railway.


We go there! We are looking for a railway crossing and as close as possible to the last point.
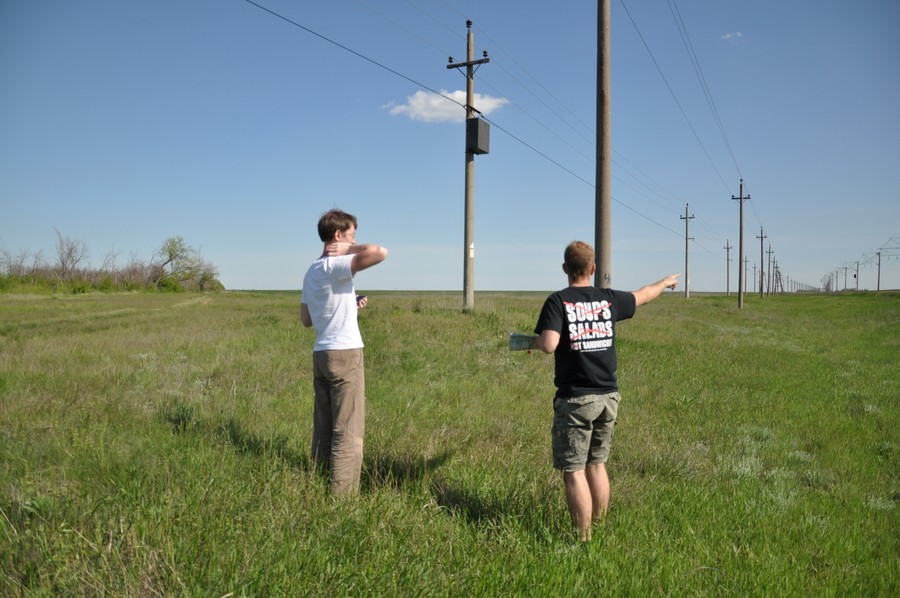

Somewhere in this field should be our probe.
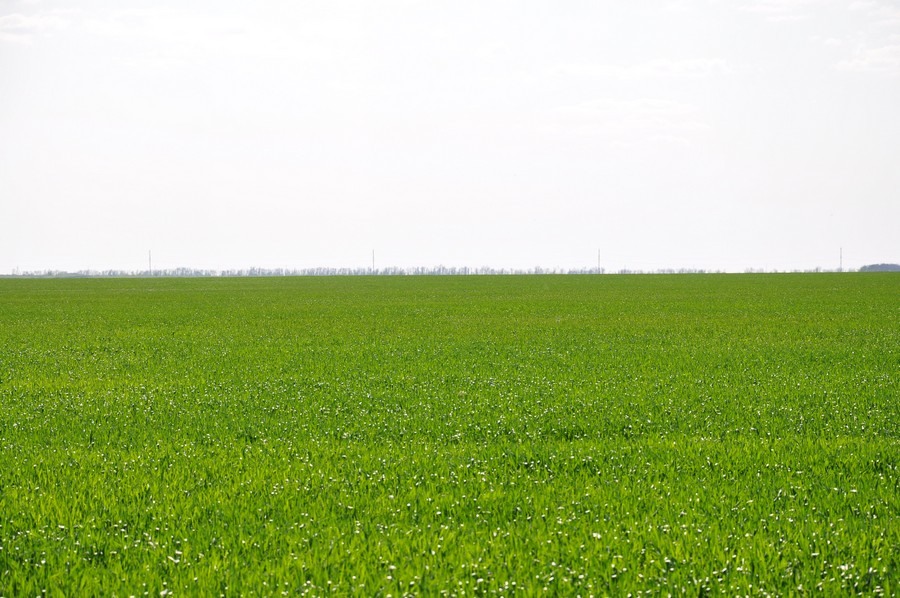

