HP Helion OpenStack Carrier Grade - cloud for carriers
We continue the series of publications on the family of solutions for building cloud HP Helion OpenStack and we want to talk about the recently released package HP Helion OpenStack carrier-grade ( Carrier for Grade ) or, in abbreviated form, HOS CG.

In recent years, Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) architecture, which implements a fundamentally new approach to the deployment of telecommunications infrastructure, has been especially popular with telecom operators. With virtualization, NFV eliminates the close connection of traditional roles and technologies used in telecommunication applications, which significantly accelerates and simplifies their implementation.
To implement NFV, operators need to solve a whole range of technological problems, for example, integrate automation and service management with already deployed operations support systems (OSS) and business support (BSS), as well as ensure compliance with increased performance requirements for telecom applications, comply with the agreement SLA service level and security requirements.
The NFV reference architecture specification was developed by the Industry Specification Group (ISG), established at the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), which included 37 leading service providers. This architecture is considered standard for NFV implementation:
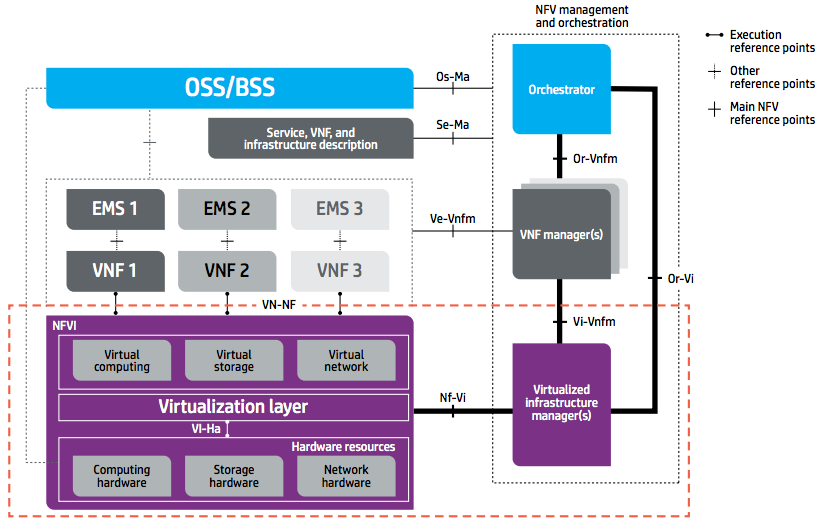
ETSI NFV Reference Architecture
One of the key components of the ETSI NFV Reference Architecture is the Virtualization Infrastructure Manager (VIM), which provides automation tools for working with virtualized resources (servers, storage systems and network equipment). These resources together constitute the NFV Infrastructure (NFVI) and are used in the NFV Infrastructure as a Service (NFVIaaS) model for hosting Virtual Network Function (VNF).
The OpenStack open source project has become the de facto standard cloud platform for building private and public clouds in the corporate sector and telecom, with which computing resources, disk space and network resources are virtualized. The use of open source means for service providers to eliminate the risk of “attachment” to one vendor, lower prices compared to proprietary solutions and the possibility of applying the various innovations that the Open Source community offers.
The first attempts to use OpenStack for virtualization of telecom applications showed that it did not reach a sufficient degree of maturity for use by telecom operators out of the box. OpenStack developers previously focused on private cloud service providers and public service provider clouds, the requirements of which differ from the cloud requirements for telecom applications. However, in recent years, the OpenStack community has begun to pay much more attention to telecom and has begun to develop the features that carriers require when implementing NFV.
To deploy a productive VIM that will manage the NFV infrastructure, you need to integrate key technologies that OpenStack does not directly deal with, including computing node operating systems (Linux), server virtualization components (KVM) and networks (vSwitch and SDN controllers), installation and management frameworks cloud application lifecycle, failover and high availability frameworks
In addition, some of these open source software components are not optimized for telecom application virtualization. So, the standard KVM without special modifications is not suitable for virtualization, for example, virtual packet gateway (vPGW) due to packet loss and high latency. Similarly, the standard open virtual switch Open vSwitch is not able to provide the required bandwidth in the telecom for fast transmission of packets of different sizes, which is necessary when processing traffic at a speed of several gigabits / sec.
