Power supply of IT equipment: security or continuity?
Good afternoon friends! Today we will have an article, the purpose of which is to share experience and show key features and frequent errors arising in the design and organization of power supply subsystems of the IT infrastructure and data center as a whole. But I would like to expand the audience a bit and devote several sections to the basic elements of electrical safety and protection of equipment and people. For those who understand what an automaton and RCDs are for, what they are needed for, what they protect against and what are they protected from - go to the section Do you need RCDs for IT equipment, server room, data center? In addition, we will look into the question of in what cases the power outages the operating system is guaranteed to work without failures. So…
Autumn, the rain gushes almost continuously. There is a rapid construction of a cottage settlement near Moscow. The commandant of the village, bypassing the territory under his control, sees the glaring fact of “abuse” of the temporary air line 380V.
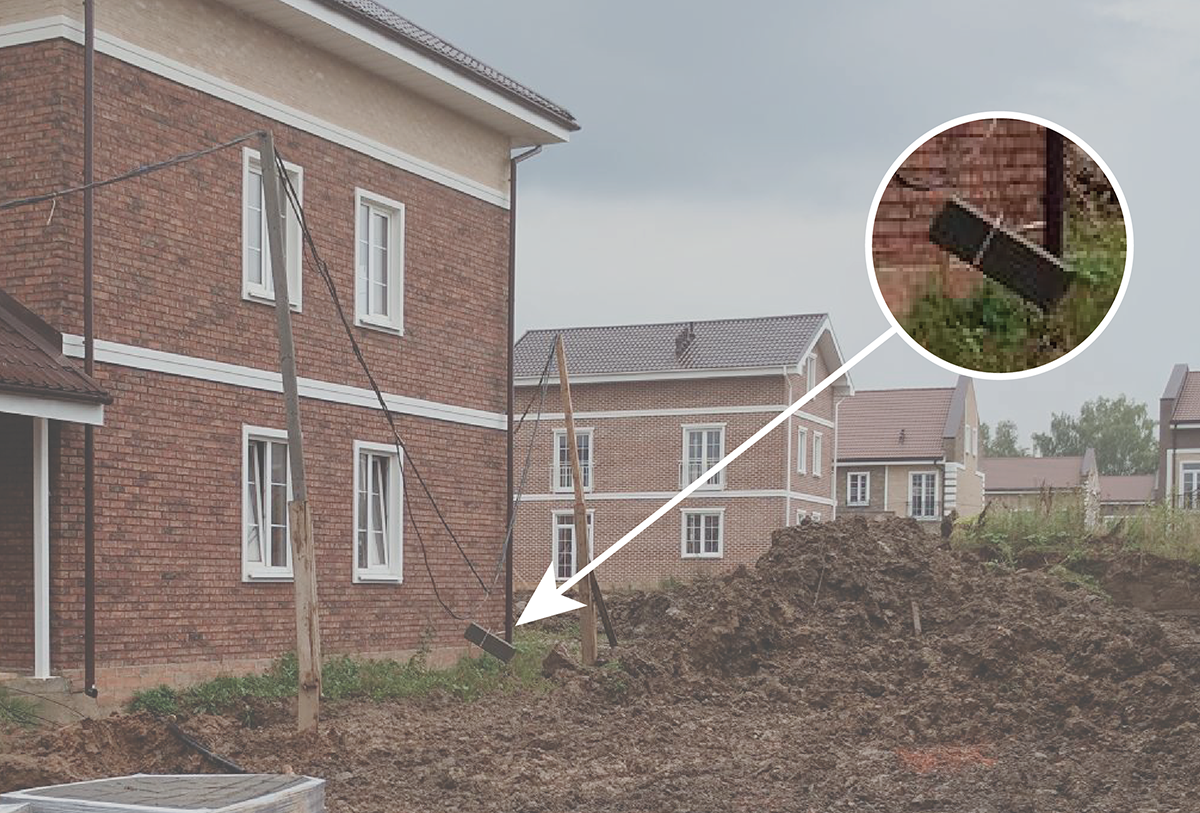

Not able to hold back emotions, he turns to the brigadier of the local construction team:
- Vadim, are you out of your mind? Are your hard workers suicide? What is this curb block hanging on an electrical cable?
- Kohl, if you remove it, then around the corner of the house will not pass an excavator!
Behind Vadim, you can see a road worker, who found a bare wire in the mud that goes somewhere in the bowels of the earth, and happily runs after a colleague, “scaring” him with electricity.
In the meantime, at the substation of the village, the tired guards, burning, for the tenth time, try to turn on a terribly hot automatic switch, which for some reason knocks out every half hour.
Why does a circuit breaker knock out and what other protection options are there for electrical equipment? What to look at first when planning electrical safety in servers and other IT equipment? In order to understand these issues, we read both parts of the article in more detail.
Since the regulations provide for a whole range of measures to protect power grids from certain accidents, we will focus on the most common household and industrial sector.

