Indeed, what is a CRM system?
We have been hearing this question for 11 years, from business owners, employees, developers, people idly strolling around the site. And now he was again asked to us here, on Habré. We changed the habit of responding to all comments and ignored the jt3k question in order to answer it as detailed as possible. It turned out to be not so simple. Do you know what CRM is?

There is no single canonical definition - and this comes from the logic of the type of software itself - the CRM system. The fact is that initially CRM is a concept of customer relationship management, and each company has its own. So, the definition of CRM as software for everyone is also their own, which we, as vendors in full, get at the input. Here is an incomplete list of how the system is called: "program", "softinka", "program for sales", "ERP", "Gantt chart", "glider", "contact manager". Meanwhile, almost any CRM combines all of these naming conventions (unless ERP is already a more confused story).
Therefore, we start with the answer to the jt3k question - what is CRM to explain to the programmer.

To put it bluntly, it’s something like Jira for a commercial service: sales people and marketers conduct users (customers) in the system, initiate incidents (transactions), register business processes (as we do in the framework of ITSM), then build reports and count money. And if you think professionally, then the CRM-system is a central repository of information about customers, transactions and other influences, which has a user interface with a set of functions. Accordingly, CRM performs the most familiar work: it accumulates data, stores data, exchanges them, automates processes and logs actions.
Speaking from the point of view of the head of the company, the CRM system is a tool for managing customers and related information, as well as a way to speed up and streamline all business processes. Notice a word about control! The entire monitoring function of CRM is monthly reports, analytics and KPI (if implemented in the company). CRM does not monitor employees, does not control traffic, doesn’t fire pirated programs, and does not prevent employee inaction — there is another type of software for this.
But most of all we like the definition that we read from colleagues from Salesforce: CRM is the company's nervous system.
It arose not so long ago - already in the early 2000s, when the market was filled with solutions of all types, which developers preferred to call CRM. In fact, everything is CRM, only they are of different types and different capabilities.
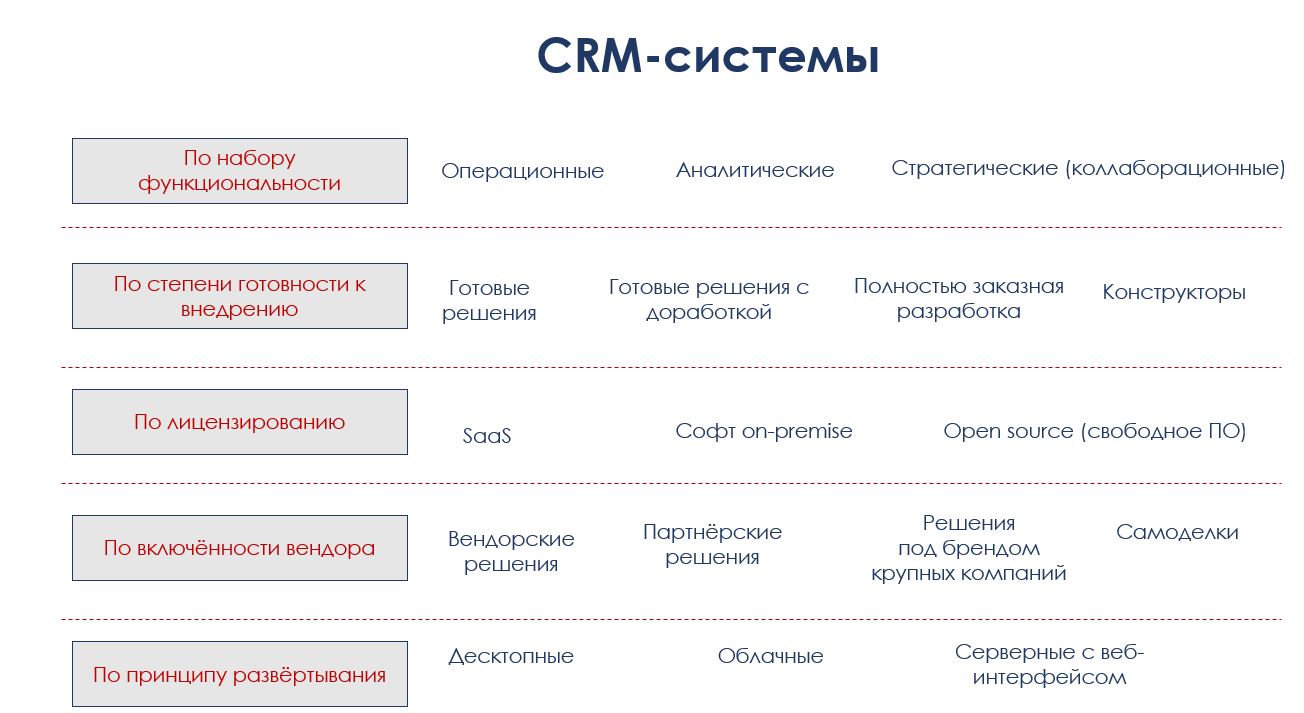
Operational CRM - systems in which operational work is carried out, sales and marketing processes are automated, transactions and documents from which mailings are made, etc. are saved. Reporting in such systems is associated, but not leading, functionality.
Analytical CRM - systems in which analytics prevails. These can be systems with flexible reports and report designers; they can include BI and OLAP modules. As a rule, these are expensive solutions that are suitable for complex integration, for example, with billing by a mobile operator or a payment system of an online store. It happens that analytical CRM does not contain part of the functions for managing sales, marketing and processes, but serves for the purposes of segmentation, assortment management, etc.