An additional factor is the hardware. Specialized communications equipment is built with six nines in mind and uses the well-proven Carrier Grade features in place. At the same time, NFV solutions use new network virtualization features and dynamic movement of virtual machines between servers, server racks and data centers, which can create traffic flows that are difficult to debug.
Thus, despite its benefits, the implementation of NFV can lead to a deterioration in the availability of network services if these and other telecom features are not taken into account during its deployment. Virtualization of telecom applications requires special refinement of general purpose componentsin order to provide the required level of reliability, performance and safety in operator networks.
To help operators deploy NFV applications on open platforms, HP, together with Wind River Systems, has created a special distribution of HP Helion OpenStack Carrier Grade (HOS CG) to implement operator functionality in NFV solutions. This product is based on the HP Helion OpenStack Enterprise Edition with a number of significant improvements to the manageability, availability and performance of the cloud infrastructure.
To improve availability and reliability, HOS CG has advanced automated recovery features and completely eliminates single points of failure. To increase productivity, an operating system based on real-time technologies is used, the virtualization subsystem and virtual switch are optimized for the requirements of telecom applications. OpenStack's manageability is enhanced with advanced scheduling and resource reservation capabilities.
It is very important to note that, from the point of view of openness, HOS CG is OpenStack in all its glory. External systems gain access to its capabilities through standard OpenStack interfaces (APIs). This allows you to use standard applications and systems compatible with OpenStack, without their customization. All of the above additional functionality from HP and Wind River is open in the form of extensions (API extensions), which, again, are implemented as standard interfaces, if any.
The HP HOS CG consists of the following key components:
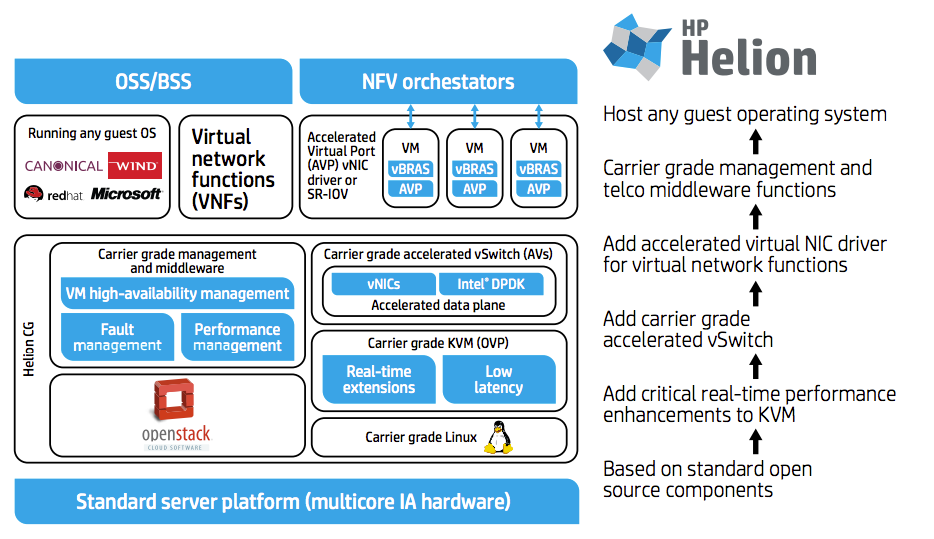
Key components of the HP Helion Carrier Grade
The current release of HOS CG is based on the OpenStack Juno edition with the Nova functionality from the Kilo edition, and has added a number of improvements and bug fixes. These services also provide plugins for integrating third-party hardware and software.
For example, HP Helion Carrier Grade includes Keystone plugins for Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) and SQL servers, Cinder plugins for HP 3PAR storage systems, and a driver for Virtual Storage Appliance (VSA). HP Helion Carrier Grade also provides an integrated Swift service.