What do we want and can protect against in the first place?
Of course, from electric shock. Secondarily, protect equipment and cables from damage by short-circuit currents, as well as from fire and fire.
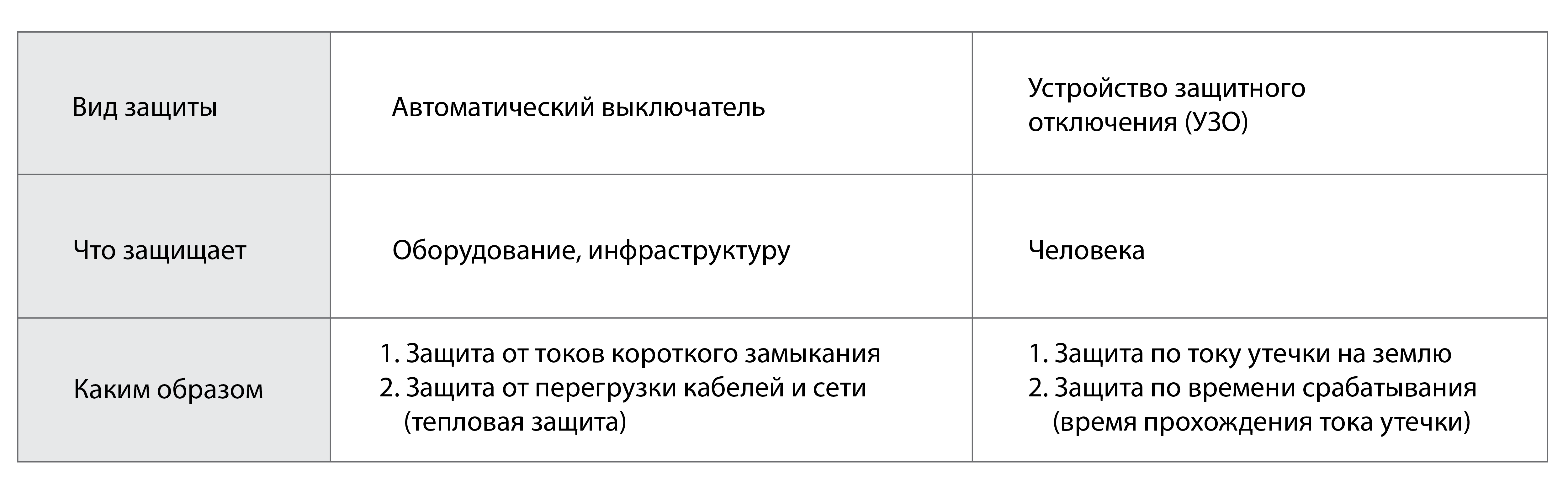
A circuit breaker (circuit breaker) - the most common means of protection of electrical networks. Of course, there are also fuses (fuses), but they are used much less due to their “disposability” and a number of technical differences compared to the automatic.
And bigger? photo clickable
"Automatic section"
1. From short-circuit
Short-circuit (short-circuit) is when the phase closes to zero or to ground if the insulation is damaged, from which the current in the circuit increases sharply (5-15 times) and turns off the machine in no more than 0.4 seconds ( for a group network according to the rules of electrical devices). If our automaton is faulty or the network operation modes do not ensure its reliable operation, then the equipment connected to this group, which itself can be a source of short circuit, suffers first. CZ also has negative effects on wires and cables. As a rule, in cases of failure of the automaton in the switchboard, local heating of the short circuit occurs, the occurrence of an arcand the burning of conductive parts with a firework of molten copper microparticles. And this development of events seems quite favorable, since in this case the accident stops by itself. In some cases, “welding” of current-carrying parts occurs at the short circuit site, and a so-called “metallic” short circuit is formed, which is much more dangerous, since it does not stop by itself, and must be turned off automatically. After that, the specialist must find the place of damage and only then try to turn on the device. But the defense may not work for various reasons, then (God forbid) it can happen
In addition, modern automata perform the function of current limiting in an accident, that is, they do not allow currents in the circuit to reach dangerous values.
2. From network overload Network
overload- this is when insulation damage (or increased load on the network) causes a prolonged increase in currents in the circuit beyond the design figures (by 110-300% or 110-500%), which leads to the disconnection of the machine during a period from several minutes to one and a half hours on the situation and the type of machine. In this case, protection against overheating, destruction of insulation and fire of elements of the group circuit is provided. That is, the machine should heat up and disconnect before the critical heating of wires, cables, contacts, sockets, switches occurs. For example, the most common automaton of characteristic C, and with a rating of 16A, will reliably protect against network overload at currents from 20.8A (1.3 nominal) and will work in approximately 60 minutes, and in the case of an overload current of 48A (3 nominal), the shutdown will occur from 5 seconds to 20-30 seconds. During this time, the temperature of the insulation of cables, wires, power consumers should not exceed the critical temperature. For this, it is sometimes required to perform cable calculations for non-flammability at short-circuit currents and to justify
The most common insulating material in the era of "developed socialism" was carbolite. Everyone remembers the smooth black plastic from which almost all electrical devices in the USSR were made? These are sockets, terminal blocks, and automatic machines, and household electrical appliances, electric plugs, etc. So, this material has a heat resistance of up to 150 degrees, which is much better than the characteristics of modern PVC insulation. However, when the temperature reaches over 100 degrees, this material begins to degrade and release hazardous toxic substances.