Collaboration (this is tracing paper), strategic CRM - systems sharpened for communication, collaboration, including with clients and partners. In such CRM systems, a personal account of a client, an internal social network, or a corporate portal can be provided. Strategic CRM has developed a set of capabilities for managing projects and tasks.
If it is just about sales management (customers + deals + analytics), then it used to be called SFA (sales force automation). Now it’s hard to find software that belongs to this class, but in Russia it’s just so impossible. Yes and to nothing.
There are still separate CRM-boxers who claim that they are operational or analytical, but in general all three types have long penetrated each other and the world of business software is ruled by large and small universal solutions in which everyone works: from telemarketers and sales people to technical support and even developers (for example, in RegionSoft we don’t have any bug trackers and project management systems - we imprisoned our own RegionSoft CRM for this ).
Ready-made solutions - you purchase ready-made components, put them as they are and adapt the business model to the installed software. This option is relatively low-cost and suitable for small companies with standard processes or companies that want to automate one or two aspects of their work (for example, to conduct customer transactions and make calls). Although today in most solutions there are options for customizing the system by the client and even tools for self-completion (for example, in RegionSoft CRM it is a report designer, document templates, business process designer, some CRMs have their own development platform or API).
Ready-made solutions with refinement- you get ready-made components and ask the vendor to finalize the system according to the features of your business in accordance with the technical task. In fact, this is the most common acquisition option, and each vendor is ready to provide revision services. The main task of the client is to correctly assemble the requirements and state them to the developer.
Fully Custom Development- A long, thorny and expensive way to implement CRM in the company. You collect requirements, describe the necessary processes and functionality, the vendor (or a custom development company) creates a detailed ToR and develops a CRM system for you. At the same time, it may turn out that you in vain insisted on such a situation, and could well manage to refine the basic solution. Despite the attractiveness of custom software “just for the company,” it has a tangible minus - in the event of a change in business or requirements in the future, each software change will also be a custom development - long and expensive.
Prefabricated solutions (designers)- software that is gaining popularity, existing in two variations: in the first you select the modules you need and at any time you can buy the rest, in the second you use some basic solution, and mail, telephony, analytics, instant messengers, etc. purchased from a third party and integrated with the main software (as a rule, these are widgets, plugins and add-ons from the marketplaces of the provider of the basic solution).