Nova in HP Helion OpenStack Carrier Grade extended by:
All of these additional features help ensure high VNF performance. HP Helion Carrier Grade also provides high-availability VNF features, such as live migration and evacuation of VMs.
Neutron, which is a key service for the HP Helion OpenStack Carrier Grade, provides:
Heat at HP Helion OpenStack Carrier Grade automates VNF orchestration throughout its life cycle, such as automatic scaling.
HP Helion OpenStack Carrier Grade adds a number of additional Heat features, enhancements, and fixes:
Refined to the carrier-class solution level, HP Helion OpenStack Carrier Grade (HOS CG) offers a reliable open cloud platform for deploying NFV for telecom customers that meets the requirements of telecom companies.

Virtualization of network functions - the main path of telecommunications development
In recent years, Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) architecture, which implements a fundamentally new approach to the deployment of telecommunications infrastructure, has been especially popular with telecom operators. With virtualization, NFV eliminates the close connection of traditional roles and technologies used in telecommunication applications, which significantly accelerates and simplifies their implementation.
To implement NFV, operators need to solve a whole range of technological problems, for example, integrate automation and service management with already deployed operations support systems (OSS) and business support (BSS), as well as ensure compliance with increased performance requirements for telecom applications, comply with the agreement SLA service level and security requirements.
The NFV reference architecture specification was developed by the Industry Specification Group (ISG), established at the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), which included 37 leading service providers. This architecture is considered standard for NFV implementation:

ETSI NFV Reference Architecture
One of the key components of the ETSI NFV Reference Architecture is the Virtualization Infrastructure Manager (VIM), which provides automation tools for working with virtualized resources (servers, storage systems and network equipment). These resources together constitute the NFV Infrastructure (NFVI) and are used in the NFV Infrastructure as a Service (NFVIaaS) model for hosting Virtual Network Function (VNF).
OpenStack - Optimal Tool for Deploying NFV Virtualized Infrastructure
The OpenStack open source project has become the de facto standard cloud platform for building private and public clouds in the corporate sector and telecom, with which computing resources, disk space and network resources are virtualized. The use of open source means for service providers to eliminate the risk of “attachment” to one vendor, lower prices compared to proprietary solutions and the possibility of applying the various innovations that the Open Source community offers.
The first attempts to use OpenStack for virtualization of telecom applications showed that it did not reach a sufficient degree of maturity for use by telecom operators out of the box. OpenStack developers previously focused on private cloud service providers and public service provider clouds, the requirements of which differ from the cloud requirements for telecom applications. However, in recent years, the OpenStack community has begun to pay much more attention to telecom and has begun to develop the features that carriers require when implementing NFV.
To deploy a productive VIM that will manage the NFV infrastructure, you need to integrate key technologies that OpenStack does not directly deal with, including computing node operating systems (Linux), server virtualization components (KVM) and networks (vSwitch and SDN controllers), installation and management frameworks cloud application lifecycle, failover and high availability frameworks
In addition, some of these open source software components are not optimized for telecom application virtualization. So, the standard KVM without special modifications is not suitable for virtualization, for example, virtual packet gateway (vPGW) due to packet loss and high latency. Similarly, the standard open virtual switch Open vSwitch is not able to provide the required bandwidth in the telecom for fast transmission of packets of different sizes, which is necessary when processing traffic at a speed of several gigabits / sec.
An additional factor is the hardware. Specialized communications equipment is built with six nines in mind and uses the well-proven Carrier Grade features in place. At the same time, NFV solutions use new network virtualization features and dynamic movement of virtual machines between servers, server racks and data centers, which can create traffic flows that are difficult to debug.
Thus, despite its benefits, the implementation of NFV can lead to a deterioration in the availability of network services if these and other telecom features are not taken into account during its deployment. Virtualization of telecom applications requires special refinement of general purpose componentsin order to provide the required level of reliability, performance and safety in operator networks.
HP Helion OpenStack Carrier Grade - OpenStack for carriers
To help operators deploy NFV applications on open platforms, HP, together with Wind River Systems, has created a special distribution of HP Helion OpenStack Carrier Grade (HOS CG) to implement operator functionality in NFV solutions. This product is based on the HP Helion OpenStack Enterprise Edition with a number of significant improvements to the manageability, availability and performance of the cloud infrastructure.
