CentOS 7 overview. Part 3: NFS, FedFS, pNFS
In the first part of the CentOS 7 review, we talked about Linux container support in Cent OS 7. In the second part, we talked about identity management . The third part of the review is devoted to the NFS network file system and its environment in CentOS 7. At the end of the post there is a link to free testing of CentOS 7 in the InfoboxCloud cloud.

The NFS network file system allows remote hosts to mount file systems over the network and interact with these file systems as if they were mounted locally.
CentOS 7 supports two versions of NFS: v3 and v4. NFSv3 supports secure asynchronous writes and more reliable error handling than NFSv2 and supports 64-bit file sizes, allowing clients to access more than two gigabytes of the given files. NFSv4 supports working through Internet firewalls, no longer requires the rcpbind service, supports ACL access control lists, and uses state operations.
CentOS 7 added support for the NFS 4.1 network file system with improved performance and security, including support for Parallel NFS on the client side. NFS 4.1 no longer requires a separate TCP connection for callbacks, which allows the NFS server to work even with NAT and firewalls.
The new version includes support for the semantics of 'exactly once' (except for reboot operations), which allows us to solve the problem when the operation could return an incorrect result if the response was lost and the operation was requested twice (provided by stateful sessions).
NFS 4.1 uses standard network protocols for better performance in congested networks. NFS over TCP allows the latest generation of NICs to use the TCP segmentation offload (TCO) feature, freeing up CPU resources for useful work. When transferring data using TCP / IP, it is often necessary to break large-sized data blocks into several small ones, due to protocol limitations. Such a partitioning process is called segmentation. Typically, a central processor is used in the segmentation process. A network adapter equipped with the TCP Segmentation function frees the computer processor from performing the segmentation function and takes it upon itself.
To deploy and support more secure environments, NFSv4.2 labeled NFS allows you to use SELinux contexts, including secure virtual machine home directories stored in NFS.
CentOS 7 supports NFSv3, NFSv4, and NFSv4.1 clients. By default, clients try to mount NFSv4 and switch to NFSv3 if the attempt fails. NFSv4 requires TCP, while NFSv3 can work over UDP (due to the ability to work over a stateless network). If the server unexpectedly becomes unavailable, UDP clients will continue to send requests to the server. Also, when a frame is lost with UDP, the entire RPC request must be retransmitted, and when using TCP, only the lost frame must be resent. Therefore, it is recommended that you use TCP to work with the NFS server.
Mount and lock protocols were included in the NFSv4 protocol. NFSv4 no longer communicates with rcpbind , lockd , and rpc.statd . The NFS server still needs rcp.mountd to configure exports, but is not involved in any other operations.
The NFS server settings that allow access to clients are still in / etc / exports . The server is still listening on TCP port 2049, so be sure to enable it in IPTables .
Another interesting feature of CentOS 7 is support for the FedFS federated file system. FedFS provides a set of open protocols that allow you to build scalable namespaces between multiple file servers using NFSv4 system links that are available to unmodified NFS clients.


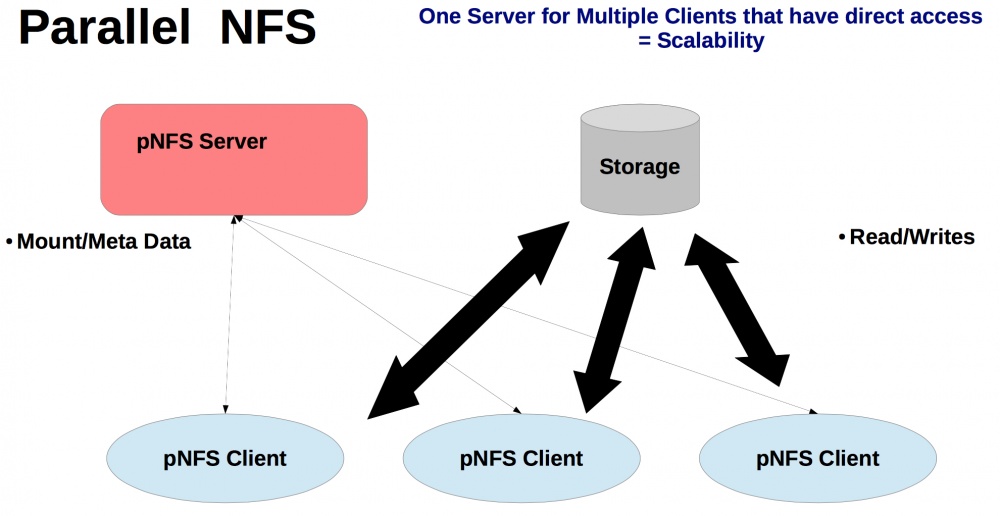
CentOS 7 is developing pNFS support that allows you to scale NFS to regular NAS to enable clients to read and write data directly and in parallel to physical storage.

