Dry breakfast in deep space
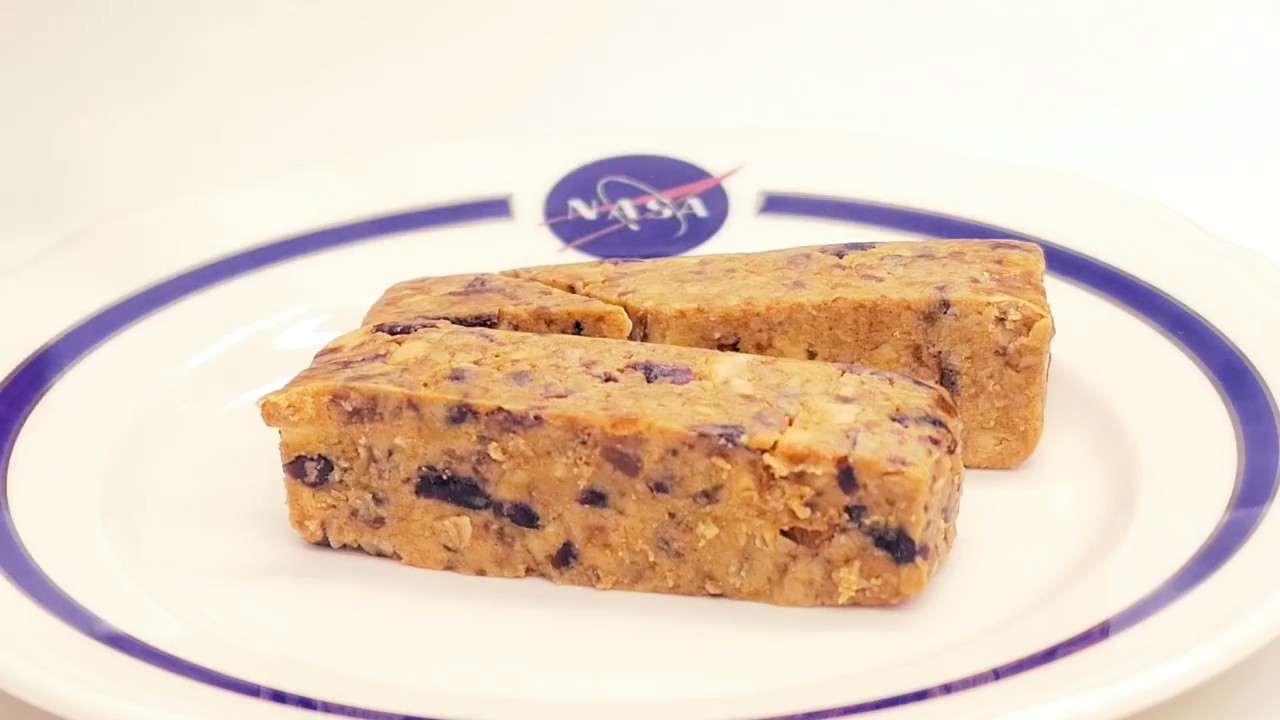

NASA has developed four types of bars with different flavors for breakfast for the crew members of the Orion spacecraft.
In 2021–2023, the Orion spacecraft with a crew of four astronauts will fly around the moon, and then to Mars. If this happens, people on board will need high-quality and healthy food. The crew of the International Space Station has no problems with food - they can choose from about 200 products, almost like in a restaurant, and they have enough space to store supplies, and new products come from the Earth regularly. With the spacecraft "Orion" the situation is fundamentally different. Power crew during a long mission in deep space puts a number of special conditions. This is a unique task that NASA scientists are now solving.