To improve availability and reliability, HOS CG has advanced automated recovery features and completely eliminates single points of failure. To increase productivity, an operating system based on real-time technologies is used, the virtualization subsystem and virtual switch are optimized for the requirements of telecom applications. OpenStack's manageability is enhanced with advanced scheduling and resource reservation capabilities.
It is very important to note that, from the point of view of openness, HOS CG is OpenStack in all its glory. External systems gain access to its capabilities through standard OpenStack interfaces (APIs). This allows you to use standard applications and systems compatible with OpenStack, without their customization. All of the above additional functionality from HP and Wind River is open in the form of extensions (API extensions), which, again, are implemented as standard interfaces, if any.
HP Helion OpenStack Carrier Grade Components
The HP HOS CG consists of the following key components:

Key components of the HP Helion Carrier Grade
- The main services of OpenStack are Horizon, Nova, Neutron, Cinder, Glance, Swift, Keystone, Ceilometer and Heat. If necessary, other OpenStack services may be added in the future;
Carrier-grade software package for computing nodes: - Carrier grade Linux (physical server operating system);
- Carrier grade KVM (for virtualization of computing nodes);
- High-performance virtual switch Carrier grade accelerated virtual switch (AVS) with support for data plane development kit (DPDK).- Management and middleware components, including high availability management (HA); operations, administration, and maintenance (OAM); software image management and fault and performance management;
- A set of utilities and drivers Guest software development kit (SDK) for inclusion in the guest operating system VNF to improve standard performance and high availability of VIM;
- HP Helion Lifecycle Manager (HLM) is a cloud installation and lifecycle management tool (not shown in the figure above).
Features of OpenStack and Linux carrier-class versions
The current release of HOS CG is based on the OpenStack Juno edition with the Nova functionality from the Kilo edition, and has added a number of improvements and bug fixes. These services also provide plugins for integrating third-party hardware and software.
For example, HP Helion Carrier Grade includes Keystone plugins for Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) and SQL servers, Cinder plugins for HP 3PAR storage systems, and a driver for Virtual Storage Appliance (VSA). HP Helion Carrier Grade also provides an integrated Swift service.
Nova in HP Helion OpenStack Carrier Grade extended by:
- single-root input / output virtualization (SR-IOV) and PCI-passthrough functions;
- support for NUMA node affinity and CPU core pinning;
- Assigning large pages of memory to virtual machines
- vCPU scaling
- network performance-based scheduling;
- scheduler taking into account the type of CPU and NUMA node.
All of these additional features help ensure high VNF performance. HP Helion Carrier Grade also provides high-availability VNF features, such as live migration and evacuation of VMs.
Neutron, which is a key service for the HP Helion OpenStack Carrier Grade, provides:
- virtual network orchestration for VNF functions;
- Isolation of residents using virtual local area networks (VLANs) and extensible VLANs (VXLANs) of the provider
- Distributed virtual routing (DVR) functionality
- security functionality and QoS policies;
- Modular Layer 2 (ML2) plug-in mechanism for programming and controlling AVS;
- the ability to send packets with VLAN tags to / from VNF.
Heat at HP Helion OpenStack Carrier Grade automates VNF orchestration throughout its life cycle, such as automatic scaling.
HP Helion OpenStack Carrier Grade adds a number of additional Heat features, enhancements, and fixes:
- composite application lifecycle management ("Stack")
- ability to define a set of resources (e.g. VM, network, Cinder volumes, Swift databases) that form complex applications
- file and template definitions
- support for lifecycle management commands like start, modif and stop
- VM instance bootstrapping / configuration using cloud-initiative and cloud-formation mechanisms
- automatic application scaling
- security groups integration
- improved usability of templates
- enhanced Heat usability in Horizon
conclusions
Refined to the carrier-class solution level, HP Helion OpenStack Carrier Grade (HOS CG) offers a reliable open cloud platform for deploying NFV for telecom customers that meets the requirements of telecom companies.