The guys go to the place of the alleged fall. But there is nothing there.
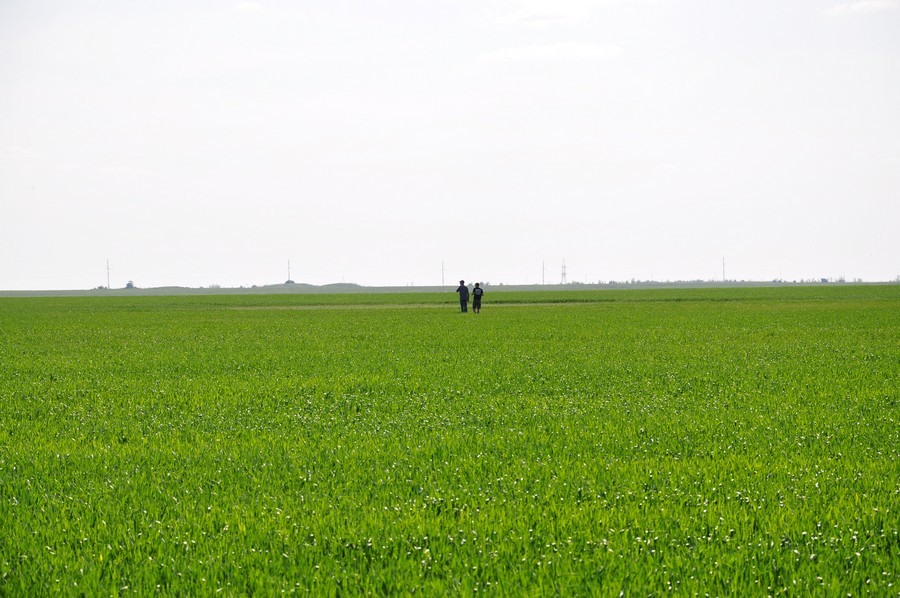

On the side of the field is a forest belt, very dense, with thorns. We put on jackets and make our way through the thickets.

We are moving along the proposed flight path. Spot may have crashed and therefore does not transmit a signal. The data that we have is obtained even at a height, and the place of the fall is further.

The probe is not visible. Back to the cars.
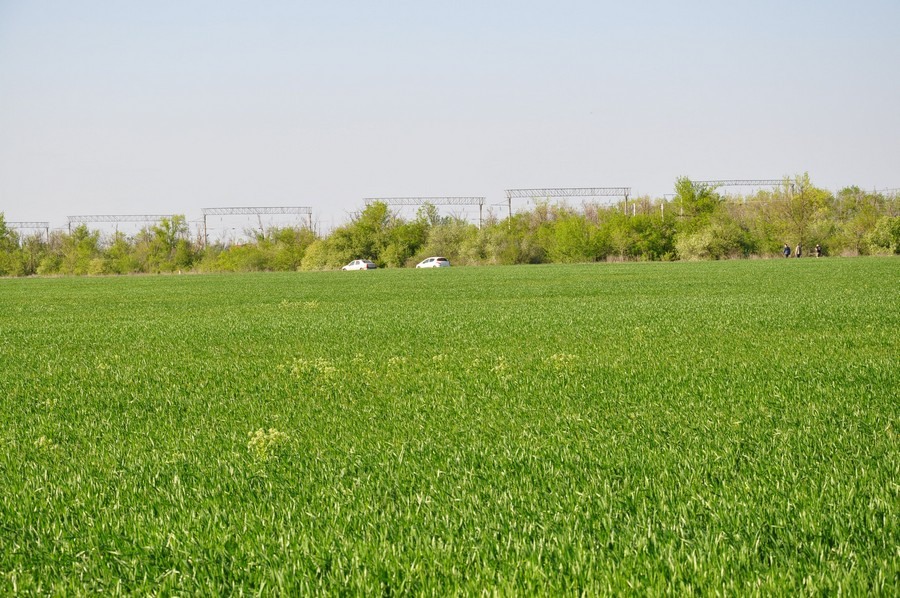

Part of the team goes deeper into the field. And again without result.

From the launch site to the last known point, only 13 km. This is very small, balls like ours fly away from 40 to 300 km.

