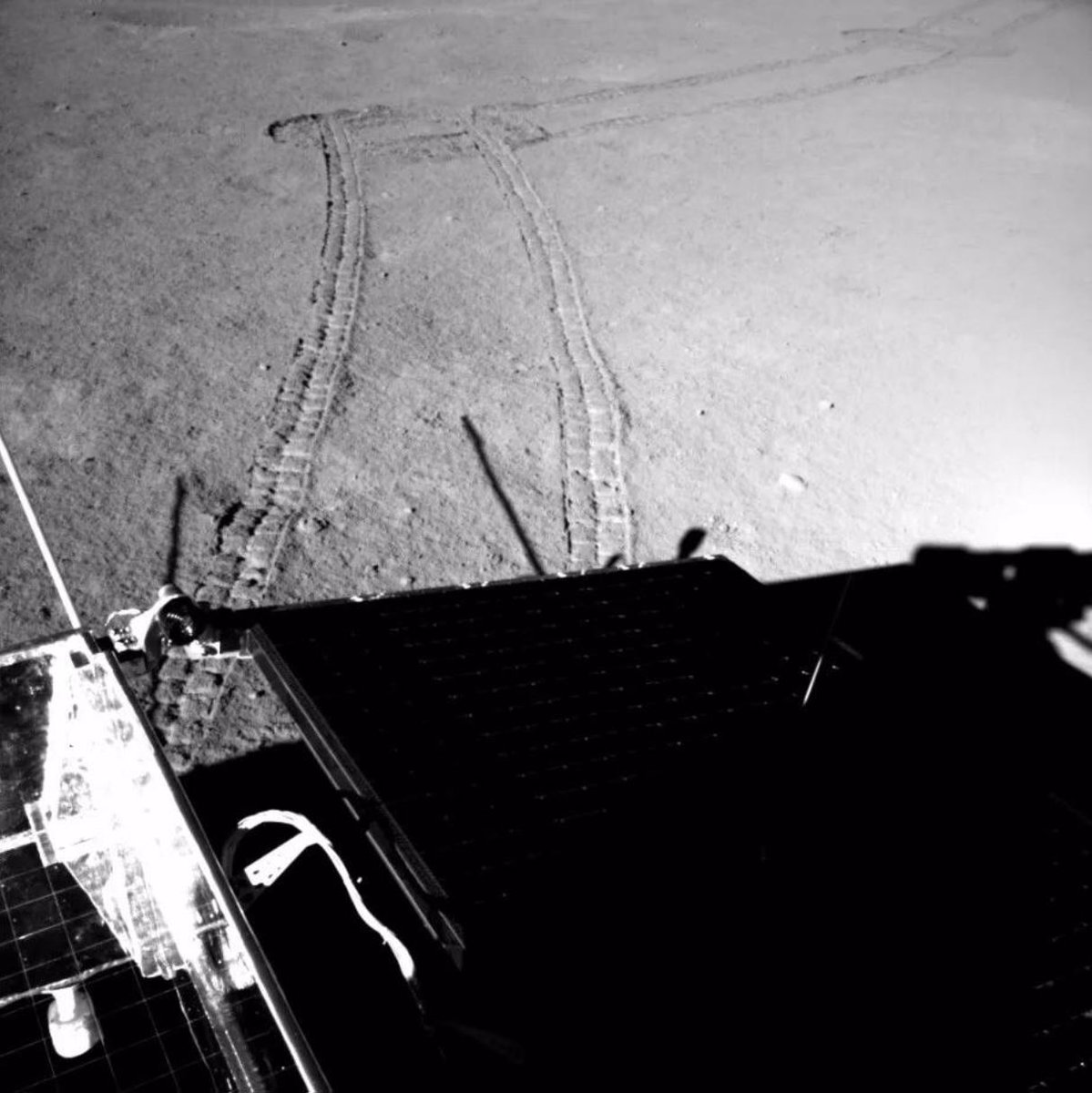
The Chang'e-4 mission is the fifth lunar day for the landing module and the Yutu-2 rover

The fifth earth month of work on the far side of the moon of the Chang'e-4 lander and the Yutu-2 rover began.
Both devices successfully survived the cold fourth moonlit night, now they have come out of sleep mode, proceeding to continue their research on the complex surface of the back of the moon and the surrounding outer space.
New photos of the back of the moon, the moments of launch and landing mission.
Attention, there are a lot of pictures inside the publication.
Previously published materials about the Chang'e-4 mission:
1. The Chang'e-4 spacecraft made a successful landing on the far side of the moon and sent the first photo
2. An on-board video of the preparation and landing processes, as well as a panorama of the reverse side of the moon from the Chang'e-4
3. Video of the rover descent process “ Yutu-2 ", its first meters on the surface of the moon. A two-week dream on the moon is over
4. Pride and passion, the story of turning a dream into a space project
5. NASA's lunar orbiting probe took the first pictures of the Chinese Chang'e-4 station - two pixels of light
6. The Chang'e-4 module and the Yut rover -2 "ready for the second night on the far side of the Moon
7. NASA's lunar orbiting probe took new pictures of the Chinese Chang'e-4 station - closer and clearer
8. Interesting facts about the history of the Chinese lunar program and the Chang'e-4 space mission
9. The Chang'e-4 mission is the third lunar day. The Yutu-2 rover in search of ... stones
10. The Chang'e-4 mission - scientific equipment on the landing module and the relay satellite
11. The Chang'e-4 mission - the fourth lunar day for the Yutu-2 landing module and rover . About cameras and controllers on devices
1. The Chang'e-4 spacecraft made a successful landing on the far side of the moon and sent the first photo
2. An on-board video of the preparation and landing processes, as well as a panorama of the reverse side of the moon from the Chang'e-4
3. Video of the rover descent process “ Yutu-2 ", its first meters on the surface of the moon. A two-week dream on the moon is over
4. Pride and passion, the story of turning a dream into a space project
5. NASA's lunar orbiting probe took the first pictures of the Chinese Chang'e-4 station - two pixels of light
6. The Chang'e-4 module and the Yut rover -2 "ready for the second night on the far side of the Moon
7. NASA's lunar orbiting probe took new pictures of the Chinese Chang'e-4 station - closer and clearer
8. Interesting facts about the history of the Chinese lunar program and the Chang'e-4 space mission
9. The Chang'e-4 mission is the third lunar day. The Yutu-2 rover in search of ... stones
10. The Chang'e-4 mission - scientific equipment on the landing module and the relay satellite
11. The Chang'e-4 mission - the fourth lunar day for the Yutu-2 landing module and rover . About cameras and controllers on devices
The Yutu-2 rover came out of sleep mode on the morning of April 28, 2019, on the evening of April 28, the Chang'e-4 lander also woke up, and both vehicles began their fifth day shift on the Moon.
At night, on the far side of the moon, according to the sensors of the Chang'e-4 modules, the temperature on the lunar surface drops (minimum) to minus 190 degrees Celsius.
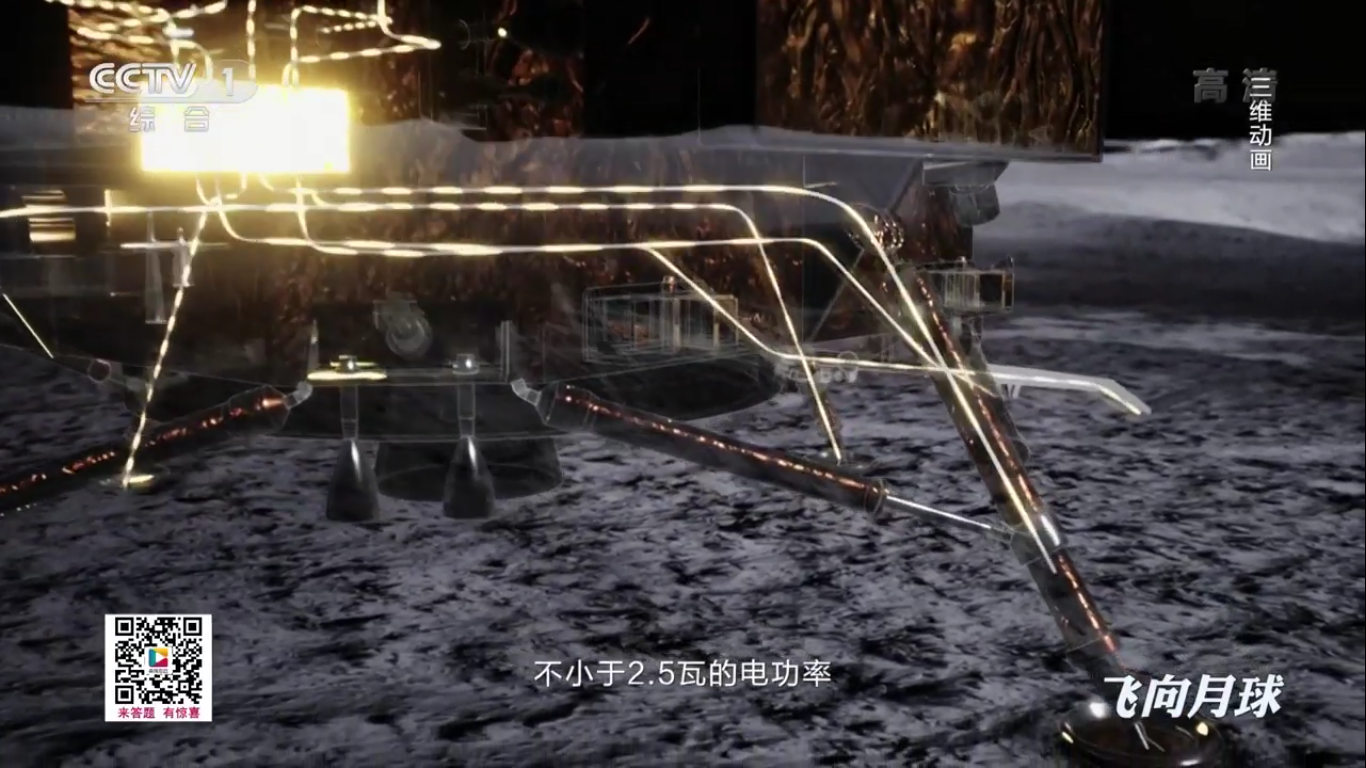
