California's drought hit a third of the forest, 102 million trees died
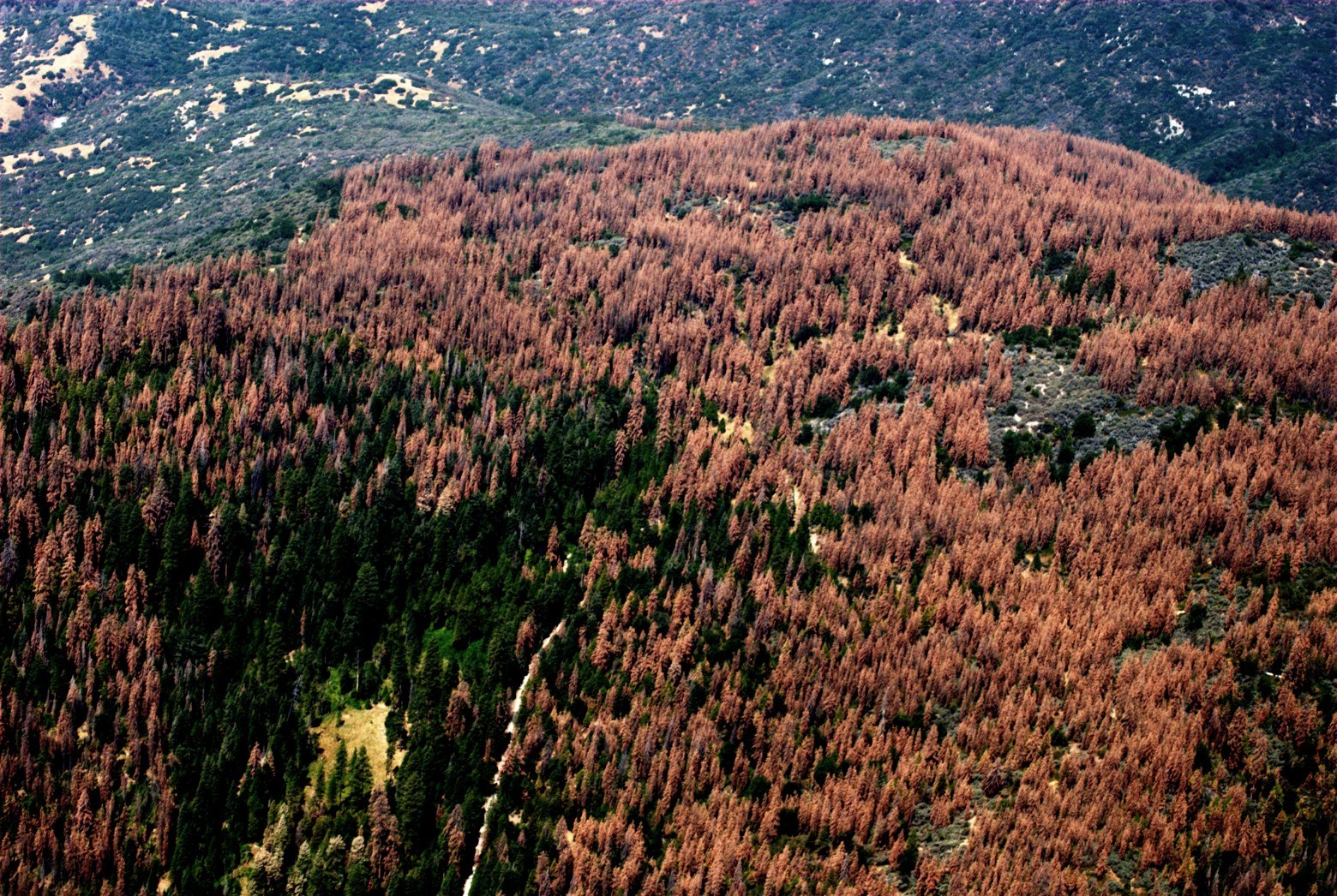

Deadwood among the surviving trees in the California forest. August 24, 2016. Photo: USFS Region 5
A new aerial view of the US Forest Service has increased the scale of the tragedy from an unprecedented drought that has hit California in the last five years. Especially in 2016. According to new data , the number of dead trees increased by 36 million units compared with the previous aerial survey in May 2016.