59. Red traced our way by car from the launch site to the last known point, near the Inga railway station. We did not expect that the last coordinates would be only 13 km, so we made a big detour.
The green dotted line is where we went.
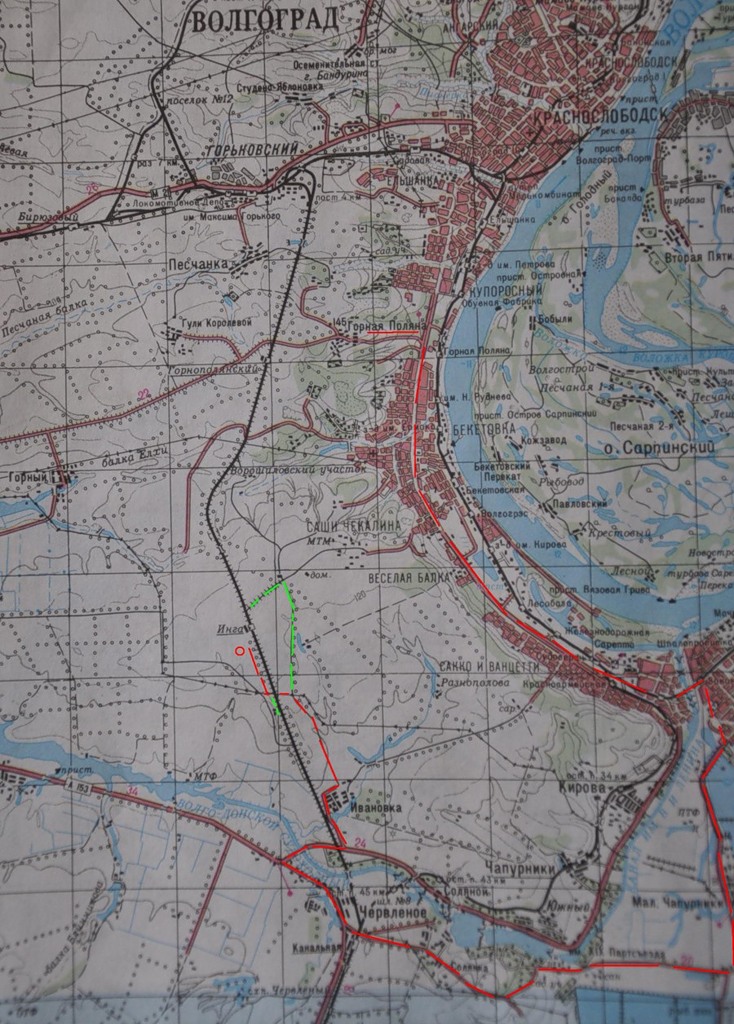
60. The movement of the balloon according to the GPS tracker Spot. Last known coordinates:
Latitude: 48.52578
Longitude: 44.33266
If you are in that area, look for a white box, please).
What happened to the ball? We have several versions.
1. The last point was transmitted before the ball went to a height of more than 8 km. Further, where the temperatures reach -50 -60, the tracker froze and stopped working (it is unlikely that Spot was in the box, where there were heating pads; and being at altitude is not so long). A more plausible version is that after the ball burst, the signal did not manage to be transmitted during a rapid fall (if the parachute did not work). When falling, Spot from a strong blow flew out of the box and crashed or batteries were displaced.
2. The ball was overloaded and the last point is the point of incidence. In this case, again, there must be a very strong blow to a hard surface so that the tracker stops working. It is strong in itself, and the box will certainly soften the blow.
3. The last point is the point of fall. Then someone found it and took out the batteries from Spot. It is unlikely that there are too many conditions. A person must quickly get to the box in the field, pull out the tracker, understand what it is and turn off the power. And for all this time, the tracker did not transmit a single signal. Very unlikely.
4. Spot left the satellite visibility range (this has already happened, usually after 19-00) and, due to some technical problems, could not return to the visibility range.
5. Our ball stole a UFO.
In any case, it was the gps tracker that let us down. It was necessary to put a backup navigator - a phone. Although he has an error in gprs much higher outside the city, but at least we knew about the place where the probe fell.
Video how we launched the ball .
Links to specific parts of this video on YouTube:
Arriving at the launch site
Probe
overview Equipment
overview Tracking technology overview
Inflate balloon
Pack up
Launch
May 14, we went to launch the ball.

Equipment that will fly:
Spot 2 GPS tracker, with it we will track the movement of the ball. The spot works via satellite, location data is sent to Google maps every 10 minutes.
Old Premier camera for video recording.
New Panasonic Lumix with 16G card for photos.
An adrenaline clock that tracks temperature, altitude (up to 7km.) And pressure (to calculate maximum altitude).
Two chemical hot-water bottles Hot hands 2. At altitudes the temperature reaches -60, we decided to warm up a bit.
Under the cut photo and video report about the launch.

Starting place: Gornaya Polyana (a village near Volgograd).
Check the parachute. Our probe will fall at a very high speed or just simply big) the

equipment will fly in a box. The video is taken by the camera below, the photo from the side.

