NetApp ONTAP 9
The release of firmware version 8.3 was probably the most important among all previous versions of ONTAP software for NetApp FAS storage. Which included a lot of new functionality and marked the transition from 7-Mode to Clustered ONTAP. The recently announced version 9.0 (already available for download ) also contains many new features and improvements, let's look at the most important of them.

Improvements in MetroCluster :
As many could already know, ONTAP software is now available not only on the FAS platform, but also in the form of SDS storage , as well as in public clouds .

In view of the increase in the volume of both mechanical and SSD drives, NetApp has developed (a long time ago) and patented a new type of RAID with three parity drives . TEC stands for Triple Erasure Coding, and TP stands for Triple-Parity — both names are used synonymously. In such a RAID group there are three parity disks. The first one calls Row Parity (Horizontal Parity), the second DP (Double Parity or Diagonal Parity), the third AP (Anti-Diogonal Parity).
RAID-TEC can be used for SSDs, SASs and larger disks, the maximum length of a RAID group is now 29 devices for all these types of disks. RAID-TEC will also be used for ADP configurations. Thanks to an additional anti-diagonal partiti drive, the resiliency of such a RAID group increased 100 times compared to RAID-DP.
Let me remind you that RAID-DP in terms of fault tolerance is slightly superior to RAID10, as it protects against the failure of any two disks (unlike RAID10, where the output of two mirrored disks leads to the loss of the entire group). RAID-TEC will be used by default for all drives of 6TB and above, and is required for drives of 10TB and above. As usual, on-the-fly conversion from RAID-DP to RAID-TEC is supported (as it is now with RAID4).

The company made a lot of efforts to increase the level of usable space for systems with a small number of disks in relation to the "raw space" using ADP technology. In the new release, this idea was developed and will save 17% more compared to 8.3.X. Improvements will affect only systems with SSDs: FAS and AFF. Where to save expensive SSD drives, partitioning of the disk into 3 parts is used by analogy with ADP Root-Data (two partitions: one for the Root aggregate, the other for the Data aggregate): one small partition to create a Root aggregate (R), and two equal partitions for Data aggregates (D2), each of which will be given under the control of each of the two controllers. This will save not only the absence of a dedicated Root unit, but also reduce the number of parity (RP, DP, AP) and Spare drives. Those. in practice, this will save 3-4 drives (RAID-DP and RAID-TP, respectively) for systems with one shelf clogged with SSD drives.

In a storage system from a company that was a pioneer in deduplication and compression for Tier 1, it was possible to fumble a deduplicated block up to 255 links to 1 block, and starting from version 8.1 and higher this number was increased to 32767: 1, i.e. 64000 identical 4KB blocks could shrink up to 2 blocks of information. But with the imposition of compression, the block size did not always equal 4KB. So came the new technology - compaction, which works in conjunction with deduplication and compression. The idea of compaction came because after dedup and compression some of the data after compression became less than 4KB of the block, while the minimum block size of the WAFL file system was 4KB, as a result, no matter how hard we squeezed such a data block, it still occupied its entire minimum amount , and compression for data with small blocks did not make sense in terms of saving space.
This technology, together with other space efficiency technologies, is guaranteed to reduce disk space usage for AFF systems from 4 times to one or more. For existing customers with ONTAP 8.3.2+, there is a calculator that allows you to estimate how much you can save by switching to ONTAP 9 and including all the mechanisms for saving space.
More details in the article .

Allows you to quickly monitor the status of the storage, consumed resources and the degree of savings through the use of compression and deduplication.

The OnCommand System Manager interface has been updated, the main purpose of the update was taken to simplify the management of cluster storage. Along with this, load information in real time about any cluster object will be displayed.
Added the ability to scan SAN initiators for adding to the moon masking list (iGroup), previously this could be done manually from the storage interface or directly from the initiating host using the NetApp Host Utilities utility.
This functionality helps with load balancing and balancing. It will help prevent excessive utilization of the node or assembly above the optimum point, thereby preventing performance degradation and tell you more precisely where additional resources are required to store data.