SaaS - solutions whose licenses you rent and pay for them every month, like for the Internet or phone. This is a profitable scheme for the vendor and not very beneficial for the company: as long as you have CRM, you pay for it - a year, two, five ... The price of ownership is simply cosmic. So, for example, if you have only 10 employees and you pay only 990 rubles per employee per month, the cost of ownership for 5 years will be 594,000 rubles. In general, consider. The calculation mainly goes to the fact that modern users are used to the monthly fee in everything and find this option convenient. Although, of course, they will tell you about scaling and flexibility. By the way, we also have a rental of our CRM-system, but it is not so bonded - just for those who desperately need a CRM-ka, but there is no money to pay for the entire purchase.
Software on-premise- You acquire ownership of the software licenses and pay once. In this case, you are insured against any negative events in the vendor’s business. In the future, you can only pay for major updates if you decide to purchase them.
Free software (open source)Is the most interesting form of CRM system existence. You can be a hardcore IT company, fork a well-known project, gash your features and take money from others for technical support (and she will have a lot of work, the money is not small). You can buy a ready fork and pay for technical support using free software. You can fork, hire a programmer and make an ideal CRM-system for yourself - this is not cheap and difficult, but it can be effective. The main thing is to always carefully watch under what license free software is distributed and for which stack you have to pay the programmer.
Vendor solutions - the CRM system is sold and implemented by the development company itself (almost all of them are Russian systems). This is ideal - you do not overpay anyone and work directly with those who created the software and are ready to answer for it, train, modify, support, etc.
Partnership solutions - a CRM system is sold by a system integrator or a certified partner. Actually, mainly for foreign CRM systems and 1C products. Partners can simply act as an intermediary, or they can modify systems, make complex implementations, develop connectors, plug-ins, etc. They are good if you have a complex implementation, remote installation and modification is impossible, and there is no vendor in the city. In general, this is more of a story for large companies.
Solutions “under the wing of a strong company”- ultra current events of the CRM market. First, Beeline released its CRM (with scandal, slurred functionality and strange promotion), the other day Sberbank reported on the CRM system (in fact, this is a beautiful reworked solution of one of the players in the Russian CRM market). Compared to Beeline, the Sberbank system is quite digestible, but promotion for free, of course, is just a marketing ploy. This type of system is bad for a number of reasons: firstly, this is not a core business of the company, and secondly, it is not CRM for the benefit of the business, but a way to keep your clients to yourself, giving them yet another tool that will tie them to the company, Thirdly, this is the need of companies for your data (it is quite possible that they will be analyzed and used to create products and services - wait and see, this is only our assumption).
Homemade products are simple CRMs that are created by internal programmers or freelancers. Typically, this is something like a simple contact manager. However, do not underestimate such decisions - sometimes they come out successful. RegionSoft CRM also once was a system for internal use, and over 11 years has grown to complex ERP in its maximum edition Enterprise Plus. Here, in general, how lucky.
Desktop - CRM is installed on the server of the company (it may just be a modern PC), and users get working applications. Remote terminal access is possible from any device with an Internet connection. Contrary to popular myth, desktop software has no restrictions for the branch or holding structure of the company. This is the safest way to deploy.
Cloud- users work through a web interface or from a mobile, and all information is stored in the cloud (in fact, on other people's physical servers in a remote data center). It is believed that this is the most convenient option from the point of view of administration (not really, but not about that now). Indeed, you do not need to worry about server status, data storage, etc. However, you pay for this, among other things, with security - data in any cloud can be compromised, there would be a desire. By the way, when buying a cloud-based CRM system, do not forget to clarify whether there is an additional charge for backups, how they are done, how much they are stored, what uptime the server has. Most likely, you will discover new financial nuances.
Server-side web-based- All data is stored in your office cloud (on your servers), and users access through the familiar web interface. This is a safer solution than the cloud, but also more vulnerable than the desktop.
