How technology creates new realities
The film "The Matrix" graphically and spectacularly depicted the concept of a virtual world. Perhaps in the future, humanity will encounter such a problem, but today digital reality technologies still take only the first, but confident steps from "childhood" to "adult" life.
To date, there are three main types of digital realities. To understand their fundamental difference, we will present a conditional scale from the familiar reality that surrounds us to the virtual one, fully modeled by digital technologies.

The first intermediate point will be Augmented Reality or AR. At the same time, the image of the real environment is complemented by digital elements. It can be animated images, text or graphic information. An example of AR is the Pokémon Go game, when an animated object is superimposed on a real image on the gadget screen.
The next item on the scale of realities will be mixed reality or MR (Mixed Reality). Elements of real, augmented, and virtual realities appear here. The basis of everything is also a real image, individual elements of which are replaced by artificially created virtual objects. Mixed reality is implemented in a translator program from Google. When you point the gadget at the translated text, the program recognizes it, translates, selects the appropriate font and inserts it in the image on the gadget instead of the original.
The end point of our reality scale is virtual reality or VR (Virtual Reality). Here the observer finds himself in a completely artificial environment created by technical means. It includes not only visual images, but also technical devices for interacting with it. The current stage of development of virtual reality can be compared with pseudographics on the first PCs. To full VR, which was shown in the "Matrix" is still far away. However, even today's level is enough to make virtual reality a powerful tool for a wide range of tasks.
There are several main areas of VR application:

And although the prospects of using VR have high potential, virtual reality has not yet received widespread use. This is due to a number of technical difficulties, one of which is the physical state of the user when immersed in virtual reality. Due to physiological characteristics, when using a VR helmet, a person often experiences dizziness and nausea. This phenomenon is called kinetosis. Its essence lies in the conflict between the information coming from the vestibular apparatus and visual images. If in the real world they are synchronized and subject to certain causal relationships, then only vision is in virtual reality, and the vestibular apparatus remains in the real world. The organism sees such a dissonance as a hallucination as a result of poisoning.
The lion's share of the VR market is in the entertainment industry. However, the importance of technology is determined by its practical application. Thanks to virtual reality, it is possible to successfully train specialists in high-risk professions without endangering them. For example, mining engineers working in difficult field conditions, rescuers, firefighters or the military. In virtual reality, you can simulate any critical situations in a safe environment for the subject.
In marketing, the wow effect of the new technology is mainly used. But there are practical applications. One such application was Canon’s free Oculus Rift helmet, called Camera Simulator by Canon Labs. (This program is available through the app store for Oculus).
The simulator allows photographers to plunge into an alternative reality to test some Canon cameras and lenses according to their features - without having to rent physical models. You can remotely familiarize yourself with the technical capabilities of three cameras (Canon EOS 5D MKIII, Canon EOS 1D X and Canon EOS 70D) and three lenses (24-105 mm F / 4, 50 mm F / 1.4 and 70-200 mm F / 2.8.
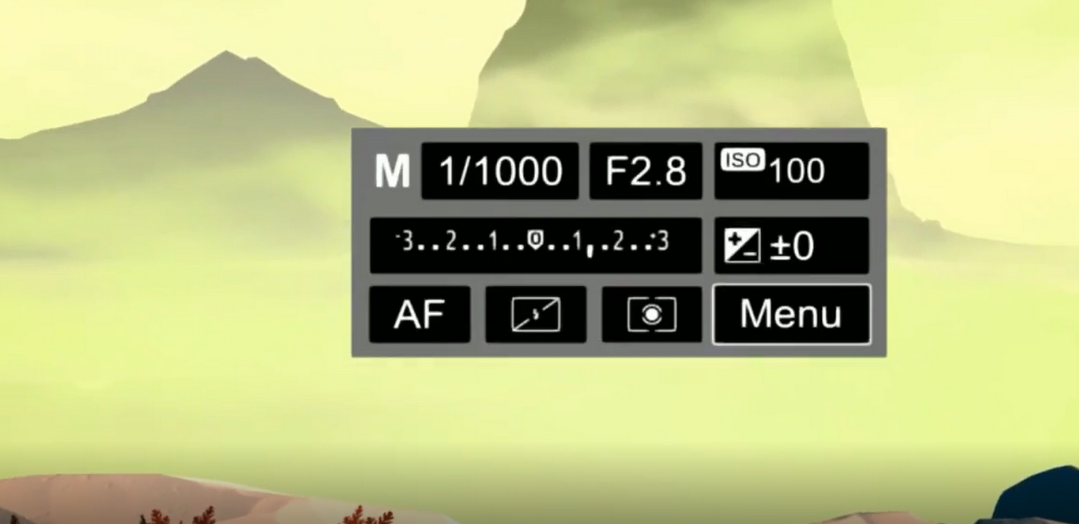
V During the familiarization process, the user can change the settings, experiment with shutter speed, aperture, photosensitivity, and check the changes by shooting the virtual landscape.The application allows you to view the captured photographs on the computer desktop.