10 liter helium cylinder.

We begin to inflate the meteorological ball.


Fooled!

A ball does not fly! Barely rising from the ground. Either the balloon was not completely filled for us, or the load was too heavy. Such a cylinder should be enough to lift 1.1 kg.

If you put the cameras, it rises, but also with insufficient speed.

I had to go to refuel the cylinder.

While team A refills the cylinder with helium, team B fries kebab.

After a snack, we pump the ball again.

Test run with insurance. Again, the lifting force is insufficient, the ball gains height slowly. As a result, we had to download it twice more. You don’t pump enough - the ball will not rise high with the load, if it is pumped, it will burst faster (at heights, due to the pressure drop, the ball inflates).





24. Ready to go!

25. Flew! The launch took place at 12-57.

26. Flies! There is no wind, the ball rises almost vertically.

The first coordinates are received. The ball moves southwest. We are going to the Krasnoarmeysky district of Volgograd and further out of town. If the wind does not change, then the ball will cross the Volga-Don canal and fly towards Kalmykia.

The last point on the map was received on 14-06. Perhaps the ball has left the signal sending zone, the tracker works up to 8 km. in height. We are waiting, but the last coordinates do not change. The flight of the ball cannot last more than 3 hours (according to the experience of the people who launched them earlier), during this time it must reach its maximum height and burst. We are going to the last known point.

37. Check the coordinates. We are in the direction of the village of Ivanovka. We tracked the flight of the ball using a netbook, iPhone and iPad. The iPad with a SIM card from MTS turned out to be the most inhibitory for some reason, while the iPhone and MTS worked more quickly. He most accurately showed our location.


41. An unpaved road of excellent quality leaves from Ivanovka towards the fields (this is better than holey asphalt in the region).

Already close, but how to get closer to the expected point of fall?

The primer rests against the railway.


We go there! We are looking for a railway crossing and as close as possible to the last point.

Somewhere in this field should be our probe.

The guys go to the place of the alleged fall. But there is nothing there.

On the side of the field is a forest belt, very dense, with thorns. We put on jackets and make our way through the thickets.

We are moving along the proposed flight path. Spot may have crashed and therefore does not transmit a signal. The data that we have is obtained even at a height, and the place of the fall is further.

The probe is not visible. Back to the cars.

Part of the team goes deeper into the field. And again without result.

From the launch site to the last known point, only 13 km. This is very small, balls like ours fly away from 40 to 300 km.

59. Red traced our way by car from the launch site to the last known point, near the Inga railway station. We did not expect that the last coordinates would be only 13 km, so we made a big detour.
The green dotted line is where we went.

60. The movement of the balloon according to the GPS tracker Spot. Last known coordinates:
Latitude: 48.52578
Longitude: 44.33266
If you are in that area, look for a white box, please).

What happened to the ball? We have several versions.
1. The last point was transmitted before the ball went to a height of more than 8 km. Further, where the temperatures reach -50 -60, the tracker froze and stopped working (it is unlikely that Spot was in the box, where there were heating pads; and being at altitude is not so long). A more plausible version is that after the ball burst, the signal did not manage to be transmitted during a rapid fall (if the parachute did not work). When falling, Spot from a strong blow flew out of the box and crashed or batteries were displaced.
2. The ball was overloaded and the last point is the point of incidence. In this case, again, there must be a very strong blow to a hard surface so that the tracker stops working. It is strong in itself, and the box will certainly soften the blow.
3. The last point is the point of fall. Then someone found it and took out the batteries from Spot. It is unlikely that there are too many conditions. A person must quickly get to the box in the field, pull out the tracker, understand what it is and turn off the power. And for all this time, the tracker did not transmit a single signal. Very unlikely.
4. Spot left the satellite visibility range (this has already happened, usually after 19-00) and, due to some technical problems, could not return to the visibility range.
5. Our ball stole a UFO.
In any case, it was the gps tracker that let us down. It was necessary to put a backup navigator - a phone. Although he has an error in gprs much higher outside the city, but at least we knew about the place where the probe fell.
Video how we launched the ball .
Links to specific parts of this video on YouTube:
Arriving at the launch site
Probe
overview Equipment
overview Tracking technology overview
Inflate balloon
Pack up
Launch
