What are smart contracts?

Smart Contract History
The principle of smart contracts was described by American cryptographer and programmer Nick Szabo in 1996 long before the advent of blockchain technology. According to the concept of Szabo, smart contracts are digital protocols for transmitting information that use mathematical algorithms to automatically complete a transaction after meeting established conditions and complete process control. This definition, which has been ahead of its time by more than ten years, remains accurate to this day. However, in 1996 this concept could not be realized: at that time the necessary technologies did not exist, in particular, a distributed book.

In 2008, bitcoin appeared, the first cryptocurrency appeared, created on the basis of revolutionary blockchain technology, which previously lacked a decentralized book. The Bitcoin blockchain does not allow setting conditions for a transaction in a new block, since it contains only information about the transaction itself. Nevertheless, the advent of technology served as an impetus for the development of smart contracts. Five years later, the Ethereum block platform allowed the use of smart contracts in practice. Today, the market offers many platforms that allow the use of smart contracts, but Ethereum remains one of the most common.
How do smart contracts work?
As mentioned above, smart contracts are computer protocols or, more simply, computer code.
The code is used to enter all the terms of the contract concluded between the parties to the transaction in the blockchain. Obligations of participants are provided in an intellectual contract in the form of “if” (for example: “if Party A transfers money, then Party B transfers the rights to the apartment”). There can be two or more participants, and they can be individuals or organizations. Once these conditions are met, the smart contract independently performs the transaction and ensures that the agreement is respected.
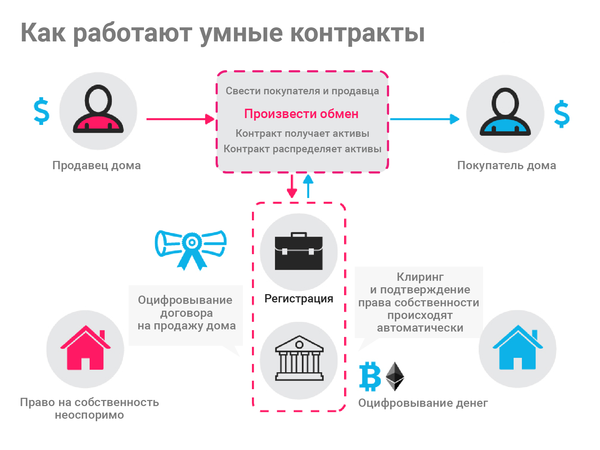
Smart contracts allow you to exchange money, goods, real estate, securities and other assets. The contract is stored and repeated in a decentralized book, in which information cannot be falsified or deleted. At the same time, data encryption ensures the anonymity of the parties to the agreement. An important feature of smart contracts is that they can only work with assets located in their digital ecosystem. How to connect the virtual and real world is currently one of the main difficulties in working with smart contracts. This is the reason for the existence of "oracles", special programs that help computer protocols to obtain the necessary information from the real world.
Benefits of Smart Contracts
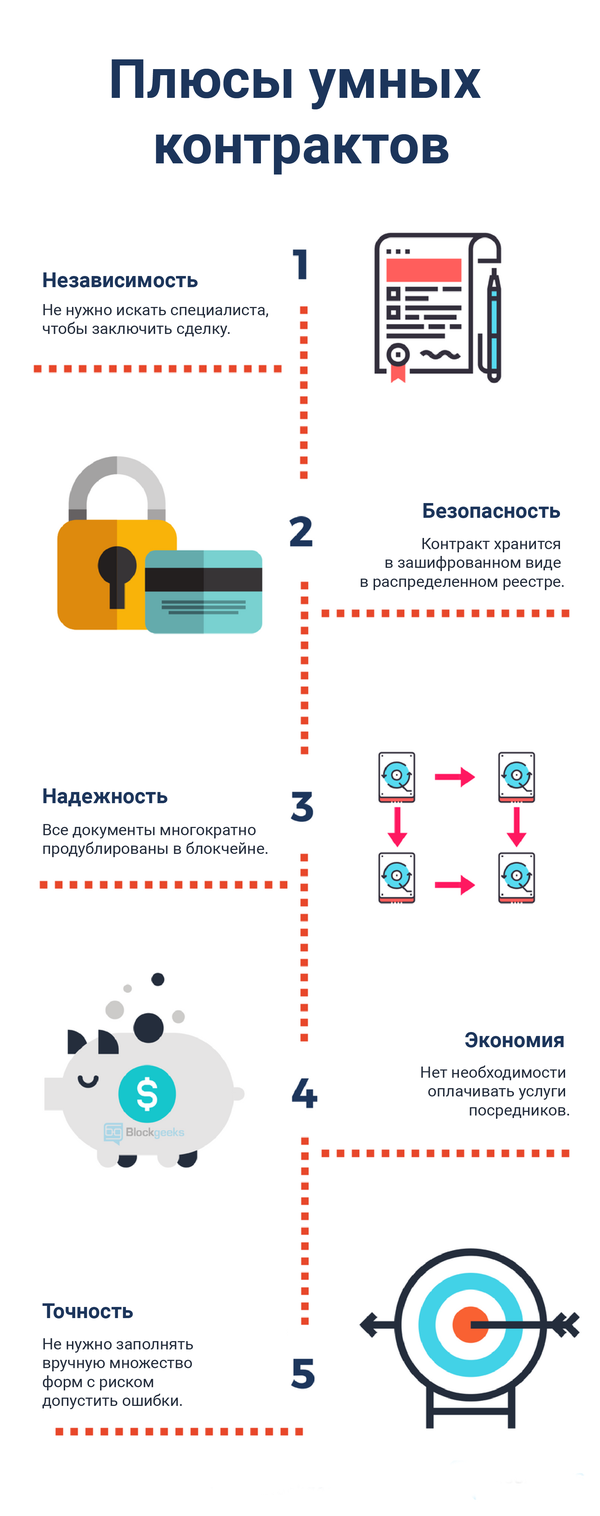
- Speed. Manual processing of documents takes a lot of time and delays the execution of tasks. Smart contracts require an automated process and in most cases do not require personal participation, which saves valuable time.
- Independence. Smart contracts exclude the possibility of third-party interference. The transaction guarantee is the program itself, which, unlike intermediaries, will not give reason to doubt its integrity.
- Reliability. The data recorded in the blockchain cannot be changed or destroyed. If one party to the transaction does not fulfill its obligations, the other side will be protected by the terms of the intellectual contract.
- No errors - An automatic system for performing transactions and removing the human factor ensures high accuracy in the execution of contracts.
- Saving. Smart contracts can provide significant savings by eliminating costs for intermediaries and reducing operating costs, as well as the opportunity for parties to work together on more favorable terms.
Disadvantages of Smart Contracrs
Despite their promising potential, smart contracts also have their drawbacks:
- Lack of regulation. In the international legal field, there are no concepts of “blockchain”, “smart contract” and “cryptocurrencies”.
- The complexity of the implementation. Integrating smart contracts with real-world elements often takes a lot of time, money, and effort.
- The impossibility of changing the intellectual contract. It is ironic that one of the main advantages of smart contracts can also be considered as a conflict. If the parties reach a better agreement or new factors arise, they will not be able to change the contract. For this reason, options for additional agreements should be implemented as new blockchain platforms are developed.
Where can I use smart contracts?
Smart contracts can change different areas. We can identify several industries in which smart contracts will be most effective:
- Finance
- Insurance
- E-commerce
- Audit and taxation
- Elections