As VR improves and becomes more prevalent, new businesses are emerging. As one example, Tim Donahay’s VR Fit can be called. Tim came to virtual fitness through VR games. At first, he noticed that certain muscle groups experienced significant stress. Then Tim decided to put on a little experiment. Over the course of 50 days, he taught 5 hours each. Two weeks later, he began to use an additional weighting vest. As a result, VR made it possible to engage in traditional fitness. Today, the number of offers of sports using virtual reality is growing. There are VR parks and playgrounds, exercise machines and gyms. Given this trend, we can soon expect the emergence of full-fledged eSports.
In parallel with virtual reality, other types of realities are developing. They can be conditionally divided into two types:
Each of these types is focused on its target audience and the implementation of a certain range of tasks.
In the modern AR market for gadgets, two main mega-players have been identified - Google and Apple. Each of them is focused on its own range of tasks. In 2016, mass user attention to AR was attracted by the Pokemon Go game. The audience amounted to more than 100 million people. At the time of application creation, there was no universal development tool. As a result, the images of the Pokémon were simply superimposed on the image of reality without spatial reference. They seemed to be hanging in the air, not interacting with the real image. Apple began to fill this gap and in June 2017 introduced its developer tool - ARKit. Among the main advantages of the tool is the ability to determine horizontal planes. Thanks to this, virtual objects have a shadow, and they become more realistic, ceasing to hang in the air. It also recognizes the user's movement in six degrees of freedom with rotations around each of the three axes.
Google’s development is significantly different from Apple’s focus and is focused mainly on navigation in space. Back in 2014, the company introduced its Tango smartphone with an infrared range finder, a fisheye camera and other sensors for building 3D-maps of rooms. The device has found application in client navigation in supermarkets and museums. Unfortunately, only a few third-party smartphone models now support Tango technology. This example just illustrates the constraining factor in the development of applications with the technical capabilities of the gadget park.
However, even for the current level of development of mobile devices, there are many interesting applications that have practical applications. We mention some of them. They are mainly intended for the visualization of goods.

Companies such as IKEA, Cimagie, Blippar, Hyundai and Lego have developed their own virtual directories. At IKEA, this is implemented as follows. To see how this or that product will fit into the interior, just put on the floor a directory open on the desired page and point the gadget’s camera at it. The image of the product is superimposed on the display over the interior picture. The FXMirror application is similar to virtual directories, but uses no gadgets. It is made in the form of a “smart mirror”. The buyer can virtually try on their favorite clothes. The Makeup Genius application for gadgets from L'Oreal company works on the same principle. By the name it is clear that the user can virtually try out a series of cosmetic products of this company.
Since the power of conventional gadgets is not enough for serious AR applications, specialized glasses are being developed for these purposes. Their functionality is sharpened only for work with augmented reality. Therefore, the price of such devices often reaches several thousand dollars apiece. It is clear that this product is not for the mass consumer.
In 2016, Microsoft released its version of augmented reality glasses Hololens. This device was equipped with many sensors and was able to draw virtual objects on a translucent screen. In Hololens, the image is built in the form of holograms.
