Scientific captcha: how puzzles interfered with people

Since the captcha from the field for entering blurry words and numbers turned into a point where you just need to click the mouse, we began to forget about the torment caused by the need to recognize extremely fuzzy characters.
CAPTCHA - how much in this word for a person who had to meet her every day. At some point, not so long ago, it seemed that only protection, which an ordinary person could hardly cope with, would be saved from bots. This belief has spawned many UX monsters, which will be discussed in the article.
Modern captcha tries to be invisible, but it has not disappeared at all. The systems determine the person in front of them or the bot, studying cookies, IP-address, cursor movement and keystrokes on the pages. Regardless of how the captcha technology is implemented, everything is built around the idea of creating a task that is difficult to solve for computers and simple for people, but questions and answers are not always obvious in practice.
Captcha is a Turing automated public test that a person can pass, but not a computer. Initially, captcha relied on a person’s ability to identify and understand visual / audio signals that bots were extremely difficult to make out. Such mechanisms were imperfect: users themselves did not always understand what was required of them. Computers, in turn, learned to recognize objects even in highly noisy images.

ReCAPTCHA: latin letters and numbers of variable length, distortion, noise, variable background color - at the time of appearance caused tons of user suffering. Today you will see (or remember) just a few examples that even people could not handle before (in some cases, bots could handle captcha better than people).
Video captcha

Canadian start-up NuCaptcha showed a video captcha: characters running along a curved line, from which a person was asked to recognize the last three. A research team from Stanford University quickly created an algorithm for hacking this video technology. They also circumvented the protection of ordinary captcha and the audioCAPTCHA project, aimed at working with visually impaired or blind users.
Game captcha
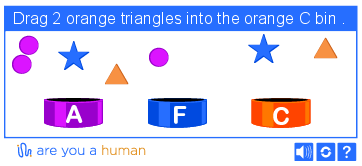
Startup Are You a Human using PlayThru technology offers to play a mini-game in which a person needs to select the desired object from a number of those present and place it in a specific place. Although this method seemed more understandable (and logical) to the user, it was also periodically subjected to hacking attempts . This captcha is inefficient because it does not have enough elements to prevent the possibility of enumerating options. In addition, there is a high probability of getting the right answer, just by accidentally guessing the desired sequence of actions. Every time a captcha tries to do something “pleasant” and fascinating for the user, a security hole arises.
Art captcha

The geee.net trash-graphics site could not do without a captcha, which would have scared visitors with one look. Users are asked to draw what they see in the picture. Art captcha cannot be considered a full-fledged defense tool - this is a joke designed to attract attention, but there is no more humor in it than the truth. With due diligence, you can get captcha.
Matcapcha
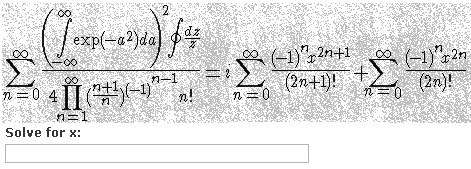
Having survived the heyday, mathematical CAPTCHA quickly went to zero, since answering the question how much “3 + 3” will be for bots is not difficult. The trick here is to find a puzzle that would be difficult for bots, but solvable for humans. Captcha, as in the example above, can be solved with a textbook on mathematical analysis or access to WolframAlpha, but how many people are willing to spend their personal time looking for an answer?
Metal captcha
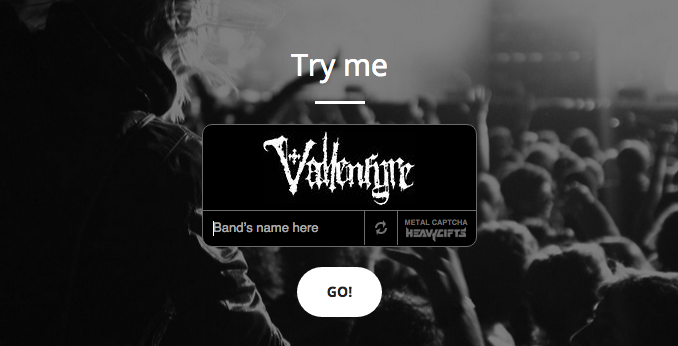
Instead of a series of letters and numbers, Metal CAPTCHA asks users to decode the logos of metal bands. If you are not familiar with this genre of music, it will be difficult, but you can always use the image search. Unfortunately, the project has now closed (for obvious reasons).
Programmer CAPTCHA

Codecha is a programmer captcha, to solve which you need to write the body of a function that solves the problem in one of the selected programming languages. It protects not only from bots (partially), but also from all people who are not familiar with programming (completely).
Unreadable captcha