NetApp systems with ONTAP support drives with hardware encryption of data (NSE, NetApp Storage Encryption) using an encryption key located on a supported Key Manager and transferred using the KMIP protocol. Starting with ONTAP version 9, along with an external Key Manager, you can store encryption keys on storage without the need for specialized equipment. To configure Onboard Key Manager, you only need a passphrase and drives with encryption support.

NetApp is the first A-Brand storage manufacturer to announce support for 15TB SSD drives. Now imagine an AFF system with ONTAP9, ADP RD2, RAID-TEC and 4: 1 compression. How much useful space can you get in one 6U system with this 2U shelf? Let's count. One 15TB disk (Physical & Right sized = 14307 GiB), out of 24 disks in the Active-Active (RD2) configuration with RAID-TEC we get 20 data disks, 3 parity disks and 1 Hot Spare. Subtract the ADP for Root aggregate 14307 - 53.88 GiB = 14253.12 GiB. We calculate the space of useful disks 20 X 14253.12 = 285062.4 GiB. Now subtract 10% WAFL Reserve 285062.4 - 10% = 256556.16 GiB. And in the end, we multiply the resulting space by the minimum guaranteed data compression ratio 256556.16 * 4 = 1026224.64 GiB, i.e. 1002 TiB effective space!
NetApp, unlike many of its competitors, has been constantly developing the same platform with ONTAP software for many years and allows you to use all its new useful and interesting functions for both new and old customers who can recycle their old equipment. As a rule, storage systems are supported about 2-3-4 generations ago. And this very well allows you to save investment to end customers. For example, take FAS6210, this system had a FAS6220 receiver, then FAS8040, and now FAS8200.
So, the following FAS platforms with ONTAP 9 are supported:
And as usual, the old disk shelves are supported.
Now the volume can be transferred from one SVM to another.
More details here .
NetApp continues to develop its flagship ONTAP software and delight not only new, but also its old customers, who can upgrade their old storage models to new firmware versions and get new functionality thus saving their investments. In the new version, a lot of effort was made in order to simplify the administration of the cluster system as much as possible, increase its reliability and increase efficiency. The rich and constantly added functionality complements the ONTAP clustering capabilities in combination with the “Share-Nothing” ideology and is very suitable for SSD media, where the new storage bottleneck is the CPU, not the disk subsystem.
» This may contain links to Habra articles that will be published later .
"Please send messages about errors in the text to the LAN .
» Comments, additions and questions on the opposite article, please comment .

