Bank of America report: 700 quintillion dollars from space
- Transfer
Note per. I would have missed such a “yellow press heading” if it weren't for the good honest name of Bank of America sponsored by the report .
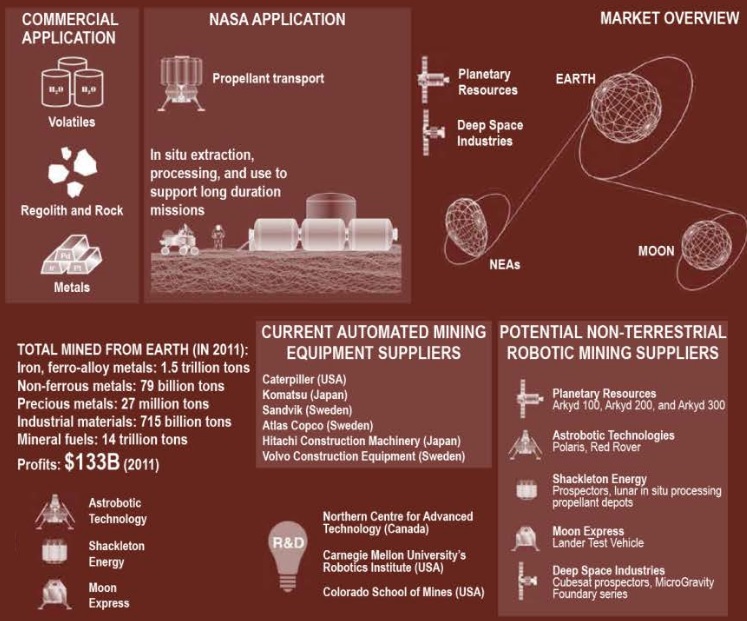
Mining of minerals with the help of robots is critical for NASA's plans for long-term space missions to asteroids, the Moon and Mars. NASA develops exploration and mining capabilities using robots with various software programs: including the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot (RASSOR), the Regolith Volunteer Extraction (RESOLVE), and the Moon Mars Analog Mission (MMAMA).
A mining competition on the moon using bots is a university competition sponsored by NASA, Caterpillar, SpaceX, Newmont Mining Corporation and Honeybee Robotics. The participants are tasked to develop and build an excavator that can extract at least 10 kg of artificial moon dust in 10 minutes.
The introduction of automation in land mining has been slow due to technical problems. However, several large mining companies, such as Rio Tinto, BHP Billiton, use autonomous or semi-autonomous equipment and remote virtual control technologies that allow miners to operate equipment from thousands of miles away, which, in principle, is also applicable in space ( source: NASA).
UAE and Saudi Arabia have space programs. Saudi Arabia signed in 2015 an agreement with Russia on cooperation in space exploration. Abu Dhabi is an investor in Richard Branson's space tourism, Virgin Galactic. In addition to money, the Middle East also has a favorable location, being close to the equator. Navitas expects companies to launch satellites seeking rare gases and metals on asteroids in the next five years, and actual production will occur in the next eight years (source: Bloomberg).
It is believed that the asteroid "3554 Amon" contains cobalt in the amount of 6 trillion. US dollars, as well as iron and nickel in the amount of 8 trillion. US dollars. (Professor John S. Lewis, Mining the Sky, 1996)

NASA plans to explore 16 Psyche asteroid worth 10,000 quadrillion dollars or 10 quintillion dollars.
Asteroids contain water, which can be the key to getting to Mars and exploring deep space. Water is an invaluable commodity in space, given the potential difficulties of ice mining on Mars and / or the possibility of bringing an asteroid to Earth.
According to some estimates, the minerals of the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter can cost 700 quintillons US dollars, which is 100 billion US dollars for each of the 7 billion people on Earth according to current prices. John S. Lewis, author of Mining the Sky, claims that an asteroid with a diameter of 1 km will have a mass of about 2 billion tons. There are probably about a million asteroids of this size in the solar system. According to Lewis, one of these asteroids will contain 30 million tons of nickel, 1.5 million tons of metallic cobalt and 7,500 tons of platinum, and the cost of platinum alone is more than 150 billion US dollars (source: Lewis 1996, Biggs 2013, NASA).
However, mining asteroids is expensive. According to NASA estimates, today it will take $ 1 billion to bring a "tennis ball from an asteroid" (weighing 58g). On the other hand, according to the Keck Space Research Institute (KISS) at Caltech, one full cycle of capturing and moving an asteroid weighing about 1.1 million pounds (500,000 kg) to the lunar orbit will cost about 2.6 billion by 2025 US dollars. An MIT study (Schuler, 2011) showed that the opening of a mine and a gas processing plant could cost about $ 1 billion.

