Internet of Things: From Backend Design to Energy Absorption
Everything smart is supposed to save a person from all worries, but so far, so that all of this could grow wiser, the developers of the Internet of things have to think a lot and solve a variety of problems.
Which ones were discussed at InoThings ++ . Since this was our first, and we are sure - not the last, conference on the Internet of Things, the program went in one day, but it was very diverse. Of course, there were reports on hardware and software design and networking (for example, such ); the participants told how everything can break , and what legal issues arise , and that it is time to take care of staff training .
The conference was open, thereforerecords of all reports are available on the channel , there are also records of the corresponding section at RIT ++ 2017. And below are reviews of some interesting reports.
Antipatterns of developing software packages for the Internet of things
This is how Sergey Aksenov from Strizh company outlined his topic , and really talked about the general principles for IoT without being tied to any particular case.

Although “funny” stories from practice were also cited, for example, as radio modems from one batch sent complete nonsense in one of 16 packages: 21 m 3 , 22 m 3 , and then the temperature on the ISS casing. Several hundred such devices were released and some of them still work with live paying customers, i.e. it was necessary to find some solution already after the fact.
The discussion begins with one of the issues that must be resolved at the preparatory stage of the backend design, the choice of the database. The specificity of the Internet of things is that devices never send data in the same format (even Strizh water meters have different firmware versions and different structures of the data sent). At the same time, there are tens / hundreds of millions of rows of data, which is a lot out of the box for relational databases, on the other hand, you can lose a little data and do not need complex calculations. As a result, we chose MongoDB, apparently having missed holivars like this , and are satisfied. ClickHouse is the current option, especially for end-to-end time-distributed business data.
Turning to testing, Alexey gives an example of an error in transferring data from the microcontroller to the modem in electric meters that are used off the beaten path 300 km from the city of Perm, which can be reached only by the winter road or KrAZ, i.e. it is impossible to quickly replace the devices. This, combined with the fact that devices are used by living people and real businesses that depend on them, drastically reduces the right to make mistakes. And Strizh is taking really serious measures, ranging from end-to-end testing of data passage to paranoid monitoring.
The last, but no less important, aspect that was highlighted in the report is security. According to Alexey, safety is the main thing that potential consumers will pay attention to in the near future. And manufacturers should be guided by the principle of “security first”, that is, immediately think about how to hack a device and how to counter it, and if you did not come up with a way to protect it, then maybe such a device should not be released.
As a result, Alexey compares the backend developers with the last frontier of defense, because they realize the last opportunity to correct erroneous data, filter, sort and do something else, and transfer to the customer the data that he needs.
Digital livestock: how and why?
The report of Evgeny Belov and Oleg Artamonov on joint work in its best manifestations, when everyone is busy with his own business and at the same time aims at a common result.

The MTS Internet Group of Things Competency Center received the task of making a product in the agricultural industry, and to get the project in demand, he turned to the agro-industrial complex with the question: “where does it hurt and how can I help?”. To get a detailed answer, the company's specialists landed on the farm and lived there for two weeks. A sort of consulting, on the contrary, we figured out the farm structure in full and began to automate the processes associated with the diagnosis of cow health. Indeed, the detection of diseases at an early stage will allow timely measures to be taken, to avoid a significant drop in milk yield and, as a result, to increase the marginality of production.
To collect data that can then be analyzed, they contacted Unwired Devices with the task: “Help us calculate the cow’s movement and her appetite.” Because if the cow walks less and eats less, then it is time to start treating it. Oleg already talked about the part of the project related to the manufacture of sensors. It is impossible to lose sight of this moment, the data necessary for analysis should be physically possible to collect, and with reasonable means. For example, you won’t hang a GPS module on a cow, because, with an average power consumption of 5 mA, it needs 95.4 Ah * for 3 years of operation, and this is approximately an accumulator - cows will mind.
In addition to weight (30 g per ear - maximum), there are other requirements for the sensor: 3-6 years from the battery, at least IP67 protection, data transmission range up to 10 km, identification of a specific cow, positioning on the ground. Thus, the design of the sensor is reduced to finding an equilibrium state, taking into account all the limitations and the possibility of physical implementation.