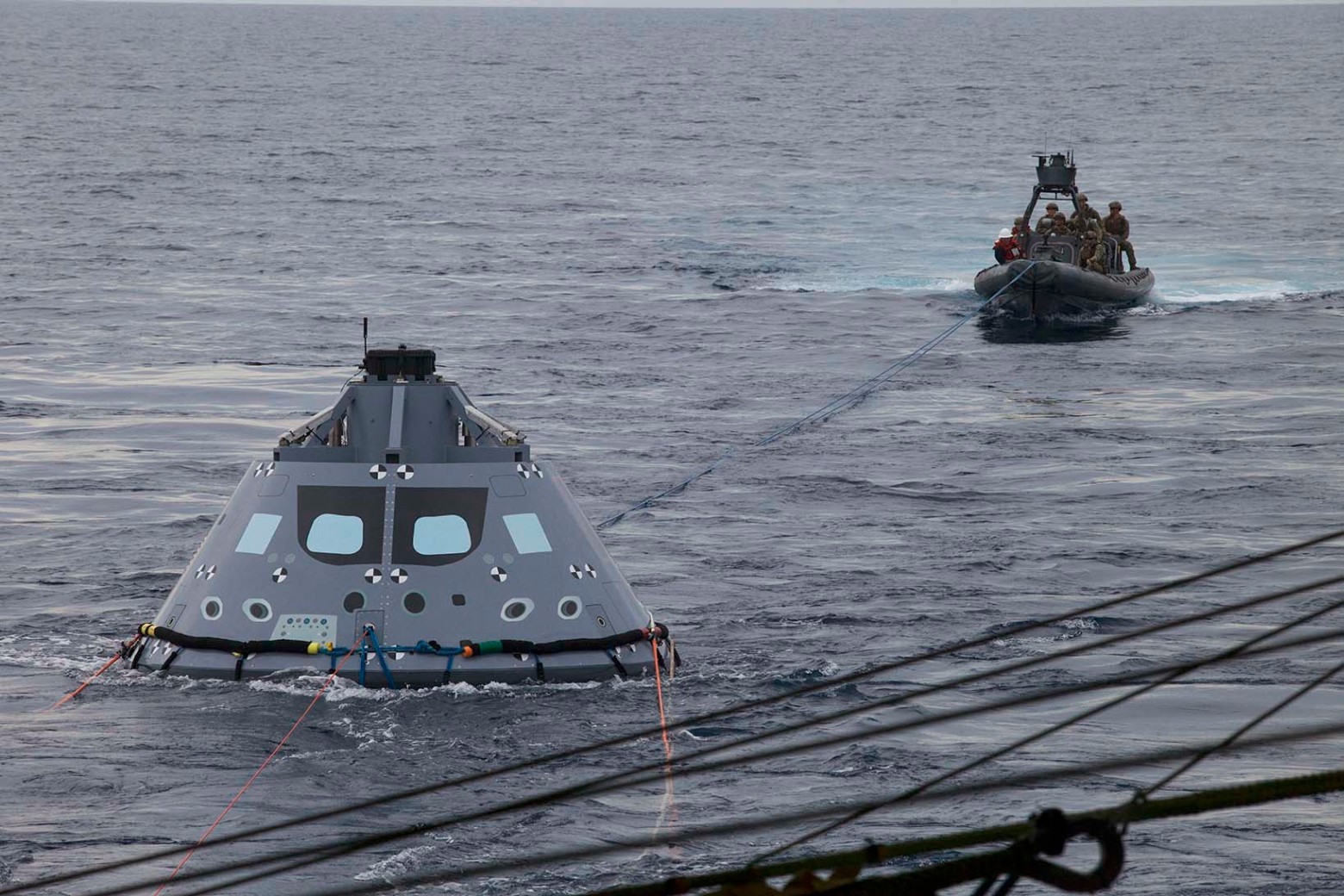

The crew module of the Orion spacecraft during the tests of the Underway Recovery Test 5 rescue operation in the Pacific Ocean. October 27, 2016. Photo: NASA / Bill White
First, Orion has limited space for storing food stocks during a mission. It is impossible to send a cargo ship to it, which will fill up the supplies and take the garbage. The crew will initially have to take with them everything they need. Considering the distance to the destination, engineers must optimize nutrition by weight, because every extra kilogram of cargo means extra kilograms of fuel with an oxidizer. This is in addition to the reserves of water and air, which, in any case, astronauts will have to take with them, at the rate of consumption, about 0.8 kg of oxygen and 2.2 kg of water per day for each crew member(water and oxygen can be partially obtained from excreted liquids and water vapor). For food in life support systems, the rate is 500 g per person per day.