An example of a Chinese captcha from 12306.com, on which you need to mark a picture (or pictures) with an image of agate. The difficulty is that the picture is of poor quality and size - in the illustration above you can evaluate it in its original form.
Radio Captcha
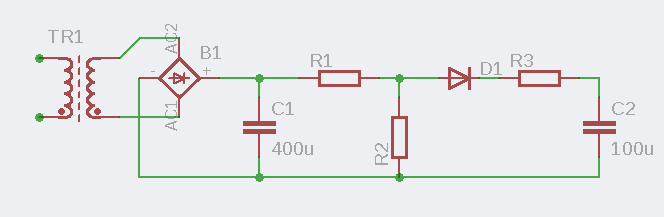
CAPTCHA from the now-dead radio forum flyback.org.ru was used when registering a new user. In the captcha, it is proposed to solve the problem of determining the energy stored in the capacitor. Description of the task: the transformer has a transformation coefficient of
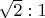
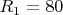 Ohms,
Ohms, 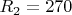 Ohms and
Ohms and 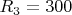 Ohms. All elements of the circuit are ideal, the voltage drop across the diode is zero. Input voltage: sinusoidal 50 Hz, with an effective value of 58 V. Determine how much J of energy will be accumulated in the capacitor
Ohms. All elements of the circuit are ideal, the voltage drop across the diode is zero. Input voltage: sinusoidal 50 Hz, with an effective value of 58 V. Determine how much J of energy will be accumulated in the capacitor  ?
? The Indians hired for a penny are unlikely to cope with such a task, immediately guessing any characters in the pictures of standard captcha. It will also scare away all users who do not have a sufficient level of knowledge.
Mobile captcha
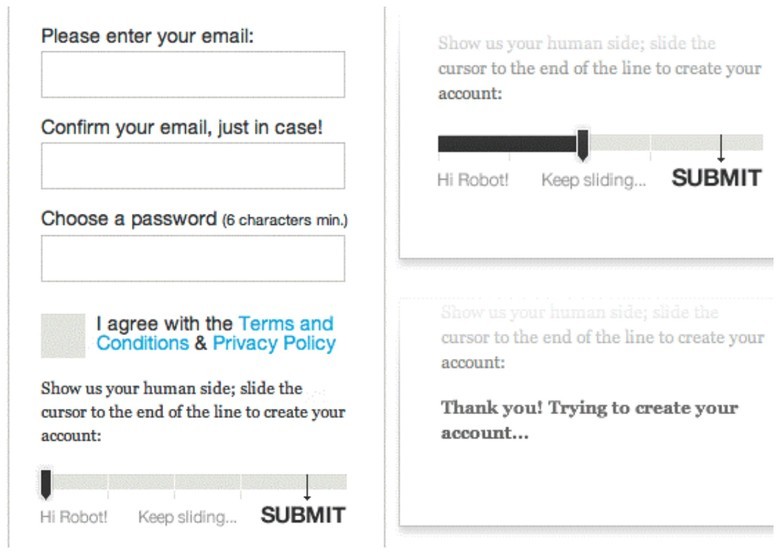
They Make Apps created a special slider in which the cursor must be positioned at the end of the line to register on the site.
Graphic captcha
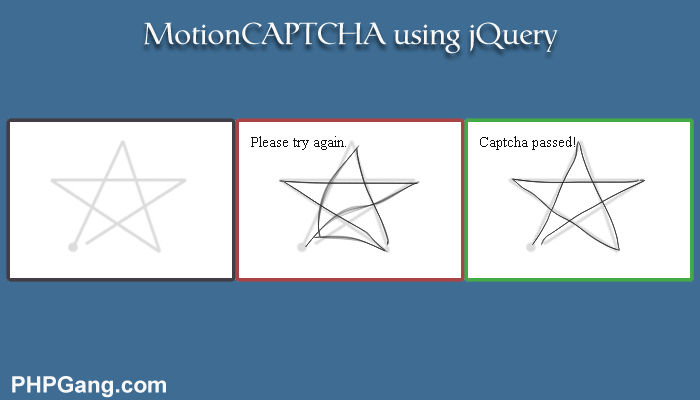
MotionCAPTCHA is a plugin that offers the user to repeat (draw) a figure from various pictures.
Interactive captcha
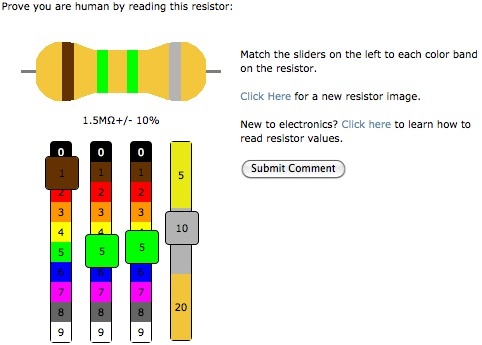
Interactive captcha . Four different sliders must be set to the correct position for posting a comment on the blog - the color of the slider must be selected according to the specified field.
Geometric captcha
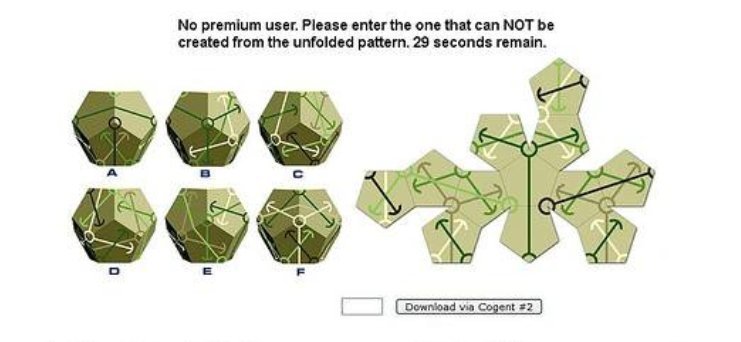
This geometric captcha is approximately on the same level as the mathematical one - equally complex tasks for humans and equally ineffective in front of bots. If you answer randomly, you have a 15 percent chance (1 chance out of 6) to give the correct answer, which, of course, does not allow for a good level of security. In order to answer the CAPTCHA question, you only have 30 seconds.
Multilingual captcha