- RAID-TEC
- ADP Enhancements: Root-Data-Data Partitioning (RD2)
- Support for SSD 15TB disks and a new disk shelf for them DS224C (the last digit means the SAS port speed in Gbit / s, the digit C when converting from hexadecimal to decimal means 12, i.e. 12 Gbit / s). In-Band ACP Support - No more external ACP required for DS224C
- HDD Support 10TB (MSATA)
- Inline Data Compaction (as part of the compression mechanism) with a guaranteed reduction of the used space 4: 1 (For more information about the conditions of the 4: 1 guarantee program, ask your integrator / distributor or the vendor directly). Enabled by default in AFF systems and optional for FAS systems. It is guaranteed that not all data will be compressed, for example, videos or already compressed archives, as you know, will not be compressed
- Performance Improvement for AFF Systems: Increased IOPS, Decreased Latency
- Headroom Manager- how much more performance remains for the current configuration / load at the aggregate and node level
- Support for SnapLock - WORM technology to protect data from changes. SnapLock is a mechanism that can lock data from being deleted for a while. It is necessary, for example, for financial institutions to provide a guarantee of the invariability of the report.
- On-board Key-Manager for storing data encryption keys on the storage itself
- Support for the new ONTAP Select platform , which can be installed on Komoditi equipment
- Simplified template system for initial installation and setup
- Mobile Autosupport mobile application, about all available mobile applications here
- OnCommand Performance Manager integrated with OnCommand System Manager
- Support for cache-retention policies on Flash Pool aggregates - data in volumes with a higher cache-retention policy will remain in the cache longer, and with a lower one - less
- Improvements in the QoS mechanism - the number of policy groups in the cluster has been increased and the ability to set maximums at the same time in both IOPS and MB / s has been added
- Improvements in SAN - ODX LUN copy between clusters
- Support for implementing root volume between aggregates
- volume rehost - Support for transferring volume from one SVM to another
- When using SnapMirror for SVM , you can exclude volumes and LIFs that do not need to be replicated to the DR site
- Support for SMB 3.1.1 and increased MTU size, now supports up to 1MB
- SMB support with Workgroup using local authentication
- Support for NDMP extension 0x2050, which allows you to manage storage snapshots and recover volumes and files from them
- Added Bad Port isolation functionality to detect unstable ports and start LIF interface migration
- RSA functionality moved from SP to ONTAP
- Fast Failover for SAN: Faster failover from 2 to 15 seconds for AFF
- iGroup ping - a function that allows the storage administrator to check the availability of initiators in iGroup
Improvements in MetroCluster :
- 8 nodes (4HA systems) on two sites - 4 nodes (2 HA systems) on each site
- 8-node system supports mix nodes: AFF and FAS
- 8-node system supports a mix of nodes: from different models of FAS / AFF systems
- MetroCluster non-Mirrored Aggregates
As many could already know, ONTAP software is now available not only on the FAS platform, but also in the form of SDS storage , as well as in public clouds .

RAID-TEC (RAID-TP)
In view of the increase in the volume of both mechanical and SSD drives, NetApp has developed (a long time ago) and patented a new type of RAID with three parity drives . TEC stands for Triple Erasure Coding, and TP stands for Triple-Parity — both names are used synonymously. In such a RAID group there are three parity disks. The first one calls Row Parity (Horizontal Parity), the second DP (Double Parity or Diagonal Parity), the third AP (Anti-Diogonal Parity).
RAID-TEC can be used for SSDs, SASs and larger disks, the maximum length of a RAID group is now 29 devices for all these types of disks. RAID-TEC will also be used for ADP configurations. Thanks to an additional anti-diagonal partiti drive, the resiliency of such a RAID group increased 100 times compared to RAID-DP.
Let me remind you that RAID-DP in terms of fault tolerance is slightly superior to RAID10, as it protects against the failure of any two disks (unlike RAID10, where the output of two mirrored disks leads to the loss of the entire group). RAID-TEC will be used by default for all drives of 6TB and above, and is required for drives of 10TB and above. As usual, on-the-fly conversion from RAID-DP to RAID-TEC is supported (as it is now with RAID4).

ADP: Root-Data-Data Partitioning (RD2)
The company made a lot of efforts to increase the level of usable space for systems with a small number of disks in relation to the "raw space" using ADP technology. In the new release, this idea was developed and will save 17% more compared to 8.3.X. Improvements will affect only systems with SSDs: FAS and AFF. Where to save expensive SSD drives, partitioning of the disk into 3 parts is used by analogy with ADP Root-Data (two partitions: one for the Root aggregate, the other for the Data aggregate): one small partition to create a Root aggregate (R), and two equal partitions for Data aggregates (D2), each of which will be given under the control of each of the two controllers. This will save not only the absence of a dedicated Root unit, but also reduce the number of parity (RP, DP, AP) and Spare drives. Those. in practice, this will save 3-4 drives (RAID-DP and RAID-TP, respectively) for systems with one shelf clogged with SSD drives.