The appearance of the branch clamp with carbolite sheath.

The appearance of the branch clamp on the overhead line after passing a lightning pulse. Phase shrink just exploded, and in the photo - zero shrink, charred by the thermal impulse of supercurrents (Fig. 1).
The temperature of cable insulation should not exceed 70-80 degrees Celsius in any type of network failure. In the case of a short circuit, the insulation heats up rapidly; in the case of an overload, the process is relatively stretched over time. So what happened at the village substation while the concrete block was hanging on the electrical cable?
The melting of PVC insulation of the power cable as a result of line overload and constant attempts to turn on the machine without eliminating the cause of the accident (Fig. 2).

Clickable
At the substation, the machine felt a constant overload on the line through one of the phases as a result of poor insulation. It was heating up, and it turned off due to thermal protection. After some time the guard came, and turned on the machine again. Of course, it is almost always possible to turn on the machine immediately after the activation of the thermal protection: But behind the guard, there were builders who demanded that the line be turned on urgently, since the power tool was not working, it was impossible to boil tea and so on and so forth ... The situation repeated throughout the day. Attempts to eliminate phase imbalance did not lead to anything on the line, because after two or three days there was an overload on the other phase ... As we see, Increased load currents have chosen the weakest link - the cable coming from above on the machine (in this case it is a self-supporting insulated aluminum wire). Insulation floated due to a temperature rise of 100 degrees. And this is at low-plus air temperatures. What would be in this situation on a hot summer day?
Of course, the fire and the failure of the main shield of the substation.
Ask why I am setting out this? Everything is very simple - if your protection has worked, a machine gun has been knocked out, or an RCD, then this is connected with something and for a reason. Before you turn on the machine you need to understand the causes of the accident. Especially if the machine is obviously warm. In addition, each machine is designed for a certain number of protection trips, and it is not recommended to turn on the machine for damage to an existing line, which reduces its life.
UZO - devices, first of all, are intended for protection of the person against defeat by electric current. If you do not go deep into the technical details, the device detects a leakage of current from the phase conductor to the ground and turns off the damaged group for up to 30 ms or 0.03 seconds. For protection of a person, a residual current device of 30 mA is installed. This figure is due to the safe level of current that can flow through the human body without cardiac fibrillation, that is, without harming the person.