The disadvantages of Hololens include a narrow viewing angle, which is only 300. This may not be a completely correct comparison, but in the Oculus Rift VR helmets, the viewing angle is 1100. However, this does not prevent Microsoft from remaining in a leading position. Much of this is due to the worldwide popularity of Microsoft products and their integration into Hololens.
Such large companies as Japan Airlines, NASA, Volvo, Autodesk and many others use Hololens in their work. Augmented reality glasses have become a new digital tool, greatly facilitating production processes and training. An example is Thyssenkrupp, an elevator service company. With the help of augmented reality glasses, company specialists at the facilities receive all the necessary information. If difficulties arise in work, then there is no need to waste time waiting for the engineer to leave for the object. The situation is analyzed online with the necessary graphic explanations on the Hololens screen.
Similarly, AR glasses are used in the learning process. In order for medical students to better understand human physiology, Hololens displays animated internal organs during practical exercises with dummies. While in the manufacturing sector AR glasses help increase productivity, in medicine these devices save lives. For example, very often the doctor urgently needs to receive additional information about the patient. These may be test results, drug intolerance, or other data. If this happens during surgery, then every extra second counts. With the help of AR-glasses, the doctor can quickly get the requested information without leaving the operating table.
Meta has embarked on its path of developing augmented reality glasses. Unlike Hololens, which contain a computer, Meta 2 glasses are essentially an input / output device. This allows developers to focus on detailing graphics. Therefore, Meta 2 glasses have a number of significant advantages. Due to the fact that data processing is performed on an external computer, the performance of the device is increased. Since Meta 2 only performs input / output of information, the developers managed, without increasing the dimensions of the device, to get a viewing angle of 900. And finally, the lack of an integrated computer allows you to keep the cost of the device at $ 950. However, with such advantages, Meta 2 glasses have a significant drawback - wired communication with an external computer.
After the first Google Glass project, Google returned to its development of AR glasses in a different format. If the first project was aimed at the mass consumer as an AR application for gadgets, then the updated Glass Enterprise Edition glasses became a tool for professionals. They have been successfully applied at the AGCO facility in Jackson. The company is engaged in the production of expensive agricultural equipment, which is made to order. Each product has unique characteristics. Therefore, during assembly, the workers had to consult the technical documentation. During each verification, the worker had to go to the computer to find the necessary information, and if the computer was busy, then additional time was lost waiting for the queue or searching for another free computer. Attempts to provide workers with tablets were unsuccessful.
Thanks to the use of Glass Enterprise Edition, the training time for workers was reduced from 10 to 3 days. This gives an idea of the prospects for using augmented reality glasses in business.
Speaking about augmented reality gadgets, one cannot fail to mention developments in the field of mixed reality (MR). This area is still underdeveloped, but there are already interesting concepts. One of them is Canon HMD. This device is an intermediate option between the AR glasses and the VR helmet. Two cameras and two screens with a resolution of 1,280 × 1,024 pixels are built into it. To minimize the processing time of the video signal and the output of the simulated image on the screen, an external computer is used, to which the device is connected by wires.
When creating the Canon HMD, developers used an interesting solution. The complexity of MR gadgets lies in the fact that they must very accurately combine real and virtual images. To achieve this effect in confined spaces is very difficult. For this, engineers used a prism to change the optical path and ensure the compactness of the device.
According to developers, Canon HMD will find the greatest application in the field of design design. Using the device, you can create full-fledged three-dimensional virtual models without the need to produce expensive real models. This is especially true for the automotive industry.
Development prospects
What is the most promising way of developing AR will turn out to be one of the types of applications that is now difficult to say. On the one hand, the constant aiming of the gadget camera to interact with virtual objects is contrary to the idea of using this technology every day, and on the other hand, AR glasses have a number of serious limitations. The answer to this question may be the emergence of any new breakthrough technologies or development ideas.
On the prospects for the development of virtual and augmented reality among experts so far there is no consensus. Digi-Capital analysts predict that in 2020, the global market for the production of VR content in different directions will exceed $ 30 billion. At the same time, more than half of this amount will be spent on films, television programs and games in virtual reality format. Jesse Shell, CEO of Schell Games and professor at Carnegie Mellon University, said that by 2025 the VR market will grow to $ 22.5 billion.