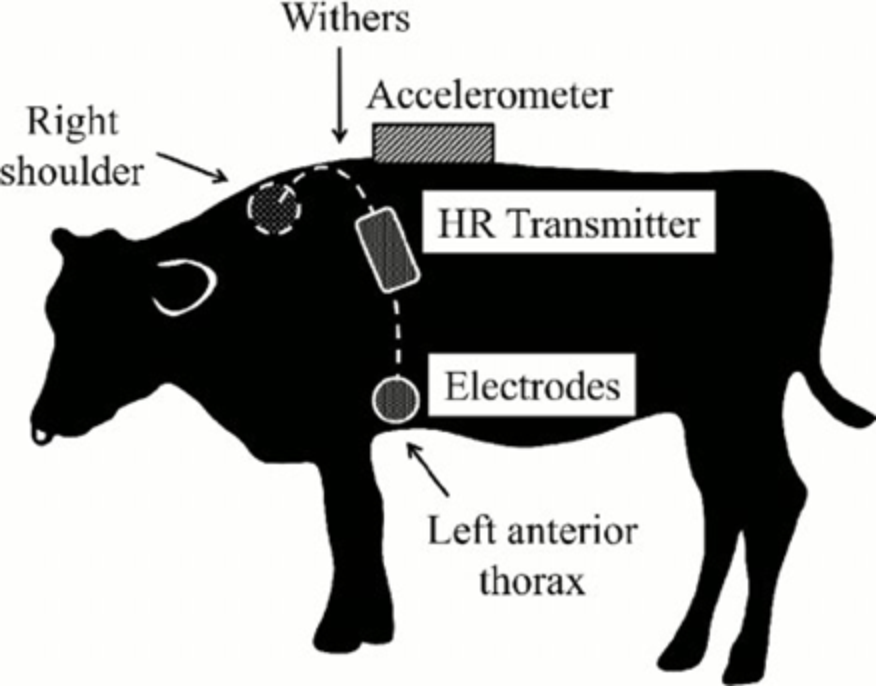
It is not known whether the views of the cows were asked directly, but nevertheless, the developers believe that they will not like the equipment scheme, as in the figure.

The project is in the pilot stage, but an ear sensor has already been implemented, in the process it is a neck sensor, which, in particular, with the help of a laryngophone will determine what the cow is chewing now. While the technology is being worked out in closed stalls without positioning, data transmission is carried out according to the LoRa protocol, 6LoWPAN is planned for the future. Although intruders are unlikely to intrude data transmission in the barn, information security is the default: encryption of user data in AE128, signing SHA256 messages, protection against replay attacks, etc.
Answering a question about a possible consumer of such a digital farm, Eugene confidently talks about the demand for the system. Moreover, MTS plans to connect the processing, storage and logistics stages to Smart Farming, so that the buyer can read the QR code and find out not only that the storage regimen was strictly observed, but also how the cow was vaccinated. Perhaps in the near future, it will be possible to like the cows, share recommendations and other insanity.
Energy absorption for powering autonomous sensors
The story of Andrei Dyumikeyev can be called greetings from the future. The national expert on solar energy for the United Nations Development Program in Belarus spoke about the possibilities of absorbing energy from our environment to power autonomous IoT devices.
For an example of why the problem is urgent, you don’t have to go far: the review released at the end of 2017 by IoT aNalytics says that Samsung recalled 600,000 devices, which, according to the announcement, should have worked for 10 years on battery, but withstood only 3 to 6 months. The matter is complicated by the fact that the supplied sensors can be difficult to replace, as in the case of the "Environmental Monitoring" in the Chernobyl zone, when a team of specialists had to change batteries all season, which supposedly were designed for the same 10 years.
Battery technology does not keep up with the pace of miniaturization and processor performance, in addition, the generation of electricity from renewable sources reduces the burden on the environment. Although in Russia, unfortunately, they are not very concerned about the issue of recycling batteries, for those who care, this is a very important point.