Inline data compaction
In a storage system from a company that was a pioneer in deduplication and compression for Tier 1, it was possible to fumble a deduplicated block up to 255 links to 1 block, and starting from version 8.1 and higher this number was increased to 32767: 1, i.e. 64000 identical 4KB blocks could shrink up to 2 blocks of information. But with the imposition of compression, the block size did not always equal 4KB. So came the new technology - compaction, which works in conjunction with deduplication and compression. The idea of compaction came because after dedup and compression some of the data after compression became less than 4KB of the block, while the minimum block size of the WAFL file system was 4KB, as a result, no matter how hard we squeezed such a data block, it still occupied its entire minimum amount , and compression for data with small blocks did not make sense in terms of saving space.
This technology, together with other space efficiency technologies, is guaranteed to reduce disk space usage for AFF systems from 4 times to one or more. For existing customers with ONTAP 8.3.2+, there is a calculator that allows you to estimate how much you can save by switching to ONTAP 9 and including all the mechanisms for saving space.
More details in the article .

Autosupport Mobile App
Allows you to quickly monitor the status of the storage, consumed resources and the degree of savings through the use of compression and deduplication.

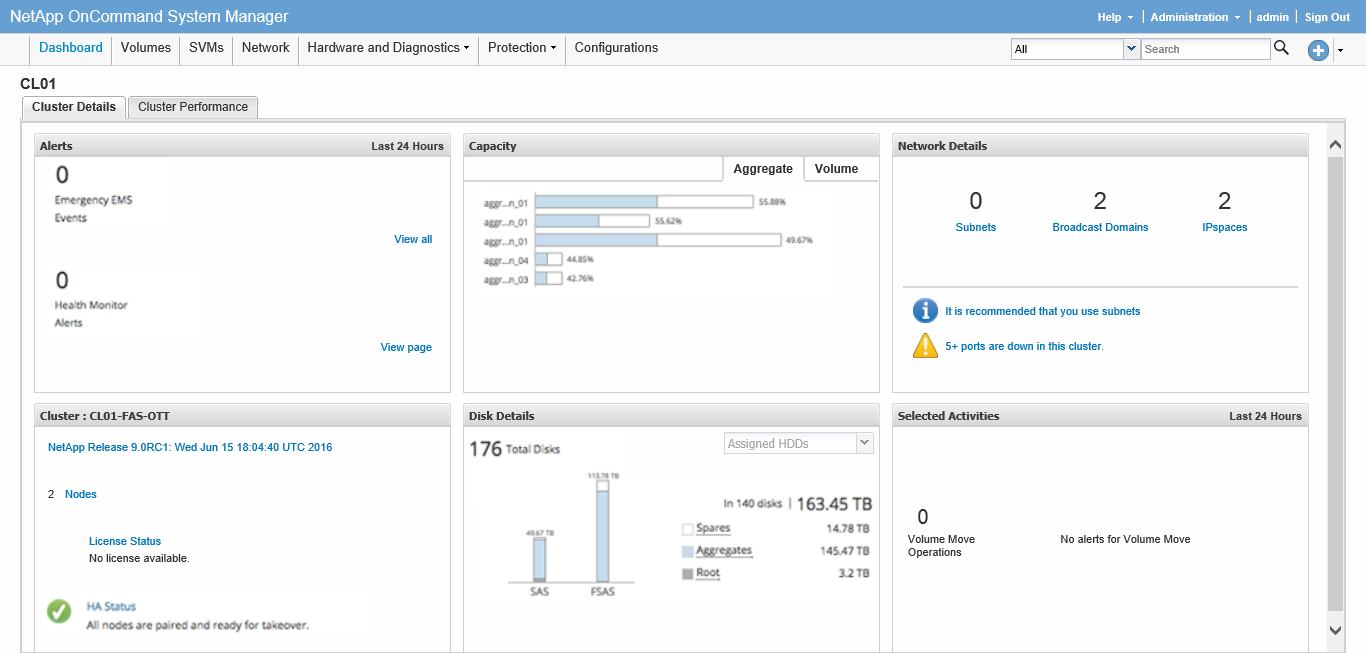
Oncommand system manager
The OnCommand System Manager interface has been updated, the main purpose of the update was taken to simplify the management of cluster storage. Along with this, load information in real time about any cluster object will be displayed.
Added the ability to scan SAN initiators for adding to the moon masking list (iGroup), previously this could be done manually from the storage interface or directly from the initiating host using the NetApp Host Utilities utility.