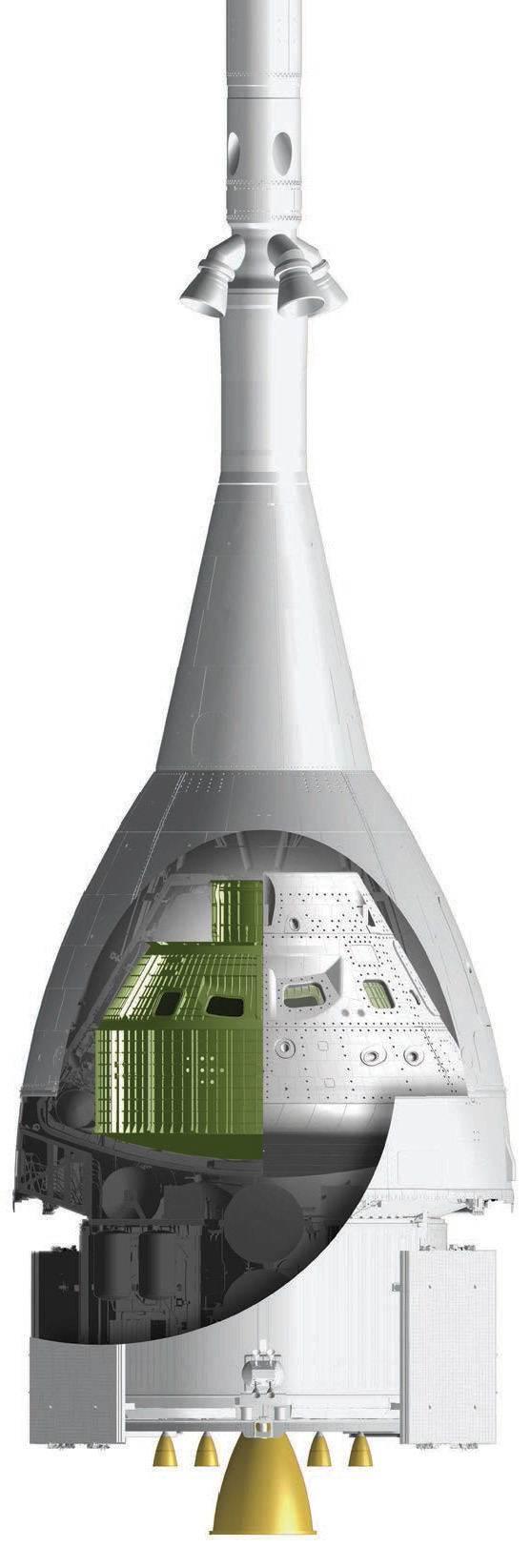
Orion spaceship with crew module and service module
In order to minimize the weight of the cargo on the Orion spacecraft, scientists are developing various options for nutritional bars. Nutritionists have determined that a dense high-calorie replacement for an ordinary breakfast will help reduce the overall weight of the load. It is clear that food with a calorie of 700−900 kcal in any case will have some significant mass and take place, so experts are experimenting with the most optimal form of the bar and its packaging. If you count on a 500-day mission for four people, this is 2000 cereal on the way only in one direction - here every millimeter and gram matters. Key differences between male and female astronauts seen during observations on Earth and in space
On the ISS for astronauts there is a large selection of thermally stabilized and dehydrated food in sealed packages. On Orion, the challenge is to develop a set of nutritional bars with different tastes. Thus, astronauts' breakfast during the long journey to Mars will also be varied. For lunch and dinner, astronauts will receive about the same set of power as on the ISS. They will have the opportunity to warm up the food and add water if necessary.
Currently developed bars calorie 700−800 kilocalories of four tastes:
- banana-nut;
- orange-cranberry;
- vanilla ginger;
- nutty barbecue.
Scientists say that there are no nutritional bars on the market right now that would satisfy NASA’s requirements for a long-term space mission in terms of mass and caloric content, so we have to develop a new product. It is desirable with a multi-year shelf life. The influence of the nutritional bars on the morale of the crew must also be taken into account. Indeed, during the many months of travel, the variety of tastes and palatability of the bars is of great importance in order to maintain optimism and good mood among the astronauts.
Nutrition bars, developed as part of the Human Research Program , have already been tested by participants in the HERA test program - the earth analog of a long-term space mission. Two men and two women are closed in an isolated small room on September 20, 2016 and at the moment have spent there 67 days and 7 hours. Tests are held in the Space Center. Johnson Such tests will help NASA avoid some problems before starting a real long-term flight. Including check how quickly people develop fatigue from a monotonous diet, how diverse should be breakfast.
Current tests should determine how often people are ready to eat these bars:
- everyday;
- every five days;
- not at all.
While scientists continue to condense nutritional bars in a smaller volume and increase the number of flavors, NASA engineers are working to develop options for regenerating products in a long mission, and also make packaging that will preserve the nutritional properties of food in conditions of strong temperatures that are possible on Mars .
The first test manned flight of the Orion is scheduled for 2021. The spacecraft will launch the Space Launch System launch vehicle into orbit, which is also currently under development.
The first unmanned test mission Exploration Mission 1on the SLS carrier rocket scheduled for September 30, 2018 from the launch complex LC-39 in the territory of the Space Center. Kennedy. Without a crew, the Orion spacecraft will spend three weeks in space, including 6 days in retrograde orbit around the moon. Next will be the manned mission of Exploration Mission 2 with four astronauts around the moon in 2021–2023.
Only registered users can participate in the survey. Sign in , please.
