Sending python packages to ppa without "life pain"
 After the post about watching serials , the desire came to add subliminal to download subtitles. Seeing its dependencies , of which only two packages are present in the repository, and those are not suitable versions. I realized that life is a pain and I have to create five debian / control, make five changelogs and create 20 tasks in jenkins.
After the post about watching serials , the desire came to add subliminal to download subtitles. Seeing its dependencies , of which only two packages are present in the repository, and those are not suitable versions. I realized that life is a pain and I have to create five debian / control, make five changelogs and create 20 tasks in jenkins. But why spend the whole two hours on all this if you can spend just a few days automating this process. The result was pytoppa , it:
- generates a changelog from the history between version changes in setup.py;
- automatically adds required dependencies;
- has a simple config in yaml.
Installation
Ubuntu
In ubuntu, a package can be delivered from ppa:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:nvbn-rm/ppa
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install pytoppa
Other distros
You need to manually install
dh-makeand cdbs, and after that put pytoppa through pip:pip install pytoppa
Using
In the root of the repository with the project you need to create .pytoppa.yml, its format:
section: секция # по умолчанию python, можно не указывать
dependencies:
- зависимость-1
- зависимость-2
releases:
- релиз-1
- релиз-2
For example, for the series_list application:
section: net
dependencies:
- python-requests
- python-beautifulsoup
- python-gevent
- python-decorator
- python-libtorrent
- python-pyside
- subliminal
releases:
- saucy
- precise
- quantal
- raring
And run:
pytoppa ключ-зарегистрированный-на-launchpad ppa
For example, I run:
pytoppa 'Vladimir Iakovlev ' 'ppa:nvbn-rm/ppa'
How does it work
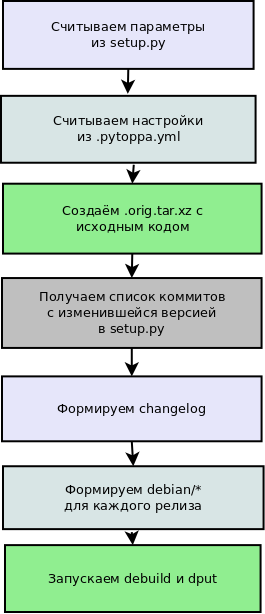
Reading the parameters from setup.py turned out to be a little non-trivial. The easiest way to replace it turned out
setuptools.setup, and distutils.core.setupon his method, simply save the parameters. And the formation of changelog , for him it was necessary:
- Get all the commits in which setup.py is present
- for each of the commits, copy the repository to a temporary folder and switch to the commit. Initially, the application passed only by commits, where setup.py changed, but often the version is imported from another file;
- read version from setup.py;
- to take changes from the commit log between different versions.
The rest of the steps are just copying or running commands.
References
github project ;
ppa with the project .
