Electrostatic cleaning of indoor air from decay products of radon. Part 1 Introduction
This publication addresses the problem of air pollution by radon and its daughter decay products ( DPR ). Various facts were collected and shown when radon is concentrated and can be detected by a household radiometer. An understanding of the dangers of radon in the west is indicated and a brief excursion into the theory of radioactive decay and tissue damage is given. And in conclusion, one idea has been proposed, not yet applied for the purification of air from DPR.
Radon is a radioactive gas, 7 times heavier than air, odorless and colorless in trace amounts, which are present everywhere on our planet. However, trace amounts are different ...
For the first time I met radon, or rather the products of its decay, about 15 years ago, by chance, not knowing what it was or why. Carrying out aimless experiments with a household radiometer, I noticed more than once that the kinescope TV screen has an increased radioactive background.

It was noteworthy that this background was present on the television screen, which worked for some time. The TV just turned on or turned off for a long time was not active.

Of course, the usual explanation for this phenomenon is the x-ray radiation of the tube itself during operation or interference from electrostatics. But soft and very insignificant x-ray radiation cannot overcome the glass of the tube or be fixed by the sensor of the used dosimeter-radiometer.

And electrostatics should give a similar effect when turned on, well, and its effect can be eliminated by slightly moistening the glass. The next time radon showed itself in fresh rainwater.

The radioactive background of the first raindrops is markedly increased and is quite observable with a household appliance. Few sources give a true interpretation of this phenomenon. In our region (the city of Gomel) it is generally easy to write off the clouds from the Chernobyl nuclear power plant (and then suddenly forest fires or the sarcophagus fell off again a little - there are enough reasons to suspect). Although "write off" such a course is certainly not worth it.

Also, if you find a good place (mines, caves, cellars), you can directly observe the increased background in the pits or caverns. This background quickly normalizes when the measured cavity is aired.

In general, radon is responsible for the increased background, clearly visible in the described cases. More precisely, the daughter products of its decay or DPR. Usually, without the so-called "special" equipment, radon is almost unlikely to find a chance.

The truth is not always required to bring such equipment to your home. For example, in the United States there is a remote primary screening program for radon in residents' homes. It is based on the exposure in the test room of the “Radon test kit” sponge [1] and its subsequent sending to the research center.

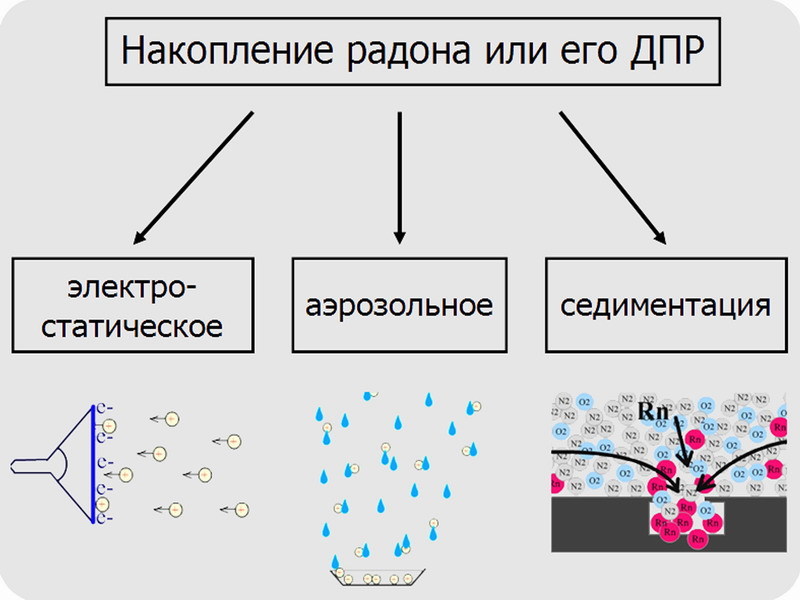
And so, the activity of radon itself and part of its decay products is not recorded by most measuring instruments, especially household ones. Only some products are visible, the proportion of which is small and becomes sufficient for measurement only when the conditions for their concentration are created. The three examples cited are precisely those cases: electrostatic accumulation by a television, aerosol rain and sedimentation in a pit (differences in density).
But where did radon come from? Sometimes the right answer to such a question is everywhere. For if there is so much radon, then its source must be solid. After all, radon, like its daughter products, does not live long - it decomposes. In general, this issue has long been studied. Radon is also a long decay daughter product, usually led by the 238th uranium. Or the 232th thorium.

The immediate ancestor of radon is radium, this is reflected in the name "radon". Uranium and thorium are present in rocks, soil, water, and of course in building materials. The average content or clark of uranium is 27–100,000 percent, and thorium is 96–100,000 [2].

To one degree or another, all descendants will exist next to the head of the series, the number of decays of each of which will be equal to the number of decays of the chapter. That is, for hundreds of thousands of years, uranium will have time (and it has been a long time already!) To produce everything, up to radium. But radon in the series of decays is special, since it is the only gas. He is able to leave the parent, migrate strongly.
Some minerals, such as the widely known granite, contain more uranium, up to 10-20 grams per ton. Normal sand is about a gram per ton.