Captcha from sveit.com (now abandoned) was based on mixing several languages at once.
Hidden code
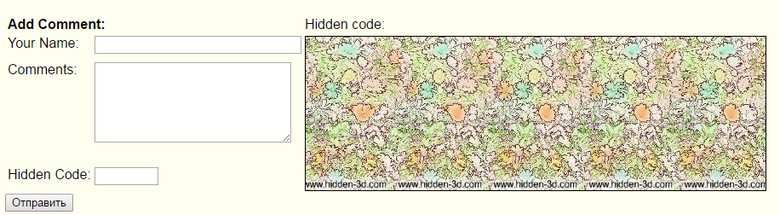
But the captcha hidden-3d.com is more alive than all the living. You just need to find the hidden code in the image.
3D image
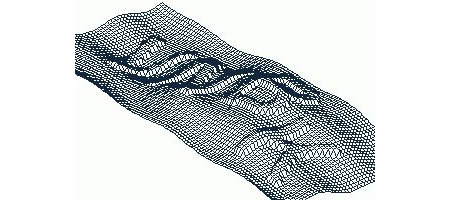
3D captcha. Actually nothing complicated if you know programming.
Logic puzzles
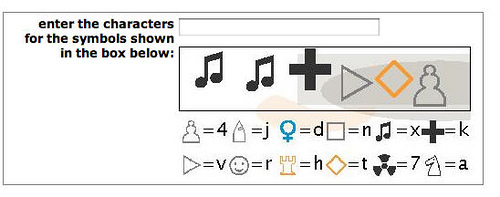
Logical riddle, not captcha. An example is taken from the selection , and on which site this type of captcha was used is now difficult to determine.
Point reading

This is not a captcha for the blind, as you might think, but the world's first captcha made using the Braille system. Now it is abandoned and, fortunately, is not used anywhere.
Music captcha
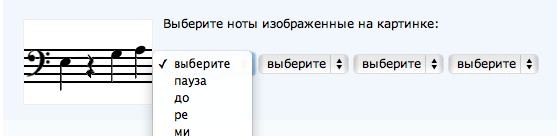
Musical captcha for the site of musicians. The server generates a picture from (pseudo) randomly selected four pictures of notes and pauses. The names of the pictures - numbers from 0 to 13 - correspond to the position number of the note on the stave, starting from the bottom incremental. The key is also random - bass or treble.
Captcha we lost
As there are ways to crack every new generation of captcha, machine learning algorithms give computers more and more opportunities to comprehend the world. At some point, captcha began to be used to teach AI, which begins to act on the same principles on which our brain works.
The evolution of captcha is a testament to the progress of AI. The first reliable puzzles that were used to protect against bots ten years ago can now be solved automatically using computers in 99.8% of cases. While computers are getting better and better at solving puzzles, people can prove their humanity by completing other types of tasks.
In addition, there are many services for solving captcha that serve thousands of live users who are ready for little money to solve any captcha that can be understood.
At one time, Mail.Ru Group came to the same conclusion: this is how an intellectual captcha service appeared that does not require a person to pass verification. We have more than 100 million users, most of which are authorized. This means that with a request to our domains, session cookies are transmitted, by which we identify the user, and then we get his profile, statistics, spam rating, etc. All this information is fed to the input of the classifier algorithm, and at the output we get an assumption about who the user is - a person or a spam bot.