The potential cost of the asteroid belt. Source: Visual Capitalist
Planetary Resources is an American company that has declared that their goal is to “expand the base of the Earth’s natural resources” by developing and implementing asteroid extraction technologies. She is supported by Peter Diamandis, James Cameron, Larry Page, Eric Schmidt, Richard Branson and Tencent besides other investors. The company is developing the Asteroid Exploration program for launch readiness by the end of 2020 and is targeting several C-type asteroids that will be explored by various spacecraft. According to President Chris Lewicki, the first mission is to take place in 2020. Luxembourg, where the company's European headquarters are located, in 2016 invested US $ 28 million in planetary resources for key research and development, as well as for conducting international business for the use of asteroids for commercial purposes. He currently employs people willing to mine resources on asteroids throughout Europe (source: Planetary Resources).
Deep Space Industries (DSI) is another US privately held company with global operations in space technology and resources. The company develops the space technologies needed for the extraction of asteroids and sells satellites using these technologies. DSI expects that space-derived materials derived from asteroids, commercially available in the early 2020s, will include space refueling, energy, asteroid processing, and manufacturing.
According to the Artemis project document, there are approximately 1,100,000 metric tons of lunar helium-3. To present this number in perspective, only 25 tons of this material would be enough to supply the entire country with energy throughout the year, while another 75 tons of helium-3 can at the same time supply the rest of the world with energy.
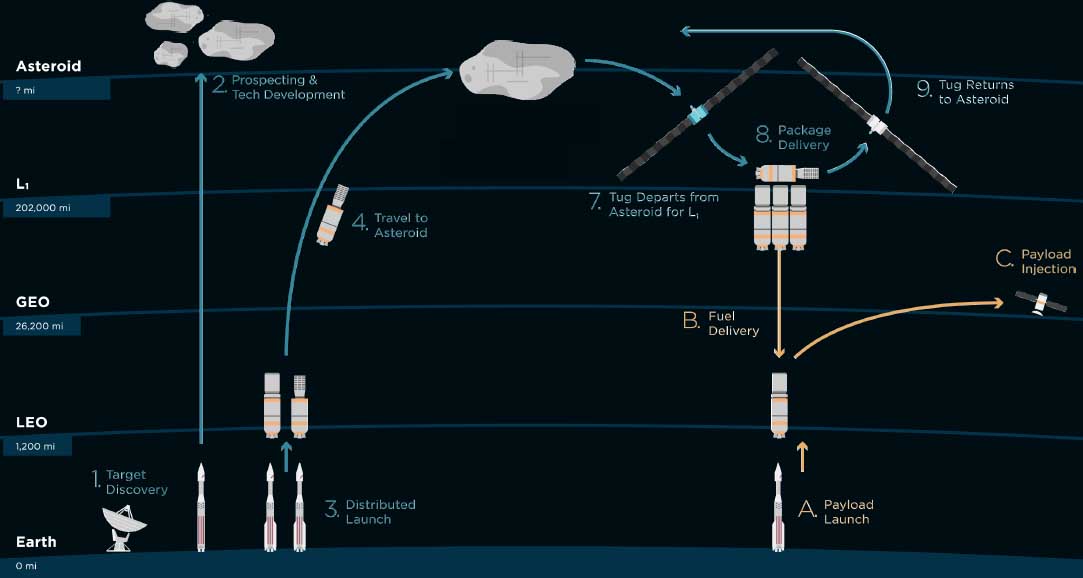
How will the extraction of asteroids
The concept of delivering solar energy to Earth from space platforms has existed for several decades. However, a new concept of a solar energy satellite (SPS) was proposed, which eliminates many, if not all, uncertainties: SPS-ALPHA (solar energy satellite using an arbitrary-sized phase array) (source: John S. Mankins, NASA). If SPS-ALPHA can be developed, it will be possible to obtain solar energy in the range from 100 to 100 GW, which can be collected in space and efficiently delivered to Earth’s markets. It will also enable high energy consumption across the entire solar system, transforming all aspects of government and commercial space. After the development of technology and all sorts of demonstrations, the SPS-ALPHA concept achieved commercial results (for example, less than 20% per kWh) with technologies
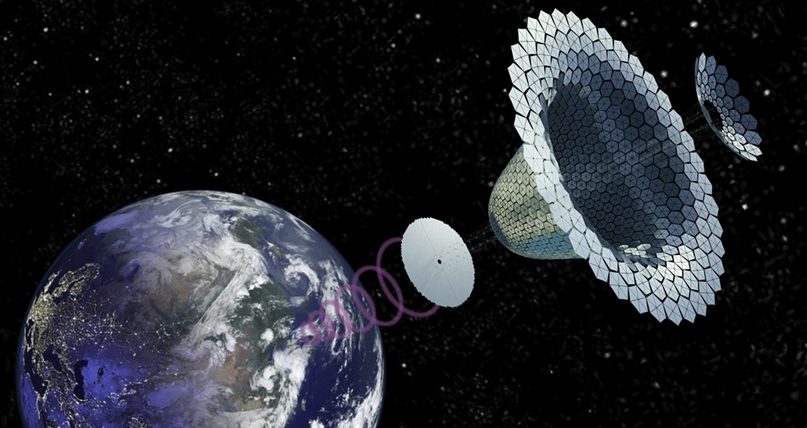