Residual current device
As you know, the danger to a person is not a voltage, but a current. For example, you can kill a person with 1 volt voltage, and it is important what current passes through the person, along which path, and in what time. So, the RCD is designed to protect a person by touching parts that are under dangerous voltage. It can be housing appliances, industrial equipment, any metal parts. As a rule, the RCD disconnects the damaged line in advance, and not at that moment when touched by a person. But there are cases when dangerous potential on the equipment may appear at the moment of the person working with him.
The first safety shutdown device was patented in 1928 by the German company RWE (Rheinisch - Westfälisches Elektrizitätswerk AG).
In 1937 the firm Schutzapparategesellschaft Paris & Co. manufactured the first operating device based on a differential transformer and a polarized relay, which had a sensitivity of 0.01 A and a speed of 0.1 s. In the same year, with the help of a volunteer (an employee of the company), an RCD test was conducted. The experiment ended successfully, the device worked clearly, the volunteer experienced only a weak electric shock, although he refused to participate in further experiments.
At the moment there are RCDs with a leakage current of 300 mA. They are designed to protect against fire and perform the function of additional protection with thermal protection of the machine.
What is the difference between the RCD and the thermal protection available in the circuit breaker? Indeed, in fact, the overload of the line can be due to leakage of current to the ground.
First , the response time of thermal protection is measured in seconds and hours, RCD - in milliseconds (usually up to 25 msec, or 0.025 seconds).
Secondly , thermal protection is designed to protect equipment, but not to protect people. In the absence of a RCD in the panel, when a person touches the equipment case, the network mode will go into a short circuit stage, the current will increase dramatically, the short circuit protection in the machine will work and turn off the line relatively quickly. But this time may be enough for a person to get an electric shock incompatible with life.
Thirdly, UZO is an additional measure of protection and is established, as a rule, for hazardous areas and for household outlets, while automatic machines are the main measure of protection and are used everywhere and always.
Fourthly, the use of RCDs without automatic switches is excluded, but automatic machines without RCDs are quite common.
The question is ambiguous and, as a rule, remains at the discretion of the Customer.
On the one hand, the safety of personnel must prevail over other considerations. Human life is a priority. On the other hand, the equipment of information systems often itself refers to the life support systems of other people, services can “spin” on them, and their work must be uninterrupted. For example, medical institutions, emergency services, emergency services and other life support organizations. And the server rooms themselves are classified, as a rule, as rooms without a permanent stay of people, without permanent jobs.
That is, quite often information equipment can be attributed to the first category of electrical receivers in terms of power supply reliability (ПУЭ П.1.2.18), along with fire-fighting systems and emergency lighting. For this group, a break in electricity supply is unacceptable , as it can lead to significant material losses and be a threat to the life and health of people. If you examine the current standards more deeply, you can find instructions that it is permissible for vital consumers to install protection only against short circuits, without thermal protection.
For example, fire pumps must operate in fire conditions until cable insulation finally burns out and does not happen.
For example, in clause 7.1.81 of the Rules for the Electrical Installations (ПУЭ) it is stated: “the installation of a UZO is prohibited for electrical receivers, the disconnection of which can lead to situations dangerous for consumers”. For information equipment today, as a rule, standard automatic switches are used, but RCDs are not used to eliminate false alarms and sudden shutdown of important servers and services. There are special types of RCDs that take into account the specifics of switching power supplies of servers and other IT equipment, but they are rarely available, are difficult to select, and lead to an increase in the cost of the project as a whole. For server and data centers, it is assumed that these rooms are, as a rule, equipped with individual gas fire extinguishing systems, and the presence of personnel is minimal in time.
As an additional level of protection for server and data center personnel, it is imperative to organize reliable earthing of metal parts of server racks, pipelines, of any accessible metal parts to the touch, including a metal fire door (s). With the proper organization of the Additional Capacity Adjustment System (DPMS) in the server room, the data center will be provided with an adequate level of personnel and information equipment safety, despite the absence of RCDs in the power distribution circuits.
For technological needs, several sockets are installed within the server rooms, which are provided with protective disconnect devices. To these sockets (and only to them) any portable power tool and / or equipment not related to the direct goals of our server should be connected.
Continued in the second part of the article , where we understand the question of network interference can lead to a fall in operating systems? why not all UPS, AVR and ATS are good? and go through the chain of the grid-server rack-power supply-electronics IT equipment-operating system
Author: Oleg Kulikov
Leading Design Engineer
Department of Integrated Solutions "Open Technologies"
okulikov@ot.ru
Registration in the National Register of Specialists "NOPRIZ" P-045870
Part one
Autumn, the rain gushes almost continuously. There is a rapid construction of a cottage settlement near Moscow. The commandant of the village, bypassing the territory under his control, sees the glaring fact of “abuse” of the temporary air line 380V.

Not able to hold back emotions, he turns to the brigadier of the local construction team:
- Vadim, are you out of your mind? Are your hard workers suicide? What is this curb block hanging on an electrical cable?
- Kohl, if you remove it, then around the corner of the house will not pass an excavator!
Behind Vadim, you can see a road worker, who found a bare wire in the mud that goes somewhere in the bowels of the earth, and happily runs after a colleague, “scaring” him with electricity.
In the meantime, at the substation of the village, the tired guards, burning, for the tenth time, try to turn on a terribly hot automatic switch, which for some reason knocks out every half hour.
Why does a circuit breaker knock out and what other protection options are there for electrical equipment? What to look at first when planning electrical safety in servers and other IT equipment? In order to understand these issues, we read both parts of the article in more detail.
Since the regulations provide for a whole range of measures to protect power grids from certain accidents, we will focus on the most common household and industrial sector.

What do we want and can protect against in the first place?
Of course, from electric shock. Secondarily, protect equipment and cables from damage by short-circuit currents, as well as from fire and fire.

A circuit breaker (circuit breaker) - the most common means of protection of electrical networks. Of course, there are also fuses (fuses), but they are used much less due to their “disposability” and a number of technical differences compared to the automatic.

