A minute of history, or what computers the USSR did
Computers have entered our life so tightly that now it is impossible to imagine it without them. Desktops, laptops, PDAs, smartphones, various gadgets, whether it is a player or a portable photobank. In addition to the various devices we see every day, there are also office computers. Many people know about where they came from and how they developed, from ENIAK to modern computers, with insanely powerful processors and amazing operating systems. But what kind of computers in the USSR were developed at that time, designed to solve industrial and military problems, is not covered much. That's what they will be discussed
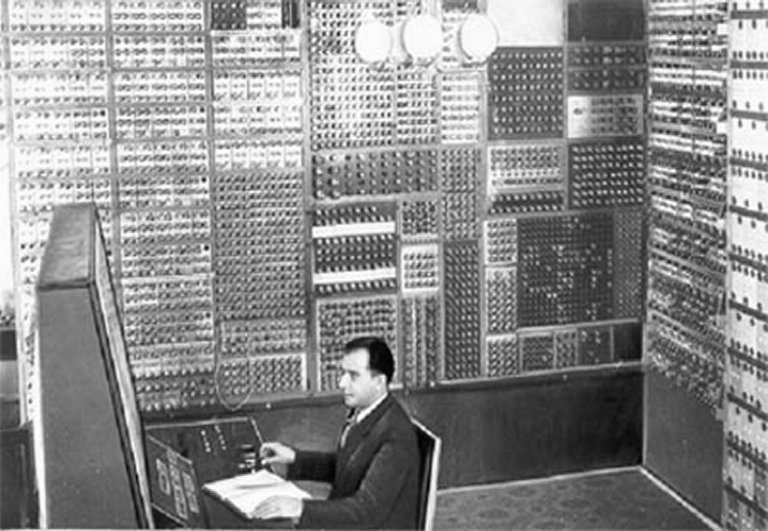
The first Soviet computer was put into operation in December 1951, developed under the guidance of S.A. Lebedev, and it was called the computer year MESM. The name is deciphered quite simply: “Small Electronic Calculating Machine” Initially, MESM was conceived as a model or model of a Large Electronic Calculating Machine (BESM), for the first time the letter “M” in the name meant “layout”. MESM embodied the basic principles of building a computing system, which Lebedev himself developed. The fact that similar principles were put forward by von Neumann, we learn from publications later.
The first control computer systems in our country were developed in the early 1960s at the Institute of Electronic Control Machines (INEUM). The creation of INEUM was associated with the rapid development of a new promising area of science and technology - with the development of electronic digital computers to automate production.
The next on the list was the UV40 M40. It was “presented” in 1958. The UV40 M40 was for special applications. It was developed at the Institute of Precision Mechanics and Computer Engineering under the direction of S.A. Lebedeva and V.S. Burtseva. On the basis of this UVK, the first Soviet missile defense system was created.
In the late 1950s and early 1960s, INEUM completed the development of the UV4 M4 (M4-M, M4-2M, M4-3M) designed to control in real time the complex of radar stations created by the Radio Engineering Institute of the USSR Academy of Sciences as part of a large geographically distributed throughout the country, an electronic surveillance system for artificial Earth satellites.
What could UVK M4:
Representation of numbers with a fixed comma
Bit depth 23 binary digits;
RAM 1024 23-bit numbers;
Permanent memory 1024 23-bit numbers;
Speed 50 thousand operations of addition or subtraction per second;
5.2 thousand division operations per second.
Transistors and diodes were used as an element base, the RAM was built on ferrite cores using tube current generators.
These UVK have been mass-produced since 1964. For 15 years, they had no foreign analogues and were created by the INEUM development team under the direction of M.A. Kartseva solely on the basis of their own technical solutions.
One of the most successful UVK developments in the early 1960s was built on semiconductor devices UM1-HX, developed in Leningrad under the guidance of F.G. Staros. These complexes were used, in particular, in the automatic control and regulation system of Beloyarsk NPP. The control system consisted of two UM1-HX operating in the hot reserve mode.