SPS-ALPHA can provide a faster, more efficient and affordable response to disasters and natural disasters, and will also have a virtually zero carbon footprint and will contribute to the achievement of greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reduction targets.
According to NASA, the roadmap for SPS-ALPHA looks program-driven: a hyper-modular architecture should allow for quick, relatively inexpensive steps forward. The total cost of a scalable satellite satellite pilot is about $ 5 billion, and the cost of the first full-scale SPS is about $ 20 billion.
These figures are significant, but significantly lower than the declared value of the ISS ($ 150 billion) or earlier estimates of the 1980s, which amounted to about $ 1 trillion. US dollars to achieve the first SPS. NASA believes that the SPS-ALPHA advanced concept is extremely promising and deserves consideration.
“If a trillionaire ever appears in the world, it will be a person who exploits natural resources on asteroids. They have endless reserves of energy and resources. ”
- Neil Degrass Tyson, astrophysicist
Minerals

Mining of minerals with the help of robots is critical for NASA's plans for long-term space missions to asteroids, the Moon and Mars. NASA develops exploration and mining capabilities using robots with various software programs: including the Regolith Advanced Surface Systems Operations Robot (RASSOR), the Regolith Volunteer Extraction (RESOLVE), and the Moon Mars Analog Mission (MMAMA).
A mining competition on the moon using bots is a university competition sponsored by NASA, Caterpillar, SpaceX, Newmont Mining Corporation and Honeybee Robotics. The participants are tasked to develop and build an excavator that can extract at least 10 kg of artificial moon dust in 10 minutes.
The introduction of automation in land mining has been slow due to technical problems. However, several large mining companies, such as Rio Tinto, BHP Billiton, use autonomous or semi-autonomous equipment and remote virtual control technologies that allow miners to operate equipment from thousands of miles away, which, in principle, is also applicable in space ( source: NASA).
In addition, not only companies are involved in mining in space. According to the consultant Navitas, the countries of the Middle East are developing space programs and investing in emerging private space initiatives for the extraction of raw materials. This aims to provide them with support for creating extraterrestrial reserves of water - a substance that can serve as a fuel for space travel - and other resources that can be used to produce something in space.
Post written with the support of the company EDISON Software, which develops software for banks , as well as deals with measurement automation and expert systems .
UAE and Saudi Arabia have space programs. Saudi Arabia signed in 2015 an agreement with Russia on cooperation in space exploration. Abu Dhabi is an investor in Richard Branson's space tourism, Virgin Galactic. In addition to money, the Middle East also has a favorable location, being close to the equator. Navitas expects companies to launch satellites seeking rare gases and metals on asteroids in the next five years, and actual production will occur in the next eight years (source: Bloomberg).
Asteroid extraction: 700 "quintillion" US dollars in the asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter
The mineral wealth of the asteroid belt would be $ 100 billion per person on Earth.Asteroids are remnants of the early formation of the solar system or debris from the destruction of the planet. Tens of thousands of asteroids revolve around the sun. In our solar system, most asteroids are grouped inside the asteroid belt, between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, where there are more than 1 million asteroids, about 200 of which have a diameter of more than 60 miles (100 km). Almost all asteroids fall into three main categories (source NASA):
- C-type (carbon) - more than 75% of known asteroids fall into this category. The composition of C-type asteroids is similar to that of the Sun without hydrogen, helium and other volatile substances.
- S-type (silicate) - about 17% of asteroids of this type. They contain solid deposits of nickel, iron and magnesium.
- M-Type (rich in metal) - a small amount of asteroids of this type, contain nickel and iron

It is believed that the asteroid "3554 Amon" contains cobalt in the amount of 6 trillion. US dollars, as well as iron and nickel in the amount of 8 trillion. US dollars. (Professor John S. Lewis, Mining the Sky, 1996)