And bigger? photo clickable
"Automatic section"
In the classic case, the circuit breaker protects:
1. From short-circuit
Short-circuit (short-circuit) is when the phase closes to zero or to ground if the insulation is damaged, from which the current in the circuit increases sharply (5-15 times) and turns off the machine in no more than 0.4 seconds ( for a group network according to the rules of electrical devices). If our automaton is faulty or the network operation modes do not ensure its reliable operation, then the equipment connected to this group, which itself can be a source of short circuit, suffers first. CZ also has negative effects on wires and cables. As a rule, in cases of failure of the automaton in the switchboard, local heating of the short circuit occurs, the occurrence of an arcand the burning of conductive parts with a firework of molten copper microparticles. And this development of events seems quite favorable, since in this case the accident stops by itself. In some cases, “welding” of current-carrying parts occurs at the short circuit site, and a so-called “metallic” short circuit is formed, which is much more dangerous, since it does not stop by itself, and must be turned off automatically. After that, the specialist must find the place of damage and only then try to turn on the device. But the defense may not work for various reasons, then (God forbid) it can happen
fire of a New Year tree, just a few seconds and oxygen remains only at the very floor
In addition, modern automata perform the function of current limiting in an accident, that is, they do not allow currents in the circuit to reach dangerous values.
A little more about current limiting
С увеличением мощности сетей в глобальном смысле токи однофазного короткого замыкания могут достигать больших значений, до десятков тысяч Ампер, особенно если наш потребитель, оборудование или розетка установлены достаточно близко к подстанции. А в таких режимах существует понятие «электродинамическое действие токов КЗ». Опять сложный термин, скажет Вы. А вот и нет. Доступным языком можно пояснить этот термин как попытки медных шин в щитах, кабелях и прочей начинки сдвинутся с места под действием больших токов, изогнуться, особенно если монтажники просто накидали кабели в лоток, а закрепили как придется: подручными средствами, остатками проволоки и т.п. И в этой ситуации развитие аварии может быть еще более плачевным – межфазное КЗ, разрушение оборудования и прочее… Таким образом правильно выбранный автомат – залог правильной работы оборудования, и если его по какой-то причине «выбивает», то не надо пытаться его включить, при этом возмущаясь, что он мгновенно отключается снова.
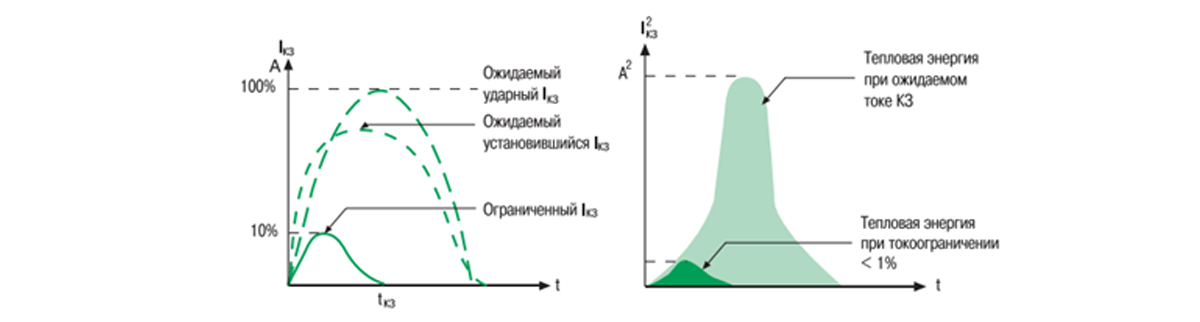
График токоограничения и снижения выделяемой тепловой энергии
What does current limiting mean and how dangerous are high short circuit currents?
С увеличением мощности сетей в глобальном смысле токи однофазного короткого замыкания могут достигать больших значений, до десятков тысяч Ампер, особенно если наш потребитель, оборудование или розетка установлены достаточно близко к подстанции. А в таких режимах существует понятие «электродинамическое действие токов КЗ». Опять сложный термин, скажет Вы. А вот и нет. Доступным языком можно пояснить этот термин как попытки медных шин в щитах, кабелях и прочей начинки сдвинутся с места под действием больших токов, изогнуться, особенно если монтажники просто накидали кабели в лоток, а закрепили как придется: подручными средствами, остатками проволоки и т.п. И в этой ситуации развитие аварии может быть еще более плачевным – межфазное КЗ, разрушение оборудования и прочее… Таким образом правильно выбранный автомат – залог правильной работы оборудования, и если его по какой-то причине «выбивает», то не надо пытаться его включить, при этом возмущаясь, что он мгновенно отключается снова.

