“Perfect” Gantt Chart Timeline

The most important tool for a project manager is a time plan. It can be built in many ways, but a Gantt chart is often used.
About the Gantt chart there were already many discussions on Habré:
- “Is the Gantt chart convenient?”
- Alternative methods “How to estimate the term of work?”
- "Planning Agile Projects with a Gantt Chart"
- “What the Gantt chart is silent about or why projects are always late”
Someone believes that the best time plan is the Gantt chart, someone even plans agile projects using this chart, and someone, on the contrary, does not see the point in it and offers alternative approaches to planning and time plans .
Let’s finally figure out why the Gantt chart is needed at all, how it should be drawn up and what good it is!
What awaits you in the article
Gantt Chart for developing a web project. We will not focus on a specific tool, we will discuss only conceptual and fundamental approaches. It is based on twelve years of experience in the market of custom web development. During this time, I was able to launch more than 100 projects. For the last three years I have been managing production at the interactive agency AGIMA.
Who is the article for?
The article will be interesting to project managers and everyone who is somehow involved in the preparation and coordination of schedules for the development, organization of the production processes of web applications and interaction with a client or business customer.
Disclaimer
This article is not a panacea, but only a purely personal opinion of the author ( Eugene Lobanov , Executive Director of AGIMA ). The critical chain method is often effective for project planning, but in this article we will not touch on it and conduct any comparative analyzes.
What are time plans for?
Time plans are needed for the correct planning of the load and the proper management of the expectations of the business customer.
Before starting any task or project in production, you should have timing agreed with the team and the business customer.
In addition to managing the expectations of the business customer and your team, the time plan is very significant from a moral point of view. I believe that if the project manager does not have a clear plan of action with intermediate control points before the start of work, then such a project is very likely to be aimed at failure.
Often used two time plans - external and internal:
- internal is discussed only with the team and includes planned risks from the list of obvious risks at the time of project evaluation;
- An external time plan is discussed with both the team and the business customer; in addition to obvious risks, it includes deviations in terms of time based on projected risks for the entire period of work on the project.
Time plans are usually presented in the form of a Gantt chart .
Let's consider what basic actions need to be performed in order to bring our time plan closer to realism, that is, to ideal.
As much as possible to detail the project at an assessment stage
An important and one of the most fundamental rules when planning a project is to remember that 20 hours per task is a lot. Such a task cannot be controlled in all the nuances and managed to be quickly returned to the temporary channel of the project (it is very difficult to minimize the implicit risks at the time of the task assessment, usually these risks become known at the time of the deadline or the day before it).
Therefore, it is important to put all tasks on the specialist’s working day (in our company, this is 6 hours of effective time; more details can be found in my article in the “work processes” section). Such tasks are easiest to control and influence, leaving them in the temporary channel of the project.
If the task is estimated at more than 6-8 hours and does not have intermediate results for detailing, then it is necessary to determine the criteria for fixing progress.
Set the current production calendar, check all exceptions, set a six-hour work day
Many people forget about production calendars when building schedules. In addition to the "standard" weekend, there are holidays "floating" from year to year, replacing them with working days, etc.
Your time plan will be irrelevant if you do not use a real production calendar.
As a rule, to add a production calendar, you need to use the exceptions in the calendar settings of the tool with which you create a Gantt chart.

Create all the necessary stages of the project. All activities (tasks) are entered inside the stages
It is very important to make the correct grouping for activities in our time plan. If the diagram is simple, then just group by project stages, for example:
- analytics,
- design,
- design,
- layout,
- development,
- testing,
- implementation.
But if the project is complex, then you have to apply a deeper grouping of activities - it helps a lot when filtering and orienting according to a complex Gantt chart. For example, I like to group by components, within the stages of a project, etc.
Put all activities on the chart
Obviously, the more detailed the business tasks for specific activities, the easier and more accurate we will be able to control the development process.
In addition to the main activities, do not forget to enter:
- iteration of edits according to the contract (if we are talking about custom development);
- time for iteration approval by the business owner;
- time for corrections in accordance with feedback and debugging in accordance with the contract (if we are talking about custom development);
- 1-2 hours for unaccounted tasks for each activity;
- primary content creation;
- Filling content;
- testing in production;
- business testing;
- implementation.
Map risk
You need to take the risk list template used for your type of project (often its use is limited to the scope of your organization).
Each risk has two main parameters regarding the project:
- The likelihood of its occurrence in the environment of the project.
- The degree of influence of risk on the course of the project.
You have to determine both parameters for each risk from the list. Next, you need to filter the risks by their real impact on the project - the easiest way to do this is by using a risk map.