Despite such an optimistic forecast, Shell believes that other expectations will not justify themselves. For example, according to him, by 2025, the share of VR will be no more than 5-15% of the entire gaming industry. That is, it is too early to talk about the massive use of virtual reality even in the short term.
Goldman Sachs predicts a combined VR and AR profit of $ 13.1 billion by 2020, and an increase to $ 35 billion by 2025. The ratio of the software market for VR and AR will be 75% to 25%, respectively.
But these are dry numbers that do not provide an answer to the most important question: what will the development of these technologies lead to, what tasks will they allow to solve in the future?
What do you think? Write in the comments.
To date, there are three main types of digital realities. To understand their fundamental difference, we will present a conditional scale from the familiar reality that surrounds us to the virtual one, fully modeled by digital technologies.

The first intermediate point will be Augmented Reality or AR. At the same time, the image of the real environment is complemented by digital elements. It can be animated images, text or graphic information. An example of AR is the Pokémon Go game, when an animated object is superimposed on a real image on the gadget screen.
The next item on the scale of realities will be mixed reality or MR (Mixed Reality). Elements of real, augmented, and virtual realities appear here. The basis of everything is also a real image, individual elements of which are replaced by artificially created virtual objects. Mixed reality is implemented in a translator program from Google. When you point the gadget at the translated text, the program recognizes it, translates, selects the appropriate font and inserts it in the image on the gadget instead of the original.
The end point of our reality scale is virtual reality or VR (Virtual Reality). Here the observer finds himself in a completely artificial environment created by technical means. It includes not only visual images, but also technical devices for interacting with it. The current stage of development of virtual reality can be compared with pseudographics on the first PCs. To full VR, which was shown in the "Matrix" is still far away. However, even today's level is enough to make virtual reality a powerful tool for a wide range of tasks.
There are several main areas of VR application:
- Entertainment industry (games, films, sports and shows, social networks)
- Marketing (trade and real estate)
- The medicine
- Education (this also includes corporate education and training of specialists in high-risk professions)
- Industry and defense industry.

And although the prospects of using VR have high potential, virtual reality has not yet received widespread use. This is due to a number of technical difficulties, one of which is the physical state of the user when immersed in virtual reality. Due to physiological characteristics, when using a VR helmet, a person often experiences dizziness and nausea. This phenomenon is called kinetosis. Its essence lies in the conflict between the information coming from the vestibular apparatus and visual images. If in the real world they are synchronized and subject to certain causal relationships, then only vision is in virtual reality, and the vestibular apparatus remains in the real world. The organism sees such a dissonance as a hallucination as a result of poisoning.
The use of virtual reality technology
The lion's share of the VR market is in the entertainment industry. However, the importance of technology is determined by its practical application. Thanks to virtual reality, it is possible to successfully train specialists in high-risk professions without endangering them. For example, mining engineers working in difficult field conditions, rescuers, firefighters or the military. In virtual reality, you can simulate any critical situations in a safe environment for the subject.
In marketing, the wow effect of the new technology is mainly used. But there are practical applications. One such application was Canon’s free Oculus Rift helmet, called Camera Simulator by Canon Labs. (This program is available through the app store for Oculus).
The simulator allows photographers to plunge into an alternative reality to test some Canon cameras and lenses according to their features - without having to rent physical models. You can remotely familiarize yourself with the technical capabilities of three cameras (Canon EOS 5D MKIII, Canon EOS 1D X and Canon EOS 70D) and three lenses (24-105 mm F / 4, 50 mm F / 1.4 and 70-200 mm F / 2.8.
V During the familiarization process, the user can change the settings, experiment with shutter speed, aperture, photosensitivity, and check the changes by shooting the virtual landscape.The application allows you to view the captured photographs on the computer desktop.

As VR improves and becomes more prevalent, new businesses are emerging. As one example, Tim Donahay’s VR Fit can be called. Tim came to virtual fitness through VR games. At first, he noticed that certain muscle groups experienced significant stress. Then Tim decided to put on a little experiment. Over the course of 50 days, he taught 5 hours each. Two weeks later, he began to use an additional weighting vest. As a result, VR made it possible to engage in traditional fitness. Today, the number of offers of sports using virtual reality is growing. There are VR parks and playgrounds, exercise machines and gyms. Given this trend, we can soon expect the emergence of full-fledged eSports.
