The authorities fundamentally change the strategy of control over the Internet
The international human rights group "Agora" published an analytical report "Internet Freedom 2018: Delegation of Repression" , which again recorded a drop in indicators for Russia. Unfortunately, last year a number of laws and bills were passed that threaten the free development of the Runet. Roskomnadzor has blocked millions of IP addresses in an attempt to interfere with the work of the Telegram messenger. Many other unpleasant things happened.
But the most important thing is that Agora analysts conclude about a fundamental turn of state policy in the Internet sphere: from blocking Internet providers and mass criminal prosecution of ordinary users, the authorities turned to an attempt to establish control over the platforms.
“By recognizing blocking at the level of Internet providers as ineffective, the state is forcing major services to cooperate and monopolizes the Internet access market,” experts concluded. “Delegating police and censor functions to private players not only minimizes the damage to reputation, but also, obviously, is more justified in terms of resource use and effective control.”
In such a situation, the platforms were actually faced with a choice - either they assume the functions and powers of the censors, or the conditions of their work in Russia will become intolerable, said the head of Agora, Pavel Chikov.
Online Ombudsman Dmitry Marinichev is inclined to agree with such conclusions. According to him, it is a collective responsibility for what is happening on the web. This is a form of total control, which is widely used in hazing in the army and prison.
Statistics of repression

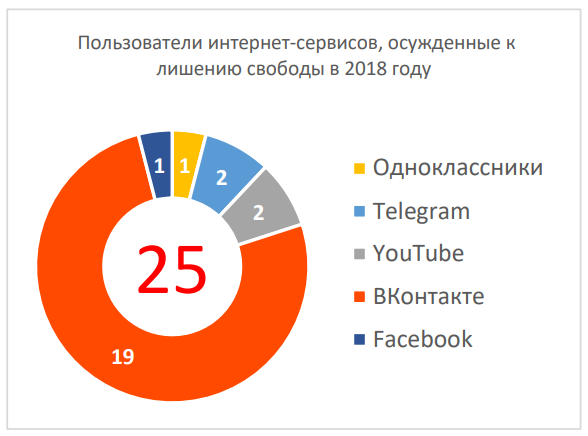
In total, last year in the Russian segment 662 842 separate facts of restriction of freedom of the Internet were recorded, which is about six times more than a year earlier. The main increase is due to blocking of Internet pages and prohibitions of information (110 thousand cases in 2017 against 649 thousand in 2018).
In 2018, the authorities blocked 1300 pages daily on the Internet; every eight days, the courts sentenced users to real terms of imprisonment.
According to experts, despite a slight decrease in the number of attacks in 2018 compared with the previous year, the overall level of violence remains high.

Tighter legislation
Summing up the year, experts draw attention to a number of laws and bills that impose additional obligations on Internet companies related to the identification of users, control of their communications and activities. There are also new categories of prohibited information.
For example, on January 1, the so-called "Messengers Act" came into force, requiring the owners of Internet instant messaging services to identify users by mobile phone number.
In April, the first reading adopted a bill on increasing fines for refusing to remove or block access to prohibited information (up to 5 million rubles for individuals and 50 million for legal entities).
In September, the law on the responsibility of search engine operators came into forcefor refusing to connect to the Registry of banned sites and remove links for blocked resources from search results. The first company brought to justice was Google, fined in December by the decision of Roskomnadzor for 500,000 rubles. Amendments were
adopted to article 17.15 of the Code of Administrative Offenses , establishing the responsibility for refusal to remove information prohibited by a court decision. At the same time, the Criminal Code introduces penalties of up to 1 year in prison for malicious failure to comply with such a requirement.
In December, amendments to the Law “On Information” entered into force , allowing out-of-court procedures to block calls to commit unlawful acts that threaten the life and health of minors and others.
In December, several new bills were introduced in the State Duma that seriously threaten the freedom of the Internet. The so-called “Law on Sovereign Runet” provides for the introduction of strict centralized control over points of exchange of cross-border Internet traffic, allowing, at the discretion of the authorities, to disable certain services, types of traffic, to restrict access to the Internet for individuals and territories in accordance with specified parameters. The draft law also provides for an emergency regime for managing the Runet, when, in the event of “threats to the integrity, stability and security of operation,” Roskomnadzor may assume centralized management of all communication networks.
At the same time, the State Duma submitted a package of bills establishing responsibility for disrespecting the authorities on the Internet and disseminating “unreliable information that creates a threat to the lives of citizens or a massive disturbance of order”, and also allows blocking such information on the Internet.
Low evaluation of Internet freedom in Russia is also noted by experts from other organizations. For example, according to the annual report Freedom on the Net 2018: The Rise of Digital Authoritarianism prepared by the non-governmental organization Freedom House, Russia with 67 points out of 100 possible for the fourth year in a row remains in a group of 19 countries with non-free Internet along with China, Ethiopia, Iran and Syria ( diagram ).
Minute of care from UFO
This material could cause contradictory feelings, so before writing a comment, refresh something important in your memory:How to write a comment and survive
- Не пишите оскорбительных комментариев, не переходите на личности.
- Воздержитесь от нецензурной лексики и токсичного поведения (даже в завуалированной форме).
- Для сообщения о комментариях, нарушающих правила сайта, используйте кнопку «Пожаловаться» (если доступна) или форму обратной связи.
Что делать, если: минусуют карму | заблокировали аккаунт
→ Кодекс авторов Хабра и хабраэтикет
→ Полная версия правил сайта