The parallel pNFS architecture allows multiple NFS servers to manage metadata and coordinate access, providing predictable and reliable access to very large datasets from many clients.
pNFS layouts are supported on CentOS 7.
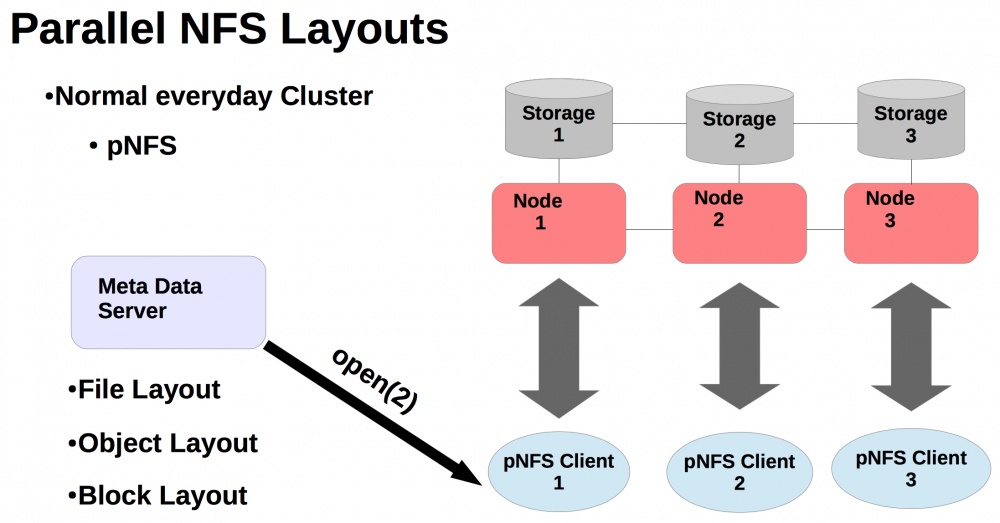
There is no full support for pNFS yet.
PNFS test results. The study was conducted on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 with the kernel 3.10.0.119 RC1 with OracleR2 OLTP. For testing, a cluster of 2 nodes with pNFS clients was used. Nearly 250,000 transactions per minute were reached with 100 users.

Sources used in preparing the article:
New world of NFS
NFS & GFS2
Official RedHat Blog RedHat
Knowledge Base
Official CentOS Blog
Especially for our readers, we provided the opportunity to try CentOS 7 in the InfoboxCloud cloud. Register a trial version for 15 days at this link . If you need more resources for testing than in the trial version - write to trukhinyuri@infoboxcloud.com

Nfs
The NFS network file system allows remote hosts to mount file systems over the network and interact with these file systems as if they were mounted locally.
CentOS 7 supports two versions of NFS: v3 and v4. NFSv3 supports secure asynchronous writes and more reliable error handling than NFSv2 and supports 64-bit file sizes, allowing clients to access more than two gigabytes of the given files. NFSv4 supports working through Internet firewalls, no longer requires the rcpbind service, supports ACL access control lists, and uses state operations.
CentOS 7 added support for the NFS 4.1 network file system with improved performance and security, including support for Parallel NFS on the client side. NFS 4.1 no longer requires a separate TCP connection for callbacks, which allows the NFS server to work even with NAT and firewalls.
The new version includes support for the semantics of 'exactly once' (except for reboot operations), which allows us to solve the problem when the operation could return an incorrect result if the response was lost and the operation was requested twice (provided by stateful sessions).
NFS 4.1 uses standard network protocols for better performance in congested networks. NFS over TCP allows the latest generation of NICs to use the TCP segmentation offload (TCO) feature, freeing up CPU resources for useful work. When transferring data using TCP / IP, it is often necessary to break large-sized data blocks into several small ones, due to protocol limitations. Such a partitioning process is called segmentation. Typically, a central processor is used in the segmentation process. A network adapter equipped with the TCP Segmentation function frees the computer processor from performing the segmentation function and takes it upon itself.
To deploy and support more secure environments, NFSv4.2 labeled NFS allows you to use SELinux contexts, including secure virtual machine home directories stored in NFS.
CentOS 7 supports NFSv3, NFSv4, and NFSv4.1 clients. By default, clients try to mount NFSv4 and switch to NFSv3 if the attempt fails. NFSv4 requires TCP, while NFSv3 can work over UDP (due to the ability to work over a stateless network). If the server unexpectedly becomes unavailable, UDP clients will continue to send requests to the server. Also, when a frame is lost with UDP, the entire RPC request must be retransmitted, and when using TCP, only the lost frame must be resent. Therefore, it is recommended that you use TCP to work with the NFS server.
Mount and lock protocols were included in the NFSv4 protocol. NFSv4 no longer communicates with rcpbind , lockd , and rpc.statd . The NFS server still needs rcp.mountd to configure exports, but is not involved in any other operations.
The NFS server settings that allow access to clients are still in / etc / exports . The server is still listening on TCP port 2049, so be sure to enable it in IPTables .
FedFS
Another interesting feature of CentOS 7 is support for the FedFS federated file system. FedFS provides a set of open protocols that allow you to build scalable namespaces between multiple file servers using NFSv4 system links that are available to unmodified NFS clients.


pNFS
CentOS 7 is developing pNFS support that allows you to scale NFS to regular NAS to enable clients to read and write data directly and in parallel to physical storage.

The parallel pNFS architecture allows multiple NFS servers to manage metadata and coordinate access, providing predictable and reliable access to very large datasets from many clients.
pNFS layouts are supported on CentOS 7.

There is no full support for pNFS yet.

PNFS test results. The study was conducted on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 with the kernel 3.10.0.119 RC1 with OracleR2 OLTP. For testing, a cluster of 2 nodes with pNFS clients was used. Nearly 250,000 transactions per minute were reached with 100 users.

Sources used in preparing the article:
New world of NFS
NFS & GFS2
Official RedHat Blog RedHat
Knowledge Base
Official CentOS Blog
Free trial in the cloud
Especially for our readers, we provided the opportunity to try CentOS 7 in the InfoboxCloud cloud. Register a trial version for 15 days at this link . If you need more resources for testing than in the trial version - write to trukhinyuri@infoboxcloud.com