График токоограничения и снижения выделяемой тепловой энергии
2. From network overload Network
overload- this is when insulation damage (or increased load on the network) causes a prolonged increase in currents in the circuit beyond the design figures (by 110-300% or 110-500%), which leads to the disconnection of the machine during a period from several minutes to one and a half hours on the situation and the type of machine. In this case, protection against overheating, destruction of insulation and fire of elements of the group circuit is provided. That is, the machine should heat up and disconnect before the critical heating of wires, cables, contacts, sockets, switches occurs. For example, the most common automaton of characteristic C, and with a rating of 16A, will reliably protect against network overload at currents from 20.8A (1.3 nominal) and will work in approximately 60 minutes, and in the case of an overload current of 48A (3 nominal), the shutdown will occur from 5 seconds to 20-30 seconds. During this time, the temperature of the insulation of cables, wires, power consumers should not exceed the critical temperature. For this, it is sometimes required to perform cable calculations for non-flammability at short-circuit currents and to justify
suitability for further use
… к дальнейшей эксплуатации. Данная тема относится больше к высоковольтным кабелям, однако иногда Заказчик оперируя циркулярами РАО ЕЭС и ведомственными нормативами требует провести расчеты и для кабелей 0,4 кВ (и мелких сечений!) по двум направлениям: проверка не невозгораемость кабеля в режиме КЗ и проверка пригодности кабеля к дальнейшей эксплуатации в послеаварийном режиме. В последнем случае это означает проверить факт «живучести» изоляции после прохождения тока короткого замыкания, факт того, что изоляция не успела нагреться до температур деградации изоляционных материалов


The most common insulating material in the era of "developed socialism" was carbolite. Everyone remembers the smooth black plastic from which almost all electrical devices in the USSR were made? These are sockets, terminal blocks, and automatic machines, and household electrical appliances, electric plugs, etc. So, this material has a heat resistance of up to 150 degrees, which is much better than the characteristics of modern PVC insulation. However, when the temperature reaches over 100 degrees, this material begins to degrade and release hazardous toxic substances.

The appearance of the branch clamp with carbolite sheath.

The appearance of the branch clamp on the overhead line after passing a lightning pulse. Phase shrink just exploded, and in the photo - zero shrink, charred by the thermal impulse of supercurrents (Fig. 1).
The temperature of cable insulation should not exceed 70-80 degrees Celsius in any type of network failure. In the case of a short circuit, the insulation heats up rapidly; in the case of an overload, the process is relatively stretched over time. So what happened at the village substation while the concrete block was hanging on the electrical cable?
The melting of PVC insulation of the power cable as a result of line overload and constant attempts to turn on the machine without eliminating the cause of the accident (Fig. 2).

Clickable
At the substation, the machine felt a constant overload on the line through one of the phases as a result of poor insulation. It was heating up, and it turned off due to thermal protection. After some time the guard came, and turned on the machine again. Of course, it is almost always possible to turn on the machine immediately after the activation of the thermal protection: But behind the guard, there were builders who demanded that the line be turned on urgently, since the power tool was not working, it was impossible to boil tea and so on and so forth ... The situation repeated throughout the day. Attempts to eliminate phase imbalance did not lead to anything on the line, because after two or three days there was an overload on the other phase ... As we see, Increased load currents have chosen the weakest link - the cable coming from above on the machine (in this case it is a self-supporting insulated aluminum wire). Insulation floated due to a temperature rise of 100 degrees. And this is at low-plus air temperatures. What would be in this situation on a hot summer day?
Of course, the fire and the failure of the main shield of the substation.
Ask why I am setting out this? Everything is very simple - if your protection has worked, a machine gun has been knocked out, or an RCD, then this is connected with something and for a reason. Before you turn on the machine you need to understand the causes of the accident. Especially if the machine is obviously warm. In addition, each machine is designed for a certain number of protection trips, and it is not recommended to turn on the machine for damage to an existing line, which reduces its life.
Now consider the RCD
UZO - devices, first of all, are intended for protection of the person against defeat by electric current. If you do not go deep into the technical details, the device detects a leakage of current from the phase conductor to the ground and turns off the damaged group for up to 30 ms or 0.03 seconds. For protection of a person, a residual current device of 30 mA is installed. This figure is due to the safe level of current that can flow through the human body without cardiac fibrillation, that is, without harming the person.