Thus, the total loss of forest from 2010 increased to 102 million trees. This is 3.11 million hectares of dried land, that is, a third of the entire forest cover of the state. In 2016 alone, 62 million trees died.
In recent years, the surface of the planet is rapidly heating up. Almost every month new temperature records are recorded. According to climate models, the temperature is unevenly distributed over the surface of the planet. In some areas there may be a slight cooling - and in others, sharp warming is much higher than average.
Under the 2015 Paris Agreement, under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, countries agreed to reduce CO 2 emissions in order to keep warming within 2 ° C above the pre-industrial level, and also to “make efforts to limit the temperature rise within 1.5 ° C above pre-industrial level But the world averagean increase in temperature of 2 ° C means a significantly greater increase in average temperatures in certain regions. At the same time, daily highs reached extreme values. This trend seriously threatens the Mediterranean climate, including Spain and southern Italy, where forests can disappear. California, too, was affected by the extremum function. Only here the threat of drought is no longer hypothetical, but has actually come true.
The US Forest Service notes that in addition to 102 million trees completely destroyed, millions more are weakened and are likely to die in the coming months and years.
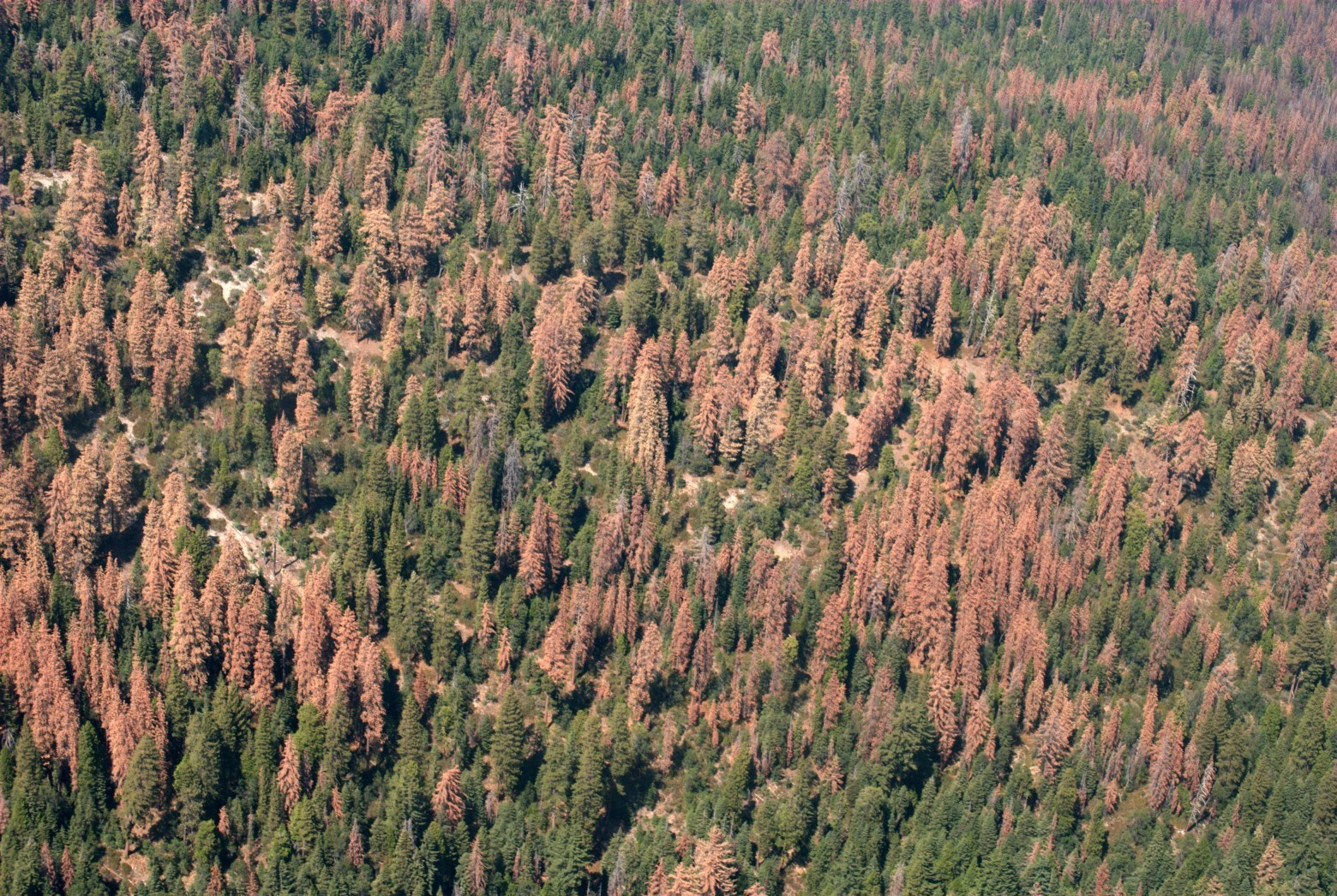

Deadwood and surviving trees. August 23, 2016. Photo: USFS Region 5
American foresters are trying to repair the damage as much as possible. Additional funds were allocated for forest restoration in priority areas: along highways and highways, in recreation areas. But experts recognize: efforts are not enough to fight the forces of nature. The mortality of trees continues much faster than we are capable of restoring a forest plant.