In 1965, INEUM led the work on the creation of the Aggregate System of Computing Equipment (ASVT), intended primarily for the automation of technological processes and automated enterprise management systems. Although in those years the first domestic integrated circuits were still under development and trial operation, already in 1970 in INEUM the country's first third-generation control computer systems were created. The hierarchical system of such complexes on a microelectronic base (ASVT-M) included the models M4000 / M4030, M400 and M40, each of which occupied its place in the integrated production systems.
Since the early 1970s, an international system of small electronic computers has been created at INEUM. SM computers as a system of compatible hardware and software began to be developed since 1974 by integrating a number of countries (USSR, Bulgaria, Hungary, East Germany, Cuba, Poland, Romania, Czechoslovakia).
Since the mid-1970s, two international systems, SM computers and EU computers (a single system of electronic computers), together complementing each other, have become the technical basis for the automation of information management and processing in all areas of the national economy of the socialist camp countries. SM computer included: a wide range of basic models of micro- and mini-computers; The basic series is the process of various performance and devices of random access memory, peripheral, information display, communication with the object, telecommunication, machine and machine communication. SM computer was designed to build control computing systems, widely used in the sectors of the economy. One of the important distinguishing features of the SM computer was that the system also included industrial controllers and communication devices with the object.
The basis for the creation of hardware and software tools of the SM computer were the following, relevant today, principles:
- the required reliability for the corresponding class of the system;
- sufficient performance;
- functional completeness for the corresponding class of the system;
- communicativeness with computer networks of various configurations;
- completeness of system software support;
- software and technical continuity of newly developed tools in relation to previously created hardware and software;
- openness and development of hardware and software;
- the simplicity and effectiveness of diagnosing the health of technical means;
- prompt and high-quality technical equipment service;
- affordability. From 1974 to 1990, about 80 thousand computer systems were produced, as well as measuring and computing systems, and general-purpose workstations based on them.
Since the beginning of the 1980s, in the INEUM, the development of the SM computer series has been carried out in two directions.
The first direction is connected with the SM1800 family. Initially, they used 8-bit processors KP580. 14 modifications of cars of this series were created.
In 1986, mass production of the 16-bit model CM1810 (processor K1810) began. Six modifications of general-purpose computers and four for working in industrial conditions (SM1814) were developed.
In 1990, the creation of the 32-bit SM1820 computing complex based on the Intel 80386 processor was completed.
The second architectural line was a series of compatible minicomputers and microcomputers of various capacities, which used 8, 16, and 32-bit microprocessors. A distinctive feature of these computers is the use of the common bus system interface.
Modern UVEK INEUM uses microprocessors corresponding to current achievements, as well as UNIX-like operating systems. You can read about INEUM projects on their official website . You can also read about EU UVM here , thanks for the prometheus link .

The first Soviet computer was put into operation in December 1951, developed under the guidance of S.A. Lebedev, and it was called the computer year MESM. The name is deciphered quite simply: “Small Electronic Calculating Machine” Initially, MESM was conceived as a model or model of a Large Electronic Calculating Machine (BESM), for the first time the letter “M” in the name meant “layout”. MESM embodied the basic principles of building a computing system, which Lebedev himself developed. The fact that similar principles were put forward by von Neumann, we learn from publications later.
The first control computer systems in our country were developed in the early 1960s at the Institute of Electronic Control Machines (INEUM). The creation of INEUM was associated with the rapid development of a new promising area of science and technology - with the development of electronic digital computers to automate production.
The next on the list was the UV40 M40. It was “presented” in 1958. The UV40 M40 was for special applications. It was developed at the Institute of Precision Mechanics and Computer Engineering under the direction of S.A. Lebedeva and V.S. Burtseva. On the basis of this UVK, the first Soviet missile defense system was created.