The heating units developed at the Russian Federal Nuclear Center (VNII Experimental Physics (VNIIEF) are responsible for heating the Chang'e-4 modules during a moonlit night, these are radiation heat sources (RIT) and radioisotope sources of electricity (RTG) designed to power Chinese systems of the lunar mission:
Data on the project and modules of the lunar mission "Chang'e-4":
May 21, 2018: Tseyuqiao relay satellite (fortieth bridge) was launched from the Xichang Chinese cosmodrome, it is necessary for organizing communication between the Earth and the far side of the moon.
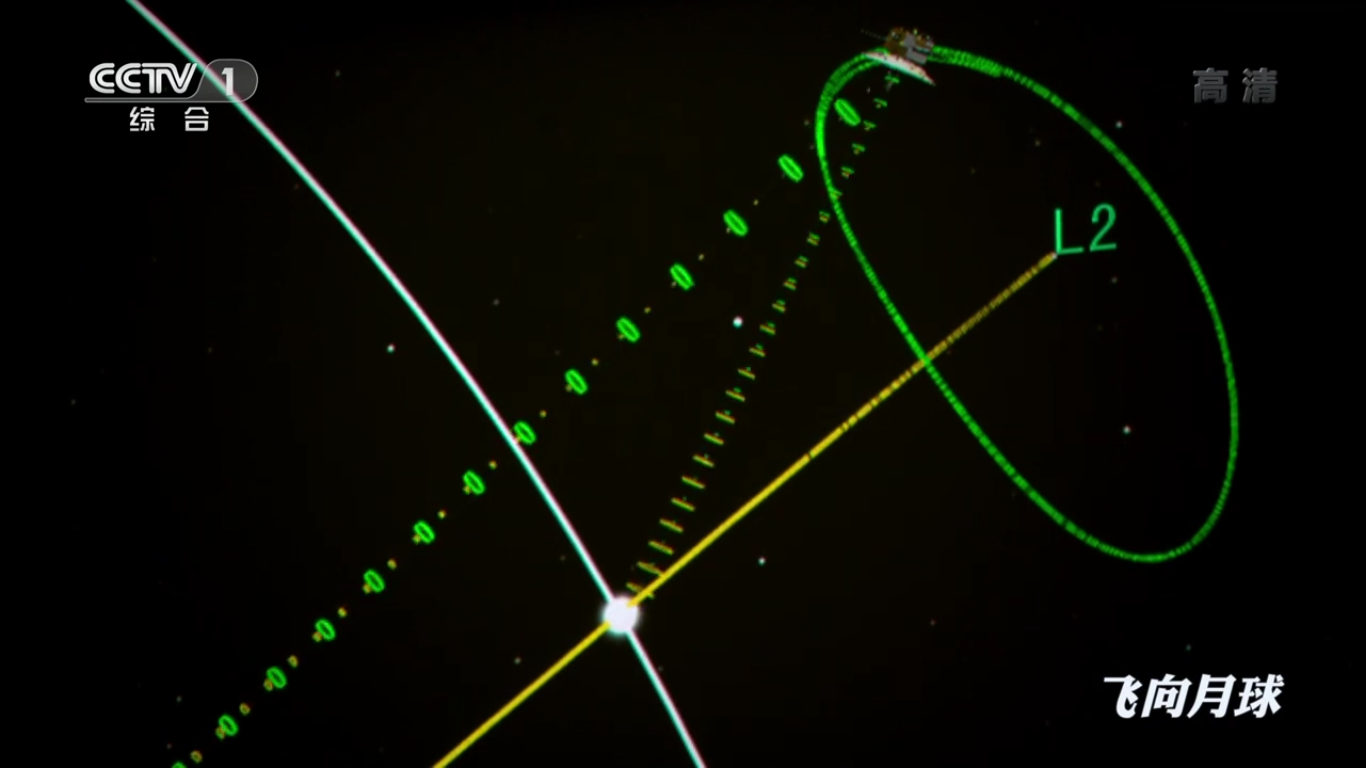
June 14, 2018: Tseyuqiao satellite relay went into orbit around the Lagrange point L2 of the Earth-Moon system, about 65,000 km from the Moon, becoming the first communication satellite in this orbit in the world.
December 8, 2018: The Changzheng-3B booster rocket with the Chang'e-4 station was successfully launched from the Sichan space center in China.
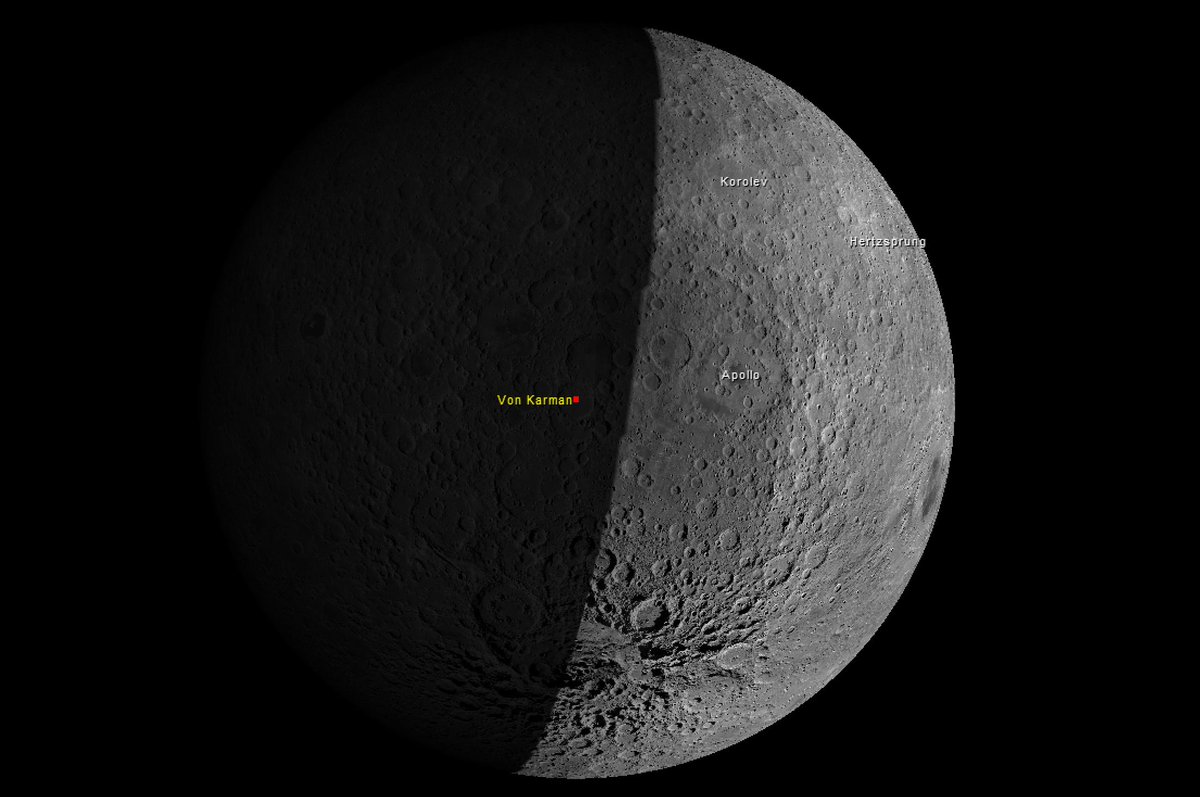
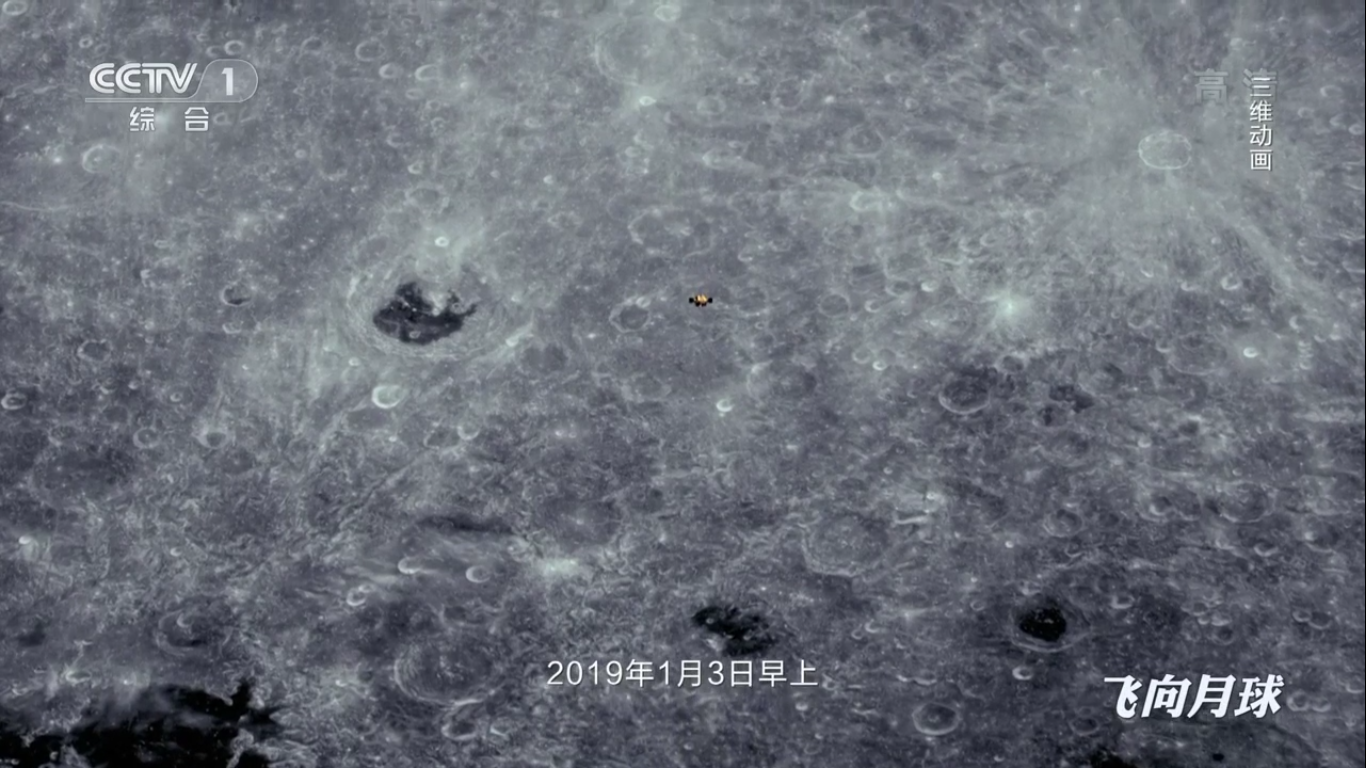
January 3, 2019: Chang'e-4 lander makes landing in the Karman crater on the far side of the moon. The Chang'e-4 lander contains the second Chinese lunar rover Yutu-2, a modernized analogue of the Yutu rover. The personnel of the Chang'e-4 mission are now continuing to operate normally.
Video of the landing procedure on the far side of the moon:
After completing all stages of the successful landing procedure and installing independent communication channels with Chang'e-4 devices (the landing module and the rover), the era of exploration of the far side of the moon began.
Video of the descent of the rover "Yutu-2":
Video of the rover trip “Yutu-2”:
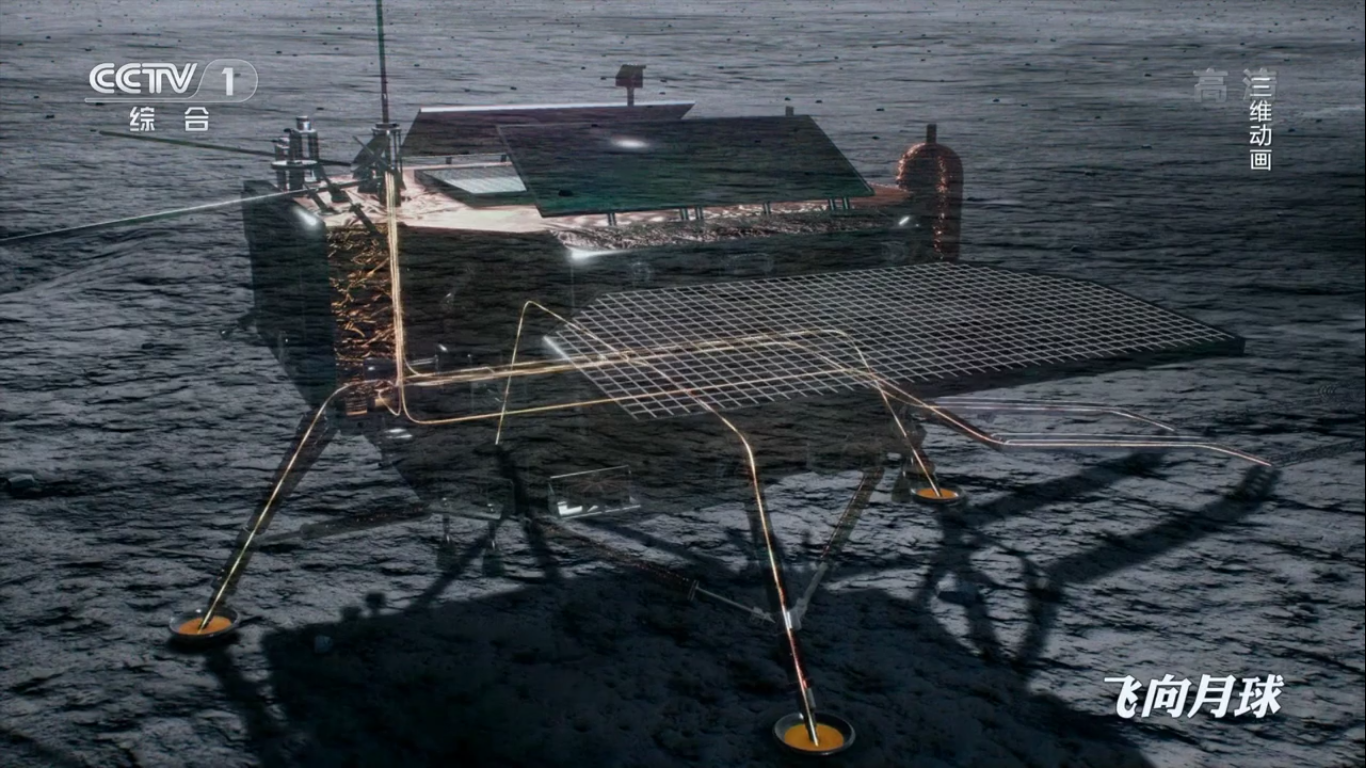
The Chang'e-4 Descent Module:
- 4.4 meters between opposite landing supports, weight 1200 kg .;
- Duration of work: one earth year.
Installed devices:
- LFS - Low Frequency Spectrometer;
- LND - Lunar Lander Neutrons and Dosimetry (neutron dosimeter);
- TCAM - Terrain Camera (landscape camera);
- LCAM - Landing Camera (landing camera).
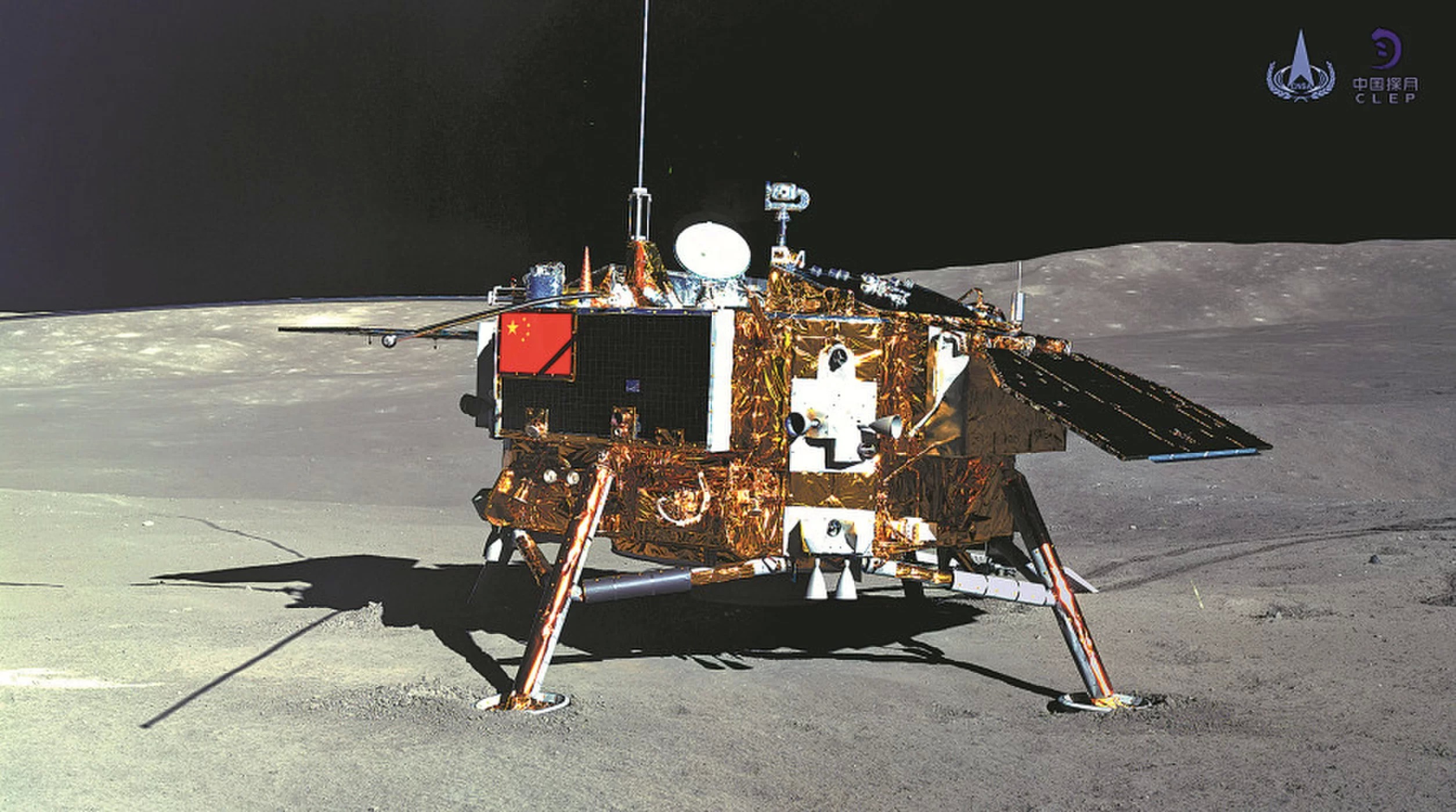
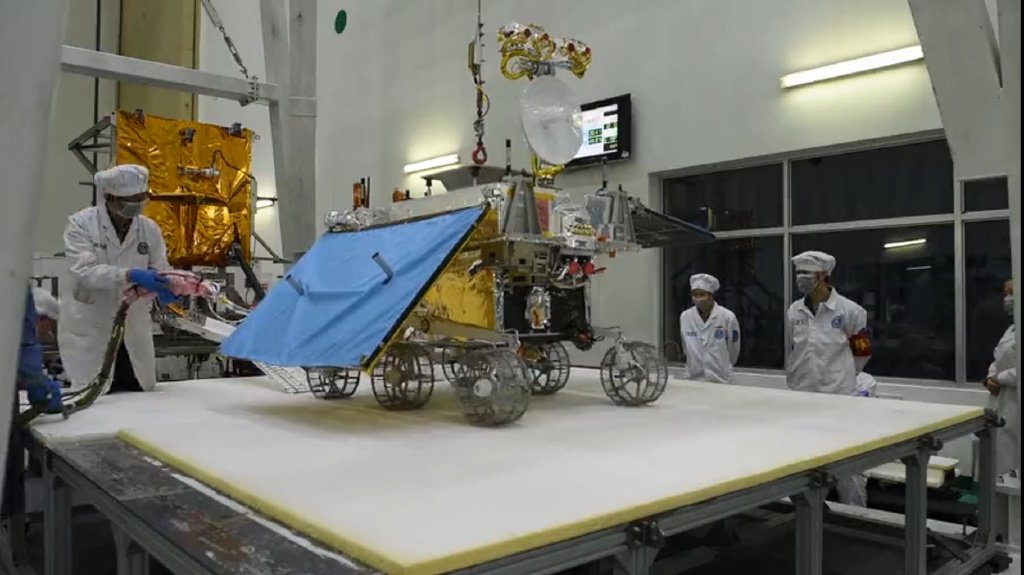
Rover "Yutu-2":
- height 1 meter, width 1 meter (without solar panels), 1.5 meters in length, two folding solar panels, six wheels;
- total rover weight is about 140 kg (310 lbs);
- load capacity of about 20 kg (44 lbs);
- can move on slopes and has automatic sensors to prevent collision with other objects;
- The rover is supplied with electricity by means of two solar panels, allowing the rover to work during a lunar day;
- maximum speed of 200 meters per hour (this speed on the Moon can still not be reached, since the elements on the surface will not allow to accelerate and damage the rover earlier);
- the maximum research area is 3 square meters. km;
- the estimated operating time is 3 months (2160 hours), the rover has already exceeded its service life;
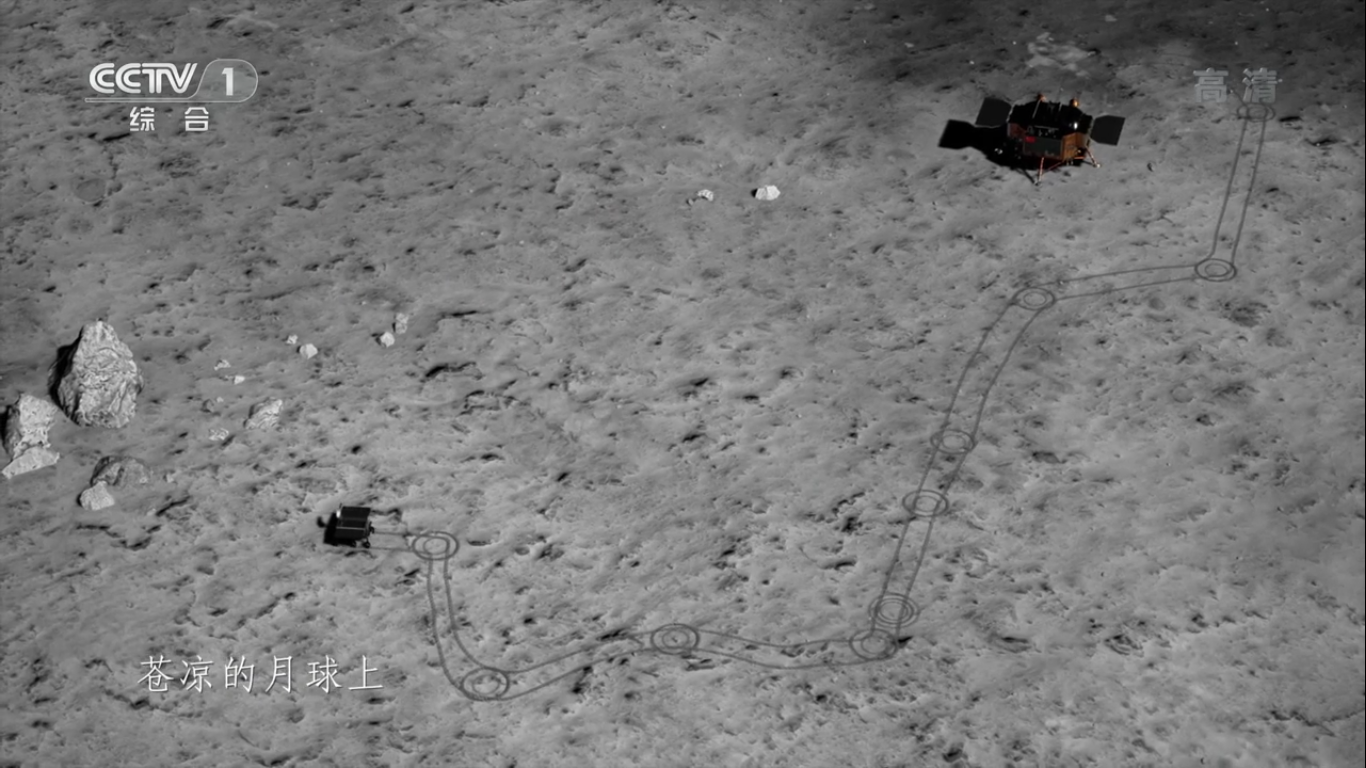
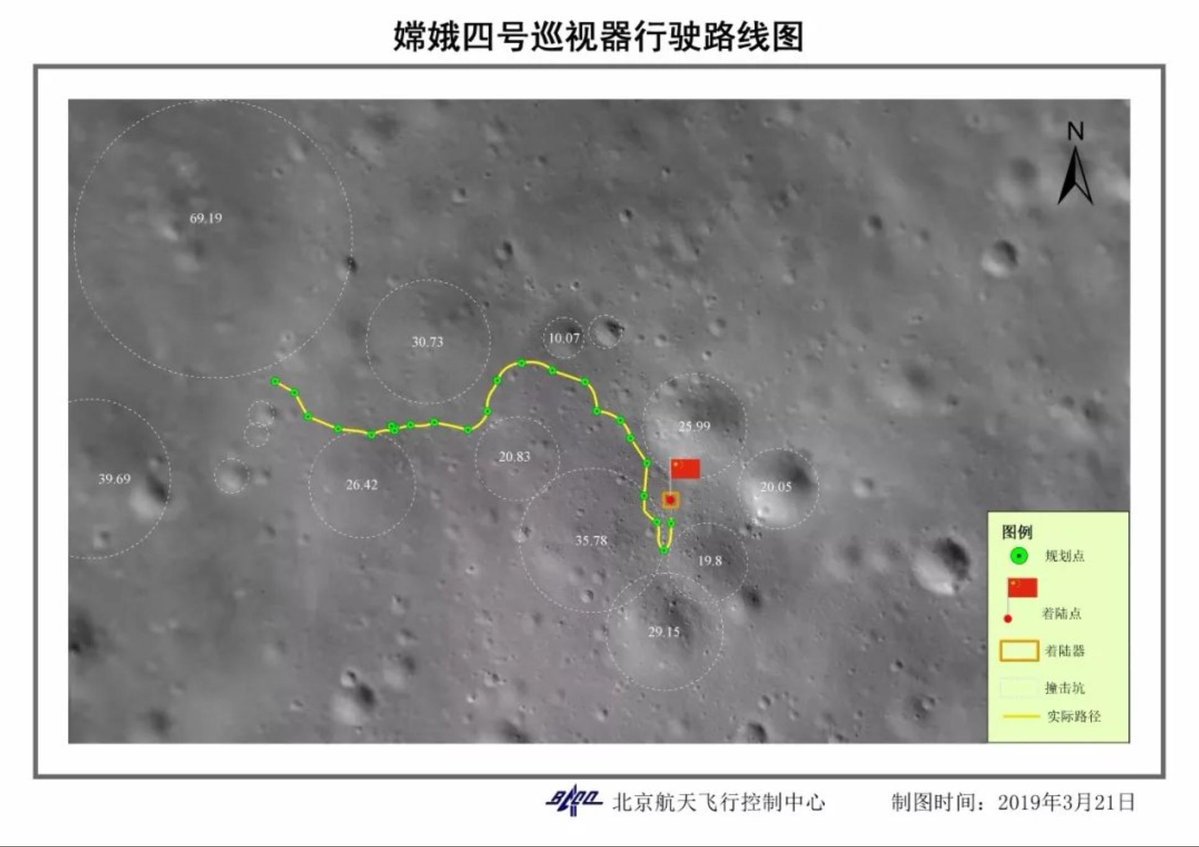
- the maximum estimated distance is 10 km, now 178.9 meters have been passed along the lunar surface in five months (1 place among rovers on the far side of the moon, sixth place among all lunar rovers), a table of the distance of rovers is given here ;
- control mode: automatic (detour of small obstacles), manual (main) - the operator controls from the Earth.
Installed devices:
- LPR - Lunar Penetrating Radar;
- ASAN - Advanced Small Analyzer for Neutrals (small analyzer of neutral particles);
- VNIS - Visible and Near-Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (infrared spectrometer);
- PCAM - Panoramic Camera (dual panoramic camera).
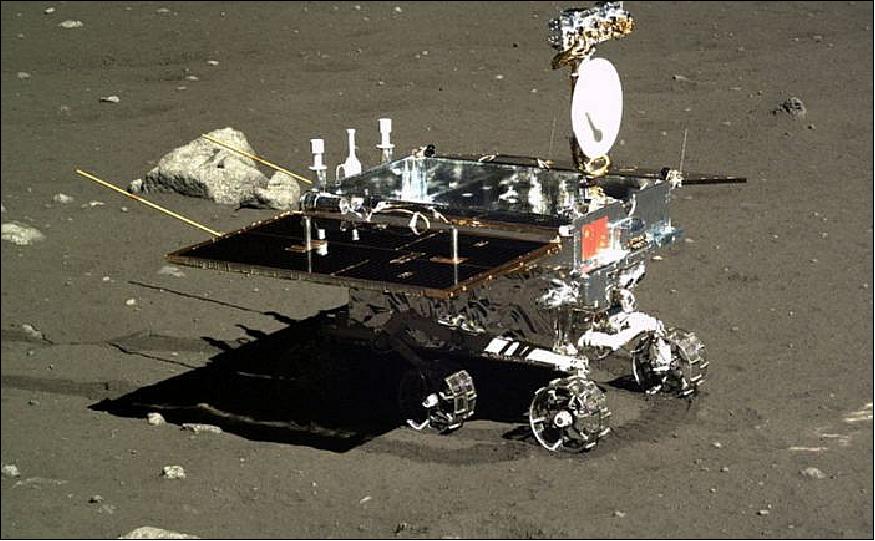