Another problem that does not allow to accurately determine CRM as a type of software is the software solutions surrounding the business zoo. And some of them, intentionally or unknowingly, are also called CRM systems. Let's review, literally in a couple of lines, go over the main types of software, which is most often found in business and intersects with CRM. By the way, we wrote about these and other types in detail .
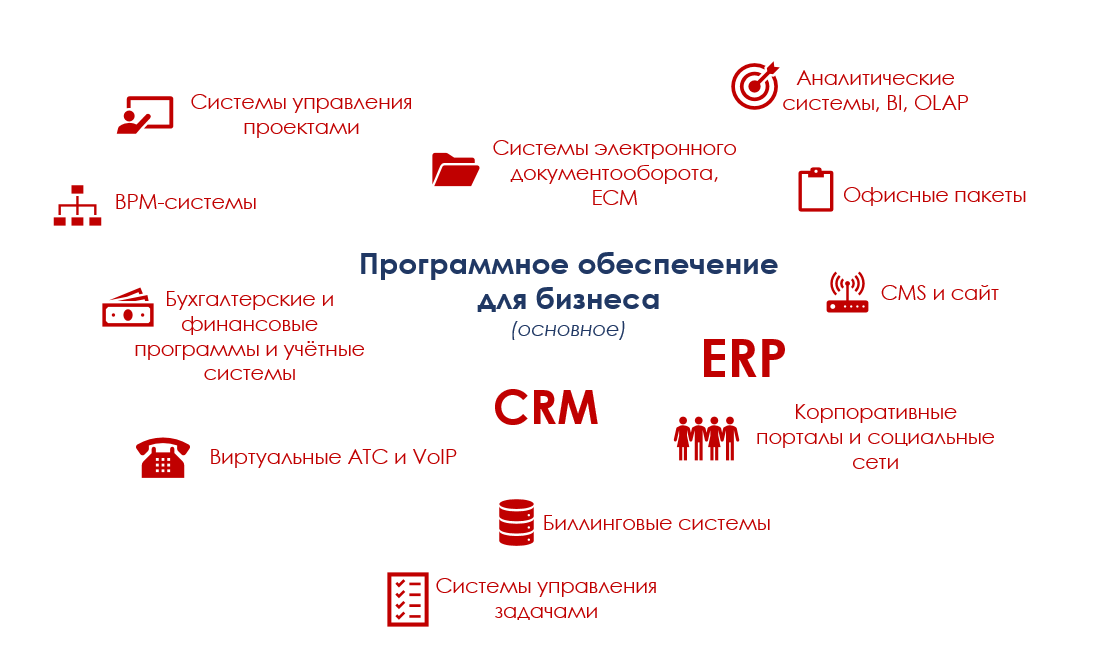
Project management systems - software solutions that allow you to manage projects, that is, plan the employment of team members and resources, prioritize, determine the order of work, set deadlines. As a rule, in the center of such systems is not the client, but the project - internal or external.
Task management systems- light version of the previous type. In fact, a collective planner with tasks, deadlines, statuses, responsible and reminders. Again, the client in such systems acts only as an attribute of the task.
Office suites are the usual text editor, spreadsheet editor and presentation editor. It has nothing to do with CRM, but often acts as a repository of the client base (there has already been a holivar on this topic).
Accounting and financial programs and accounting systems- The eternal competitor of CRM-systems, their own headache. On the one hand, finances and cash flows are at the center of accounting systems, on the other hand, they are trying to adapt them by hook or by crook to the jurisdiction of clients. With the third, everyone needs to integrate with this if the business has such requirements for CRM. The main problem is that system administrators, sales people, and accountants have completely different entities and objects with which they work. Therefore, understanding is rarely achieved.
ERP- huge complex enterprise resource planning systems. Used in companies with numerous financial flows, in production corporations, factories, etc. They differ from CRM in that they focus not on the client, but on the company's resources and production processes. However, nothing prevents combining the capabilities of CRM and ERP in one system.
CMS - content management system for a site and / or blog. It has nothing to do with CRM, confused by consonance.