Residual current device
As you know, the danger to a person is not a voltage, but a current. For example, you can kill a person with 1 volt voltage, and it is important what current passes through the person, along which path, and in what time. So, the RCD is designed to protect a person by touching parts that are under dangerous voltage. It can be housing appliances, industrial equipment, any metal parts. As a rule, the RCD disconnects the damaged line in advance, and not at that moment when touched by a person. But there are cases when dangerous potential on the equipment may appear at the moment of the person working with him.
History reference:
The first safety shutdown device was patented in 1928 by the German company RWE (Rheinisch - Westfälisches Elektrizitätswerk AG).
In 1937 the firm Schutzapparategesellschaft Paris & Co. manufactured the first operating device based on a differential transformer and a polarized relay, which had a sensitivity of 0.01 A and a speed of 0.1 s. In the same year, with the help of a volunteer (an employee of the company), an RCD test was conducted. The experiment ended successfully, the device worked clearly, the volunteer experienced only a weak electric shock, although he refused to participate in further experiments.
At the moment there are RCDs with a leakage current of 300 mA. They are designed to protect against fire and perform the function of additional protection with thermal protection of the machine.
What is the difference between the RCD and the thermal protection available in the circuit breaker? Indeed, in fact, the overload of the line can be due to leakage of current to the ground.
First , the response time of thermal protection is measured in seconds and hours, RCD - in milliseconds (usually up to 25 msec, or 0.025 seconds).
Secondly , thermal protection is designed to protect equipment, but not to protect people. In the absence of a RCD in the panel, when a person touches the equipment case, the network mode will go into a short circuit stage, the current will increase dramatically, the short circuit protection in the machine will work and turn off the line relatively quickly. But this time may be enough for a person to get an electric shock incompatible with life.
Thirdly, UZO is an additional measure of protection and is established, as a rule, for hazardous areas and for household outlets, while automatic machines are the main measure of protection and are used everywhere and always.
Fourthly, the use of RCDs without automatic switches is excluded, but automatic machines without RCDs are quite common.
Why should the RCD application be paired with a gun?
Поскольку основную защиту обеспечивает автоматический выключатель, то он же и защищает устройство защитного отключения. Для корректной работы схемы номинал контактов УЗО выбирается на шаг выше, чем у автомата. Например, автомат устанавливается на 16А, а УЗО устанавливается на 25А. В этом случае УЗО безопасно пропустит через себя токи короткого замыкания к автомату, который и обеспечит защиту. Со своей стороны, УЗО обеспечит дополнительную защиту человека при утечке на корпус (землю). Существуют комбинированные устройства «автомат+УЗО» в едином корпусе, так называемые дифавтоматы. Их я рассматривать не буду, желающие могут изучить вопрос Вики об УЗО, Вики о дифавтоматах (или АВДТ). Скажу лишь, что дифавтоматы экономят место в щите, так как занимают меньше модулей на DIN-рейке.
В промышленном секторе УЗО как правило применяют номиналом на 100 и 300 миллиампер как средство защиты от пожара на линиях уличных светильников, уличного оборудования и т.п.
В промышленном секторе УЗО как правило применяют номиналом на 100 и 300 миллиампер как средство защиты от пожара на линиях уличных светильников, уличного оборудования и т.п.
Do RCDs for IT equipment, server, data center?
The question is ambiguous and, as a rule, remains at the discretion of the Customer.
On the one hand, the safety of personnel must prevail over other considerations. Human life is a priority. On the other hand, the equipment of information systems often itself refers to the life support systems of other people, services can “spin” on them, and their work must be uninterrupted. For example, medical institutions, emergency services, emergency services and other life support organizations. And the server rooms themselves are classified, as a rule, as rooms without a permanent stay of people, without permanent jobs.
That is, quite often information equipment can be attributed to the first category of electrical receivers in terms of power supply reliability (ПУЭ П.1.2.18), along with fire-fighting systems and emergency lighting. For this group, a break in electricity supply is unacceptable , as it can lead to significant material losses and be a threat to the life and health of people. If you examine the current standards more deeply, you can find instructions that it is permissible for vital consumers to install protection only against short circuits, without thermal protection.
For example, fire pumps must operate in fire conditions until cable insulation finally burns out and does not happen.
metal short circuit
Металлическое, или глухое короткое замыкание – это сваривание проводников (например, фазы и ноля) в месте пробоя изоляции. Образуется замкнутая цепь короткого замыкания, и в этом случае обязательно должно быть обеспечено срабатывание аппарата защиты. В большинстве случаев глухое короткое замыкание не случается, но вероятность его существует. Для противопожарных систем, в частности систем пожаротушения основная мысль изложенная в нормативах- в случае ЧП противопожарные системы должны работать несмотря ни на что и обеспечить безопасность людей даже в случае повреждения изоляции кабелей. Время работы противопожарных систем определяется временем, необходимым для эвакуации людей и персонала.
Для питания ответственных электроприемников применяют огнестойкие кабели с маркой FRLS, которые обладают свойствами выдерживать нагрев изоляции без возгорания и оплавления. В составе изоляции таких кабелей применяется слюда, которая дает дополнительное время нормальной работы линии без коротких замыканий в условиях пожара.
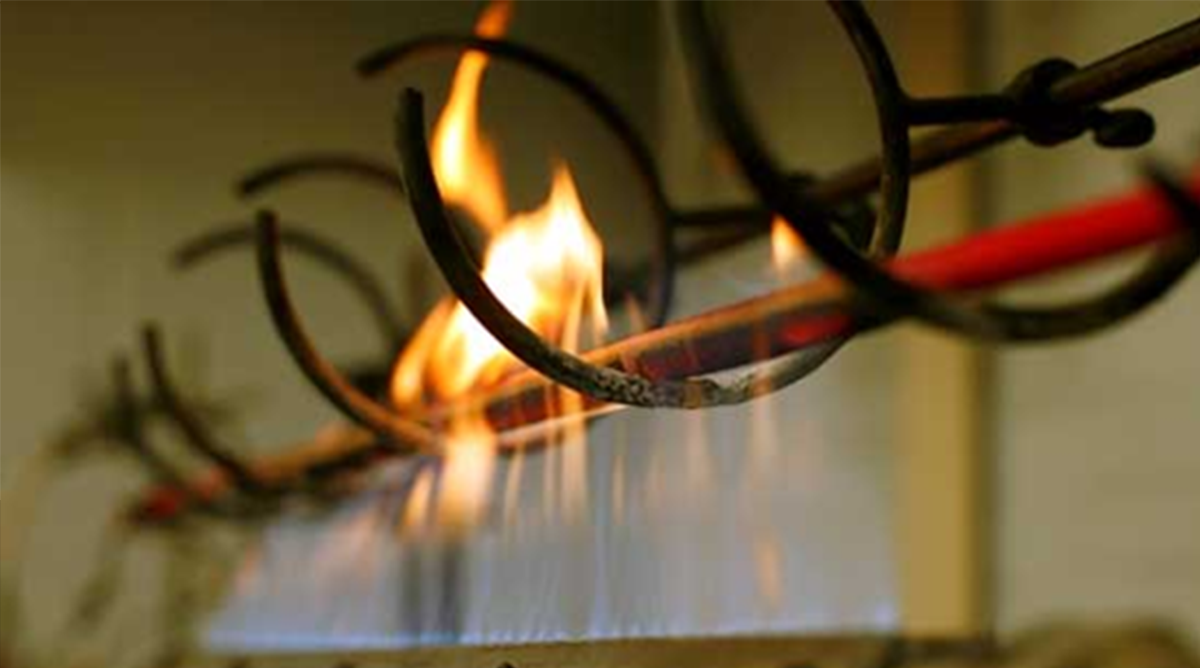

