Minimal mail server based on Postfix and Dovecot. Part 1: Dovecot
- Tutorial
Purpose: to get a minimally working mail server using only Postfix and Dovecot, with a minimum change in the default settings. Get the framework of the system, on the basis of which you can, in the future, configure spam filters, work with databases, LDAP ... The
mail system should:
The configuration was carried out in CentOS 6. Postfix 2.6.6, Dovecot 2.0.9. No OS features were applied.
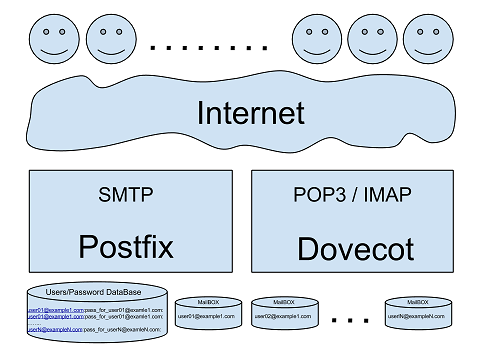
By convention, mail systems can be divided by the method of access to mailboxes and the list of users.
The main advantages of the classical system compared to the simplified one:
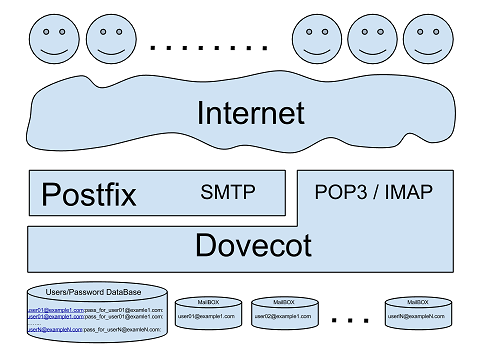
The main disadvantages of the classical system compared to the simplified one:
Despite the fact that Dovecot is the core of the system, it performs many functions. Its setting should not cause any difficulties. Perhaps this is due to the fact that Dovecot deals only with authenticated clients, which cannot be said about Postfix. We will set the names in the format username @ domainname.
mail system should:
- Support any number of domains and users.
- Serve users who are not tied to local accounts.
- Provide access to mailboxes via POP3, IMAP with TLS support.
- Provide sending and receiving emails using SMTP protocol with TLS support.
The configuration was carried out in CentOS 6. Postfix 2.6.6, Dovecot 2.0.9. No OS features were applied.
Mail system structure
By convention, mail systems can be divided by the method of access to mailboxes and the list of users.
The main advantages of the classical system compared to the simplified one:
- Performance. Postfix has access to mailboxes and can deliver mail directly to the user faster and easier than in the second case.
- The independence of the parts of the system from each other. In case of disconnection of Dovecot, Postfix will continue its main function - to receive letters.
The main disadvantages of the classical system compared to the simplified one:
- The format of the mailboxes should be clear to both programs.
- It is necessary to synchronize access to mailboxes.
- Security. Additional authority is required for Postfix. Postfix must have direct access to mailboxes and a list of users.
- The setup and maintenance is a little more complicated.
Docot
Despite the fact that Dovecot is the core of the system, it performs many functions. Its setting should not cause any difficulties. Perhaps this is due to the fact that Dovecot deals only with authenticated clients, which cannot be said about Postfix. We will set the names in the format username @ domainname.
- Let's create a user “vmail” to store mail, without “shell” access, but with the home folder “/ home / vmail”.
- Set up authentication.
(login is the same plain, but for Outlook)auth_mechanisms = plain login
Restriction of password transmission only after establishing a TLS connection is performed by default in Dovecot and does not require additional settings. Since we will use TLS, we do not need any other authentication mechanisms, only PLAIN. A self-signed certificate, in CentOS, is created when Dovecot is installed in the folder, / etc / pki / dovecot / certs /, we will use it for now to configure TLS.mail_gid = vmail mail_uid = vmail
I want to draw your attention to one important point. It is necessary to distinguish the authentication mechanism from the method of storing authentication data. Although these two concepts may be called the same, they are two different things. Details here and here . - Set up where we will store user mailboxes.
For each virtual user, set the home folder in the format - / home / vmail / domain / username,
and the location of mail in the home folder - / home / vmail / domain / username / Maildir,mail_home = /home/vmail/%d/%n
The format of Maildir mailboxes is chosen to simplify the transition to the classical system, if necessary, because Postfix supports Maildir. But if you do not plan to return to the classical system, you can choose any mailbox format supported by Dovecot .mail_location = maildir:~/Maildir - The following two directives specify where and how Dovecot will look up user names and passwords.
We used the file, / etc / dovecot / users, which has the format of the standard password file / etc / passwd.userdb { args = username_format=%u /etc/dovecot/users driver = passwd-file } passdb { args = scheme=ssha512 username_format=%u /etc/dovecot/users driver = passwd-file }
Example password file (password is truncated):
For security, we do not store user passwords in clear text, but store their salted SHA512. To fill in the file “/ etc / dovecot / users”, we will use this script with two parameters, username and password of the user.user1@example1.com:{SSHA512}2YT51xuhilbvb4vYRIb1oj1EvrKFszhf2MNw=:::::: user3@example3.com:{SSHA512}GdBv9GEE1rfFpd4+fzXS+UKh4x6gTpTaH4=::::::#!/bin/sh echo $1:$(doveadm pw -s ssha512 -p $2):::::: >> /etc/dovecot/users - Set up services for communication with Postfix.
To search for usernames and SASL authentication.
To access user mailboxes.service auth { unix_listener /var/spool/postfix/private/auth { group = postfix mode = 0660 user = postfix } unix_listener auth-userdb { mode = 0600 user = vmail } }
You can read in more detail: here about LMTP , here about LMTP and Postfix , and here about SASL .service lmtp { unix_listener /var/spool/postfix/private/dovecot-lmtp { group = postfix mode = 0600 user = postfix } user = vmail } protocol lmtp { postmaster_address = postmaster@example1.ru }
The resulting "devconf –N":
# 2.0.9: /etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf
# OS: Linux 2.6.32-504.16.2.el6.x86_64 x86_64 CentOS release 6.6 (Final)
auth_mechanisms = plain login
mail_gid = vmail
mail_home = /home/vmail/%d/%n
mail_location = maildir:~/Maildir
mail_uid = vmail
mbox_write_locks = fcntl
passdb {
args = scheme=ssha512 username_format=%u /etc/dovecot/users
driver = passwd-file
}
service auth {
unix_listener /var/spool/postfix/private/auth {
group = postfix
mode = 0660
user = postfix
}
unix_listener auth-userdb {
mode = 0600
user = vmail
}
}
service lmtp {
unix_listener /var/spool/postfix/private/dovecot-lmtp {
group = postfix
mode = 0600
user = postfix
}
user = vmail
}
ssl_cert =
Теперь достаточно добавлять имена и пароли пользователей в файл /etc/dovecot/users, и почтовые ящики будут созданы автоматически, после первой успешной аутентификации пользователя. Или, забегая вперед, после получения пользователем письма.
Часть 2: Postfix.