In parallel with virtual reality, other types of realities are developing. They can be conditionally divided into two types:
- applications for gadgets (smartphones, tablets);
- applications for special devices (glasses, helmets).
Each of these types is focused on its target audience and the implementation of a certain range of tasks.
AR apps for gadgets
In the modern AR market for gadgets, two main mega-players have been identified - Google and Apple. Each of them is focused on its own range of tasks. In 2016, mass user attention to AR was attracted by the Pokemon Go game. The audience amounted to more than 100 million people. At the time of application creation, there was no universal development tool. As a result, the images of the Pokémon were simply superimposed on the image of reality without spatial reference. They seemed to be hanging in the air, not interacting with the real image. Apple began to fill this gap and in June 2017 introduced its developer tool - ARKit. Among the main advantages of the tool is the ability to determine horizontal planes. Thanks to this, virtual objects have a shadow, and they become more realistic, ceasing to hang in the air. It also recognizes the user's movement in six degrees of freedom with rotations around each of the three axes.
Google’s development is significantly different from Apple’s focus and is focused mainly on navigation in space. Back in 2014, the company introduced its Tango smartphone with an infrared range finder, a fisheye camera and other sensors for building 3D-maps of rooms. The device has found application in client navigation in supermarkets and museums. Unfortunately, only a few third-party smartphone models now support Tango technology. This example just illustrates the constraining factor in the development of applications with the technical capabilities of the gadget park.
However, even for the current level of development of mobile devices, there are many interesting applications that have practical applications. We mention some of them. They are mainly intended for the visualization of goods.

Companies such as IKEA, Cimagie, Blippar, Hyundai and Lego have developed their own virtual directories. At IKEA, this is implemented as follows. To see how this or that product will fit into the interior, just put on the floor a directory open on the desired page and point the gadget’s camera at it. The image of the product is superimposed on the display over the interior picture. The FXMirror application is similar to virtual directories, but uses no gadgets. It is made in the form of a “smart mirror”. The buyer can virtually try on their favorite clothes. The Makeup Genius application for gadgets from L'Oreal company works on the same principle. By the name it is clear that the user can virtually try out a series of cosmetic products of this company.
AR applications for special devices
Since the power of conventional gadgets is not enough for serious AR applications, specialized glasses are being developed for these purposes. Their functionality is sharpened only for work with augmented reality. Therefore, the price of such devices often reaches several thousand dollars apiece. It is clear that this product is not for the mass consumer.
In 2016, Microsoft released its version of augmented reality glasses Hololens. This device was equipped with many sensors and was able to draw virtual objects on a translucent screen. In Hololens, the image is built in the form of holograms.
The disadvantages of Hololens include a narrow viewing angle, which is only 300. This may not be a completely correct comparison, but in the Oculus Rift VR helmets, the viewing angle is 1100. However, this does not prevent Microsoft from remaining in a leading position. Much of this is due to the worldwide popularity of Microsoft products and their integration into Hololens.
Such large companies as Japan Airlines, NASA, Volvo, Autodesk and many others use Hololens in their work. Augmented reality glasses have become a new digital tool, greatly facilitating production processes and training. An example is Thyssenkrupp, an elevator service company. With the help of augmented reality glasses, company specialists at the facilities receive all the necessary information. If difficulties arise in work, then there is no need to waste time waiting for the engineer to leave for the object. The situation is analyzed online with the necessary graphic explanations on the Hololens screen.
Similarly, AR glasses are used in the learning process. In order for medical students to better understand human physiology, Hololens displays animated internal organs during practical exercises with dummies. While in the manufacturing sector AR glasses help increase productivity, in medicine these devices save lives. For example, very often the doctor urgently needs to receive additional information about the patient. These may be test results, drug intolerance, or other data. If this happens during surgery, then every extra second counts. With the help of AR-glasses, the doctor can quickly get the requested information without leaving the operating table.