Photo of the rover on Earth:
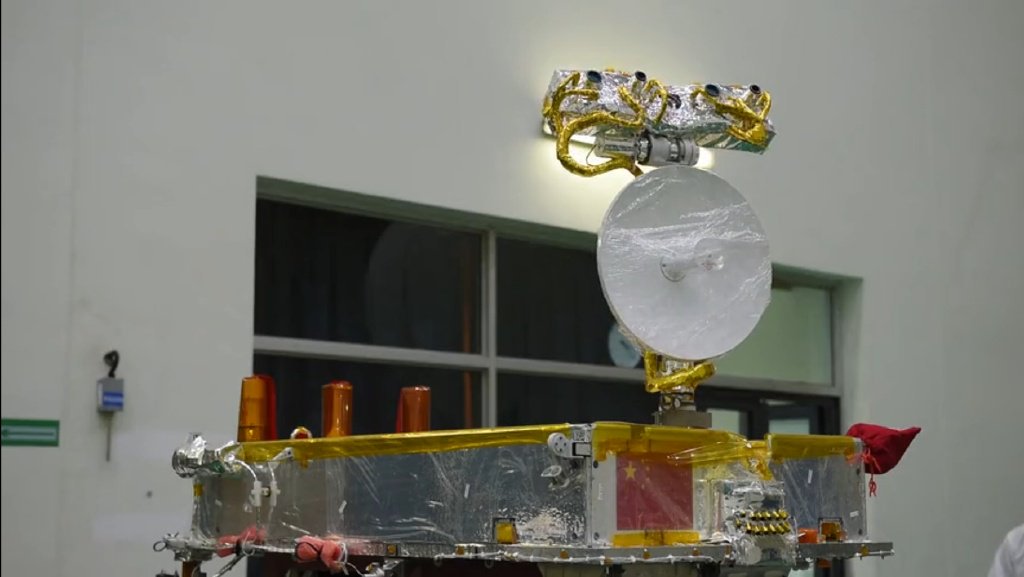




Tseyuqiao satellite relay (fortieth bridge), launched on May 21, 2018, operates in a halo orbit around the special gravitationally stable Lagrange point Earth-Moon L2, from which it can maintain direct visibility with the Earth and the lunar the reverse side at any time for the exchange of data between the MCC and the modules of the Chang'e-4 project.
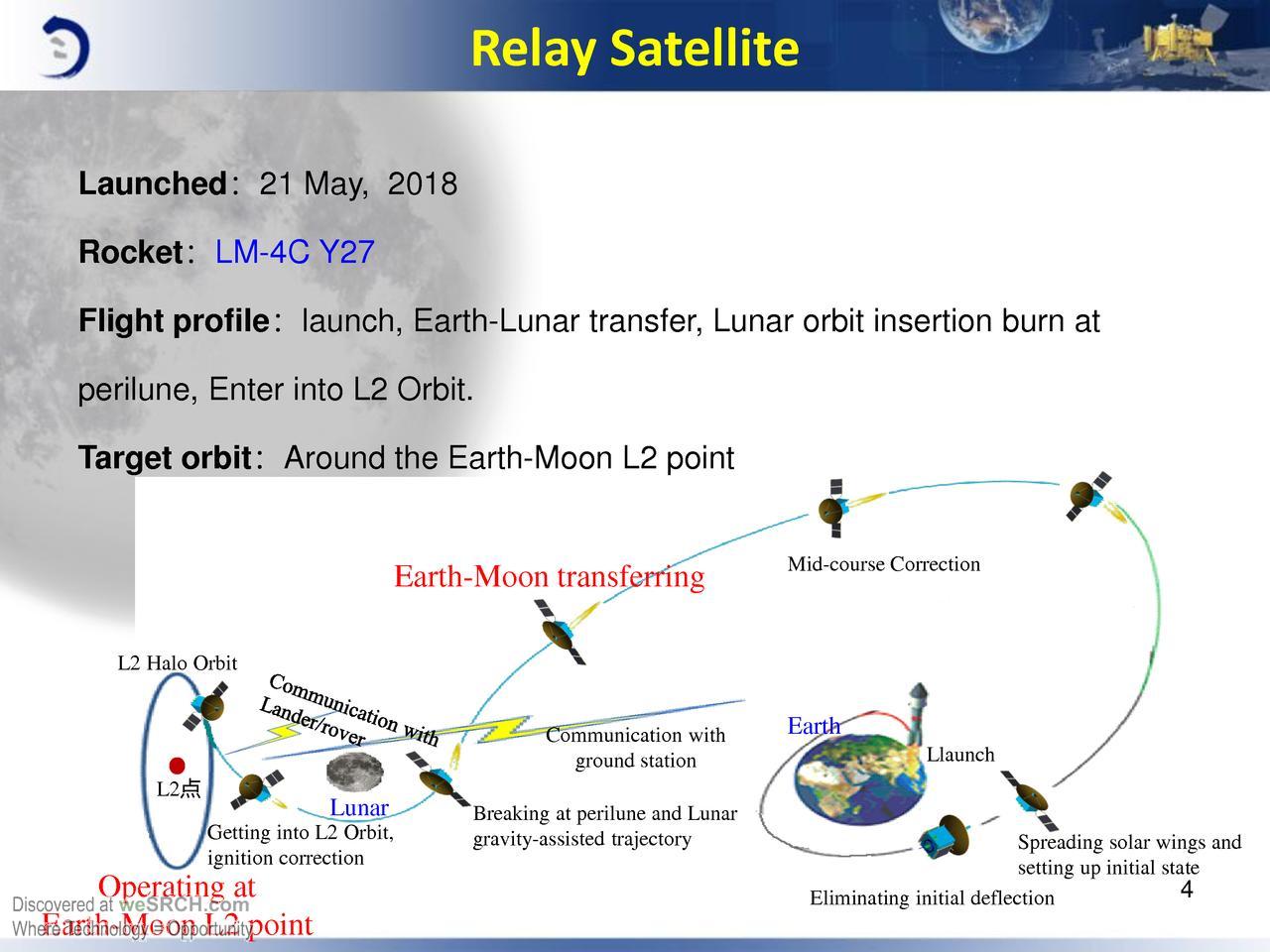
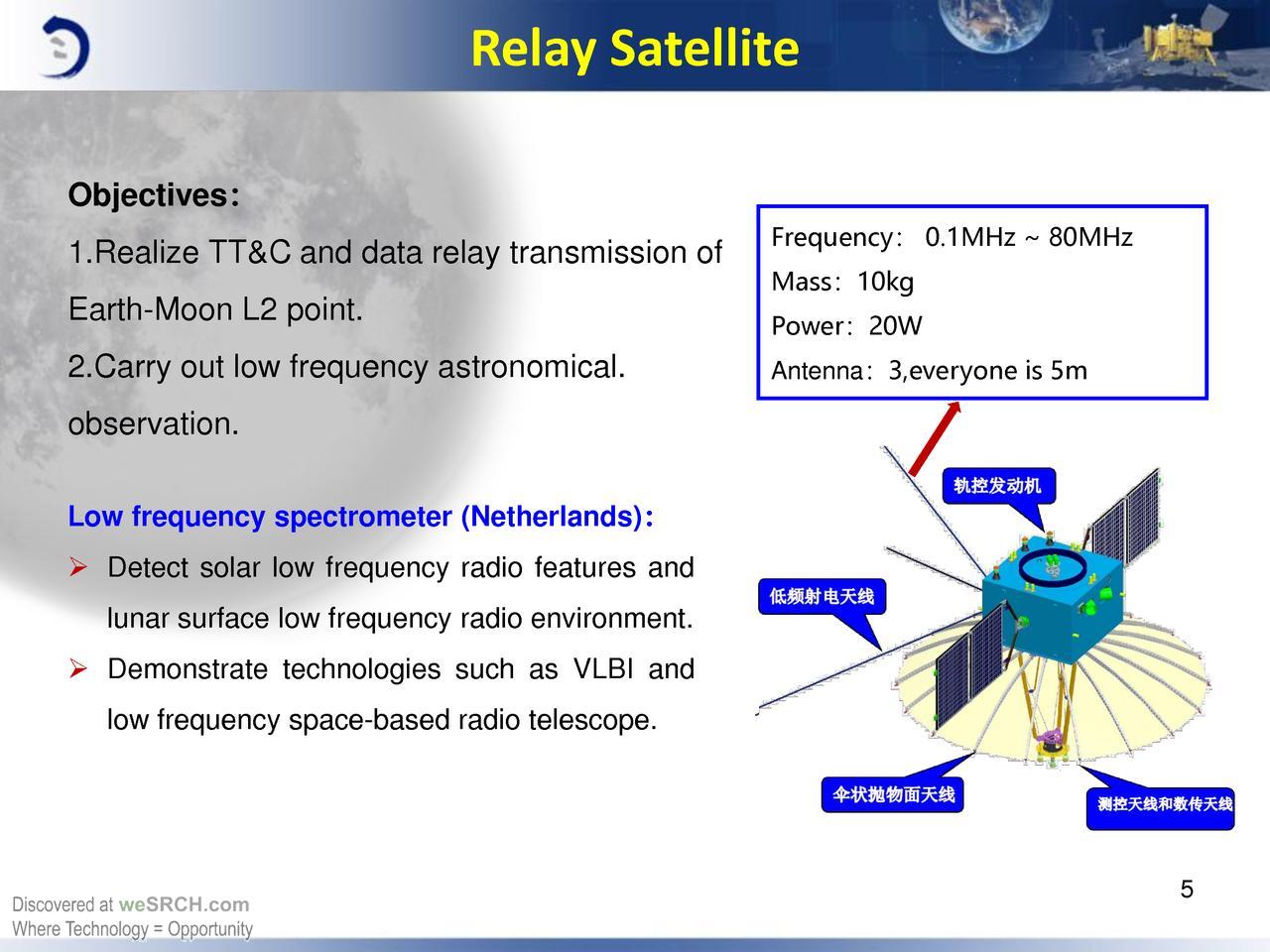
Also, a low-frequency spectrometer (relay LFS) with three five-meter antennas is installed on the Tseyuqiao repeater satellite, with which low-frequency radio emission from the early Universe is recorded, which makes it possible to study its structure.
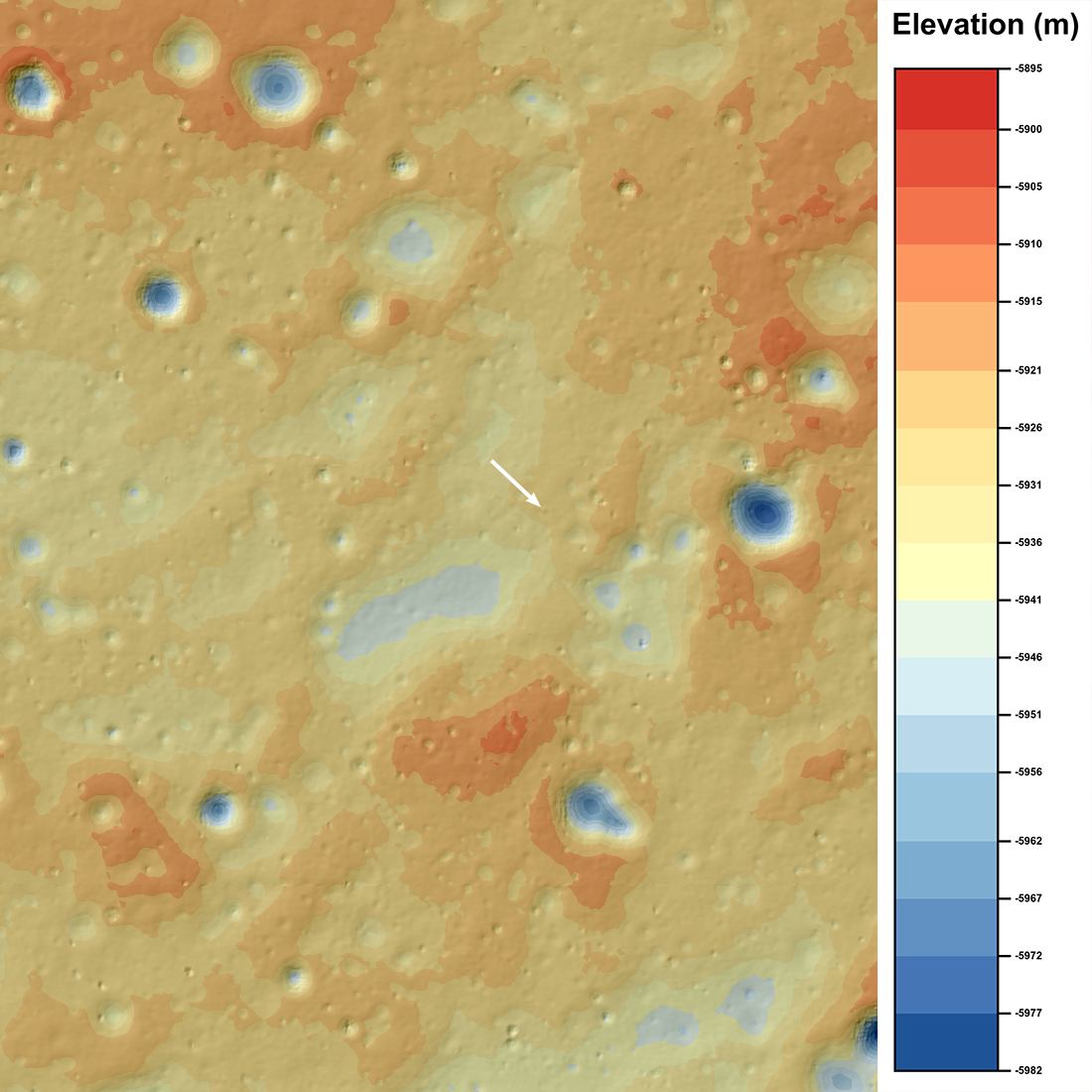
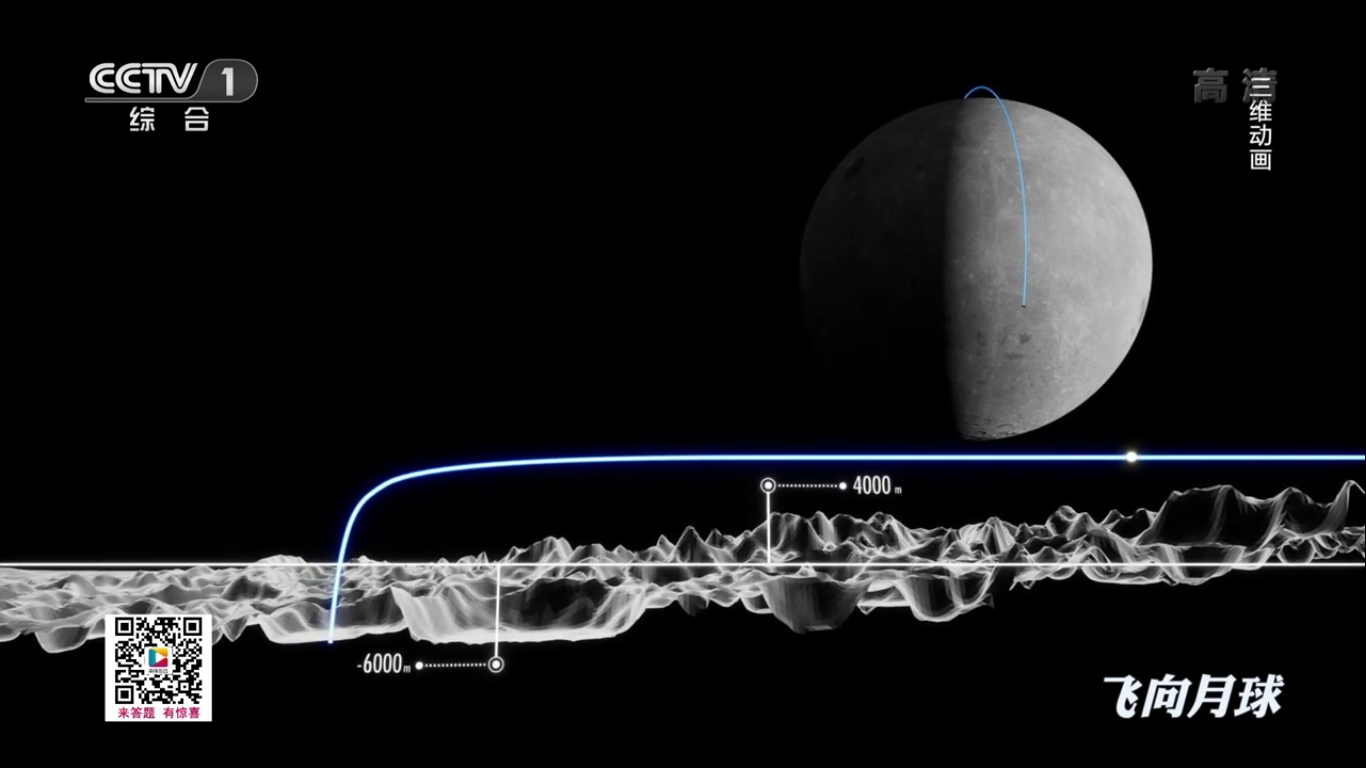
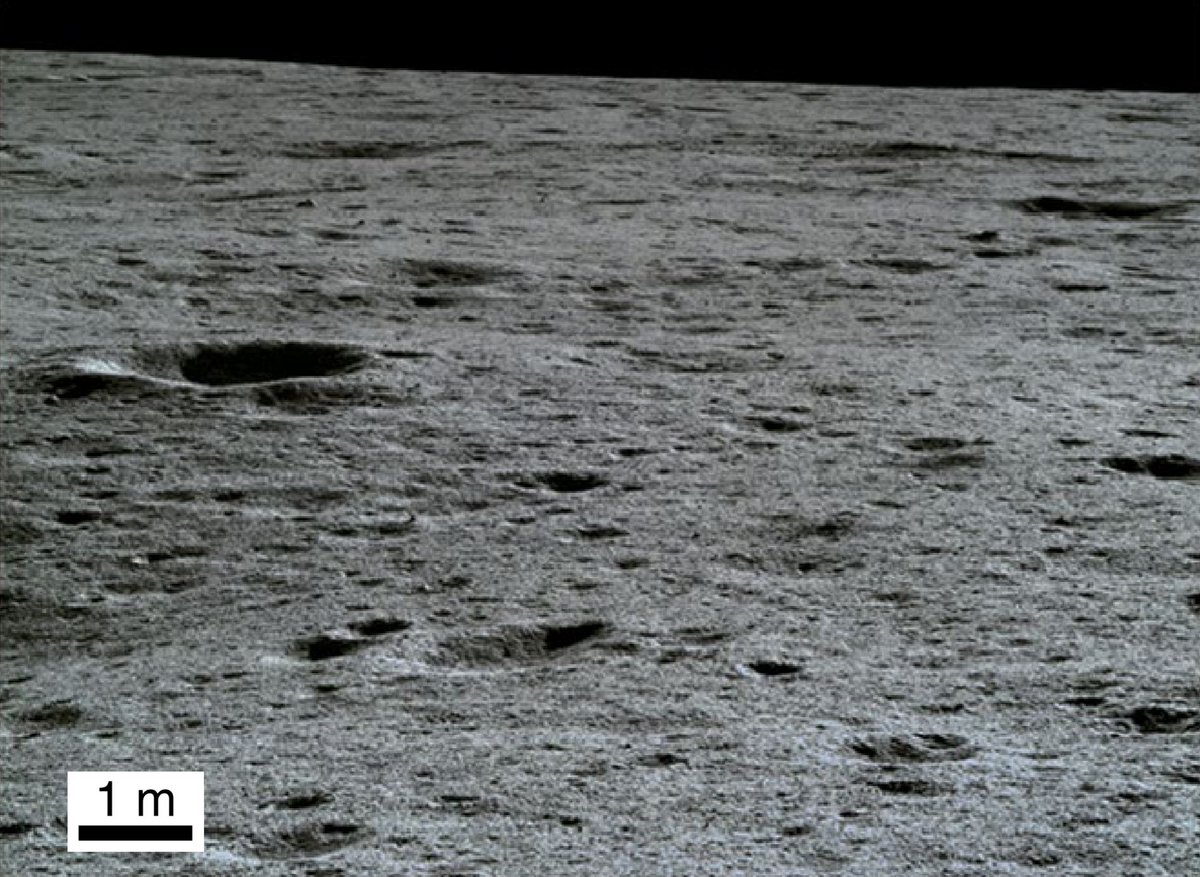
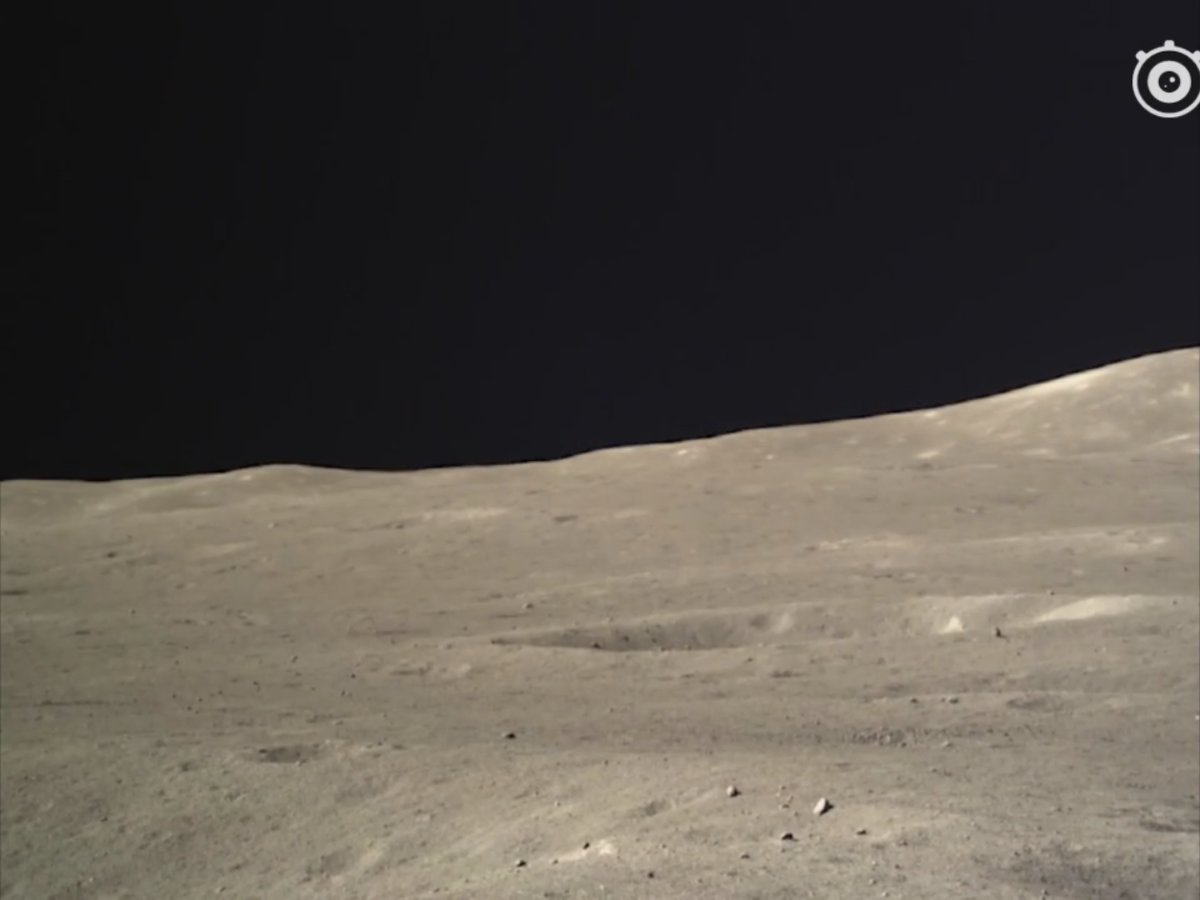
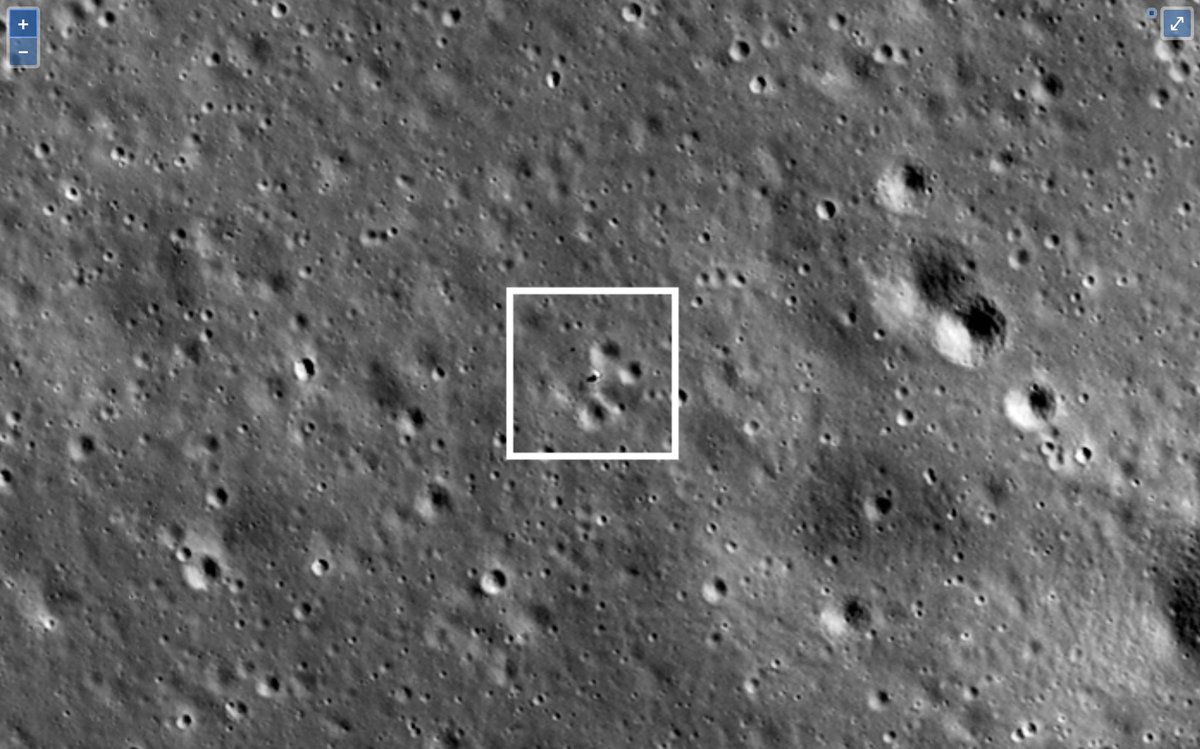
The reverse side of the moon has a more complex relief than the side visible from the earth. The lunar surface in the landing zone of the Chang'e-4 landing module is replete with folds, numerous pebbles and small craters.


Топографическая фотография зоны посадки в кратере Карман обратной стороны Луны спускаемого модуля «Чанъэ-4» (сделано зондом LRO, NASA):

Новые фотографии лунной поверхности с камер посадочного модуля «Чанъэ-4» и ровера «Юйту-2».
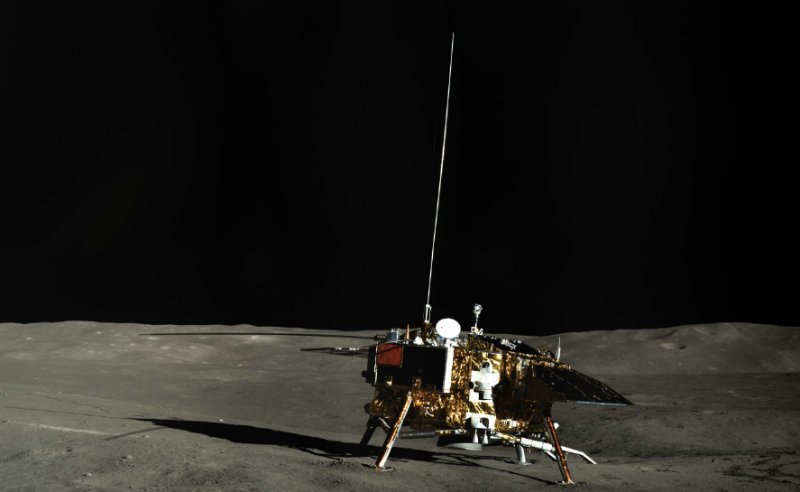
Очень одинокий посадочный модуль «Чанъэ-4»:

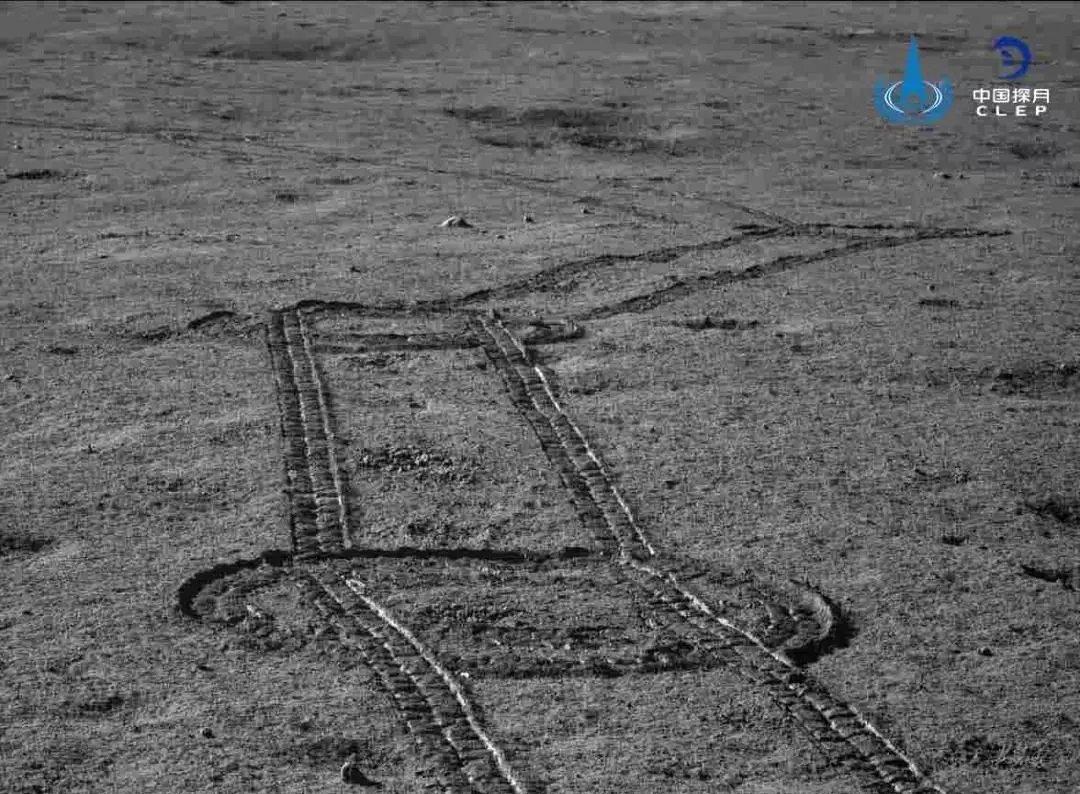
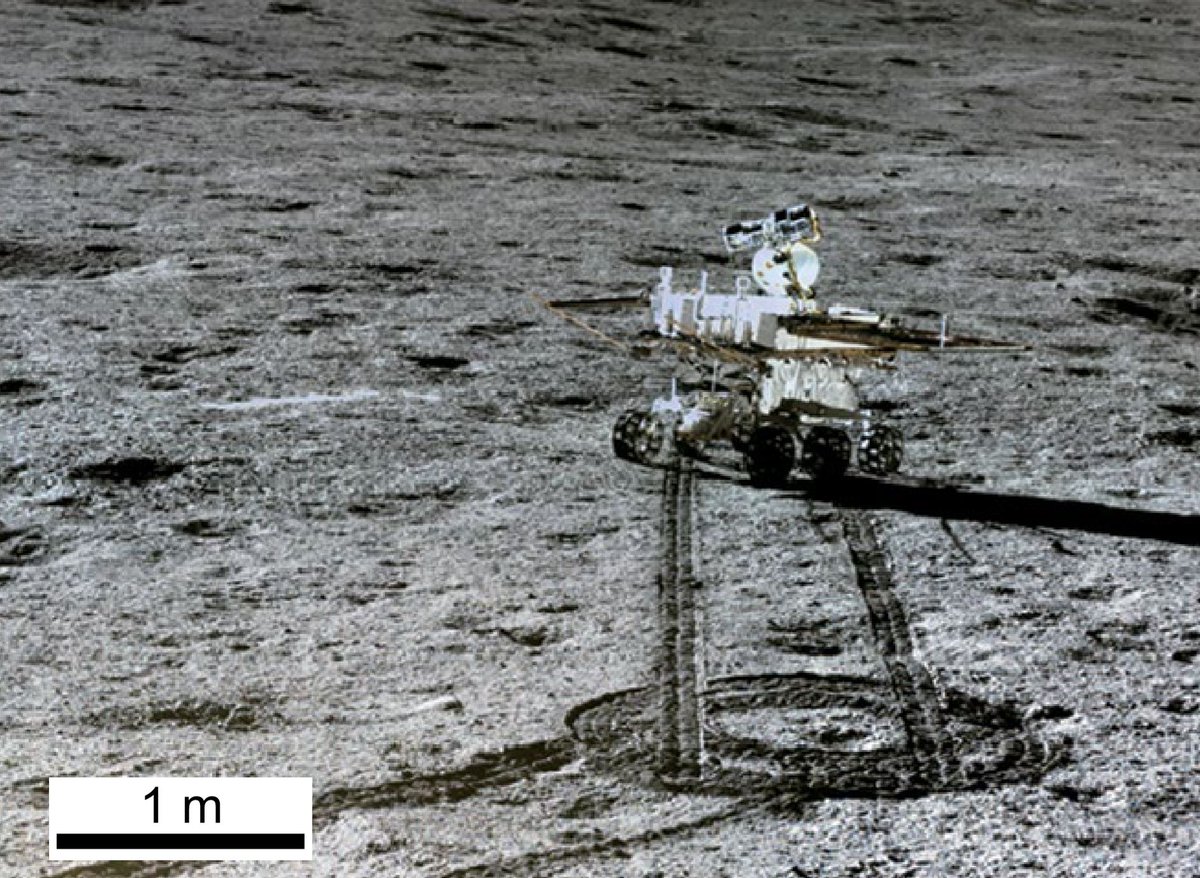
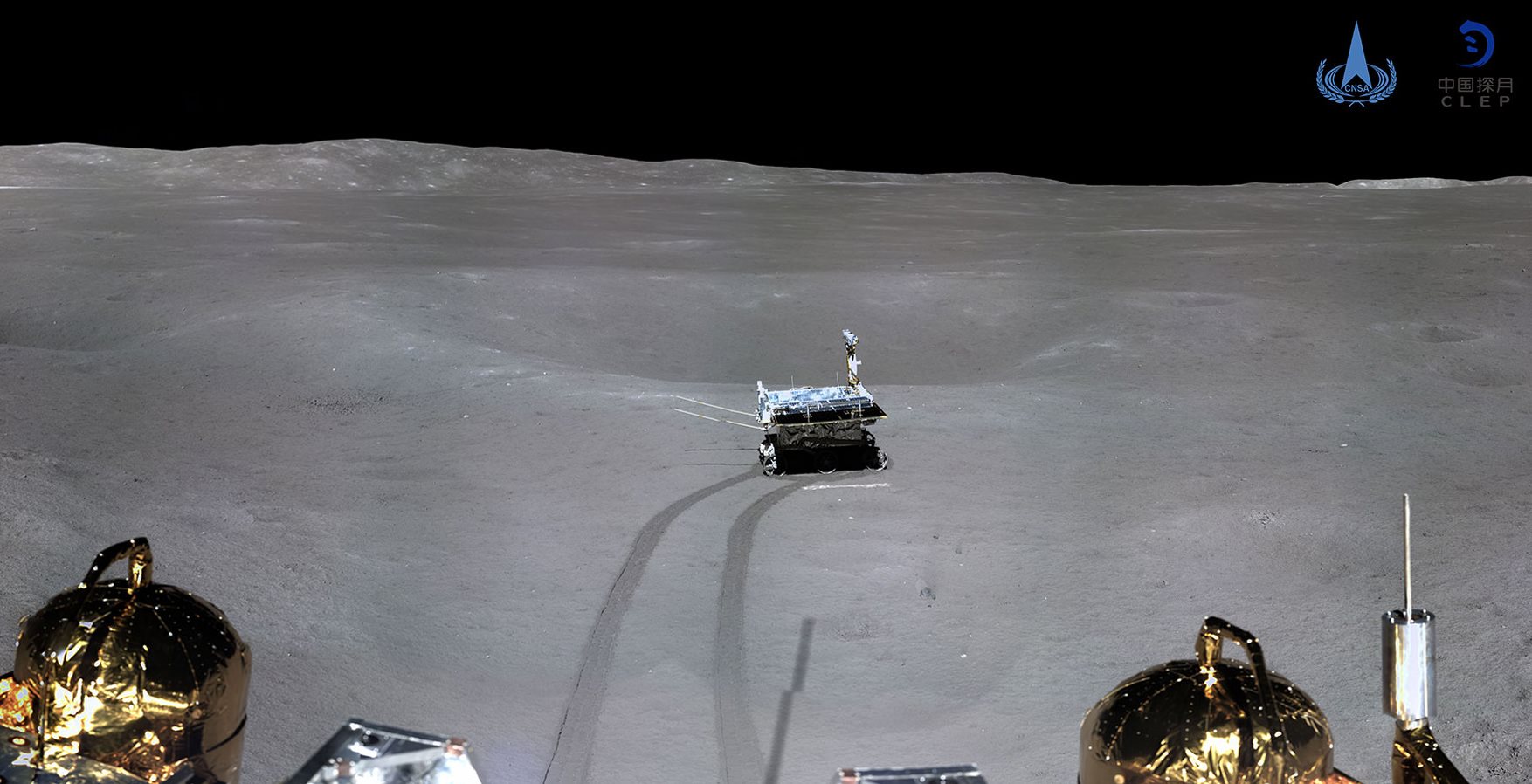
Следы ровера «Юйту-2».:


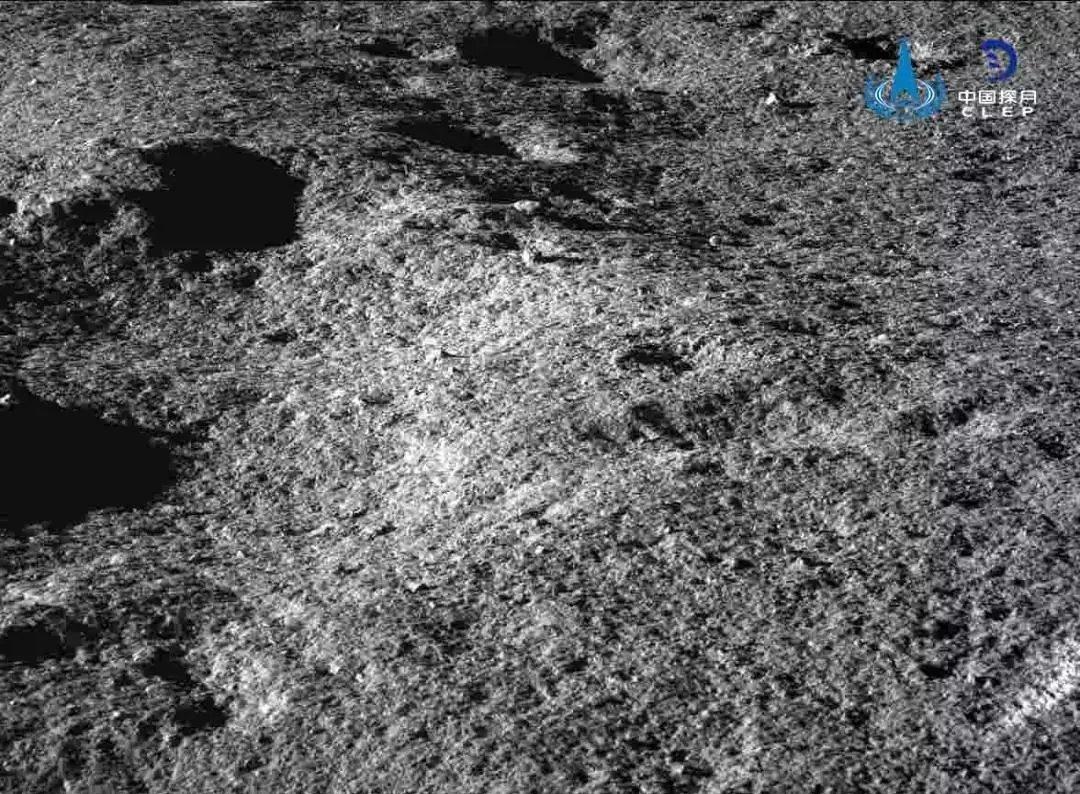
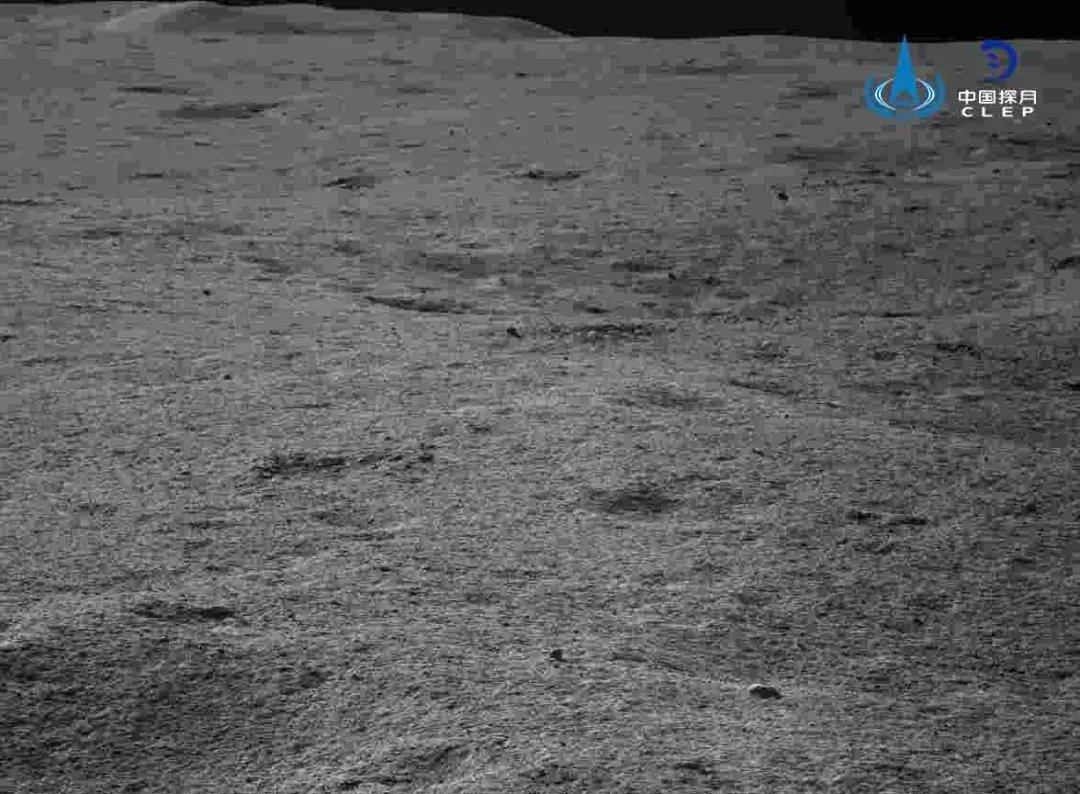
Поверхность обратной стороны Луны:
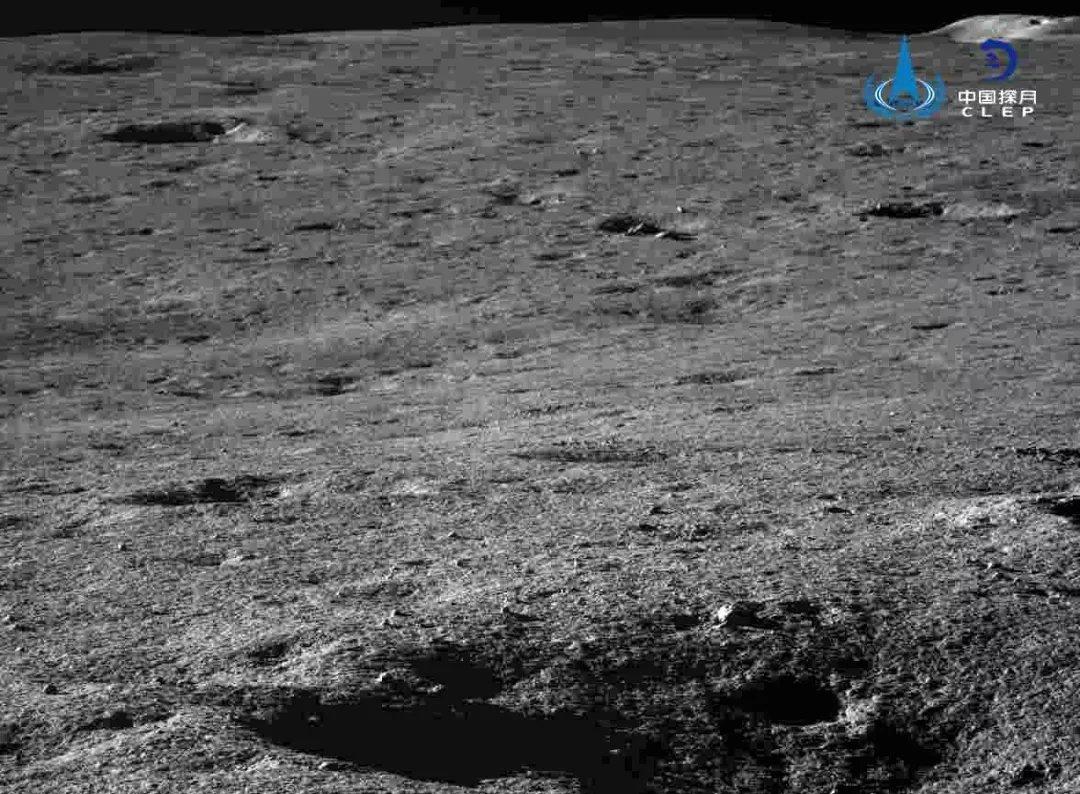
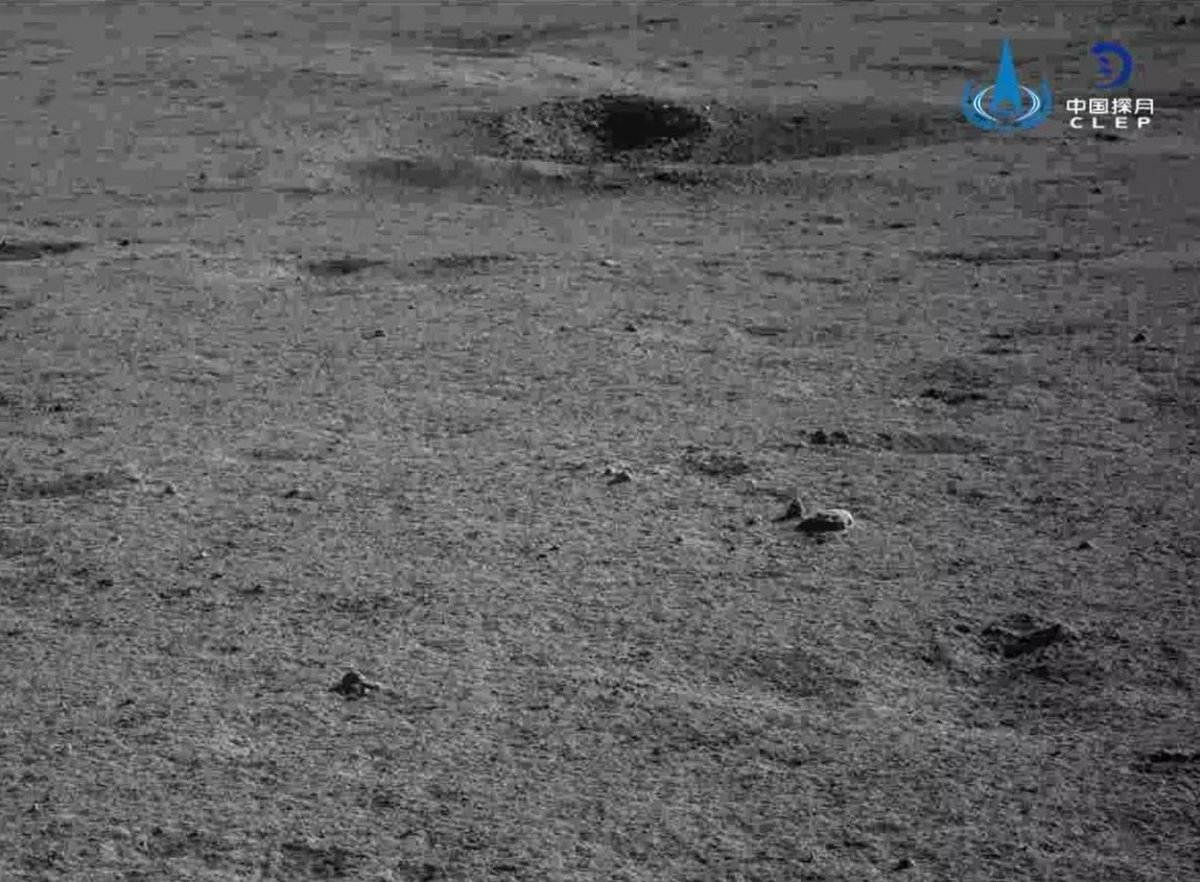
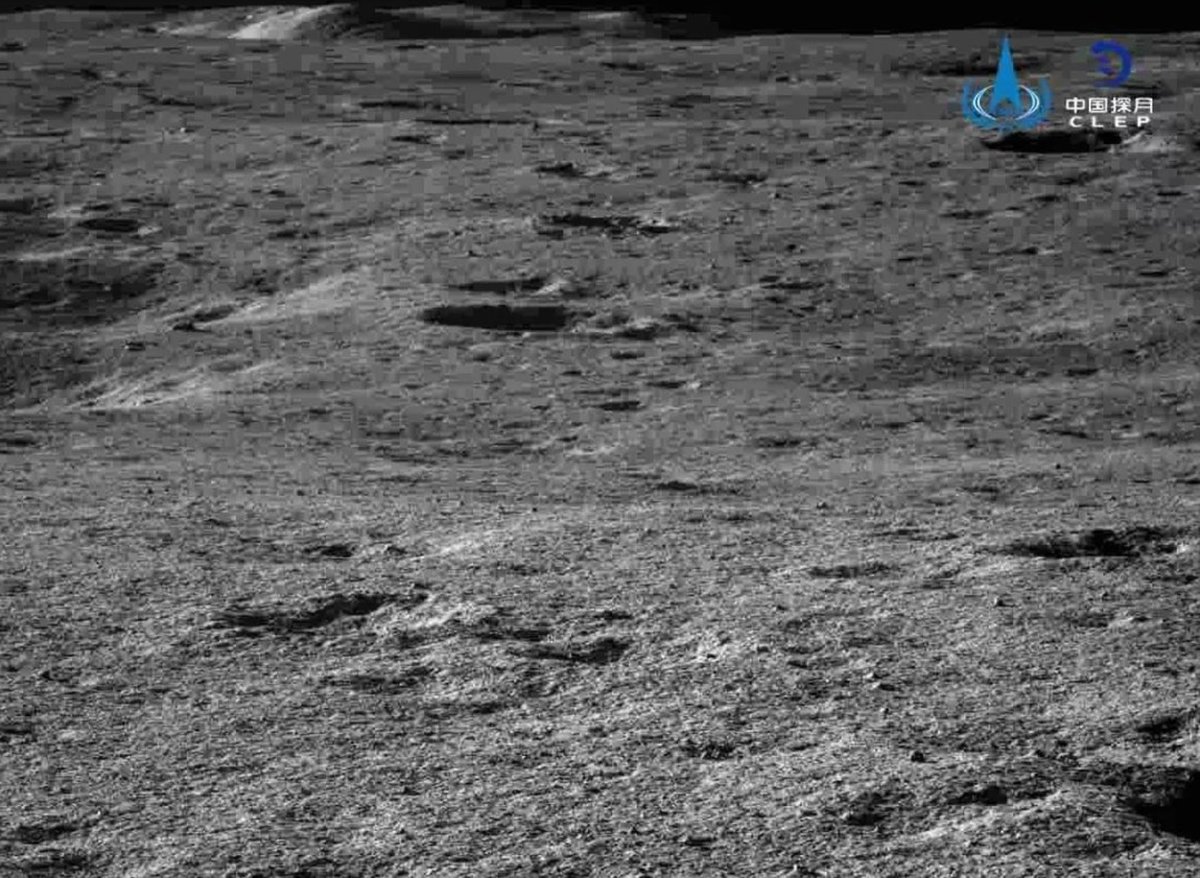






Ранее присланные на Землю фотографии поверхности обратной стороны Луны:
Лунная колея от колес ровера «Юйту-2» и тень от антенны и площадки с панорамной камерой:
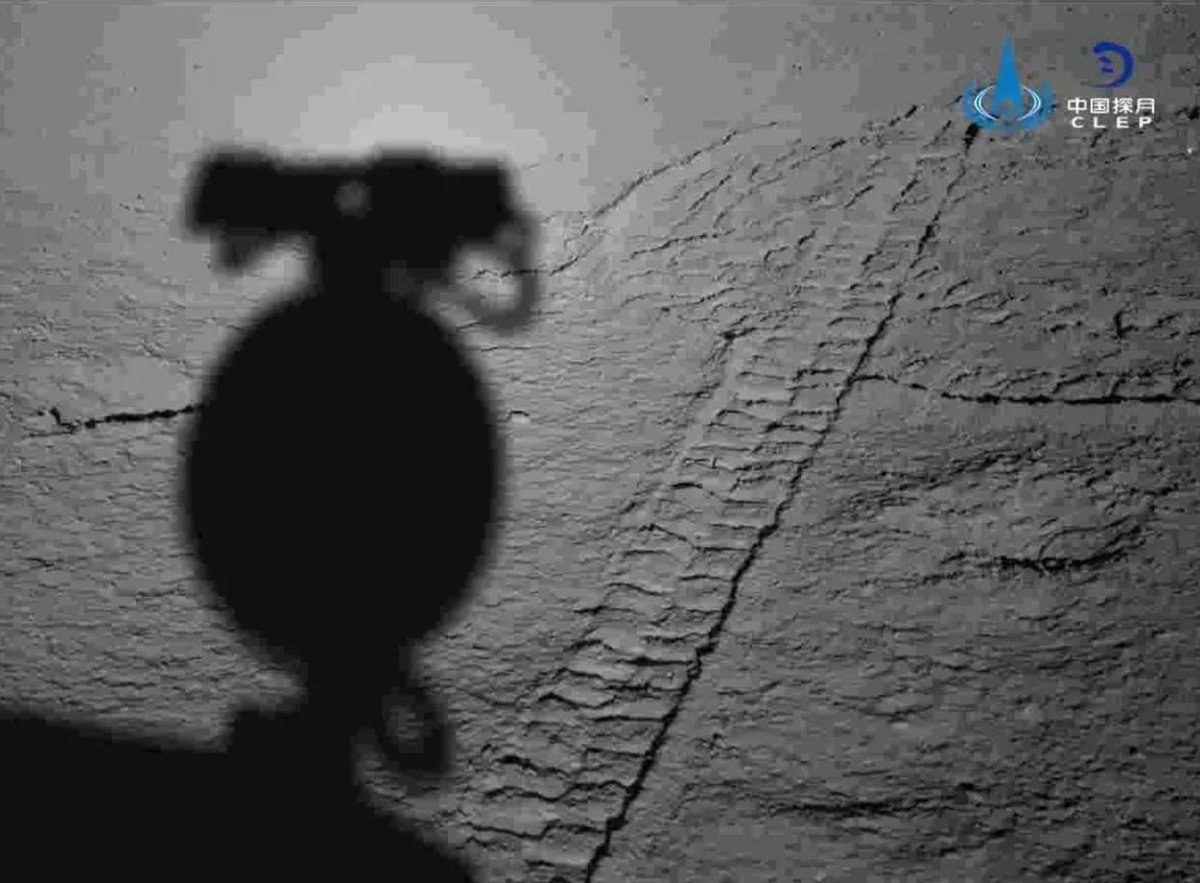

Несколько кратеров (с тенями красиво) и горы на заднем плане:

А вот эти фотографии из научной статьи «Lunar farside to be explored by Chang’e-4» апрельского номера журнала «Nature Geoscience».