It turns out that almost any building material is capable of emitting radon. This means that the basement is not more profitable, not cleaner than the cave. In the countries of Europe and the USA, they are already seriously concerned [3] with the radon problem - they are trying to solve it in the following ways: through preliminary verification and non-use of materials and places emitting radon for construction purposes; establishing forced ventilation in places of direct emission of radon. In the United States alone, this translates into a billion dollar annual cost.

Why should radon be considered more dangerous if its source has a total activity an order of magnitude higher, and radon itself also constantly volatilizes due to gas? To explain this, you need to talk a little about radioactive radiation in general. Another school physics course states that radioactive rays are alpha, beta and gamma.

In fact, of course, there are more varieties, but these are the main ones. Gamma rays are electromagnetic radiation, in nature the same as radio waves or ordinary light, but with a "high" level of energy (a thousand or more times higher).

This means that one portion or quantum of gamma rays will transmit as much energy as a thousand servings of ordinary light, and sometimes a million, a billion. But in the nano-world of quantum mechanics, quantity does not mean quality: that which is beyond the power of a million portions of light is available to one portion of gamma rays. Rays obtained artificially or having a small level of energy are called x-rays. Beta and alpha rays are different - a stream of very fast particles.

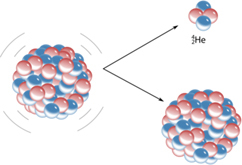
Beta rays - a stream of ordinary electrons, light particles with a negative charge. Alpha rays are helium atoms, devoid of all electrons, that is, their nuclei with a mass of 7300 times the mass of an electron. Charged positively.
The ability of rays to penetrate objects and the strength of the damage they cause (for example, biological) is directly related to these factors. So, gamma rays are the most penetrating, beta rays are worse. And alpha rays almost do not overcome dense obstacles, even a small layer of air slows them down well.

The biological effect is the opposite. If we take for 1 damage caused by the gamma, then beta also has 1, but alpha has a coefficient of 20 [4]. The alpha particle is heavy and large, it quickly dissipates its energy in the substance. One particle, before being converted into an ordinary helium atom, breaks off the electronic layers of the atoms encountered, thereby destroying any chemical bonds.

One can imagine that at one point in the volume of a living organism the size of a cubic nanometer appears a lot of random aggressive chemical compounds called free radicals. Each of which can damage another complex molecule that survived after the first attack of an alpha particle. For example, a DNA macromolecule. Theoretically, one alpha particle is enough to damage one cell: sterilization or, worse, mutations.
The radon of the 220th and 222nd decay, releasing an alpha particle and polonium. The decay of half of radon takes a little less than four days. Polonium, in turn, also decays, giving already a beta particle. And so on down the chain to lead.

As a result, wherever there is a source of radon, where there is radon itself and its daughter products, there is also gamma, beta, alpha radiation. Summarizing, you might think that only gamma rays or beta can do real harm. And this is true if we are talking about ordinary sources, since the upper dead layer of human skin does not pass alpha rays to living cells and cannot be damaged by itself.

But we remember that radon is a gas. In addition, the product of its decay, although not gas, is born in the air in a monatomic form. Like subsequent nuclides, it will be very fine dust. Gas and dust can enter parts of the body where there is no protective layer - the airways and lungs. All 20-fold harm from alpha rays is realized in them, plus part from beta and gamma.

According to the report of the World Health Organization, indoor air pollution with radon causes lung cancer in the region from 3 to 14% of cases, which is the second most common after smoking [5] [6].
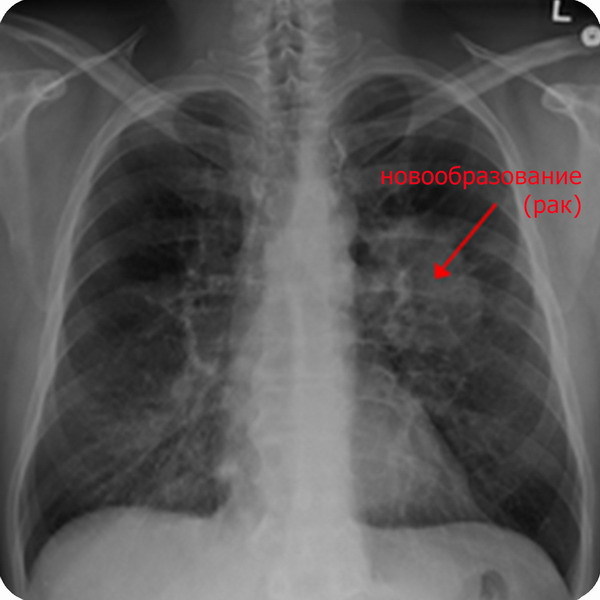
Given that 1.5 million people die from lung cancer each year, among them 150 thousand cases are caused precisely by radon. Thus, among non-smokers, radon in carcinogenicity comes first. A person breathing gassed air near a factory or avenue is less likely to get lung cancer than a person breathing only fresh air, but living or working in rooms where land or building materials inconspicuously emit radioactive gas without color and odor.