In the late 1950s and early 1960s, INEUM completed the development of the UV4 M4 (M4-M, M4-2M, M4-3M) designed to control in real time the complex of radar stations created by the Radio Engineering Institute of the USSR Academy of Sciences as part of a large geographically distributed throughout the country, an electronic surveillance system for artificial Earth satellites.
What could UVK M4:
Representation of numbers with a fixed comma
Bit depth 23 binary digits;
RAM 1024 23-bit numbers;
Permanent memory 1024 23-bit numbers;
Speed 50 thousand operations of addition or subtraction per second;
5.2 thousand division operations per second.
Transistors and diodes were used as an element base, the RAM was built on ferrite cores using tube current generators.
These UVK have been mass-produced since 1964. For 15 years, they had no foreign analogues and were created by the INEUM development team under the direction of M.A. Kartseva solely on the basis of their own technical solutions.
One of the most successful UVK developments in the early 1960s was built on semiconductor devices UM1-HX, developed in Leningrad under the guidance of F.G. Staros. These complexes were used, in particular, in the automatic control and regulation system of Beloyarsk NPP. The control system consisted of two UM1-HX operating in the hot reserve mode.
In 1965, INEUM led the work on the creation of the Aggregate System of Computing Equipment (ASVT), intended primarily for the automation of technological processes and automated enterprise management systems. Although in those years the first domestic integrated circuits were still under development and trial operation, already in 1970 in INEUM the country's first third-generation control computer systems were created. The hierarchical system of such complexes on a microelectronic base (ASVT-M) included the models M4000 / M4030, M400 and M40, each of which occupied its place in the integrated production systems.
Since the early 1970s, an international system of small electronic computers has been created at INEUM. SM computers as a system of compatible hardware and software began to be developed since 1974 by integrating a number of countries (USSR, Bulgaria, Hungary, East Germany, Cuba, Poland, Romania, Czechoslovakia).
Since the mid-1970s, two international systems, SM computers and EU computers (a single system of electronic computers), together complementing each other, have become the technical basis for the automation of information management and processing in all areas of the national economy of the socialist camp countries. SM computer included: a wide range of basic models of micro- and mini-computers; The basic series is the process of various performance and devices of random access memory, peripheral, information display, communication with the object, telecommunication, machine and machine communication. SM computer was designed to build control computing systems, widely used in the sectors of the economy. One of the important distinguishing features of the SM computer was that the system also included industrial controllers and communication devices with the object.
The basis for the creation of hardware and software tools of the SM computer were the following, relevant today, principles:
- the required reliability for the corresponding class of the system;
- sufficient performance;
- functional completeness for the corresponding class of the system;
- communicativeness with computer networks of various configurations;
- completeness of system software support;
- software and technical continuity of newly developed tools in relation to previously created hardware and software;
- openness and development of hardware and software;
- the simplicity and effectiveness of diagnosing the health of technical means;
- prompt and high-quality technical equipment service;
- affordability. From 1974 to 1990, about 80 thousand computer systems were produced, as well as measuring and computing systems, and general-purpose workstations based on them.
Since the beginning of the 1980s, in the INEUM, the development of the SM computer series has been carried out in two directions.
The first direction is connected with the SM1800 family. Initially, they used 8-bit processors KP580. 14 modifications of cars of this series were created.
In 1986, mass production of the 16-bit model CM1810 (processor K1810) began. Six modifications of general-purpose computers and four for working in industrial conditions (SM1814) were developed.
In 1990, the creation of the 32-bit SM1820 computing complex based on the Intel 80386 processor was completed.
The second architectural line was a series of compatible minicomputers and microcomputers of various capacities, which used 8, 16, and 32-bit microprocessors. A distinctive feature of these computers is the use of the common bus system interface.
Modern UVEK INEUM uses microprocessors corresponding to current achievements, as well as UNIX-like operating systems. You can read about INEUM projects on their official website . You can also read about EU UVM here , thanks for the prometheus link .