BPM systems- systems for designing and modeling business processes of the company. They allow you to automate literally everything: from a shallow routine to large production processes. In its pure form are needed only by large specialized companies. At the center of such systems are the company's internal business processes, their debugging, and flawless functioning. As a CRM module - a very interesting and necessary thing, even for small companies. Be sure to set up business processes, it is useful to review and automate them.
Virtual PBX and Integrated VoIP- the type of software that they say "we have enough dialers." Indeed, many IP telephony operators have their own contact managers and even minimal CRM. As a rule, functionality begins to be quickly lacking, therefore it is better to take a normal developed CRM and integrate it with telephony and a virtual telephone exchange. It turns out well. And most importantly, it is in demand by almost all customers - so much so that, for example, we have developed our own SIP-background and our VoIP-connector for telephony routing.
Billing systems are systems in which customer payments are taken into account and analyzed (not to be confused with processing payment systems). If necessary, integrate with the CRM-system.
Analytical systems- are found mainly in large companies. These are systems for processing data received from customers. can be vendor, or can samopisny. The simplest option is that all data is accumulated in the DBMS, and programmers prepare custom uploads for employees: an SQL query is written, an array is unloaded, and transferred to an interested manager. The most difficult is expensive import solutions like SAP.
ECM-systems (aka EDMS) - electronic document management systems with the formation, storage, coordination and archiving of documents. Usually used on their own, it is extremely rare to be integrated with or included in CRM.
Corporate portals and corporate social networks- Previously, they were exclusively aimed at communicating between employees within the company and maintaining a corporate knowledge base, today they have grown in CRM capabilities and come close to them. The big minus is a lot of distractions while working in the interface and the limited CRM functionality. Plus - all in one, the employee does not need to switch between programs.
So, introducing enterprise software, the main thing is not to mix it up and choose the right solutions based on the size and needs of the business.
So what is the definition? We do not pretend to be the ultimate truth, so we just offer our own version. A CRM system is software that serves as a tool for accumulating, storing and developing a client base, as well as designing and automating business processes in a company. Although, we repeat, for each company, the goals of implementation are different and, as a result, the definition is also different. Therefore, we will give an informal, but global definition: CRM is a business-specific program that will accelerate processes, help you bypass competitors, and preserve your valuable asset — your customer base. Of course, if you yourself want it. Well, or give your definition in the comments - if we collectively think of something, we will update the article.
If you love IT and you are interested in getting a job at RegonSoft, we will be happy to consider your candidacy, regardless of the availability of vacancies.
We are interested in specialists in the field of developing IT solutions and technical support with a wide stack of technologies, as well as experienced salespeople. Call +7 (499) 709-81-41 (Moscow), +7 (831) 233-13-03 (N. Novgorod) or send your resume to personal@regionsoft.ru

We are trying to formulate a definition
There is no single canonical definition - and this comes from the logic of the type of software itself - the CRM system. The fact is that initially CRM is a concept of customer relationship management, and each company has its own. So, the definition of CRM as software for everyone is also their own, which we, as vendors in full, get at the input. Here is an incomplete list of how the system is called: "program", "softinka", "program for sales", "ERP", "Gantt chart", "glider", "contact manager". Meanwhile, almost any CRM combines all of these naming conventions (unless ERP is already a more confused story).
Therefore, we start with the answer to the jt3k question - what is CRM to explain to the programmer.

To put it bluntly, it’s something like Jira for a commercial service: sales people and marketers conduct users (customers) in the system, initiate incidents (transactions), register business processes (as we do in the framework of ITSM), then build reports and count money. And if you think professionally, then the CRM-system is a central repository of information about customers, transactions and other influences, which has a user interface with a set of functions. Accordingly, CRM performs the most familiar work: it accumulates data, stores data, exchanges them, automates processes and logs actions.