NASA plans to explore 16 Psyche asteroid worth 10,000 quadrillion dollars or 10 quintillion dollars.
Asteroids contain water, which can be the key to getting to Mars and exploring deep space. Water is an invaluable commodity in space, given the potential difficulties of ice mining on Mars and / or the possibility of bringing an asteroid to Earth.
According to some estimates, the minerals of the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter can cost 700 quintillons US dollars, which is 100 billion US dollars for each of the 7 billion people on Earth according to current prices. John S. Lewis, author of Mining the Sky, claims that an asteroid with a diameter of 1 km will have a mass of about 2 billion tons. There are probably about a million asteroids of this size in the solar system. According to Lewis, one of these asteroids will contain 30 million tons of nickel, 1.5 million tons of metallic cobalt and 7,500 tons of platinum, and the cost of platinum alone is more than 150 billion US dollars (source: Lewis 1996, Biggs 2013, NASA).
However, mining asteroids is expensive. According to NASA estimates, today it will take $ 1 billion to bring a "tennis ball from an asteroid" (weighing 58g). On the other hand, according to the Keck Space Research Institute (KISS) at Caltech, one full cycle of capturing and moving an asteroid weighing about 1.1 million pounds (500,000 kg) to the lunar orbit will cost about 2.6 billion by 2025 US dollars. An MIT study (Schuler, 2011) showed that the opening of a mine and a gas processing plant could cost about $ 1 billion.

The potential cost of the asteroid belt. Source: Visual Capitalist
Planetary Resources
Planetary Resources is an American company that has declared that their goal is to “expand the base of the Earth’s natural resources” by developing and implementing asteroid extraction technologies. She is supported by Peter Diamandis, James Cameron, Larry Page, Eric Schmidt, Richard Branson and Tencent besides other investors. The company is developing the Asteroid Exploration program for launch readiness by the end of 2020 and is targeting several C-type asteroids that will be explored by various spacecraft. According to President Chris Lewicki, the first mission is to take place in 2020. Luxembourg, where the company's European headquarters are located, in 2016 invested US $ 28 million in planetary resources for key research and development, as well as for conducting international business for the use of asteroids for commercial purposes. He currently employs people willing to mine resources on asteroids throughout Europe (source: Planetary Resources).
Deep Space Industries
Deep Space Industries (DSI) is another US privately held company with global operations in space technology and resources. The company develops the space technologies needed for the extraction of asteroids and sells satellites using these technologies. DSI expects that space-derived materials derived from asteroids, commercially available in the early 2020s, will include space refueling, energy, asteroid processing, and manufacturing.
According to the Artemis project document, there are approximately 1,100,000 metric tons of lunar helium-3. To present this number in perspective, only 25 tons of this material would be enough to supply the entire country with energy throughout the year, while another 75 tons of helium-3 can at the same time supply the rest of the world with energy.

How will the extraction of asteroids
Energy
“Energy on Earth is limited. At least in a few hundred years ... all of our heavy industry will be transferred out of the planet ... The land will be divided into areas of residence and areas of light industry. You do not have to produce high power energy on Earth. ” We can build giant factories for the production of diamond chips (chip) in space. "Space could be a fair wind for the Cleantech revolutionaries regarding solar energy and battery storage. NASA has invested in solid state lithium and sulfur (Li / S) batteries for space exploration. Li / S batteries have a higher energy density, allowing rocket planes to travel long distances. They are also more durable because they can cope better with temperature changes than batteries filled with liquid. This is very important at extreme temperatures in space.
- Jeff Bezos
SPS-ALPHA concept: deliver energy on demand to> 90% of the Earth
The concept of delivering solar energy to Earth from space platforms has existed for several decades. However, a new concept of a solar energy satellite (SPS) was proposed, which eliminates many, if not all, uncertainties: SPS-ALPHA (solar energy satellite using an arbitrary-sized phase array) (source: John S. Mankins, NASA). If SPS-ALPHA can be developed, it will be possible to obtain solar energy in the range from 100 to 100 GW, which can be collected in space and efficiently delivered to Earth’s markets. It will also enable high energy consumption across the entire solar system, transforming all aspects of government and commercial space. After the development of technology and all sorts of demonstrations, the SPS-ALPHA concept achieved commercial results (for example, less than 20% per kWh) with technologies
Every hour, planet Earth reaches a greater amount of solar energy than the amount of energy that people use during the year
- US Department of Energy
About 30% of all incoming solar radiation never hits the Earth's
surface
- US Department of Energy
Solar energy satellites based on SPS-ALPHA can provide energy on demand to more than 90% of the world's population around the globe
- NASA, John S. Mankins

SPS-ALPHA can provide a faster, more efficient and affordable response to disasters and natural disasters, and will also have a virtually zero carbon footprint and will contribute to the achievement of greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reduction targets.
According to NASA, the roadmap for SPS-ALPHA looks program-driven: a hyper-modular architecture should allow for quick, relatively inexpensive steps forward. The total cost of a scalable satellite satellite pilot is about $ 5 billion, and the cost of the first full-scale SPS is about $ 20 billion.
These figures are significant, but significantly lower than the declared value of the ISS ($ 150 billion) or earlier estimates of the 1980s, which amounted to about $ 1 trillion. US dollars to achieve the first SPS. NASA believes that the SPS-ALPHA advanced concept is extremely promising and deserves consideration.