When all the obvious risks for the project are identified, it is necessary to take their minimization into account when constructing the time plan on the Gantt chart.
I share three main ways to minimize the obvious risks that affect the main time and budget characteristics of the project:
- duplication of resources;
- minimization of functionality relative to the cost of development;
- the definition of “points of no return” with respect to the activities of third parties in the form of a milestone based on a calendar date.
Three risk management scenarios can be built: negative, normal, and positive. It is more convenient to look at all three scenarios of the project development on the Gantt chart.
Enter all the control points for the provision of information from the owner of the business or customer
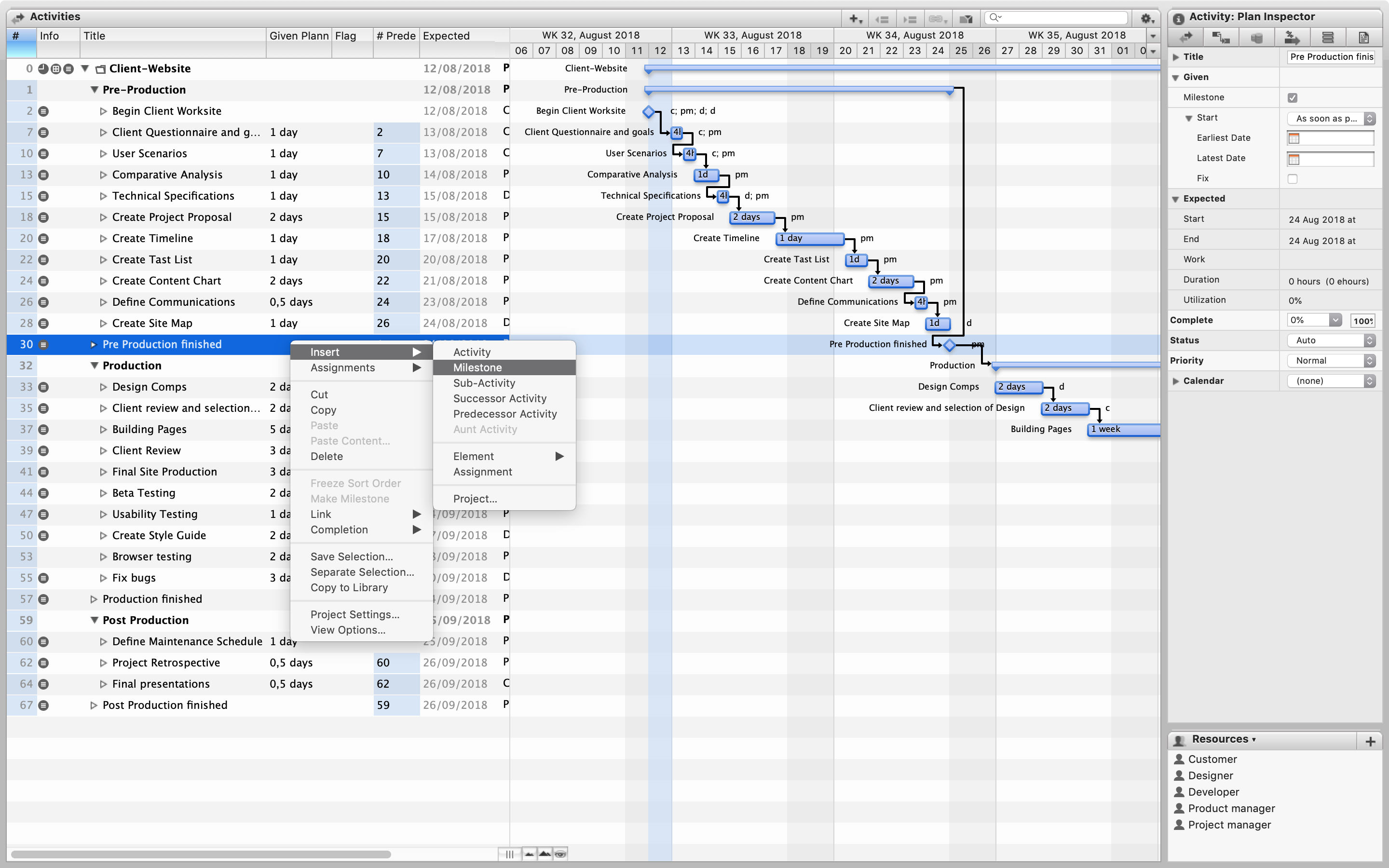
It is important not to forget:
- specifications;
- stubs or work services;
- brand book;
- all the necessary content for implementation;
- closing works by acts (if we are talking about custom development);
- signing of key interim documents;
- prepayment (if we are talking about custom development);
- other formal obligations.