Yes, and planted trees take decades to grow. Trees in the lowlands, which for the first time in their lives were faced with a lack of moisture, are suffering from drought: “We have sugar pines there - great trees that live 500 years,” says ecologist of the United States. “Now wherever you go, at least half of these giants are dead in certain parts of the forest.”
The situation is aggravated by the budget deficit in California, which does not allow for a truly massive campaign of planting trees and additional measures to clear the forest from dead wood. State authorities take money from foresters — and redistribute it to firefighters, so fewer resources are left for clearing, planting and restoring the forest.
This year the number of fires was a record. Only in California, 12.1 thousand hectares of forest were completely burned out. 80,000 people were evacuated, and the total fire area in the south-western United States exceeded 48.6 thousand hectares.
At the same time, the presence of millions of dead, dry and weakened trees increases the risk of new fires and prevents them from effectively extinguishing them. That is, the authorities are struggling not with the cause, but with the investigation, allocating more money to the firefighters, but without prioritizing clearing the wood from deadwood.
In addition, dead wood and falling trees increase the number of incidents with injuries to people and property damage. According to the California program of falling trees , by the middle of October 2016, 5902 such incidents were registered, compared to 2587 in the "normal" 2010.
The Forest Service hopes that the State Congress will adopt amendments to the budget that will avoid further redistribution of funds by firefighters at the expense of foresters. Last year, firefighters allocated 56% of the total budget of the Forest Service, and if the situation does not change, then in subsequent years it will grow even more.
Most of the dead forest is located in central and southern Sierra Nevada. Experts speak of a significant forest mortality in some northern regions. The unprecedented scale of forest extinction is explained by five continuous years of drought, an increase in average temperatures, a decrease in snow cover in the mountains, and a sharp increase in bark beetle lesions.