Испытания огнестойких кабелей завода Спецкабель для систем пожарной сигнализации
Для питания ответственных электроприемников применяют огнестойкие кабели с маркой FRLS, которые обладают свойствами выдерживать нагрев изоляции без возгорания и оплавления. В составе изоляции таких кабелей применяется слюда, которая дает дополнительное время нормальной работы линии без коротких замыканий в условиях пожара.

Испытания огнестойких кабелей завода Спецкабель для систем пожарной сигнализации
For example, in clause 7.1.81 of the Rules for the Electrical Installations (ПУЭ) it is stated: “the installation of a UZO is prohibited for electrical receivers, the disconnection of which can lead to situations dangerous for consumers”. For information equipment today, as a rule, standard automatic switches are used, but RCDs are not used to eliminate false alarms and sudden shutdown of important servers and services. There are special types of RCDs that take into account the specifics of switching power supplies of servers and other IT equipment, but they are rarely available, are difficult to select, and lead to an increase in the cost of the project as a whole. For server and data centers, it is assumed that these rooms are, as a rule, equipped with individual gas fire extinguishing systems, and the presence of personnel is minimal in time.
As an additional level of protection for server and data center personnel, it is imperative to organize reliable earthing of metal parts of server racks, pipelines, of any accessible metal parts to the touch, including a metal fire door (s). With the proper organization of the Additional Capacity Adjustment System (DPMS) in the server room, the data center will be provided with an adequate level of personnel and information equipment safety, despite the absence of RCDs in the power distribution circuits.
For technological needs, several sockets are installed within the server rooms, which are provided with protective disconnect devices. To these sockets (and only to them) any portable power tool and / or equipment not related to the direct goals of our server should be connected.
Continued in the second part of the article , where we understand the question of network interference can lead to a fall in operating systems? why not all UPS, AVR and ATS are good? and go through the chain of the grid-server rack-power supply-electronics IT equipment-operating system
Author: Oleg Kulikov
Leading Design Engineer
Department of Integrated Solutions "Open Technologies"
okulikov@ot.ru
Registration in the National Register of Specialists "NOPRIZ" P-045870