Enter all resources (including time of specialists / customer employees)
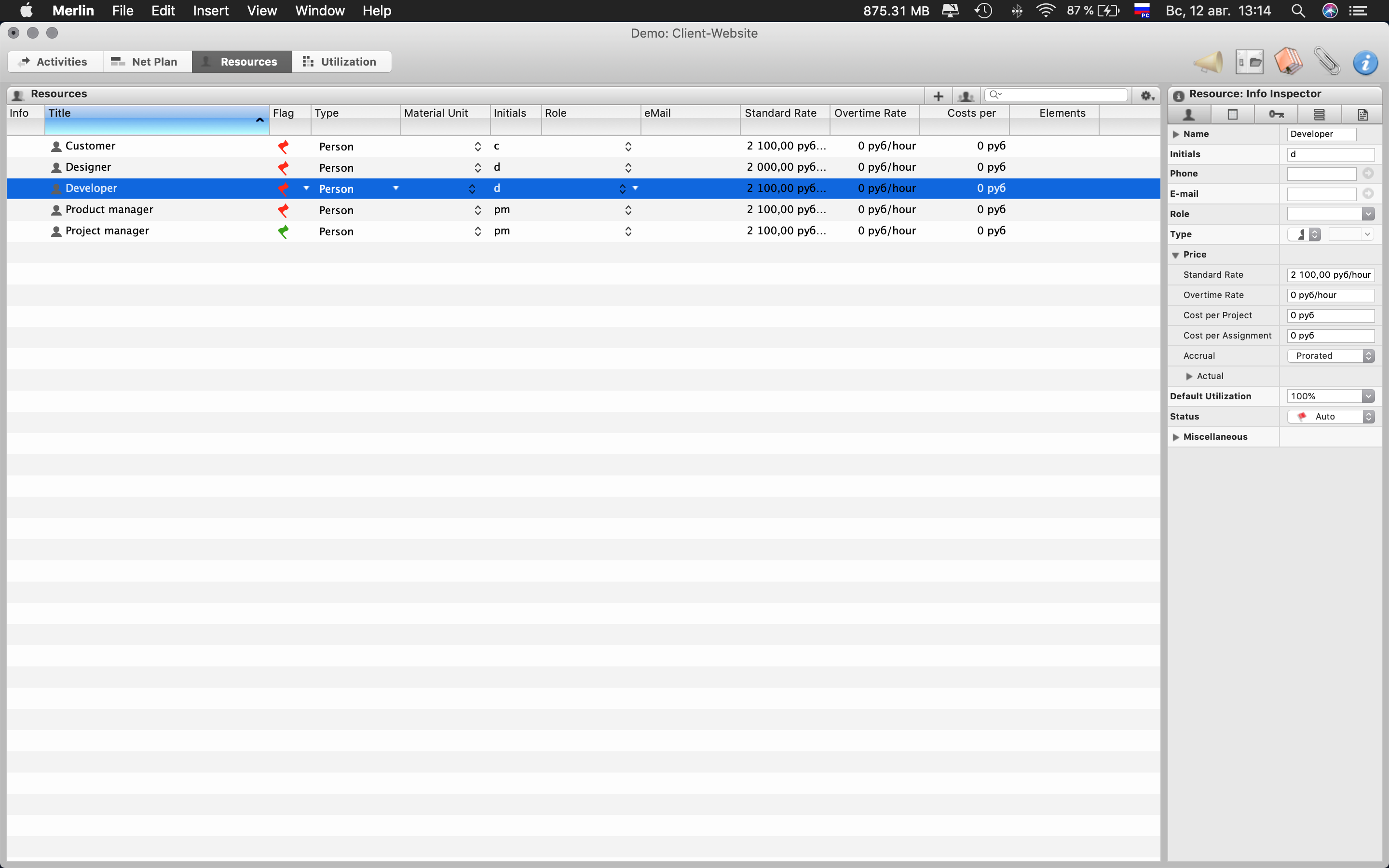
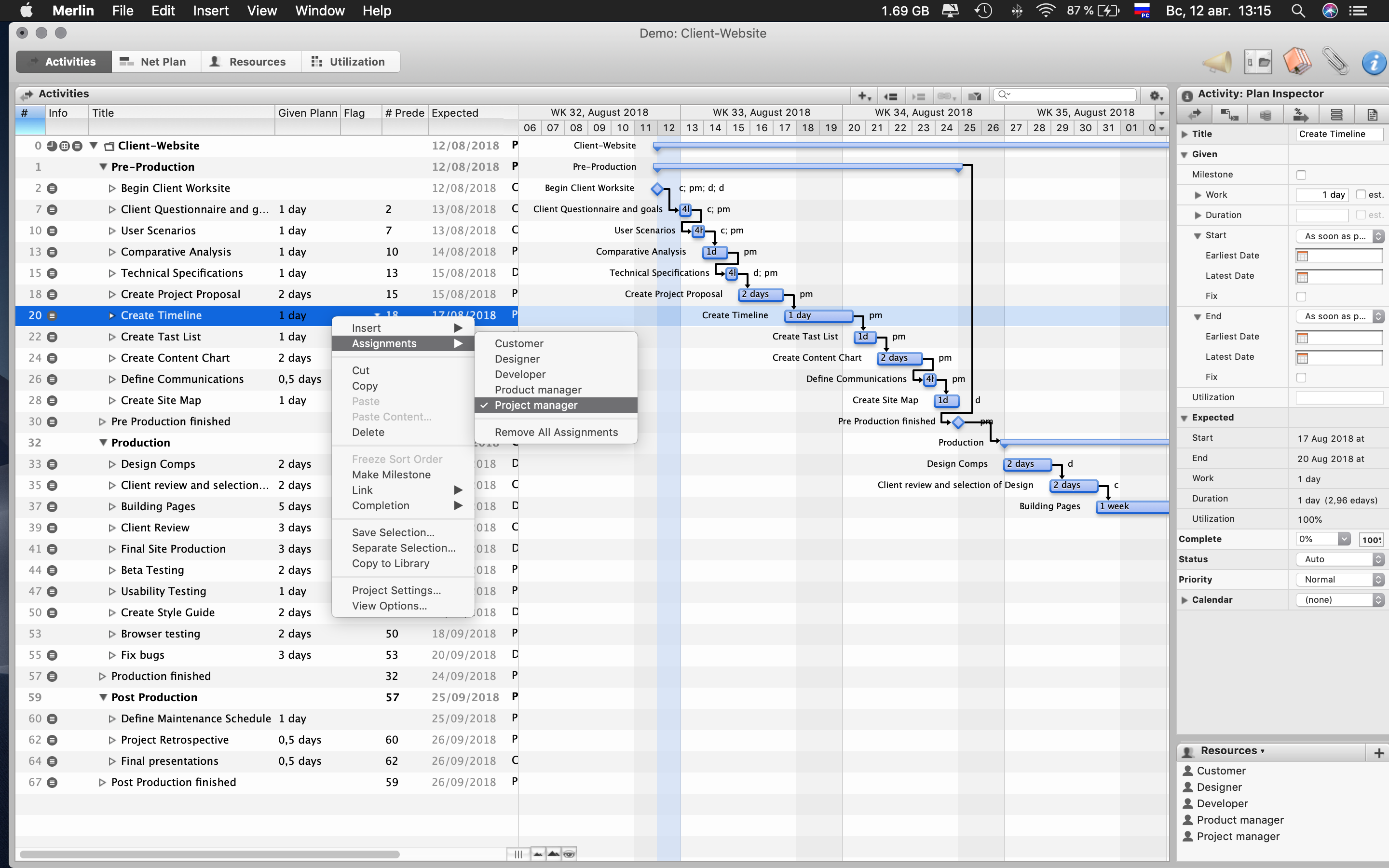
This will allow you to understand the peak points of the maximum time intersection of the same specialist. Thus, you will see how many development threads can be launched and tested in parallel.
Additionally, you can enter the cost of resources and peak budgets, making a more accurate forecast for the cost of developing the project.
Indicate critical path
After minimizing the risks in the diagram and solving all the critical intersection points of resources, we were able to get the critical path of the project.
Essentially, the minimum project path will match your internal timing. In which we have already taken into account:
- working hours of specialists;
- obvious risks that may occur and the time required to resolve them;
- loading specialists with a normal distribution of working time (excluding overtime).
What's next

Subsequently, from the internal time plan, we can do the external one, eliminating obvious risks, but adding deviations in terms of time based on projected risks for the entire period of work on the project.
And yet, the Gantt chart is just a tool. Not a goal, but a means. If you know how to deal with risks and changing requirements, then the Gantt chart, together with the roadmap , is one of the most effective tools for planning an entire project or development iterations.
It is such a time plan that will at least somehow display the really necessary time for the implementation of the project. By the way, to calculate deviations in terms of time based on projected risks, you can often use the combustion chart ( Burn Down Chart) I’ll tell you in the next article about the parameters by which it can be built, in addition to the primitive “burning features”, and how to collect statistics about deviations. Stay tuned ...