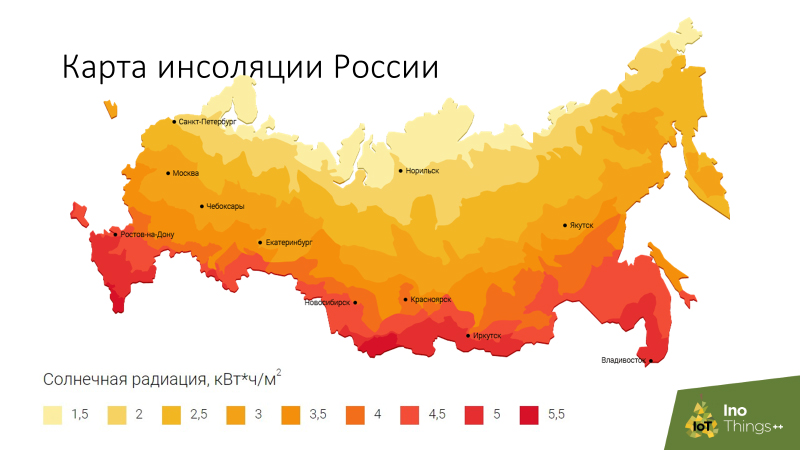
As a solution, the speaker suggests robbing that much unused energy that is around us. The most profitable technologies in terms of energy density are solar cells, thermoelectric and electromagnetic, and a combination of these types can further increase efficiency. The insolation map shows that the sun is very even in Russia and its energy can be safely used as the main one in various combinations.
SolarEnrg compensates the seasonality, familiar to all of us, in the form of low winter temperatures, with a Peltier element, which collects thermal power and almost doubles solar energy when the temperature difference between the environment and the solar module is 40 degrees. The laboratory device is ready and all those present could look at it and even, perhaps, touch it.
Like other speakers, Andrey provides several important recommendations for manufacturers of IoT devices:
- Use the latest microprocessors and chips with the lowest power consumption.
- Flexible adjustment of the frequency of data transmission where possible.
- Mandatory use of sleep modes of processors and communication modules.
- Adaptive power consumption (for example, changing the transmission frequency, depending on the voltage on the battery).
And the conclusion is that it is possible to build IoT systems and platforms based on sensors using energy harvesting devices. However, since the harvester cannot provide excessive consumption, it is necessary to design systems that are balanced in terms of power consumption and absorbed power.

And for an appetizer, students were shown yet another developed device - an integrated cardiomonitor, which collects energy for recording an ecg signal from the potential of a person’s hands, without using any battery.
Exact positioning of personnel using highly hazardous production as an example
The object for the implementation of the positioning system, which was described by Konstantin Nekhaev from Geyser Telecom, is a metallurgical plant. It contains a whole set of complicating factors for radio systems: a large amount of metal, high voltage and electromagnetic noise in which. In addition to the main goal, improving the level of industrial safety and improving production discipline, the project pursues other goals, for example, improving public opinion and increasing the authority of the city-forming enterprise.

In previously completed projects, Geyser-Telecom already faced positioning in metal containers, lack of visibility, low temperatures, underground positioning and other difficulties.
The first objects used nanoLoc technology, but when UWB (Ultra-Wide Band) stabilized in 2016, they switched to it. Its most important advantage in this case is a wide frequency band of 500 MHz or 900 MHz, which allows not only not to notice the iron, but nevertheless not bad to cope with. Both basic methods are used to determine coordinates: TDoA (Time Difference of Arrival) and ToF (Time of Flight). Such a technological bundle at the moment extends the life of the tag up to 12 months of operation with every second survey. This, coupled with preliminary testing on the most difficult part of the facility, prompted the decision to take on such a new complex project.