Headroom manager
This functionality helps with load balancing and balancing. It will help prevent excessive utilization of the node or assembly above the optimum point, thereby preventing performance degradation and tell you more precisely where additional resources are required to store data.

Onboard Key Manager (OKM)
NetApp systems with ONTAP support drives with hardware encryption of data (NSE, NetApp Storage Encryption) using an encryption key located on a supported Key Manager and transferred using the KMIP protocol. Starting with ONTAP version 9, along with an external Key Manager, you can store encryption keys on storage without the need for specialized equipment. To configure Onboard Key Manager, you only need a passphrase and drives with encryption support.

1PB in a 24-disk shelf
NetApp is the first A-Brand storage manufacturer to announce support for 15TB SSD drives. Now imagine an AFF system with ONTAP9, ADP RD2, RAID-TEC and 4: 1 compression. How much useful space can you get in one 6U system with this 2U shelf? Let's count. One 15TB disk (Physical & Right sized = 14307 GiB), out of 24 disks in the Active-Active (RD2) configuration with RAID-TEC we get 20 data disks, 3 parity disks and 1 Hot Spare. Subtract the ADP for Root aggregate 14307 - 53.88 GiB = 14253.12 GiB. We calculate the space of useful disks 20 X 14253.12 = 285062.4 GiB. Now subtract 10% WAFL Reserve 285062.4 - 10% = 256556.16 GiB. And in the end, we multiply the resulting space by the minimum guaranteed data compression ratio 256556.16 * 4 = 1026224.64 GiB, i.e. 1002 TiB effective space!
Who can upgrade to ONTAP 9
NetApp, unlike many of its competitors, has been constantly developing the same platform with ONTAP software for many years and allows you to use all its new useful and interesting functions for both new and old customers who can recycle their old equipment. As a rule, storage systems are supported about 2-3-4 generations ago. And this very well allows you to save investment to end customers. For example, take FAS6210, this system had a FAS6220 receiver, then FAS8040, and now FAS8200.
So, the following FAS platforms with ONTAP 9 are supported:
- FAS2200: 2220, 2240
- FAS2500: 2520, 2552, 2554
- FAS2600: 2620, 2650
- FAS / V 3200: 3220, 3250, 3270
- FAS / V 6200: 6210, 6220, 6240, 6250, 6280, 6290
- FAS8000: 8020, 8040, 8060, 8080
- FAS8200
- FAS9000
- All Flash FAS: A300, A700
And as usual, the old disk shelves are supported.
Volume rehost
Now the volume can be transferred from one SVM to another.
ontap9::*> vserver show -vserver * -fields uuid
vserver uuid
------- ------------------------------------
SVM1 04c6bb98-3d74-11e6-a895-00b098596ec6
SVM2 204877e8-4d54-11e6-a895-00b098596ec6
2 entries were displayed.
ontap9::*> volume rehost -vserver SVM1 -volume my_vol_to_move -destination-vserver SVM2
ontap9::*> volume show -vserver SVM1 -fields msid,dsid,uuid,vserver -volume my_vol_to_move
There are no entries matching your query.More details here .
conclusions
NetApp continues to develop its flagship ONTAP software and delight not only new, but also its old customers, who can upgrade their old storage models to new firmware versions and get new functionality thus saving their investments. In the new version, a lot of effort was made in order to simplify the administration of the cluster system as much as possible, increase its reliability and increase efficiency. The rich and constantly added functionality complements the ONTAP clustering capabilities in combination with the “Share-Nothing” ideology and is very suitable for SSD media, where the new storage bottleneck is the CPU, not the disk subsystem.
» This may contain links to Habra articles that will be published later .
"Please send messages about errors in the text to the LAN .
» Comments, additions and questions on the opposite article, please comment .