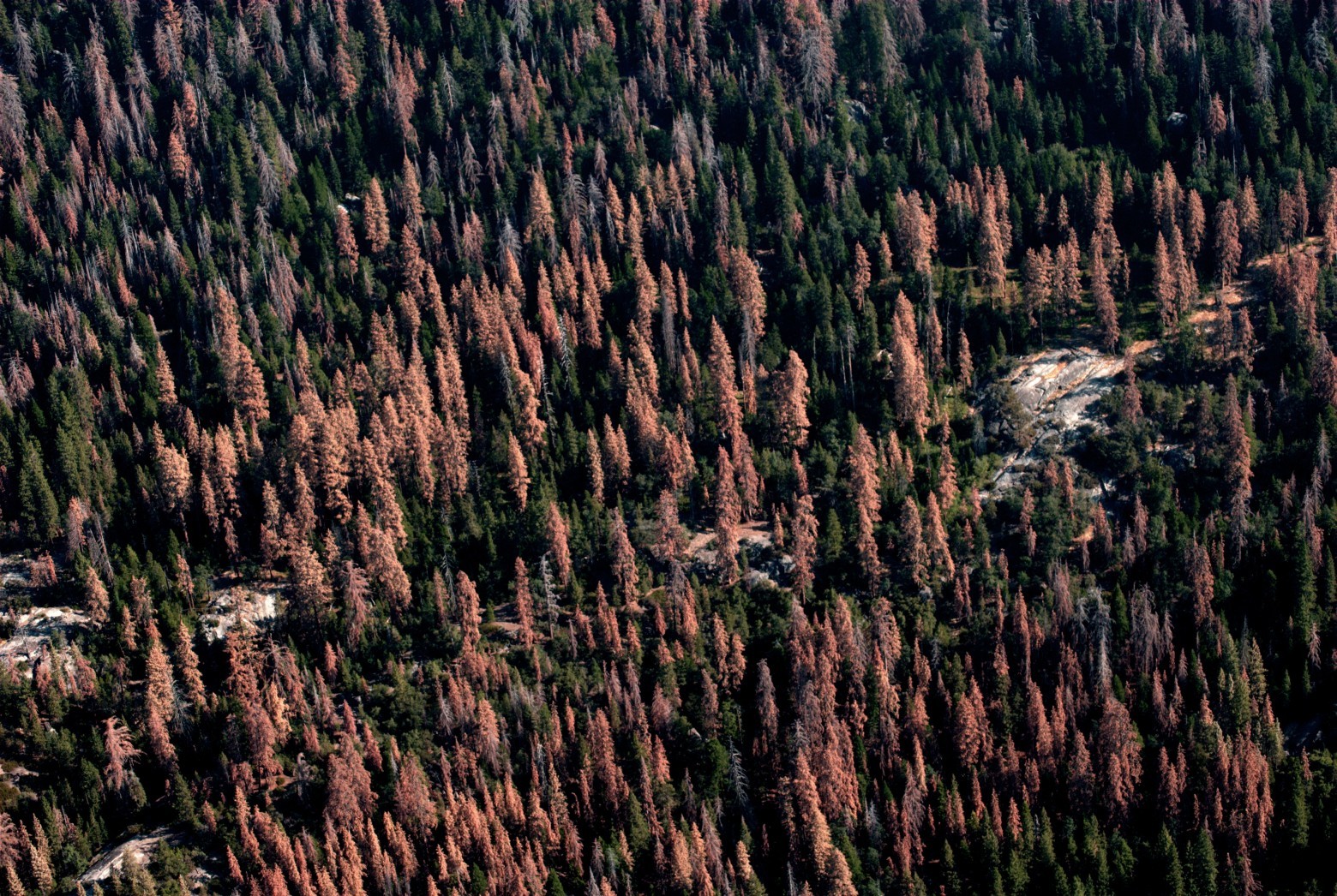

Deadwood and surviving trees. August 24, 2016. Photo: USFS Region 5
In connection with the massive forest extinction in California in 2015, the state governor declared a state of emergency and formed a special service, the Tree Mortality Task Force, to help mobilize additional resources for the safe removal of dead wood.
In new climatic conditions, prolonged heat seasons have become normal. Because of this, it is necessary to drastically increase the cost of protecting the forest from fires, including laying the glades, protecting the catchment area and restoring the forest.
The state of emergency in California persists to this day. In some places there was no rain for 95 days. Sunny weather is predicted for the next two weeks, although long-awaited showers took place in some areas yesterday.