Speaking from the point of view of the head of the company, the CRM system is a tool for managing customers and related information, as well as a way to speed up and streamline all business processes. Notice a word about control! The entire monitoring function of CRM is monthly reports, analytics and KPI (if implemented in the company). CRM does not monitor employees, does not control traffic, doesn’t fire pirated programs, and does not prevent employee inaction — there is another type of software for this.
But most of all we like the definition that we read from colleagues from Salesforce: CRM is the company's nervous system.
Why is there so many faces?
It arose not so long ago - already in the early 2000s, when the market was filled with solutions of all types, which developers preferred to call CRM. In fact, everything is CRM, only they are of different types and different capabilities.

The main classification you may come across is the separation of all CRM systems into three types
Operational CRM - systems in which operational work is carried out, sales and marketing processes are automated, transactions and documents from which mailings are made, etc. are saved. Reporting in such systems is associated, but not leading, functionality.
Analytical CRM - systems in which analytics prevails. These can be systems with flexible reports and report designers; they can include BI and OLAP modules. As a rule, these are expensive solutions that are suitable for complex integration, for example, with billing by a mobile operator or a payment system of an online store. It happens that analytical CRM does not contain part of the functions for managing sales, marketing and processes, but serves for the purposes of segmentation, assortment management, etc.
Collaboration (this is tracing paper), strategic CRM - systems sharpened for communication, collaboration, including with clients and partners. In such CRM systems, a personal account of a client, an internal social network, or a corporate portal can be provided. Strategic CRM has developed a set of capabilities for managing projects and tasks.
If it is just about sales management (customers + deals + analytics), then it used to be called SFA (sales force automation). Now it’s hard to find software that belongs to this class, but in Russia it’s just so impossible. Yes and to nothing.
There are still separate CRM-boxers who claim that they are operational or analytical, but in general all three types have long penetrated each other and the world of business software is ruled by large and small universal solutions in which everyone works: from telemarketers and sales people to technical support and even developers (for example, in RegionSoft we don’t have any bug trackers and project management systems - we imprisoned our own RegionSoft CRM for this ).
By the degree of readiness for implementation
Ready-made solutions - you purchase ready-made components, put them as they are and adapt the business model to the installed software. This option is relatively low-cost and suitable for small companies with standard processes or companies that want to automate one or two aspects of their work (for example, to conduct customer transactions and make calls). Although today in most solutions there are options for customizing the system by the client and even tools for self-completion (for example, in RegionSoft CRM it is a report designer, document templates, business process designer, some CRMs have their own development platform or API).
Ready-made solutions with refinement- you get ready-made components and ask the vendor to finalize the system according to the features of your business in accordance with the technical task. In fact, this is the most common acquisition option, and each vendor is ready to provide revision services. The main task of the client is to correctly assemble the requirements and state them to the developer.
Fully Custom Development- A long, thorny and expensive way to implement CRM in the company. You collect requirements, describe the necessary processes and functionality, the vendor (or a custom development company) creates a detailed ToR and develops a CRM system for you. At the same time, it may turn out that you in vain insisted on such a situation, and could well manage to refine the basic solution. Despite the attractiveness of custom software “just for the company,” it has a tangible minus - in the event of a change in business or requirements in the future, each software change will also be a custom development - long and expensive.
Prefabricated solutions (designers)- software that is gaining popularity, existing in two variations: in the first you select the modules you need and at any time you can buy the rest, in the second you use some basic solution, and mail, telephony, analytics, instant messengers, etc. purchased from a third party and integrated with the main software (as a rule, these are widgets, plugins and add-ons from the marketplaces of the provider of the basic solution).
Licensing
SaaS - solutions whose licenses you rent and pay for them every month, like for the Internet or phone. This is a profitable scheme for the vendor and not very beneficial for the company: as long as you have CRM, you pay for it - a year, two, five ... The price of ownership is simply cosmic. So, for example, if you have only 10 employees and you pay only 990 rubles per employee per month, the cost of ownership for 5 years will be 594,000 rubles. In general, consider. The calculation mainly goes to the fact that modern users are used to the monthly fee in everything and find this option convenient. Although, of course, they will tell you about scaling and flexibility. By the way, we also have a rental of our CRM-system, but it is not so bonded - just for those who desperately need a CRM-ka, but there is no money to pay for the entire purchase.