Небольшие кратеры около места посадки:
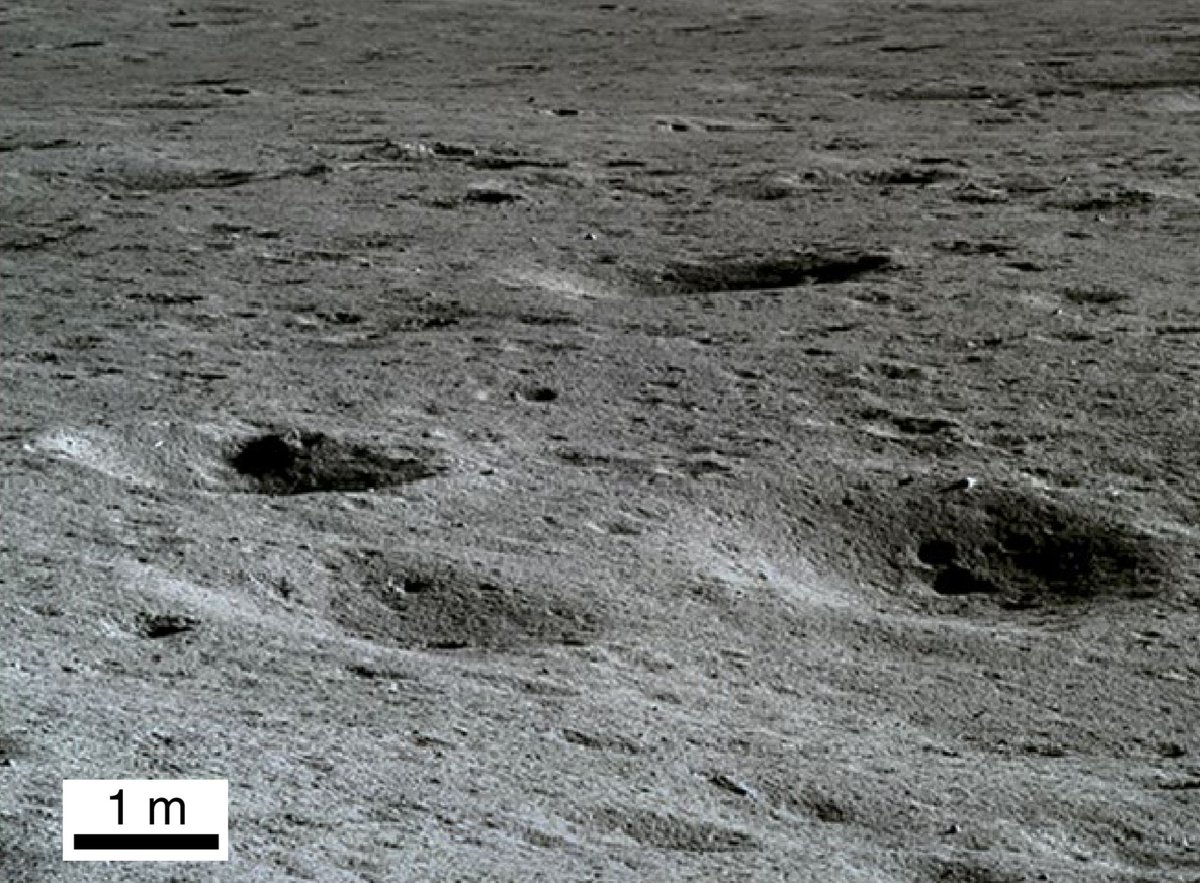


Ровер «Юйту-2» исследует поверхность Луны:
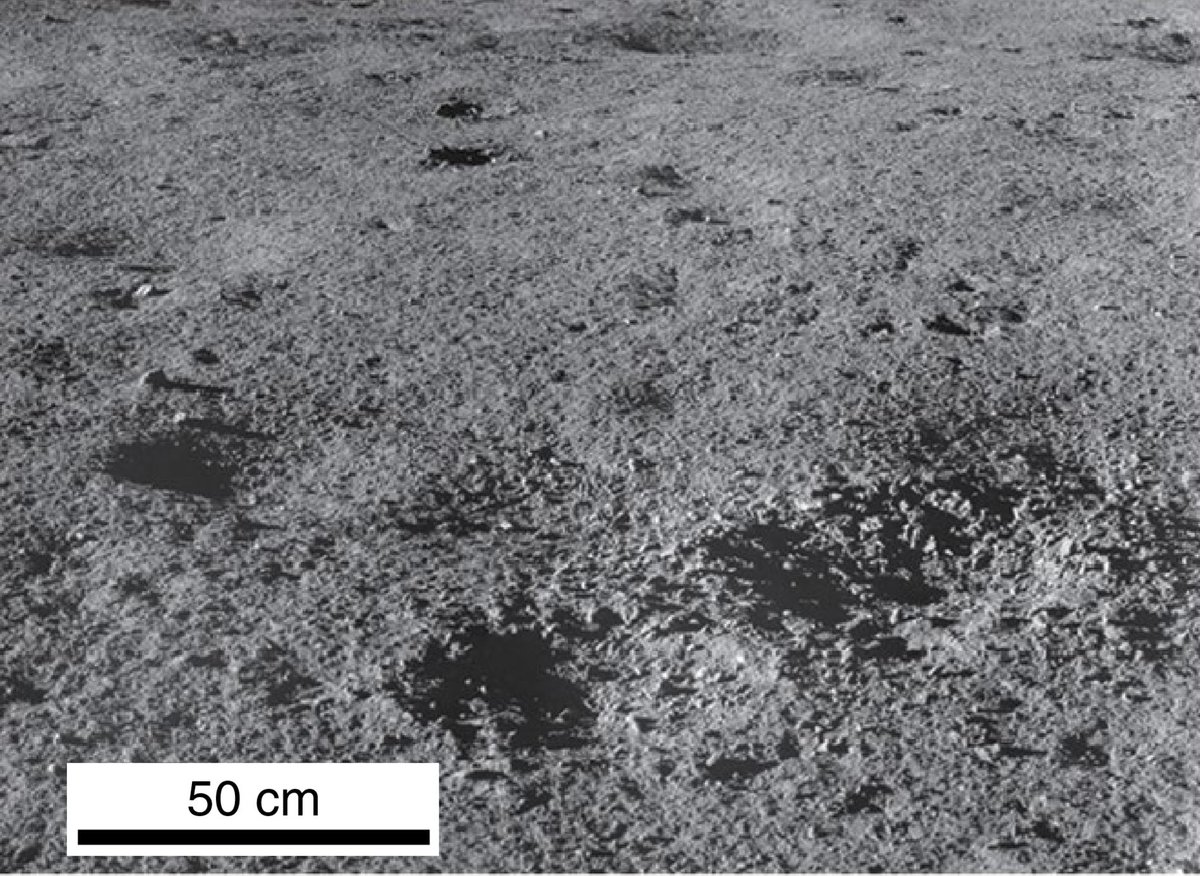
Осколки камней в небольших кратерах (фото с ровера «Юйту-2»):
Небольшие камни по ходу движения ровера «Юйту-2»:

Очень необычные темные камни около места посадки:
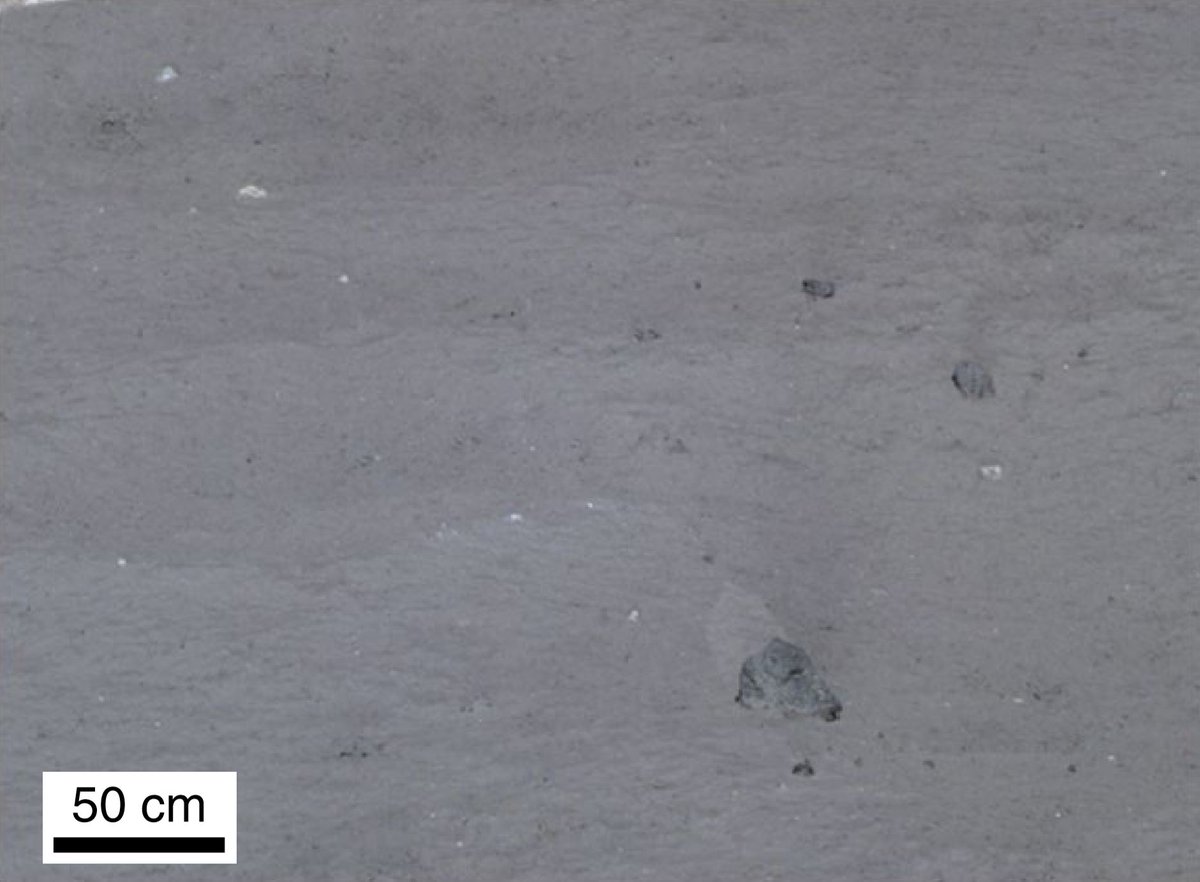

Фотографии с камер аппаратов:
Landing camera LCAM:














Terrain camera TCAM:
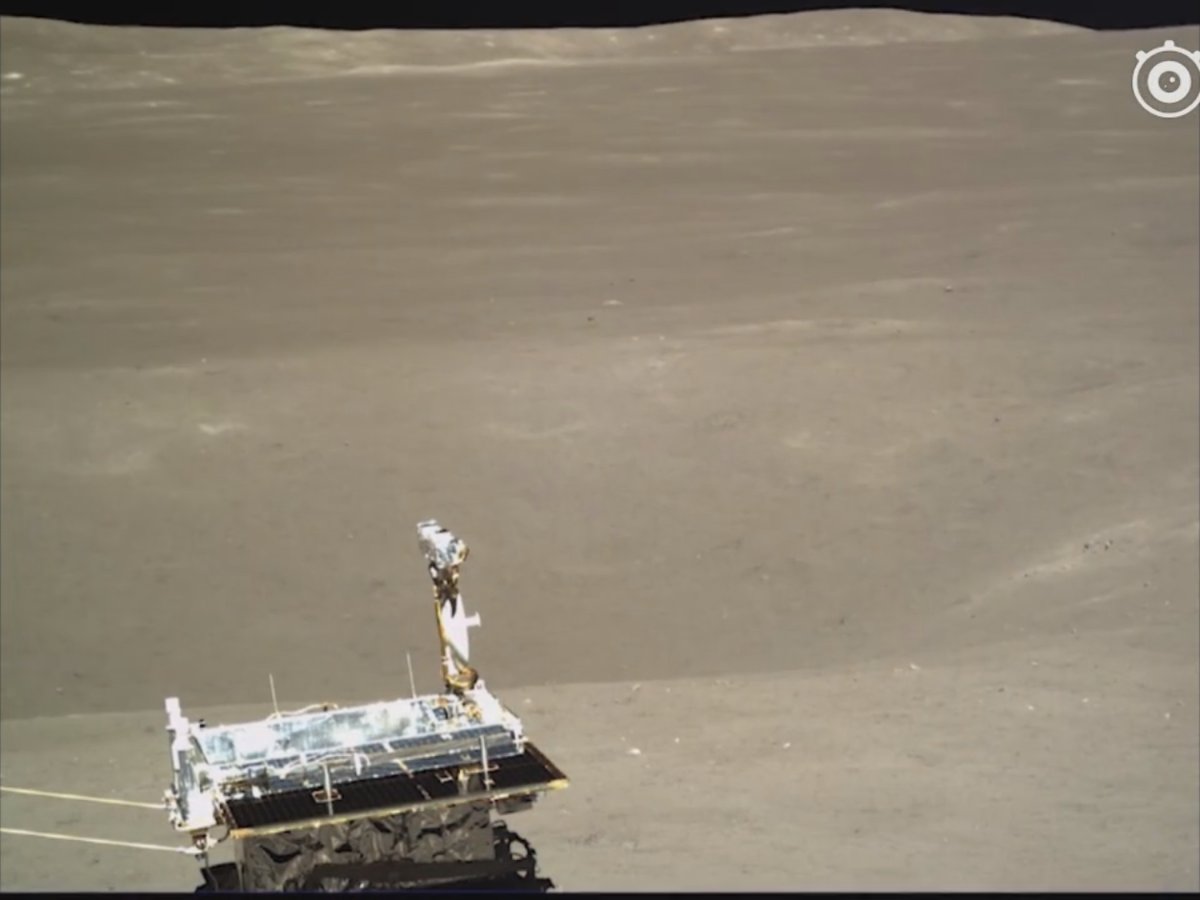

























Panoramic camera PCAM (ровер):








New moments in the history of the implementation of the Chang'e-4 project
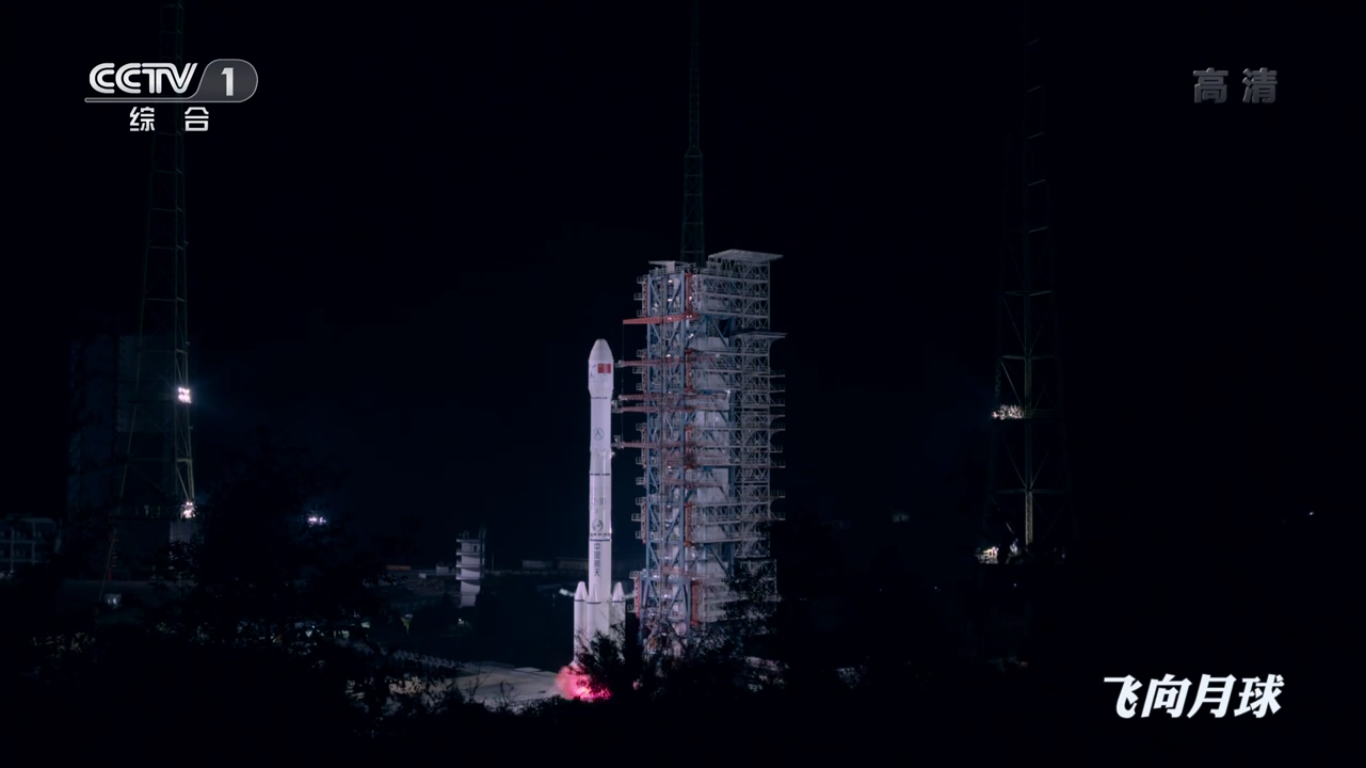
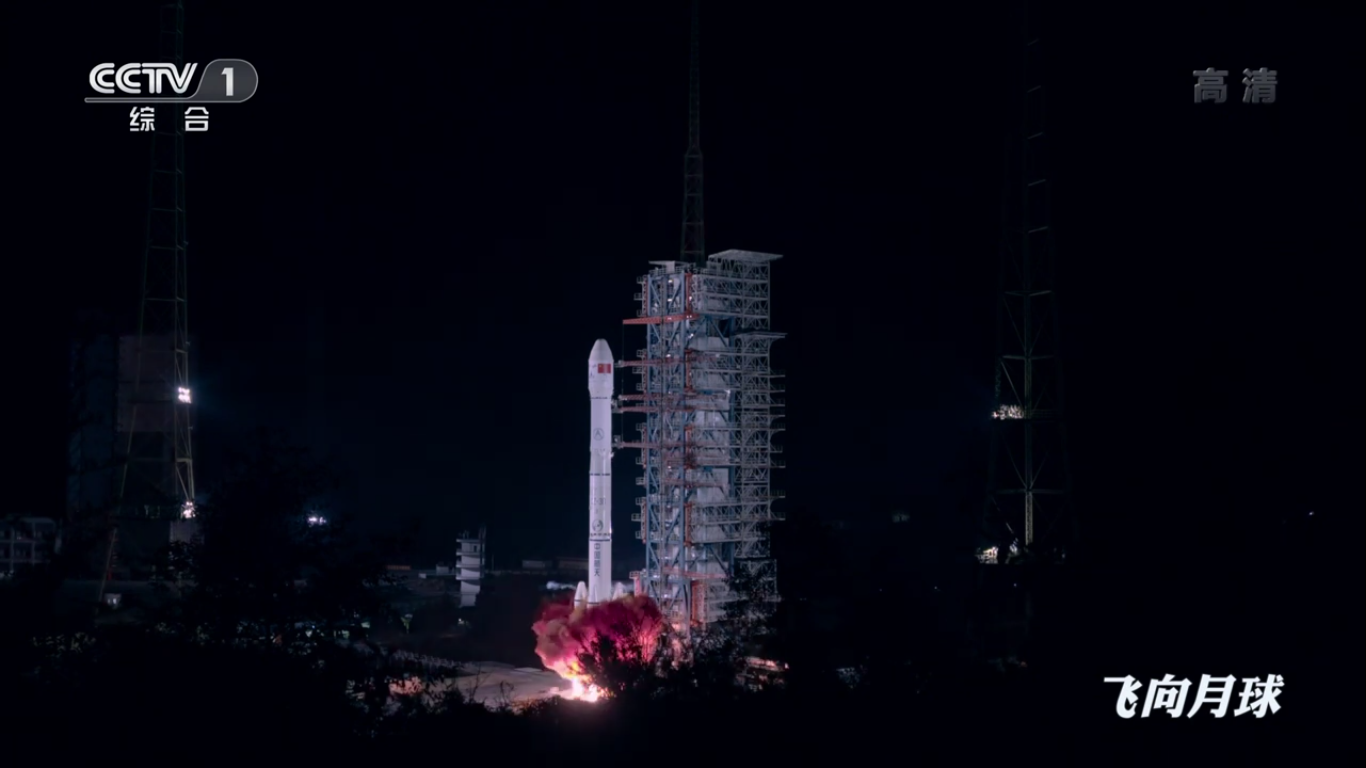
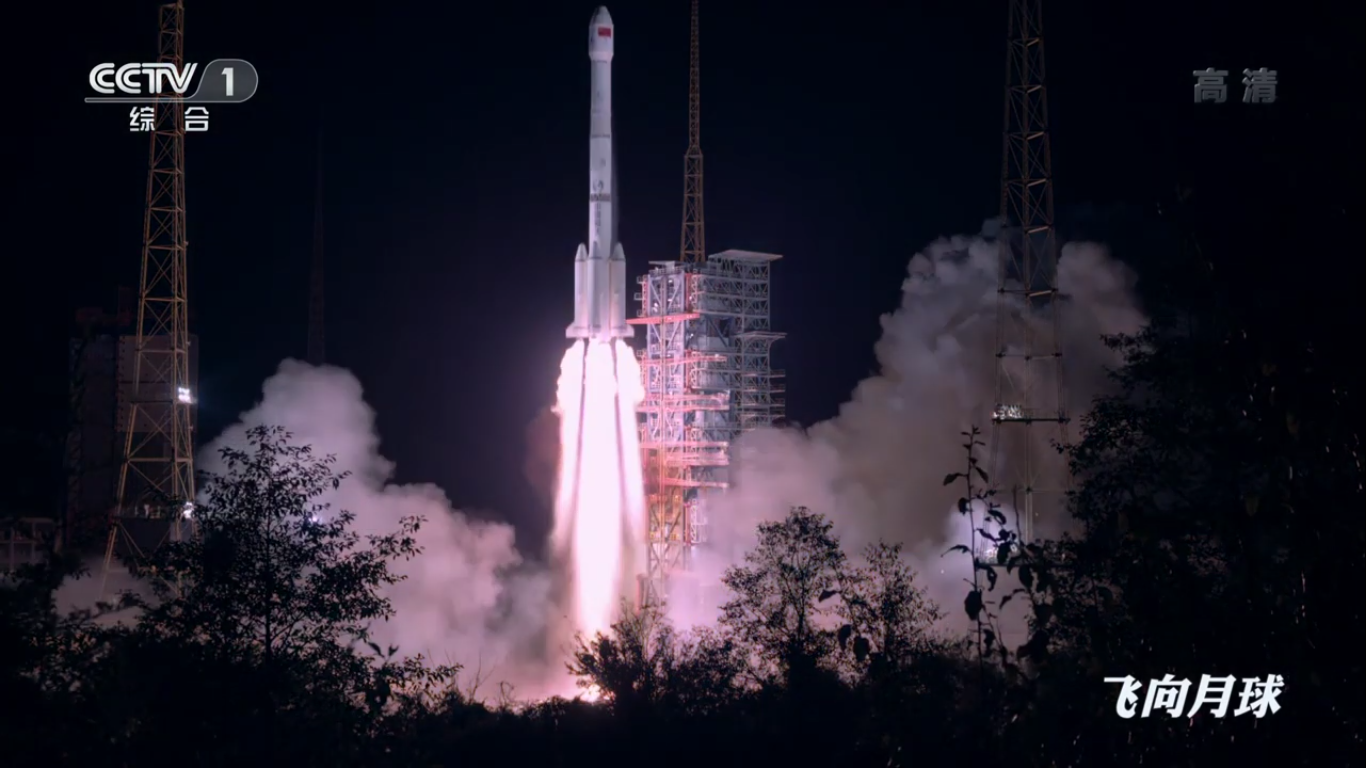
on December 8, 2018: The Changzheng-3B booster rocket with payload (Chang'e-4 station) was successfully launched from the Sichan Chinese spaceport.
Launch of the Changzheng-3B launch vehicle:
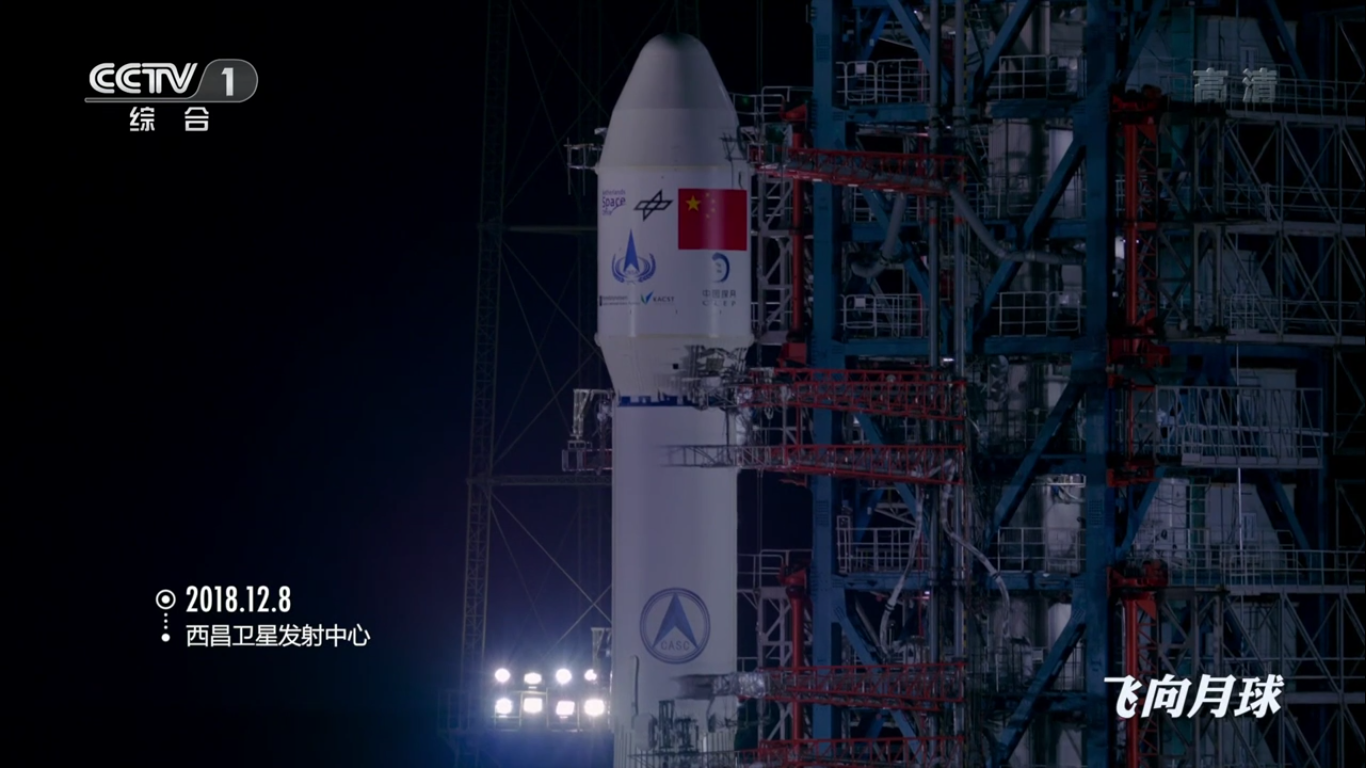