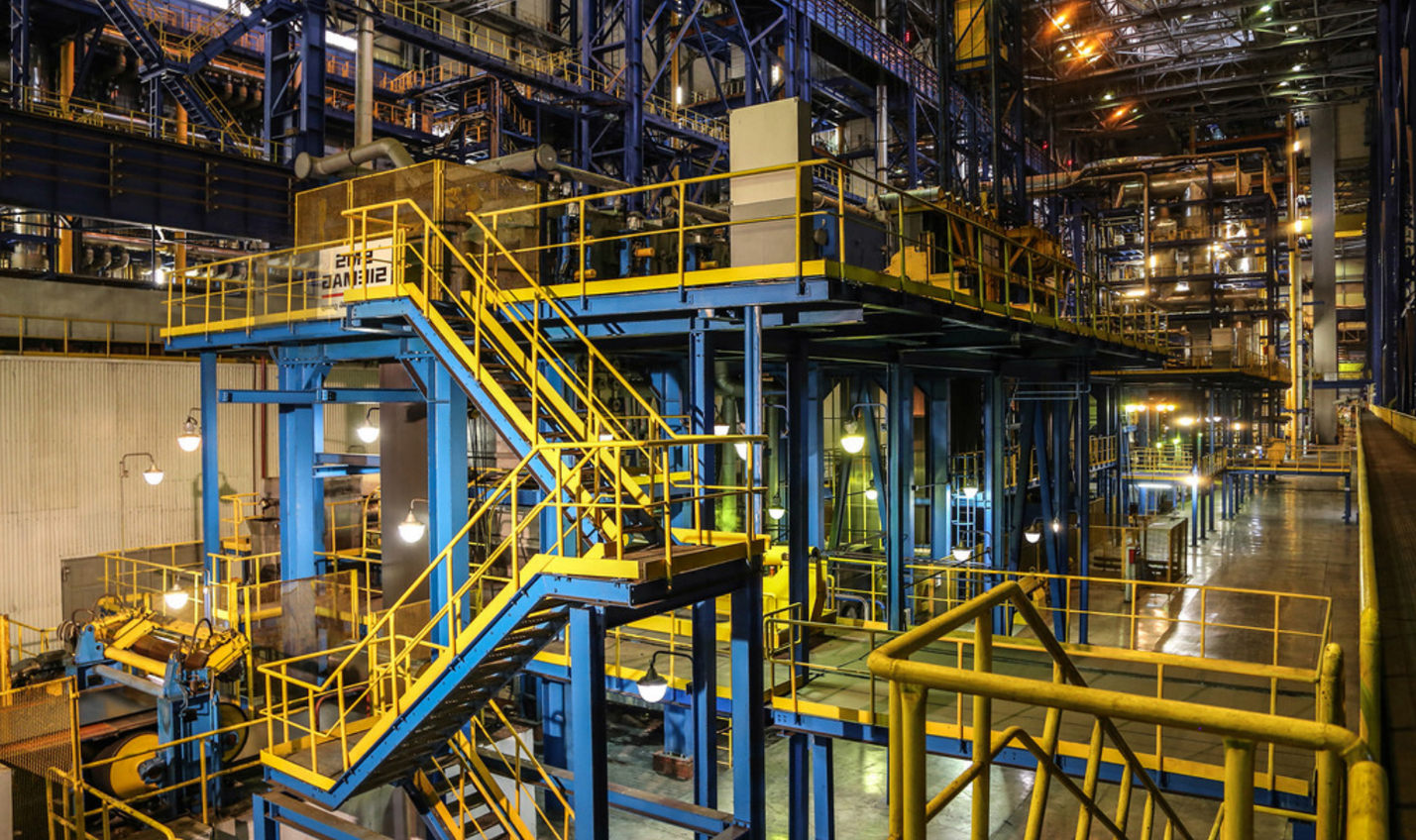

Oddly enough, the bureaucracy added a lot of complexity, but this is normal for objects of increased danger. In addition, it was necessary to install all the equipment, and this is 70 base stations, the first time, there would be no possibility to transfer the necessary cables.
Based on the results of the four-month operation of the system in the statistics mode, it turned out that 40% of the personnel commit at least one violation every day, such as leaving the post, entering an unacceptable zone or boldly walking with a squeaking gas sensor. And yet, on average 66% of the time, the staff is outside the danger zones, and this largely corresponds to the goals of the customer in optimizing wages - the payback of the project is very good. Well, security cannot be overestimated, although you can’t pay for it.
Concluding his speech, Konstantin recalls that accurate information about the capabilities of technologies or devices can only be obtained in practice and that testing on complex sites will eventually make it right the first time.
And concluding our review, we want to note that the Internet of things is not the only topic outside of highly loaded systems that we dedicate to and plan to devote our events to. So stay tuned and see you soon.
PS: You can ask questions and discuss your own cases not only in the comments on this article, but also in the Telegram chat , in which there are most of the speakers and participants of the conference and just a lot of interesting people.