Software on-premise- You acquire ownership of the software licenses and pay once. In this case, you are insured against any negative events in the vendor’s business. In the future, you can only pay for major updates if you decide to purchase them.
Free software (open source)Is the most interesting form of CRM system existence. You can be a hardcore IT company, fork a well-known project, gash your features and take money from others for technical support (and she will have a lot of work, the money is not small). You can buy a ready fork and pay for technical support using free software. You can fork, hire a programmer and make an ideal CRM-system for yourself - this is not cheap and difficult, but it can be effective. The main thing is to always carefully watch under what license free software is distributed and for which stack you have to pay the programmer.
By inclusion vendor
Vendor solutions - the CRM system is sold and implemented by the development company itself (almost all of them are Russian systems). This is ideal - you do not overpay anyone and work directly with those who created the software and are ready to answer for it, train, modify, support, etc.
Partnership solutions - a CRM system is sold by a system integrator or a certified partner. Actually, mainly for foreign CRM systems and 1C products. Partners can simply act as an intermediary, or they can modify systems, make complex implementations, develop connectors, plug-ins, etc. They are good if you have a complex implementation, remote installation and modification is impossible, and there is no vendor in the city. In general, this is more of a story for large companies.
Solutions “under the wing of a strong company”- ultra current events of the CRM market. First, Beeline released its CRM (with scandal, slurred functionality and strange promotion), the other day Sberbank reported on the CRM system (in fact, this is a beautiful reworked solution of one of the players in the Russian CRM market). Compared to Beeline, the Sberbank system is quite digestible, but promotion for free, of course, is just a marketing ploy. This type of system is bad for a number of reasons: firstly, this is not a core business of the company, and secondly, it is not CRM for the benefit of the business, but a way to keep your clients to yourself, giving them yet another tool that will tie them to the company, Thirdly, this is the need of companies for your data (it is quite possible that they will be analyzed and used to create products and services - wait and see, this is only our assumption).
Homemade products are simple CRMs that are created by internal programmers or freelancers. Typically, this is something like a simple contact manager. However, do not underestimate such decisions - sometimes they come out successful. RegionSoft CRM also once was a system for internal use, and over 11 years has grown to complex ERP in its maximum edition Enterprise Plus. Here, in general, how lucky.
Deployment Principle
Desktop - CRM is installed on the server of the company (it may just be a modern PC), and users get working applications. Remote terminal access is possible from any device with an Internet connection. Contrary to popular myth, desktop software has no restrictions for the branch or holding structure of the company. This is the safest way to deploy.
Cloud- users work through a web interface or from a mobile, and all information is stored in the cloud (in fact, on other people's physical servers in a remote data center). It is believed that this is the most convenient option from the point of view of administration (not really, but not about that now). Indeed, you do not need to worry about server status, data storage, etc. However, you pay for this, among other things, with security - data in any cloud can be compromised, there would be a desire. By the way, when buying a cloud-based CRM system, do not forget to clarify whether there is an additional charge for backups, how they are done, how much they are stored, what uptime the server has. Most likely, you will discover new financial nuances.
Server-side web-based- All data is stored in your office cloud (on your servers), and users access through the familiar web interface. This is a safer solution than the cloud, but also more vulnerable than the desktop.
Business Software Zoo
Another problem that does not allow to accurately determine CRM as a type of software is the software solutions surrounding the business zoo. And some of them, intentionally or unknowingly, are also called CRM systems. Let's review, literally in a couple of lines, go over the main types of software, which is most often found in business and intersects with CRM. By the way, we wrote about these and other types in detail .

Project management systems - software solutions that allow you to manage projects, that is, plan the employment of team members and resources, prioritize, determine the order of work, set deadlines. As a rule, in the center of such systems is not the client, but the project - internal or external.