Countdown finish:
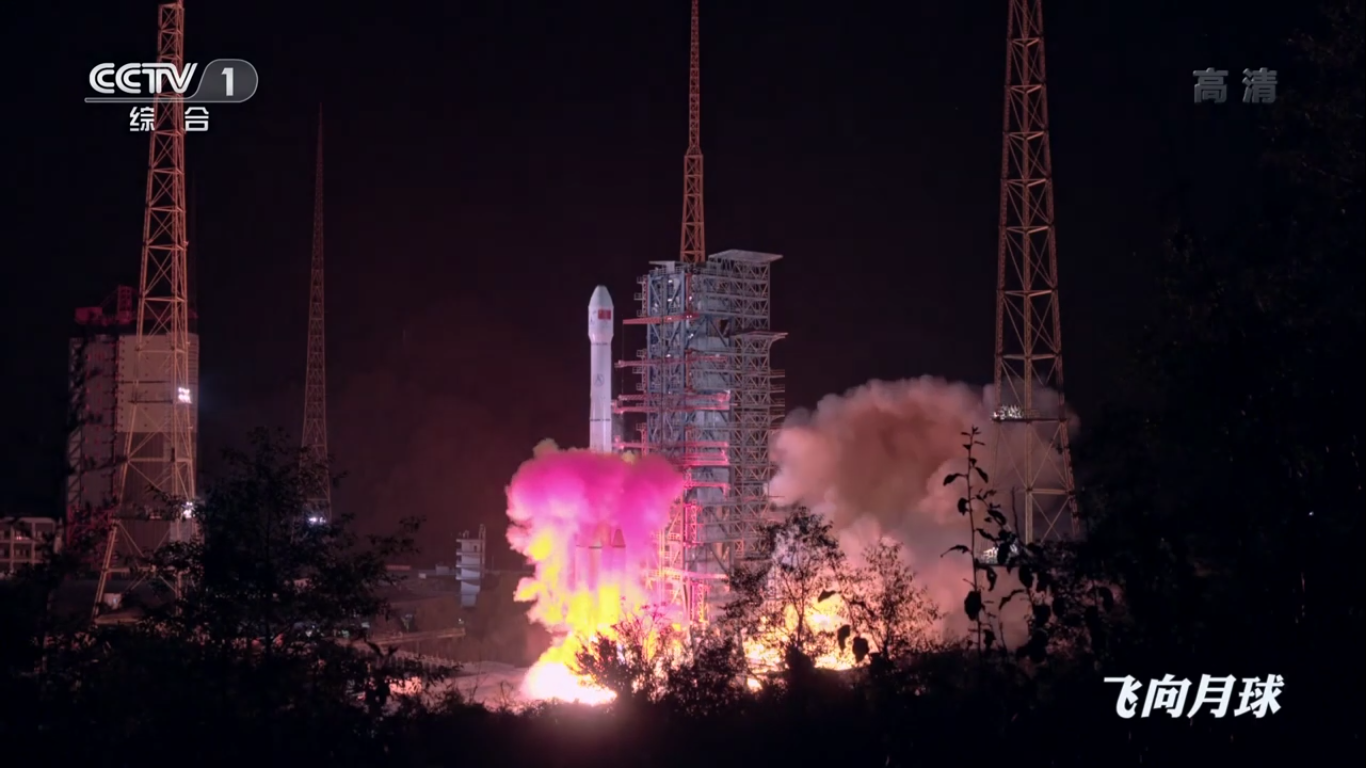
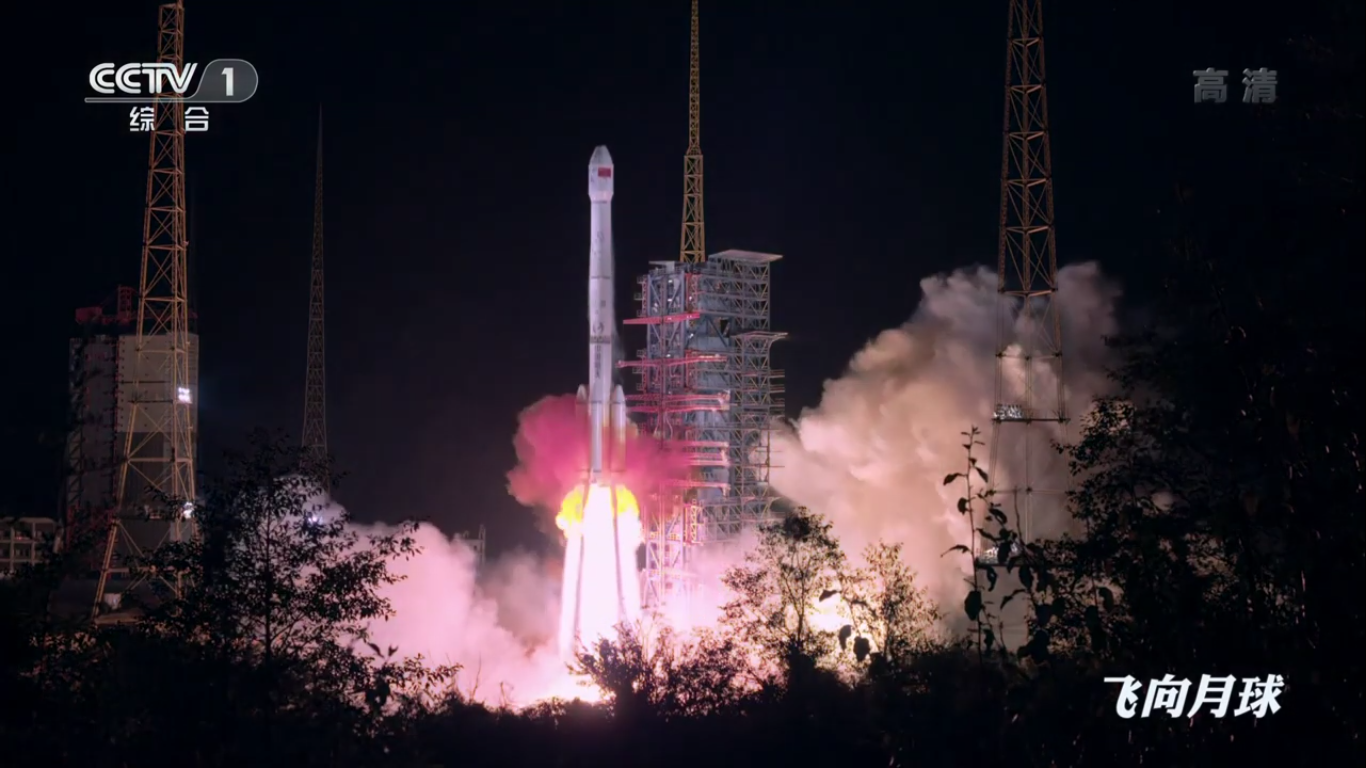






Payload separation:
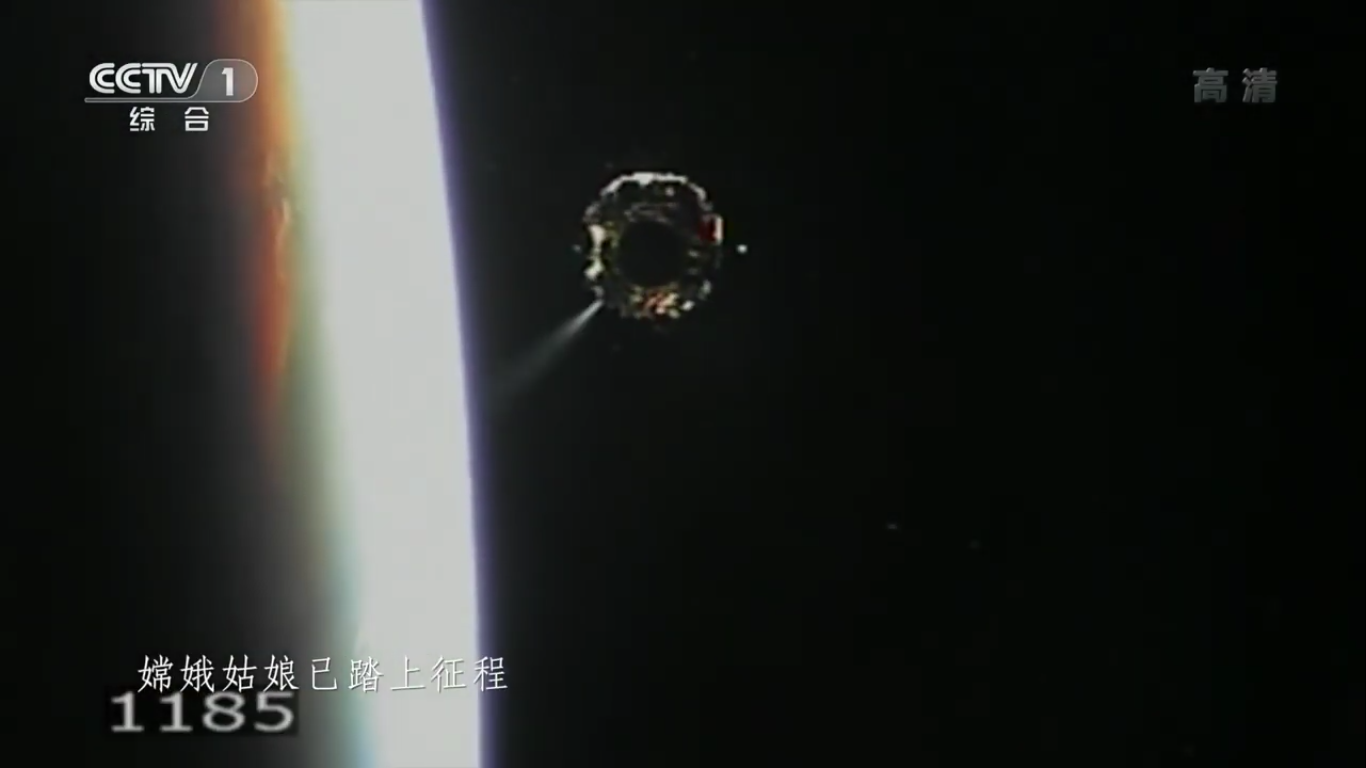


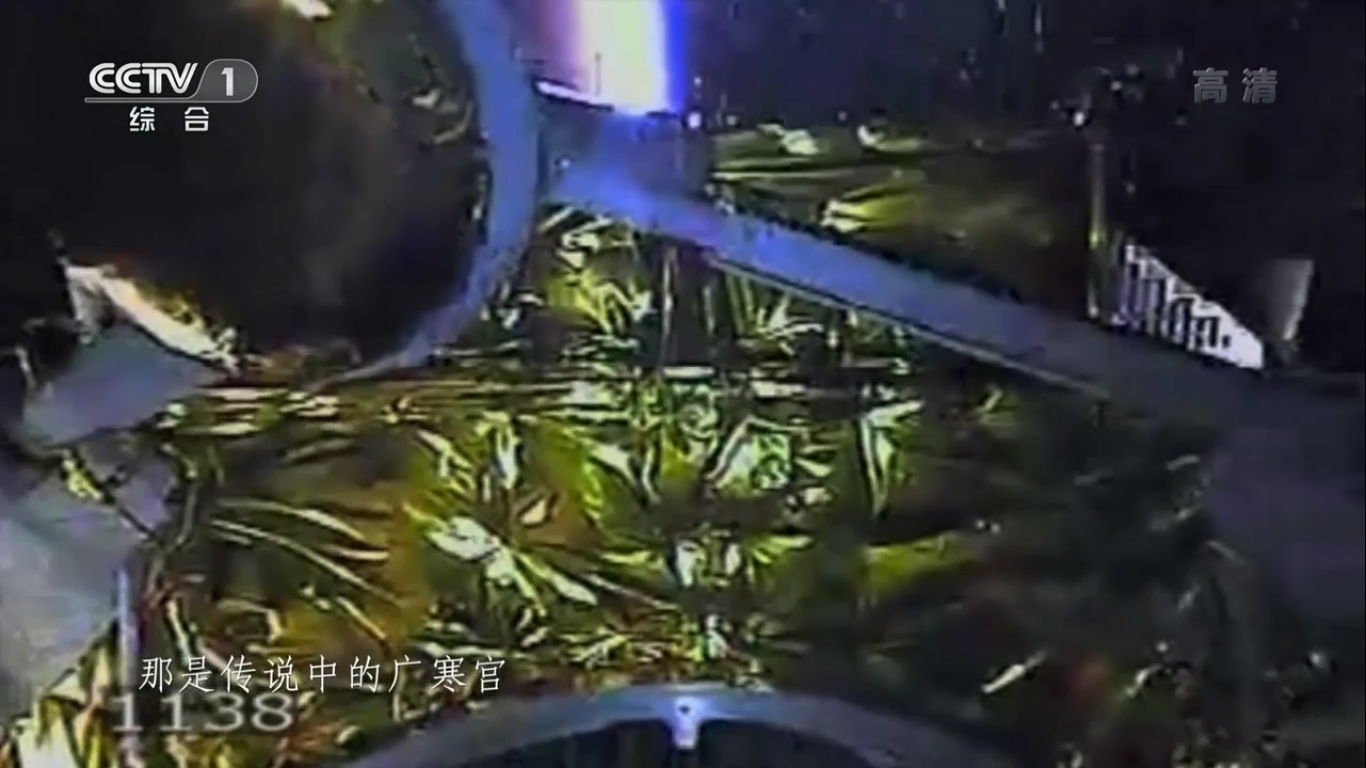
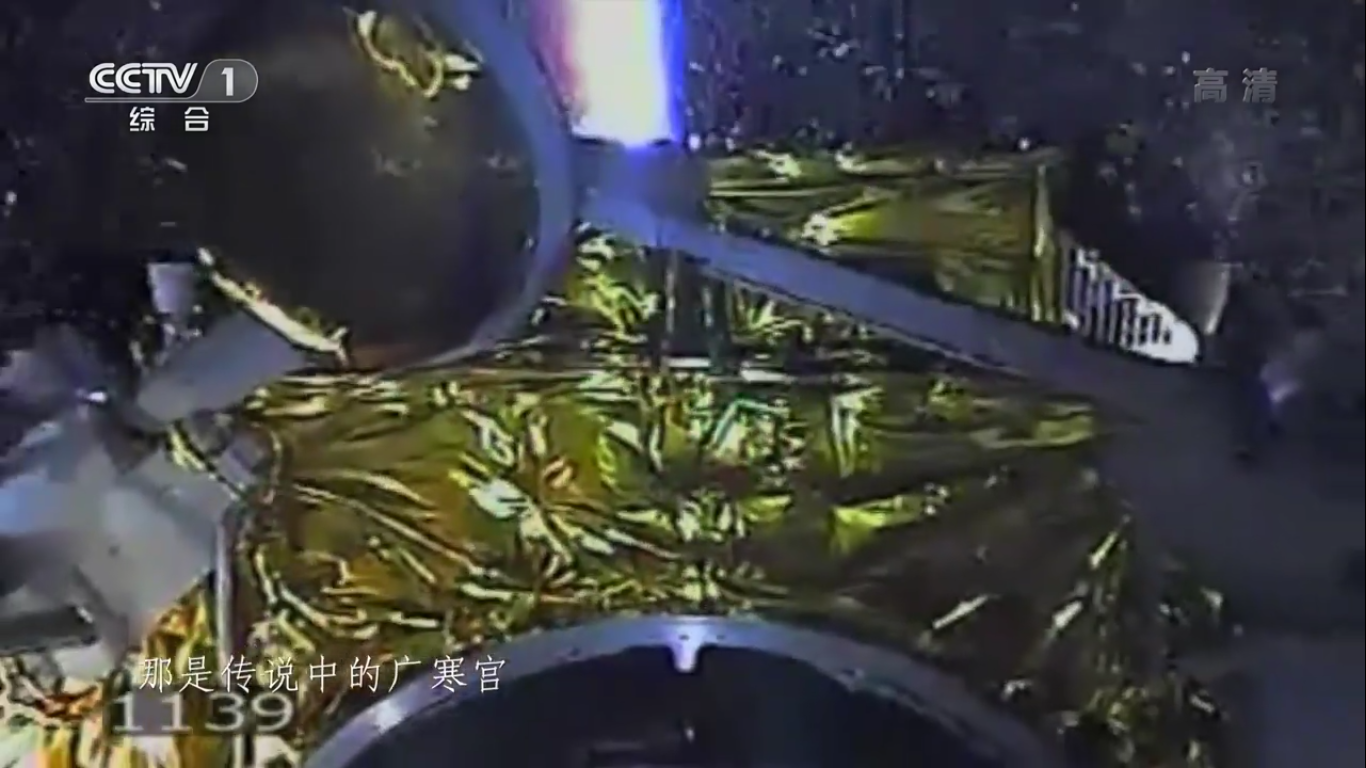


Positioning the payload already in outer space:

January 3, 2019: Chang'e-4 lander makes landing in the Karman crater on the far side of the moon.

At the flight control center of the Chinese Academy of Space Technology:
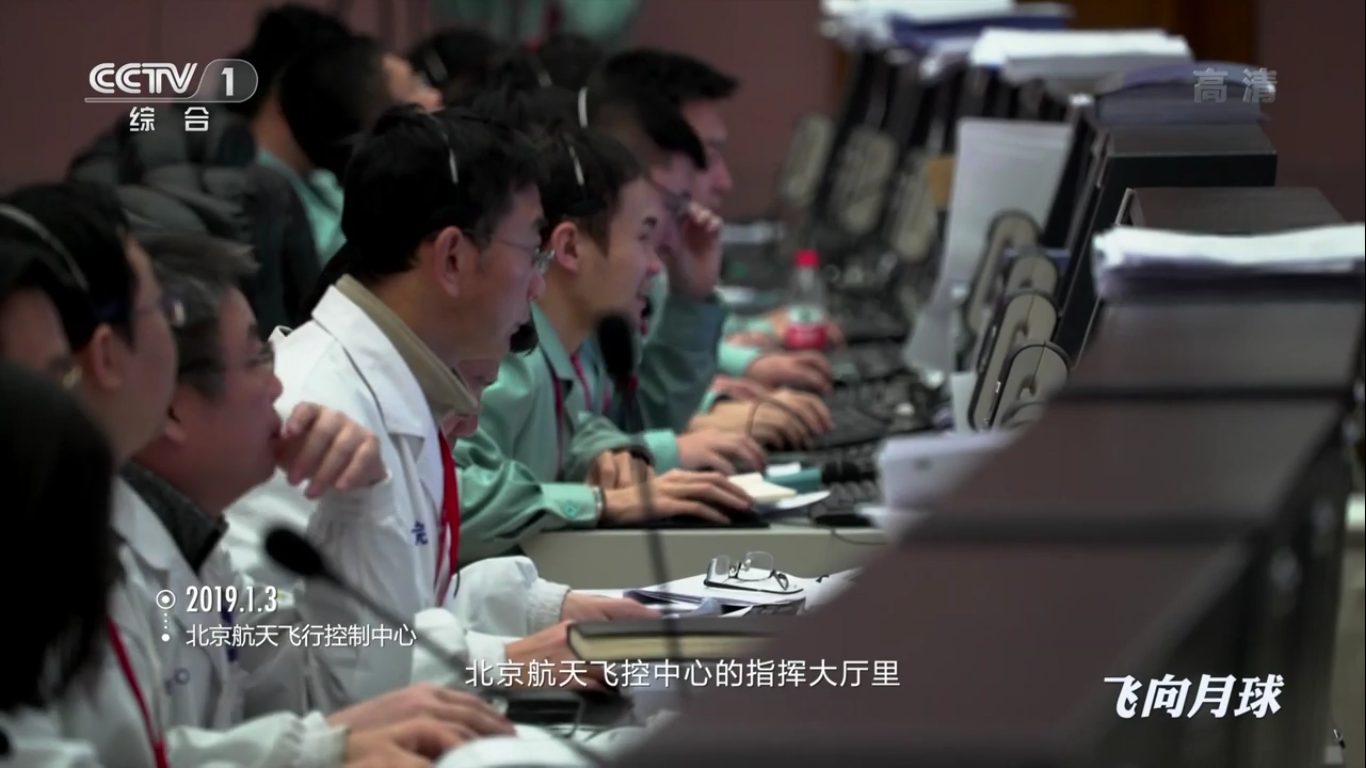
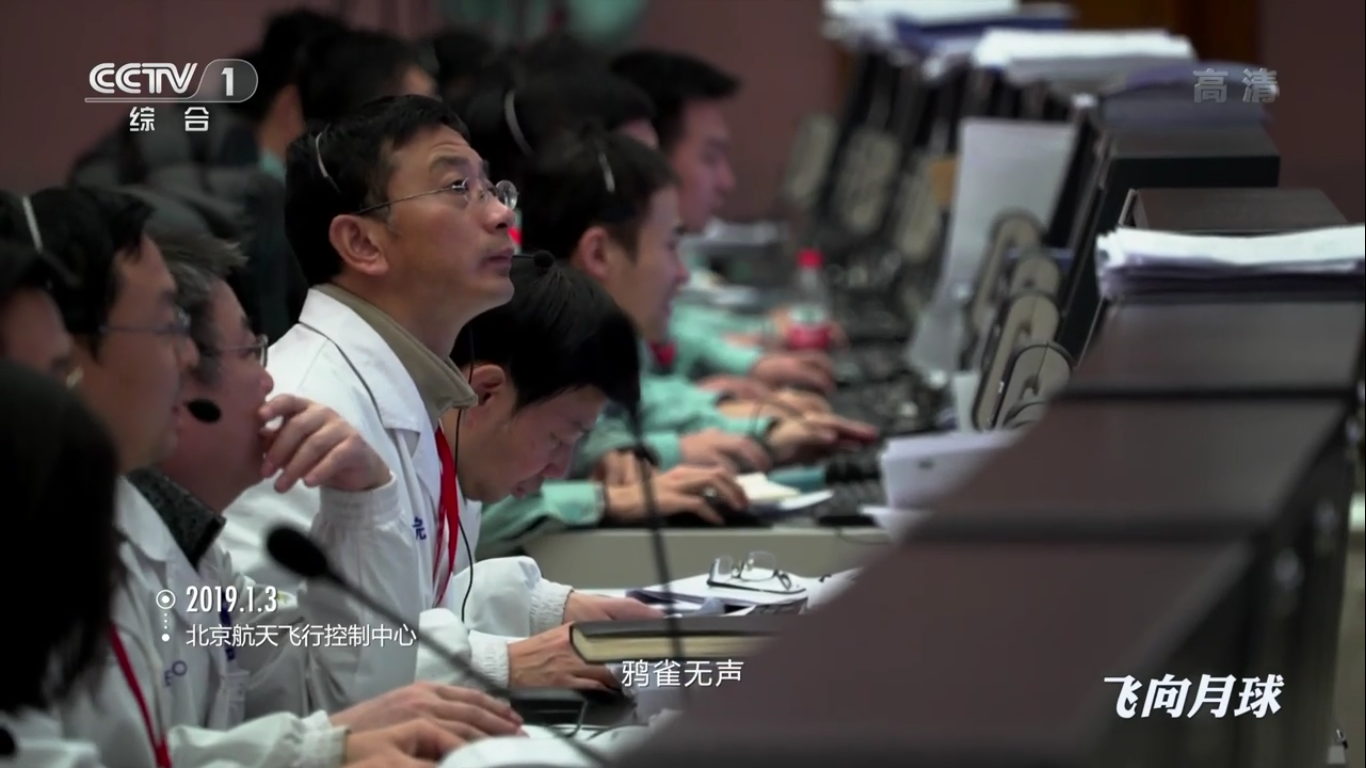



Zhang He - executive director of the Chang'e-4 project at his post:

Interesting icons:
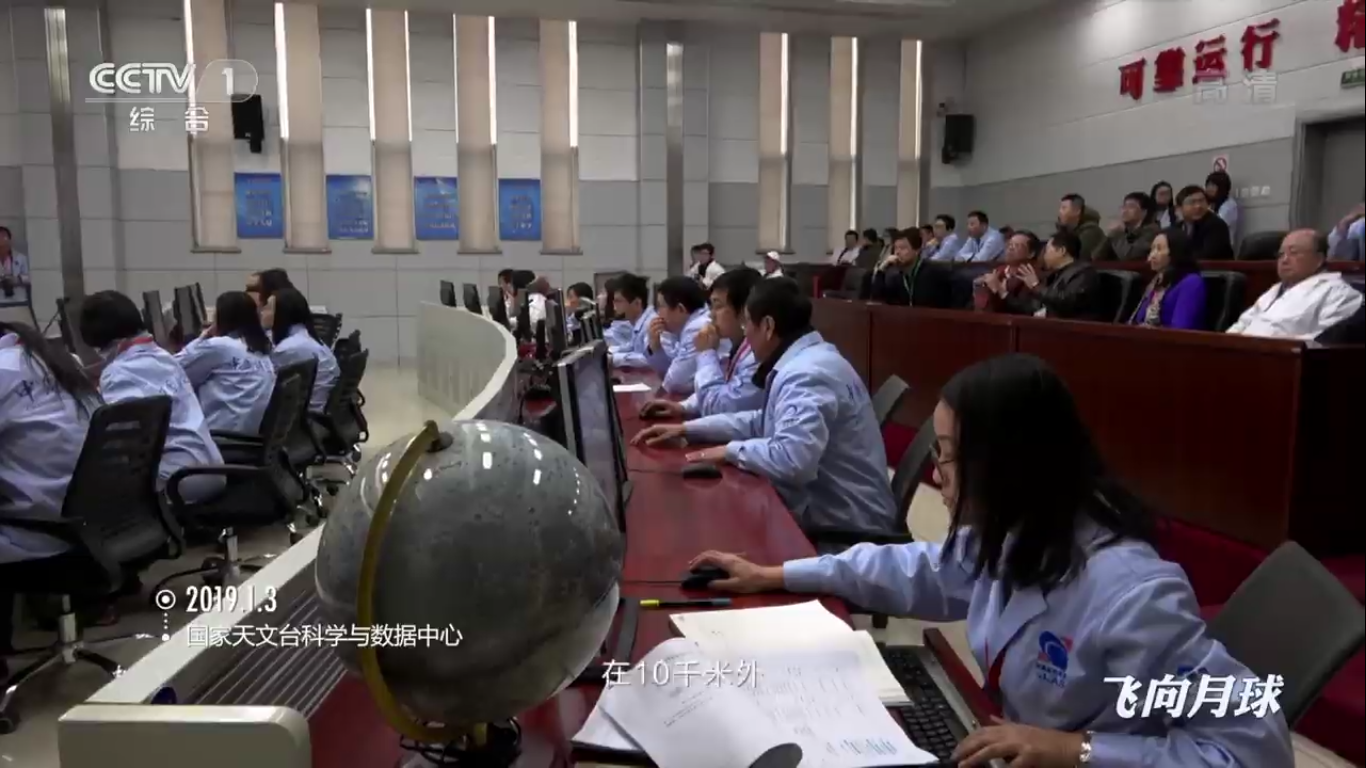
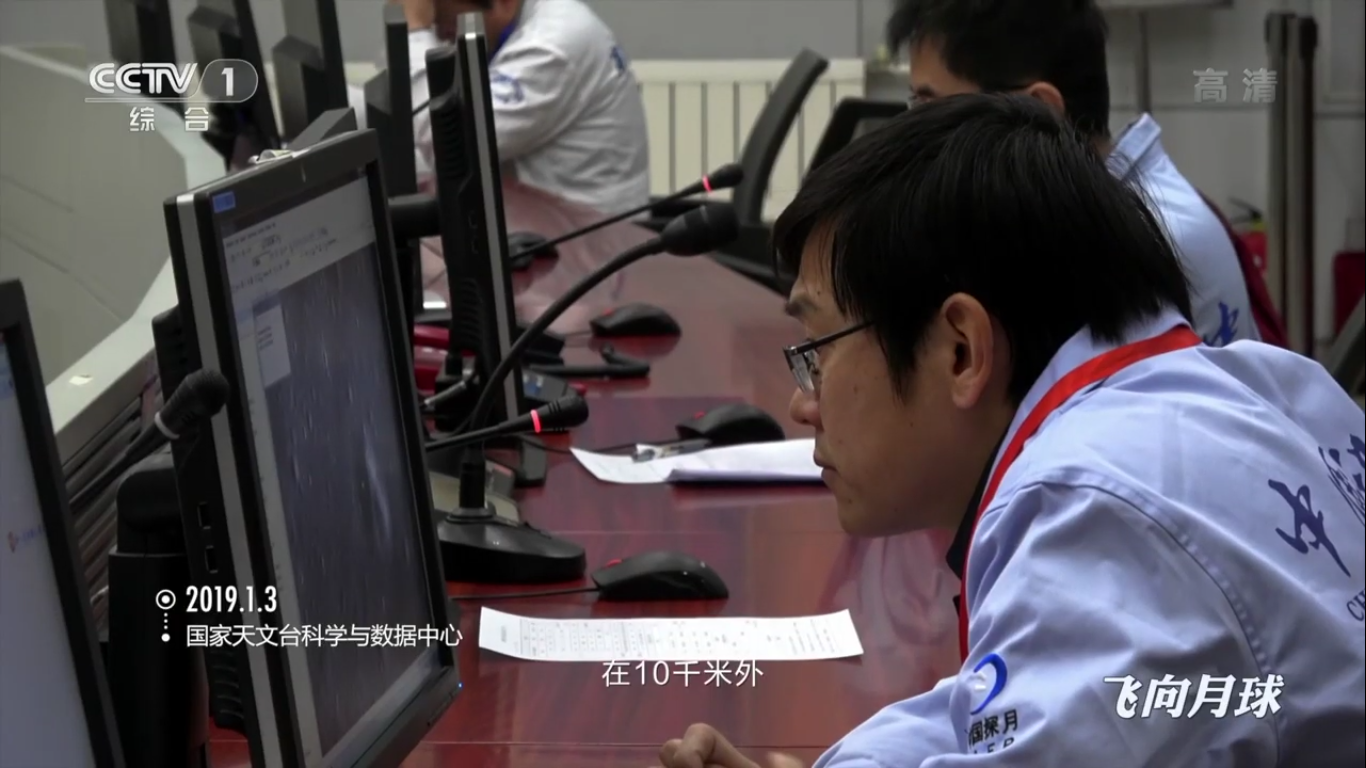
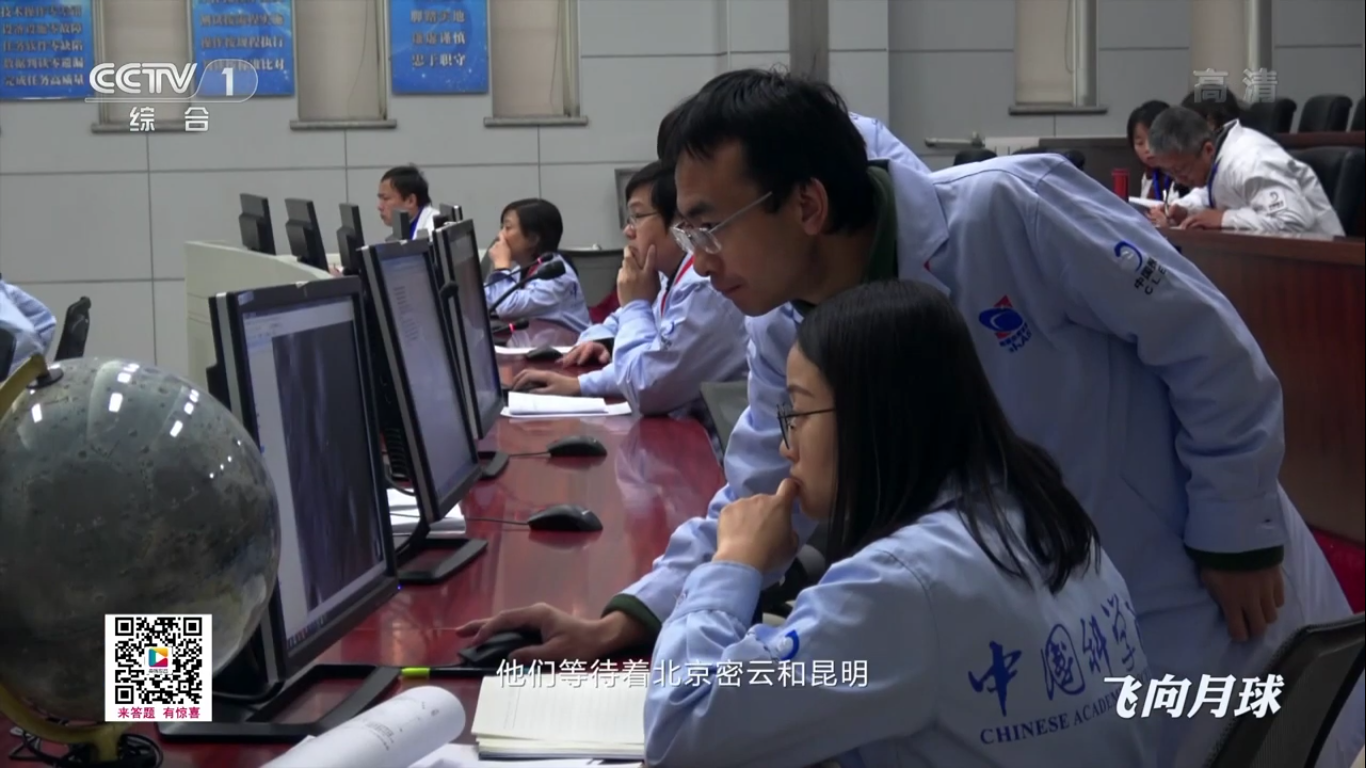


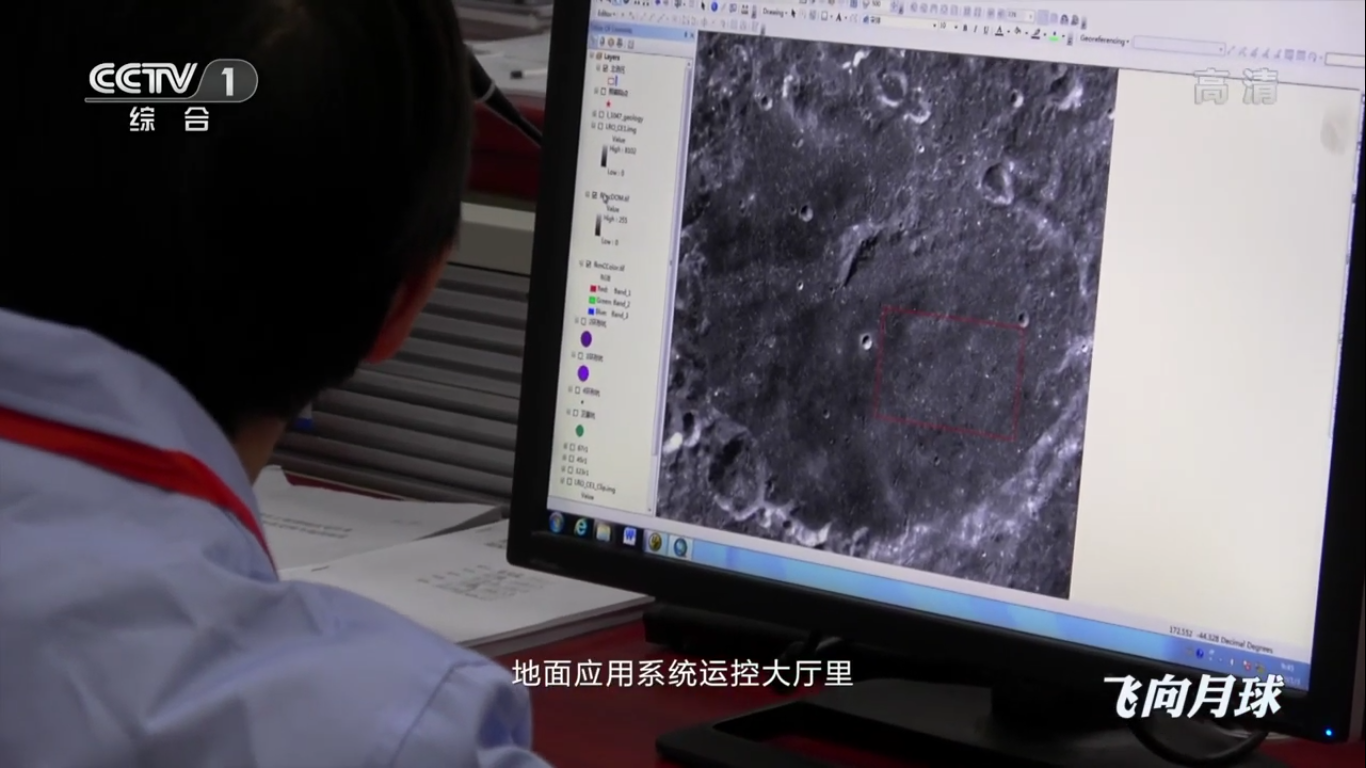


At the space communications center:
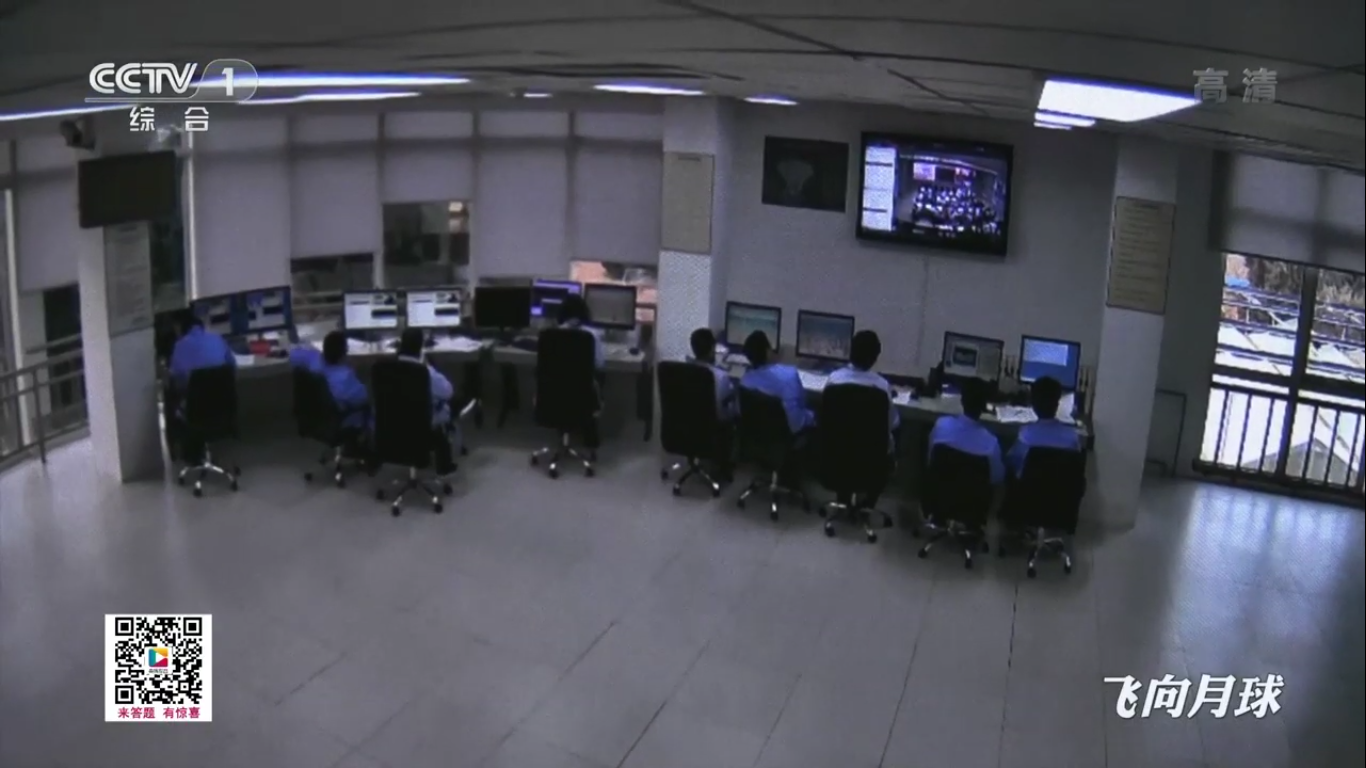

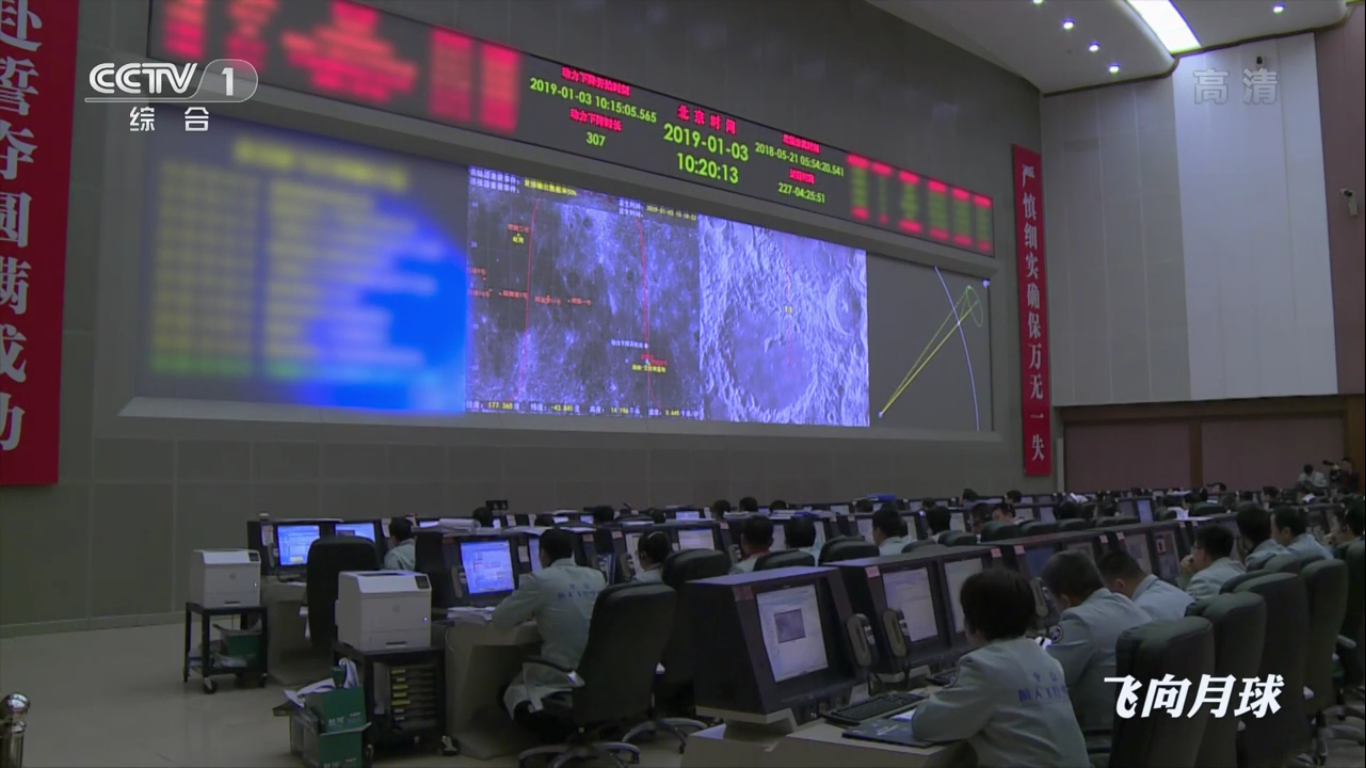
Preparing for landing:

The landing site “needs to be caught” very carefully:




Some operators do not have a keyboard:


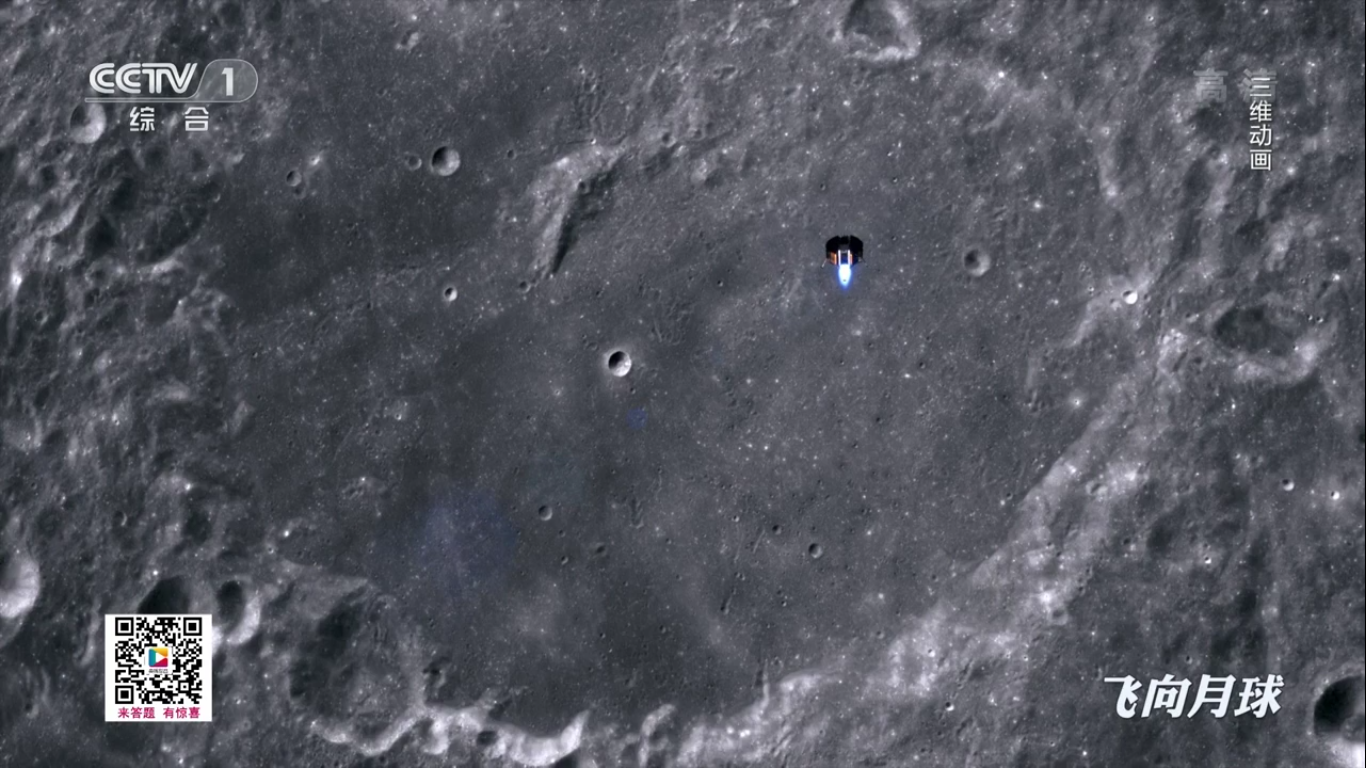
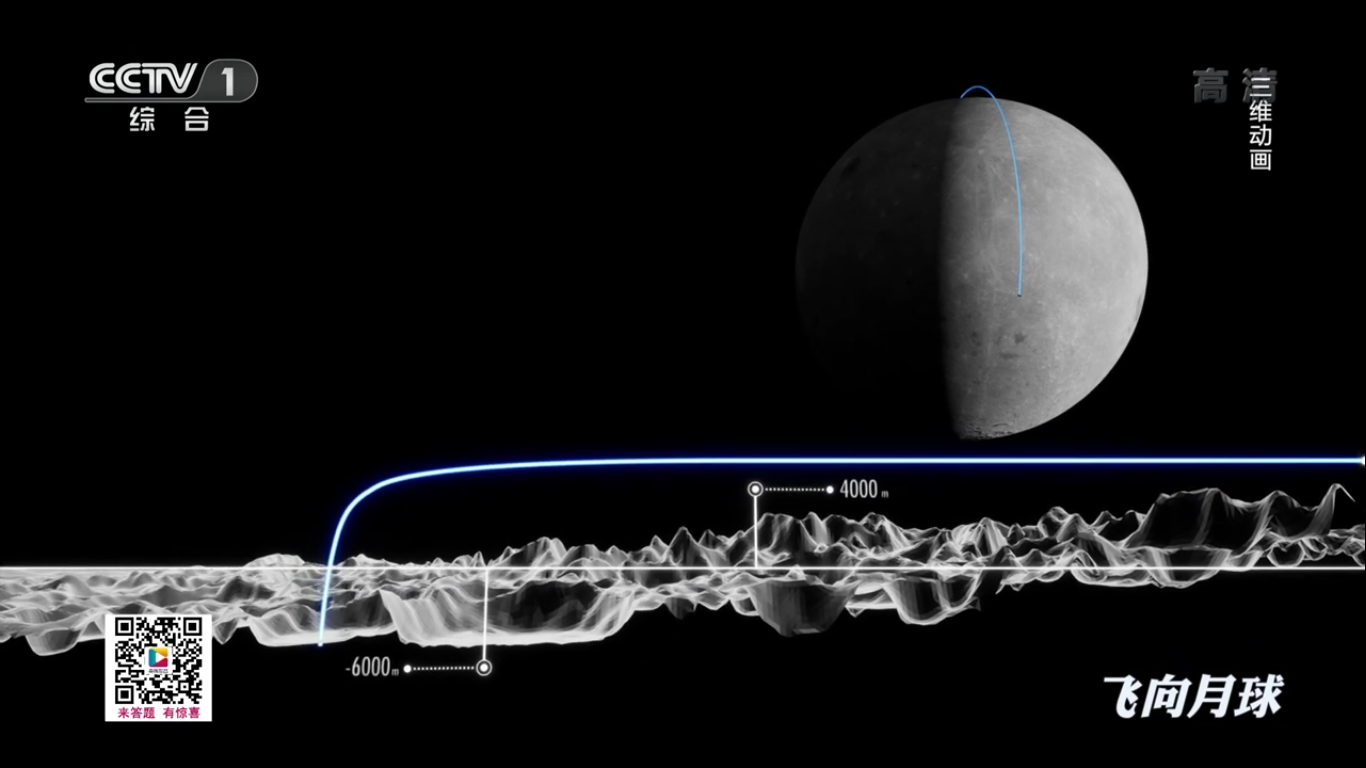
Landing process:

Communication using a satellite-relay:
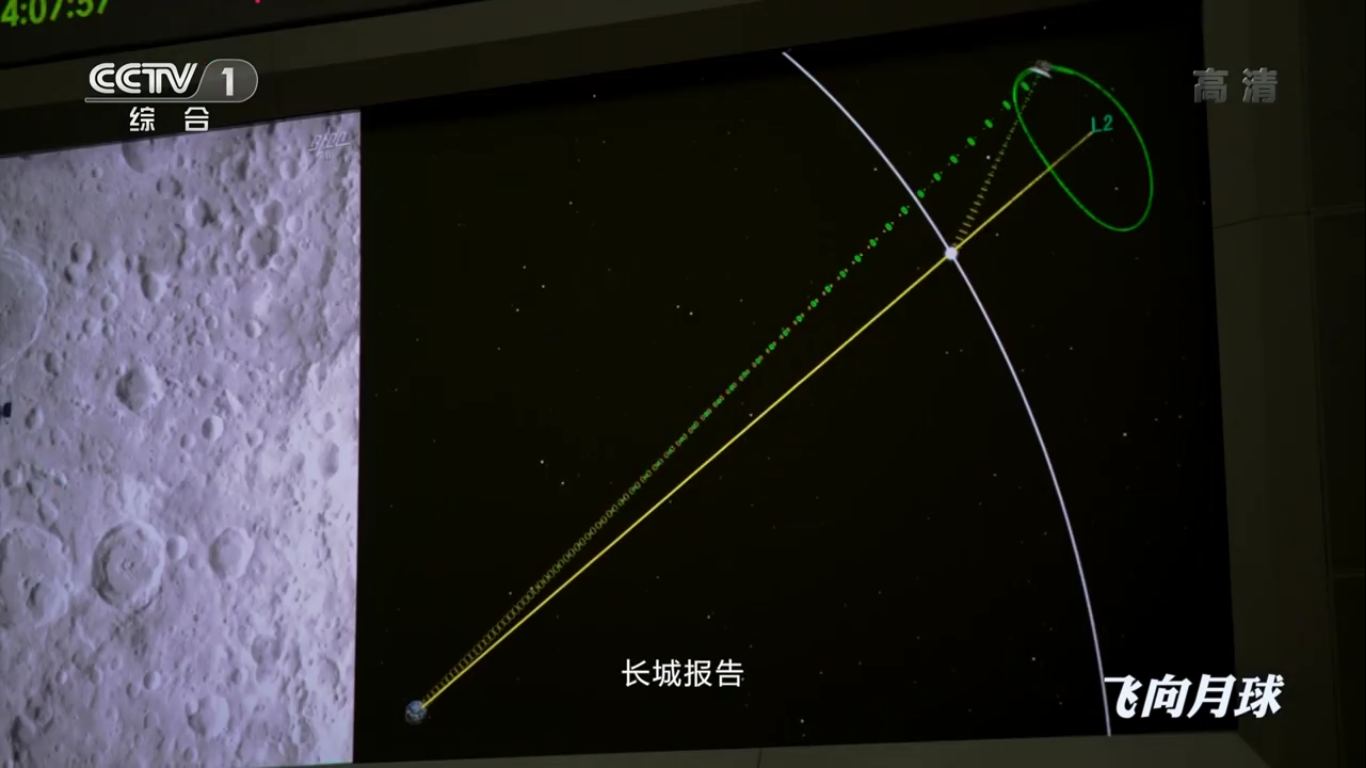



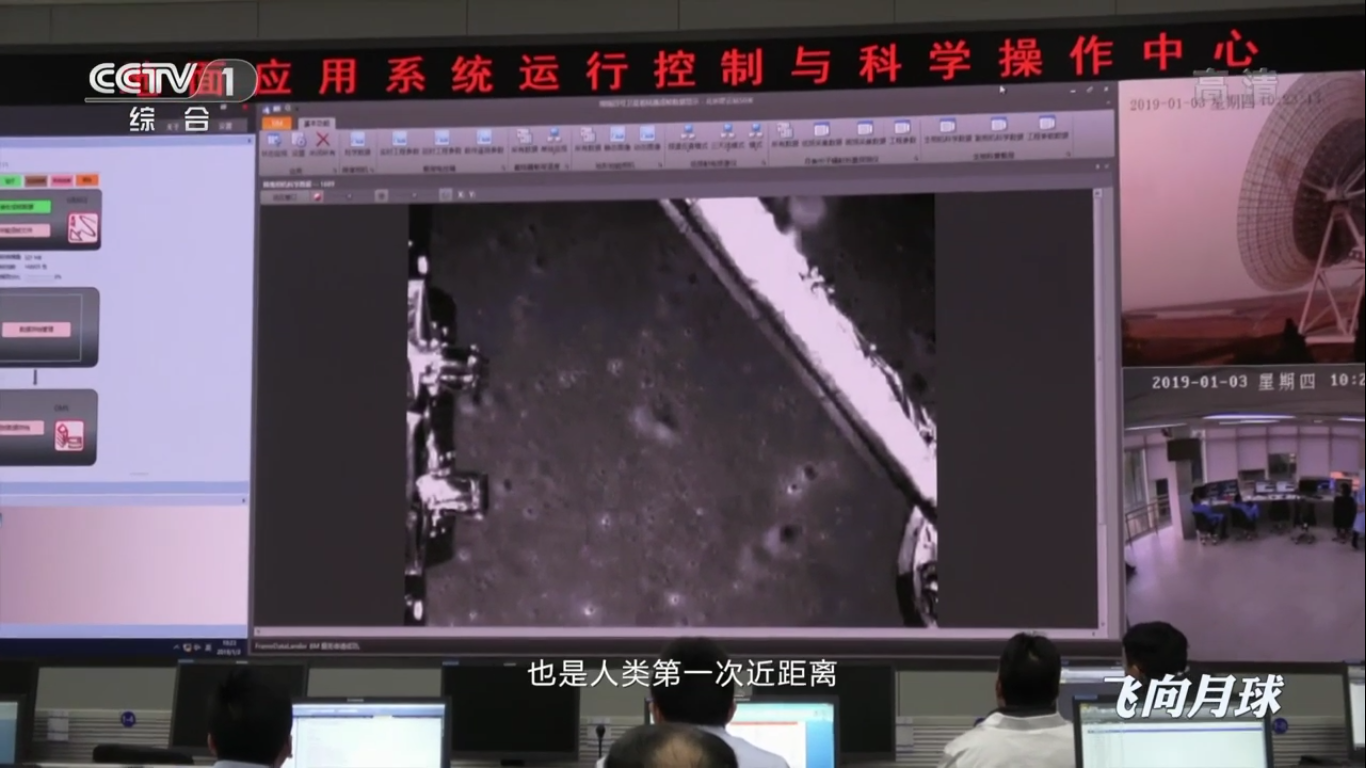
There is a landing:



Preparing to launch the rover:
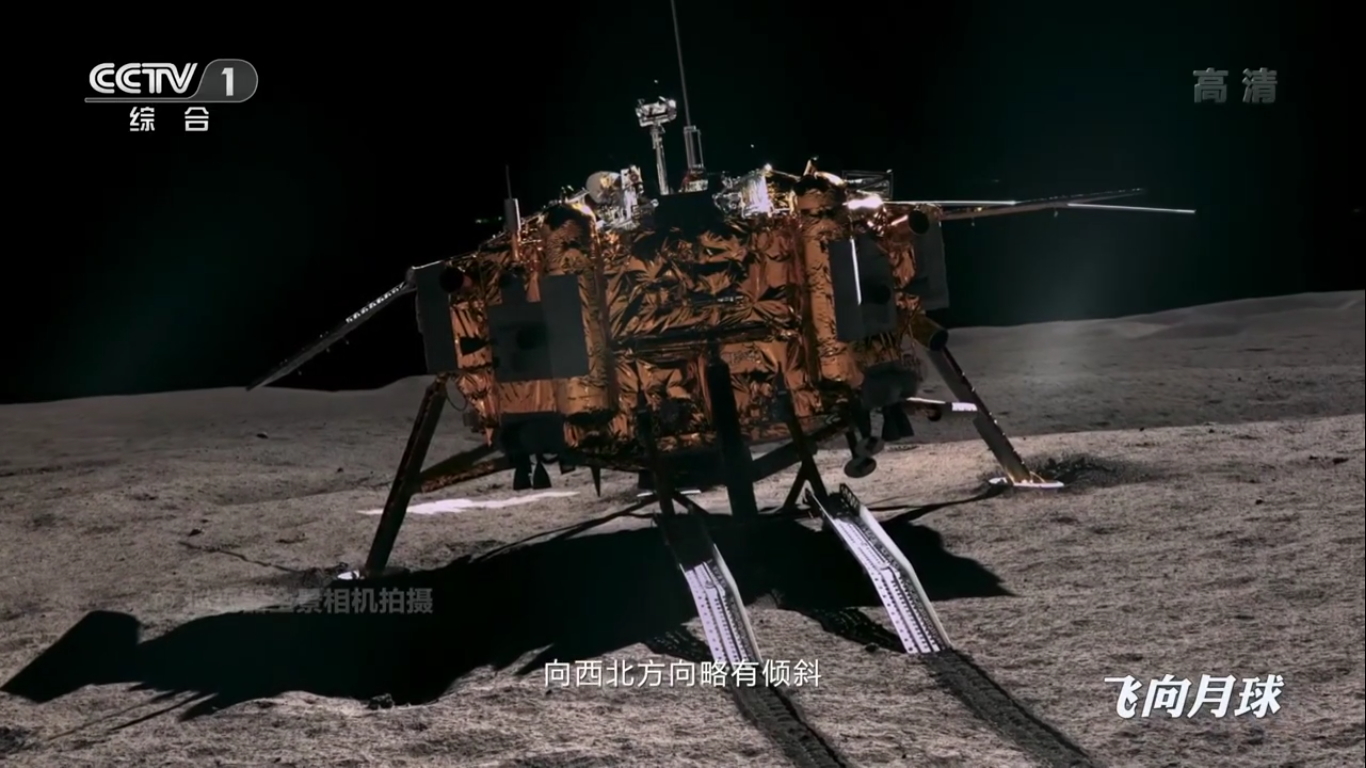


Each landing support of the Chang'e-4 launching module has a surface touch sensor, and temperature sensors that worked on a moonlit night, recording data on the surface temperature of the moon, are built into the supports and the launching ramp for the rover.
According to the sensors of the Chang'e-4 modules, the temperature on the lunar surface at night dropped (minimum) to minus 190 degrees Celsius.









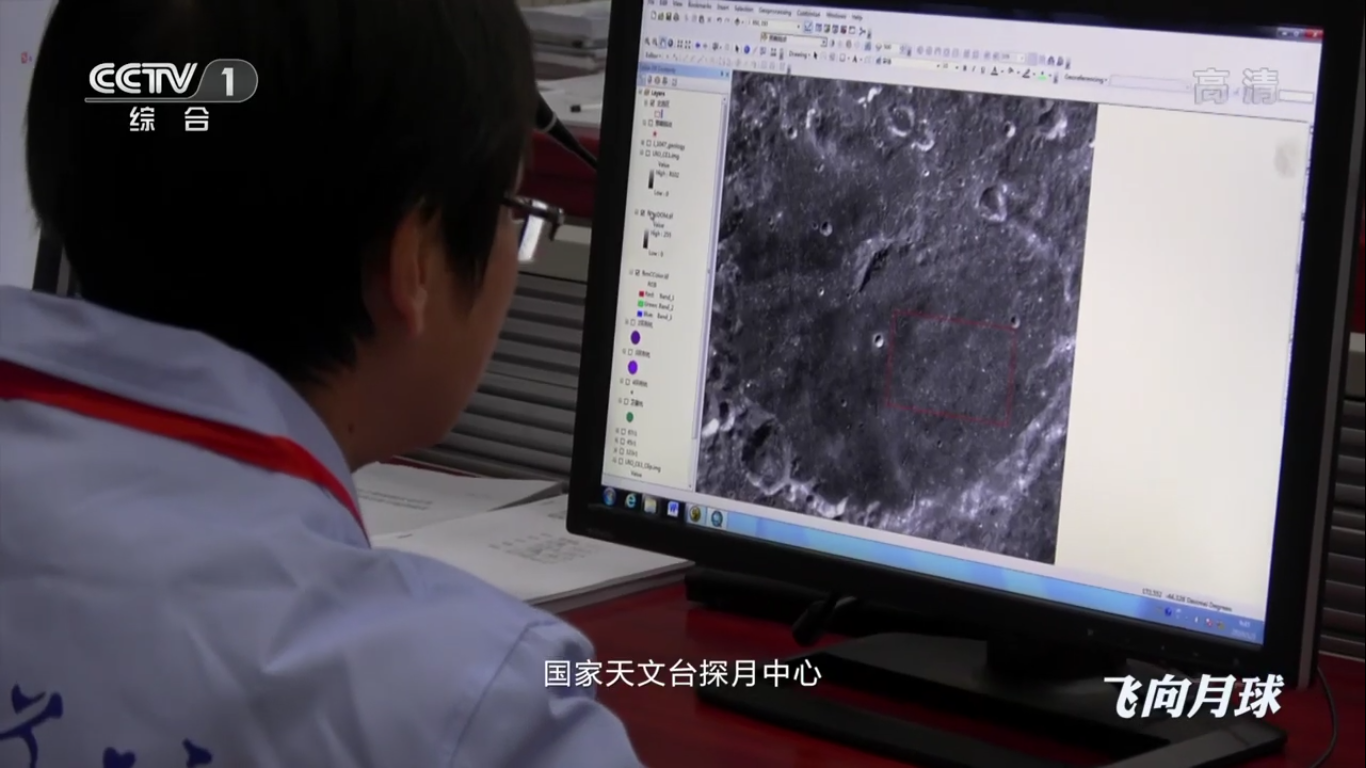
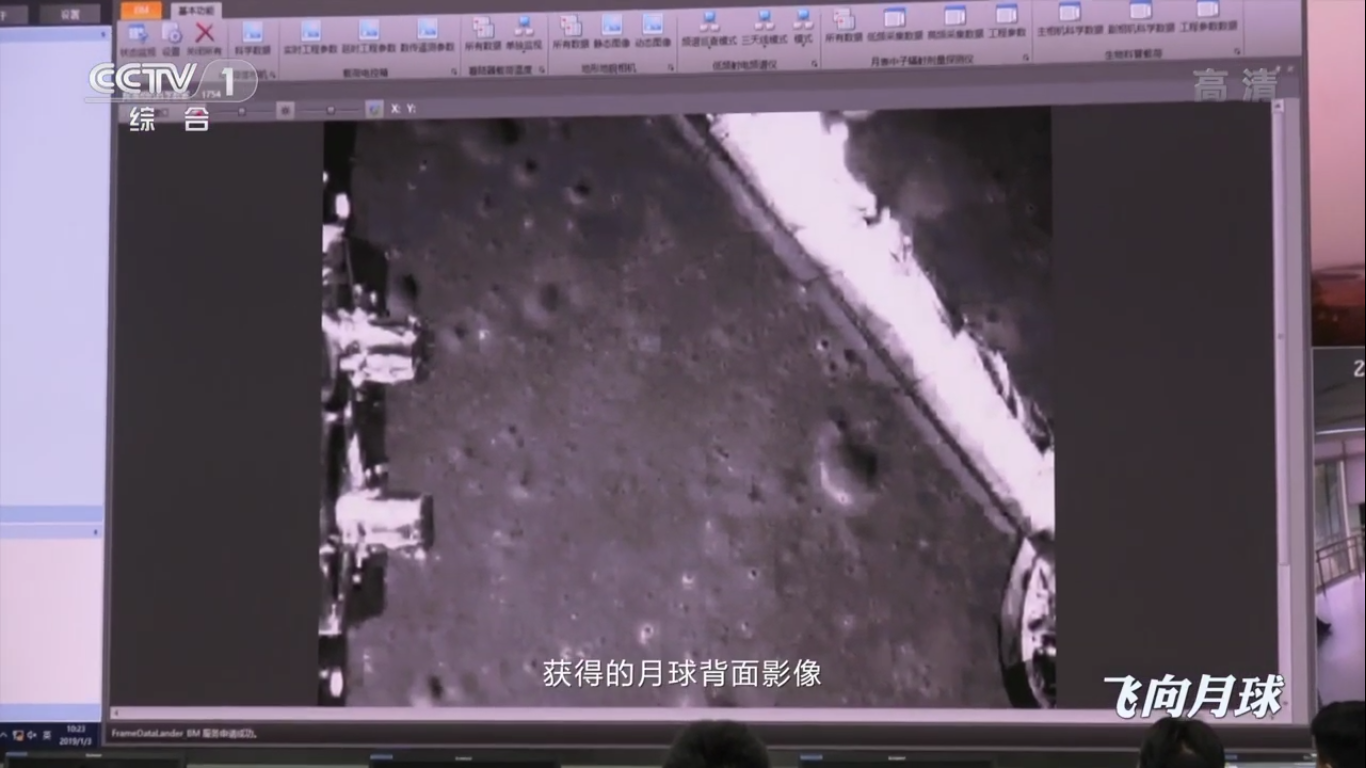
Receiving and processing data in the space communications center:

Operators of the Yutu-2 rover rely on their virtual surface maps:

Photos of the landing site of the Chang'e-4 modules made by the LRO lunar orbiting probe (NASA) :


Using a special radar (the outer part of which is two antennae antennae and a flat antenna under the bottom), whose rays penetrate the surface of the moon (LPR - Lunar Penetrating Radar) Yutu-2 rover creates a three-dimensional map of the underground part of the lunar surface:
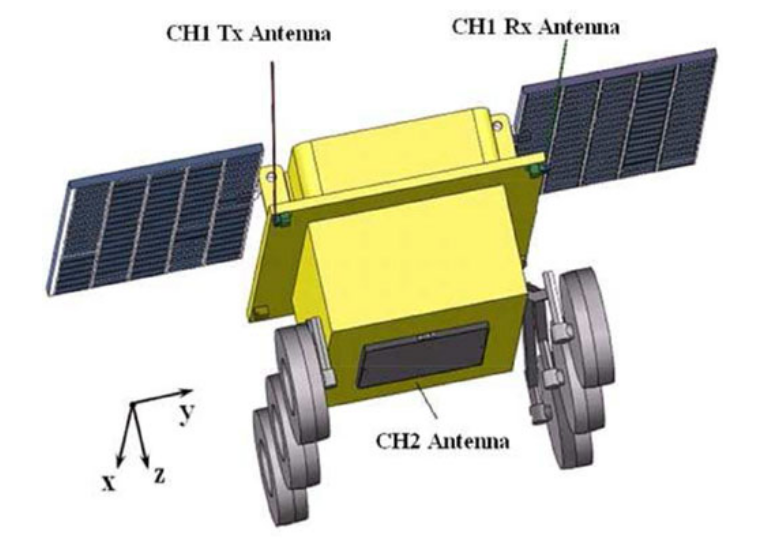
Lunar Penetrating Radar (LPR) characteristics:
Channel 1:
- Transmitter Voltage - 1000 V (error <5%)
- Transmitter Pulse frequency - 0.5, 1, 2 kHz
- Transmitter Pulse time of arrival - <= 5 ns
- Receiver frequency - 10-175 MHz
- Receiver input dynamic range -> 90 dB
- Antenna central frequency - 60 MHz
- Antenna bandwidth -> = 40 MHz
- Standing wave function - <= 3
- Maximum detection depth -> = 100 m
- Depth resolution - 1 m
Channel 2:
- Transmitter Voltage -> = 400 V (error <5%)
- Transmitter Pulse frequency - 5, 10, 20 kHz
- Transmitter Pulse time of arrival - <= 1 ns
- Receiver frequency - 10-1000 MHz
- Receiver input dynamic range -> 90 dB
- Antenna central frequency - 500 MHz
- Antenna bandwidth -> = 450 MHz
- Standing wave function - <= 2.5
- Maximum detection depth -> = 30 m
- Depth resolution - <= 30 cm
The Lunar Penetrating Radar (LPR) installed on the Yutu-2 rover is similar in its device to the radar installed on the first Yutu rover of the Chang'e-3 mission.
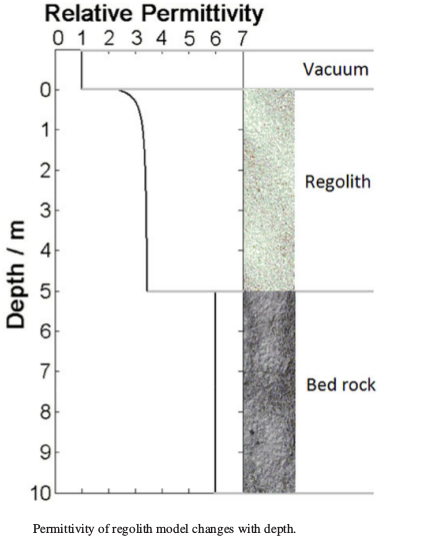
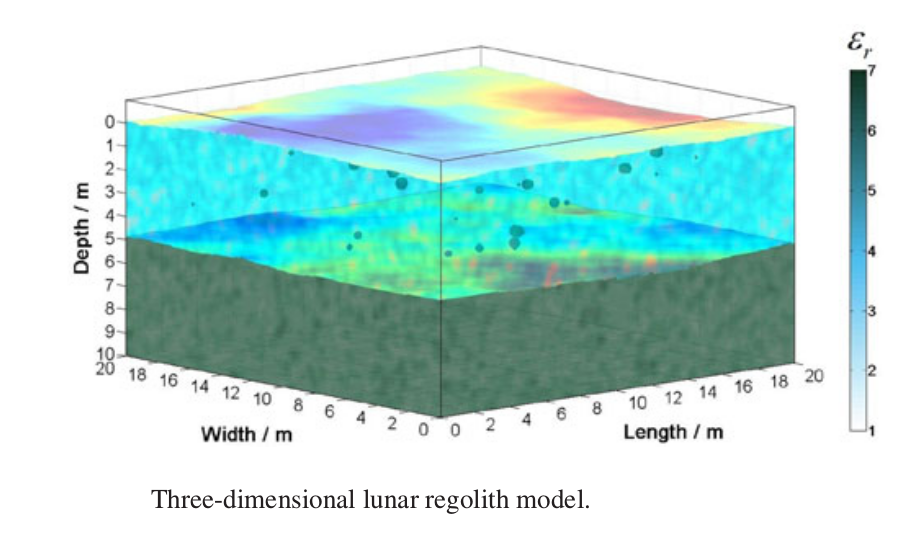
The data received from the LPR radar is analyzed and reduced to graphs on which you can track the geological composition and characteristics of the lunar surface in the landing area:
Scientists and engineers at the flight control center of the Chinese Academy of Space Technologies try to make the most of the time of the fifth lunar day (two Earth weeks) for conducting research and obtaining data from the devices of the Chang'e-4 landing module and the Yutu-2 rover.
You can read more about the scientific equipment of the Chang'e-4 landing module and the Yutu-2 rover here:
The Chang'e-4 mission is the third lunar day. Rover "Yutu-2" in search of ... stones
The Chang'e-4 mission is scientific equipment on the landing module and relay satellite.
By the way, on April 24, 2019 (the day of Chinese cosmonautics), a children's art contest organized by the Chinese Aerospace Society dedicated to the conquest of space and the Moon was held.
The children's work is great.
Guo Zhichen - Exploring the Universe in the Future
Han Jiaxin - We went into space

Deng Xianue - Garden outside the Universe

Tian Xian - Space Station of the Future

Zheng Yufeng - Coloring Space Together

Fang Yongxin -

Li Mengying Energy Transformation Station -

Xu Zhiyun Global Solar System - Explorers

Yang Haovan - Space base

Yang Tszinru - Vacuum City
Zhuo Siyuan - Floating spaceship

Zhou Yin-Mora No.1451

I like these works especially:
Wei Wei - My heart is full of stars

Dai Jiai - Dreaming of space

Liu Ruiyang - My music in space