How to solve the problem of radon? Before you solve the problem, study it. In our case, the study of the problem suggested one of the options for solving it, although not quite directly. For radiometry of radon in air, it is necessary to concentrate this gas and use a radiometer sensitive to alpha rays. The traditional way is to draw a large volume of air through a special filter and measure the alpha activity of the filter with the mentioned radiometer.

An alternative method is indirect, by measuring beta and gamma activity of daughter decay products [7]. Electrostatics work here, because the decay products of radon are atomic nuclei with a significant positive charge. Of course, having lost speed, they will take part of the electrons from the air or ordinary dust particles, sticking to the latter with the formation of an aerosol. However, a positive charge which will remain. Imagine that we have an electrode charged negatively. An electric field will propagate around it, and when positively charged dust particles fall under its action, they will rush to the source of the field - to the electrode.

Thus, the DPR will be collected in a small area, where their decays are easier to accurately measure. And then we thought, is it possible to use the effect for another purpose - cleaning. After all, this is quite logical: since we took the DPR from the nearest volume of air, it will take time until radon regains their concentration. By the way, even freshly formed radon itself will have a charge, therefore it will be captured.
Currently, in order to identify the effectiveness of the electrostatic accumulation of DPR in relation to cleaning, we are conducting research. We have already assembled and tested the storage installation.

The results of this setup were subjected to radio spectrographic analysis.

The analysis revealed gamma and beta-active DPR radon, although it is not surprising that the spectrograph revealed them. Even a household dosimeter-radiometer in gamma measurement mode will record 5 times more decay events than background ones, and in beta + gamma mode - 50 times.

Of course, this is if the accumulation was sufficient time in the "infected" room.
The research facility itself consists of a high voltage source and a prefabricated electrode, the role of which is an activated carbon tablet. Activated carbon adsorbs heavy vapors and gases, and this property is multiplied under a charge.
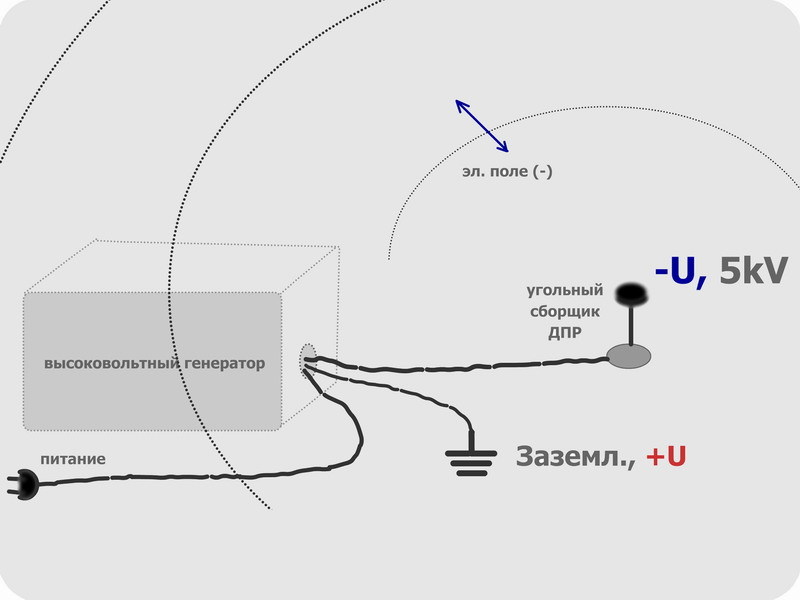
The electrical circuit is still very simple:

Before developing a commercially effective installation that solves the problem with radon, we still have to solve a number of problems, scientific and technical. For example, to reveal how much better it is than aerosol air purification with water. Or to prove effectiveness quantitatively, in the context of an official scientific methodology. Find out the optimal voltage value, the shape and location of the electrodes, their number for minimum energy consumption, cost and a convenient design in the form of a household appliance.

The project at the current stage is far from a ready-made solution, but it is no longer just an idea. It works.
Sources of information used:
- Radon Test Kit .
- Clark numbers of elements . Wikipedia
- WHO handbook on indoor radon: a public health perspective / edited by Hajo Zeeb, and Ferid Shannoun. World Health Organization, 2009.
- Dosimetry in nuclear medicine .
- A. Demkin. Indoor radioactive soil gas and the risk of lung cancer .
- Lung cancer . Wikipedia
- Mahdi Mohamed Ramdan. Radiometry of exhalation of radon from building materials: abstract dis. Candidate of Technical Sciences: Minsk, 1995.
The authors of the project Dzmitry Kalesnikau and Ivan Krauchanka already spoke with this topic on February 6 at the Party Hard conference ! 2016 in Minsk. Work on the project is still ongoing ...
Only registered users can participate in the survey. Please come in.
How do you feel about the problem of radon air pollution?
- 23.7% do not agree that there is at least some threat 51
- 40.4% I didn’t know, but now I see such a danger 87
- 35.8% knew about the problem and is convinced that it is real 77