Task management systems- light version of the previous type. In fact, a collective planner with tasks, deadlines, statuses, responsible and reminders. Again, the client in such systems acts only as an attribute of the task.
Office suites are the usual text editor, spreadsheet editor and presentation editor. It has nothing to do with CRM, but often acts as a repository of the client base (there has already been a holivar on this topic).
Accounting and financial programs and accounting systems- The eternal competitor of CRM-systems, their own headache. On the one hand, finances and cash flows are at the center of accounting systems, on the other hand, they are trying to adapt them by hook or by crook to the jurisdiction of clients. With the third, everyone needs to integrate with this if the business has such requirements for CRM. The main problem is that system administrators, sales people, and accountants have completely different entities and objects with which they work. Therefore, understanding is rarely achieved.
ERP- huge complex enterprise resource planning systems. Used in companies with numerous financial flows, in production corporations, factories, etc. They differ from CRM in that they focus not on the client, but on the company's resources and production processes. However, nothing prevents combining the capabilities of CRM and ERP in one system.
CMS - content management system for a site and / or blog. It has nothing to do with CRM, confused by consonance.
BPM systems- systems for designing and modeling business processes of the company. They allow you to automate literally everything: from a shallow routine to large production processes. In its pure form are needed only by large specialized companies. At the center of such systems are the company's internal business processes, their debugging, and flawless functioning. As a CRM module - a very interesting and necessary thing, even for small companies. Be sure to set up business processes, it is useful to review and automate them.
Virtual PBX and Integrated VoIP- the type of software that they say "we have enough dialers." Indeed, many IP telephony operators have their own contact managers and even minimal CRM. As a rule, functionality begins to be quickly lacking, therefore it is better to take a normal developed CRM and integrate it with telephony and a virtual telephone exchange. It turns out well. And most importantly, it is in demand by almost all customers - so much so that, for example, we have developed our own SIP-background and our VoIP-connector for telephony routing.
Billing systems are systems in which customer payments are taken into account and analyzed (not to be confused with processing payment systems). If necessary, integrate with the CRM-system.
Analytical systems- are found mainly in large companies. These are systems for processing data received from customers. can be vendor, or can samopisny. The simplest option is that all data is accumulated in the DBMS, and programmers prepare custom uploads for employees: an SQL query is written, an array is unloaded, and transferred to an interested manager. The most difficult is expensive import solutions like SAP.
ECM-systems (aka EDMS) - electronic document management systems with the formation, storage, coordination and archiving of documents. Usually used on their own, it is extremely rare to be integrated with or included in CRM.
Corporate portals and corporate social networks- Previously, they were exclusively aimed at communicating between employees within the company and maintaining a corporate knowledge base, today they have grown in CRM capabilities and come close to them. The big minus is a lot of distractions while working in the interface and the limited CRM functionality. Plus - all in one, the employee does not need to switch between programs.
So, introducing enterprise software, the main thing is not to mix it up and choose the right solutions based on the size and needs of the business.
So what is the definition? We do not pretend to be the ultimate truth, so we just offer our own version. A CRM system is software that serves as a tool for accumulating, storing and developing a client base, as well as designing and automating business processes in a company. Although, we repeat, for each company, the goals of implementation are different and, as a result, the definition is also different. Therefore, we will give an informal, but global definition: CRM is a business-specific program that will accelerate processes, help you bypass competitors, and preserve your valuable asset — your customer base. Of course, if you yourself want it. Well, or give your definition in the comments - if we collectively think of something, we will update the article.
If you love IT and you are interested in getting a job at RegonSoft, we will be happy to consider your candidacy, regardless of the availability of vacancies.
We are interested in specialists in the field of developing IT solutions and technical support with a wide stack of technologies, as well as experienced salespeople. Call +7 (499) 709-81-41 (Moscow), +7 (831) 233-13-03 (N. Novgorod) or send your resume to personal@regionsoft.ru