Meta has embarked on its path of developing augmented reality glasses. Unlike Hololens, which contain a computer, Meta 2 glasses are essentially an input / output device. This allows developers to focus on detailing graphics. Therefore, Meta 2 glasses have a number of significant advantages. Due to the fact that data processing is performed on an external computer, the performance of the device is increased. Since Meta 2 only performs input / output of information, the developers managed, without increasing the dimensions of the device, to get a viewing angle of 900. And finally, the lack of an integrated computer allows you to keep the cost of the device at $ 950. However, with such advantages, Meta 2 glasses have a significant drawback - wired communication with an external computer.
After the first Google Glass project, Google returned to its development of AR glasses in a different format. If the first project was aimed at the mass consumer as an AR application for gadgets, then the updated Glass Enterprise Edition glasses became a tool for professionals. They have been successfully applied at the AGCO facility in Jackson. The company is engaged in the production of expensive agricultural equipment, which is made to order. Each product has unique characteristics. Therefore, during assembly, the workers had to consult the technical documentation. During each verification, the worker had to go to the computer to find the necessary information, and if the computer was busy, then additional time was lost waiting for the queue or searching for another free computer. Attempts to provide workers with tablets were unsuccessful.
Thanks to the use of Glass Enterprise Edition, the training time for workers was reduced from 10 to 3 days. This gives an idea of the prospects for using augmented reality glasses in business.
Speaking about augmented reality gadgets, one cannot fail to mention developments in the field of mixed reality (MR). This area is still underdeveloped, but there are already interesting concepts. One of them is Canon HMD. This device is an intermediate option between the AR glasses and the VR helmet. Two cameras and two screens with a resolution of 1,280 × 1,024 pixels are built into it. To minimize the processing time of the video signal and the output of the simulated image on the screen, an external computer is used, to which the device is connected by wires.
When creating the Canon HMD, developers used an interesting solution. The complexity of MR gadgets lies in the fact that they must very accurately combine real and virtual images. To achieve this effect in confined spaces is very difficult. For this, engineers used a prism to change the optical path and ensure the compactness of the device.
According to developers, Canon HMD will find the greatest application in the field of design design. Using the device, you can create full-fledged three-dimensional virtual models without the need to produce expensive real models. This is especially true for the automotive industry.
Development prospects
What is the most promising way of developing AR will turn out to be one of the types of applications that is now difficult to say. On the one hand, the constant aiming of the gadget camera to interact with virtual objects is contrary to the idea of using this technology every day, and on the other hand, AR glasses have a number of serious limitations. The answer to this question may be the emergence of any new breakthrough technologies or development ideas.
On the prospects for the development of virtual and augmented reality among experts so far there is no consensus. Digi-Capital analysts predict that in 2020, the global market for the production of VR content in different directions will exceed $ 30 billion. At the same time, more than half of this amount will be spent on films, television programs and games in virtual reality format. Jesse Shell, CEO of Schell Games and professor at Carnegie Mellon University, said that by 2025 the VR market will grow to $ 22.5 billion.
Despite such an optimistic forecast, Shell believes that other expectations will not justify themselves. For example, according to him, by 2025, the share of VR will be no more than 5-15% of the entire gaming industry. That is, it is too early to talk about the massive use of virtual reality even in the short term.
Goldman Sachs predicts a combined VR and AR profit of $ 13.1 billion by 2020, and an increase to $ 35 billion by 2025. The ratio of the software market for VR and AR will be 75% to 25%, respectively.
But these are dry numbers that do not provide an answer to the most important question: what will the development of these technologies lead to, what tasks will they allow to solve in the future?
What do you think? Write in the comments.
Only registered users can participate in the survey. Please come in.
What will the development of these technologies lead to? In which industries can VR and AR technologies be implemented with maximum efficiency?
- 63.8% VR and AR will for a long time remain, first of all, technologies for the entertainment industry, games 23
- 22.2% In design and marketing 8
- 58.3% Technologies will be useful in education, industry, medicine and in work related to life risk 21
- 2.7% I will write the answer in comments 1
