NASA: 715 new planets found, 4 of them may be livable
On February 27, NASA reported the discovery of 715 new planets that were recently found in our Milky Way region, which almost doubles the number of exoplanets known to us. The planets were discovered using the Kepler space telescope and new technology.

Under a cat there is a lot of traffic.
Since the launch of Kepler in 2009 to 2011, scientists have discovered 3,600 potential planets. They saw objects by detecting small moving dark dots against the bright background of nearby stars:
A sufficiently effective detection method, but still asking scientists a question - is this really a planet or another unknown phenomenon in space ...? To solve this problem, scientists used a technology called "plurality checking", which is based on probability. Here's how NASA explains it:
“Kepler explores 150,000 stars, and found among them several thousand of those in whose systems there are potential planets. If all the stars observed were studied, then only a small number of them would have more than one potential planet. Kepler has explored hundreds of stars with many potential planets. "
Everything is quite simple, where there is a greater accumulation of objects, there is a higher probability of finding a planet. Thus, 715 planets were found and confirmed. 95% of them are smaller than Neptune. Below you can see how sharply the number of planets discovered after scientists began to use the new method:
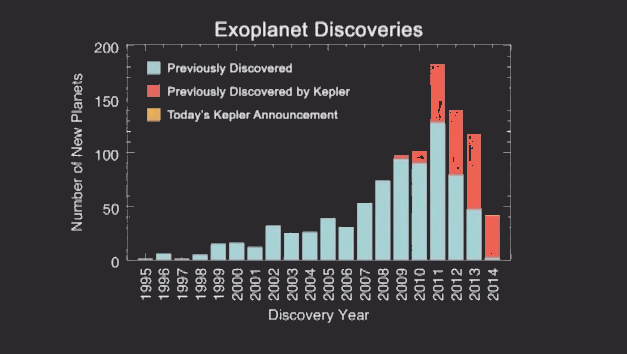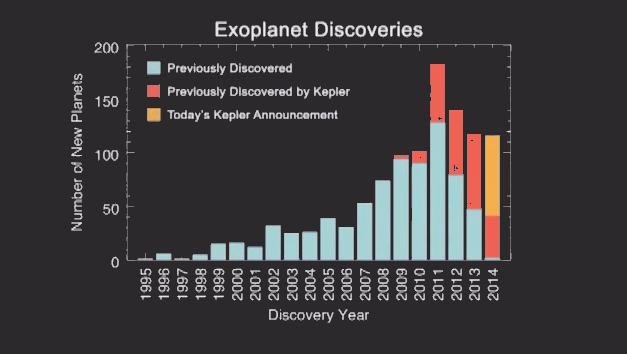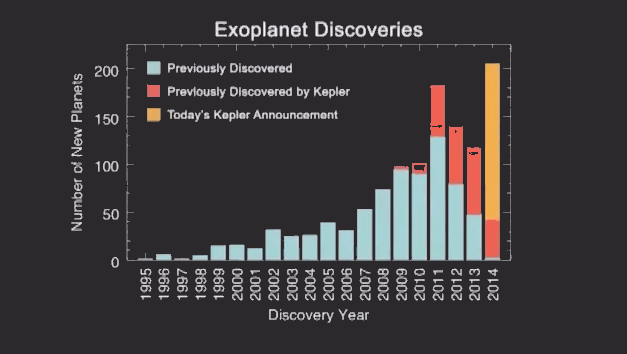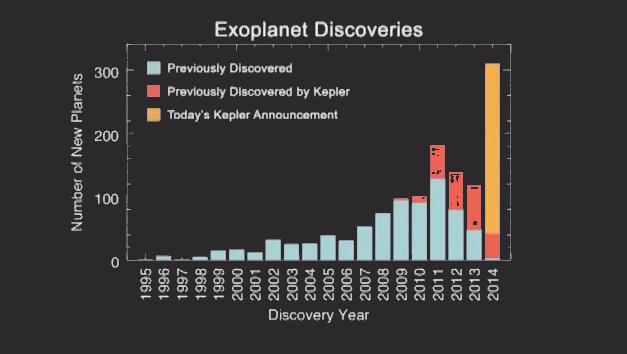
During the study, scientists discovered four planets in the so-called "habitable zone" - a certain range of distances from the star, where the temperature of the planet's surface may be suitable for the existence of water. Currently, scientists are trying to determine whether the planets are gaseous (for example, Saturn) or relate to having a water world (like Earth).
Based on the data on sizes and remoteness from their stars, scientists believe that these 4 planets look like this:
Kepler-69c is 70% larger than Earth. It orbits around its star in 242 days.
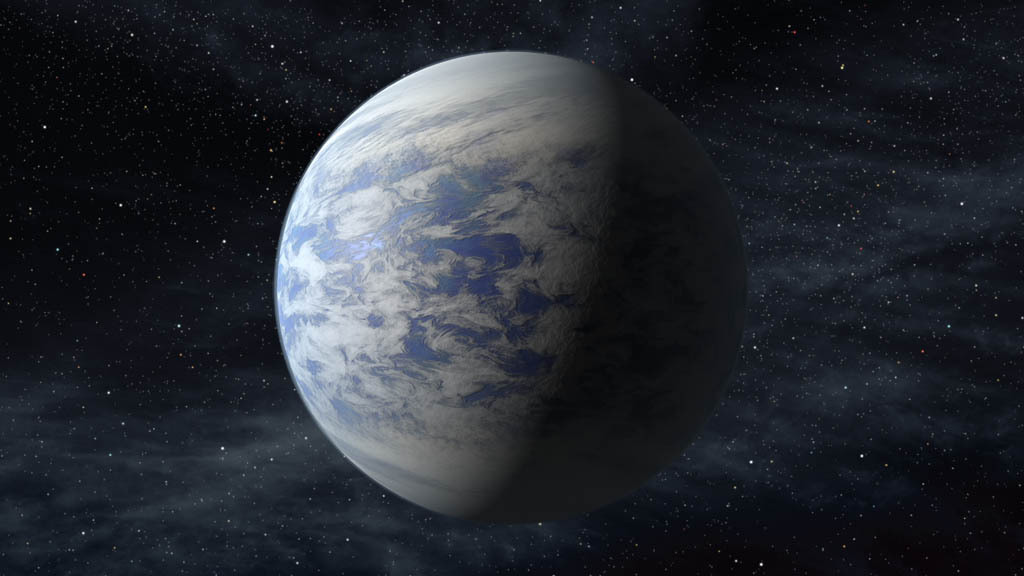

Kepler-62e is 60% larger than Earth. It orbits around its star in 122 days.

Kepler-62f is 40% larger than Earth. It revolves in orbit around a star, which is located at a distance of 1'200 light-years from Earth.

Kepler-296f orbits around the star, which is half smaller and has a brightness of only 5% compared to our sun.

More information about the Kepler telescope and the new method in the following video (in English):
