Programming as a new kind of human activity
“A programmer must have the ability of a first-class mathematician to abstraction and logical thinking, combined with the Edison talent, to build anything from zero and ones. He must combine the accuracy of an accountant with the insight of a scout, the imagination of the author of detective novels and the sober practicality of an economist. ”Academician A.P. Ershov

Foreword
There is a popular opinion: “if builders built houses in the same way as programmers write a program, the first flying woodpecker would destroy civilization.” With the submission of an Indian guru programmer Murali Krishna Chimuturi ( Murali Krishna Chemuturi ), Internet persistently attributed the authorship of this quote Gerald Weinberg ( by Gerald Weinberg ), although on a personal site Gerald is not searched. Most likely, the person who first spoke about psychology in programming has nothing to do with this statement. And that's why.
This adage is an example of a demagogic receiver. The main premise is missing here: software development is the same as building houses. This premise, by default, is implied as a reliable fact that does not require proof. The use of this trick forces an inexperienced reader to make a false conclusion that programmers, unlike builders, do not grow their hands from the right place.
Material production (processing of objects of the physical world) totals tens of thousands of years of history. A tremendous amount of knowledge of the natural sciences was accumulated along this path: mathematics, physics, chemistry, geography, geology, biology, etc.
Let the seditious thought. Software development is a new type of human activity, the history of which totals a little more than half a century. In a post I want to present my vision of the fundamental features of software development that distinguish it from material production and the consequences that arise from them.
Features and their consequences
Feature # 1. Programming - Intellectual Activity
Simply put, the path from the idea of a new building, bridge, car or rocket to its implementation is as follows: NIR-OKR-Zavod. At the top of this pyramid are industry research institutes that produce ideas and design new products. On the second floor of the pyramid, designers work in design bureaus, whose task is to implement a new project in the drawings of parts, material specifications, manufacturing and assembly technologies. At the lower level are production facilities - plants in which engineers and workers embody these drawings, specifications and technologies “in iron”.What programmers produce is immaterial - this is brainware, the result of the collective thinking process of the project team, materialized in one of the programming languages.
Programming guru F. Brooks wrote in 1975: “A programmer, like a poet, works almost directly with pure thought. He builds his castles in and out of the air, creating with the power of imagination. It is difficult to find other material used in the work, which is just as flexible, easy to polish or process, and available to realize grandiose designs. ”
If we draw an analogy, then programmers work exclusively at the top of the described pyramid. Programming is design and design only. The role of the design bureau for a software project is played by the compiler and program collector. And the programmer's analogue of the plant, which translates design documentation into a product accessible to the consumer, is the computer complex on which the created program is executed.
Corollary # 1. The performance of programmers with the same experience will still be tenfold different.
Brooks talked about 10 times the difference in performance. Robert Glass referred to experiments that demonstrated a 27-fold variation in performance.
No one knows what place a person thinks and how he makes this place. In any other industry, a specialist in the scientific organization of labor was immediately placed behind the back of the Stakhanovite worker, who would draw up a map of the progressive technological process and establish new production standards. And what will the specialist see from behind the programmer? Habrahabr.ru?
Corollary # 2. The statistics of failed software development projects are unlikely to change in the foreseeable future.
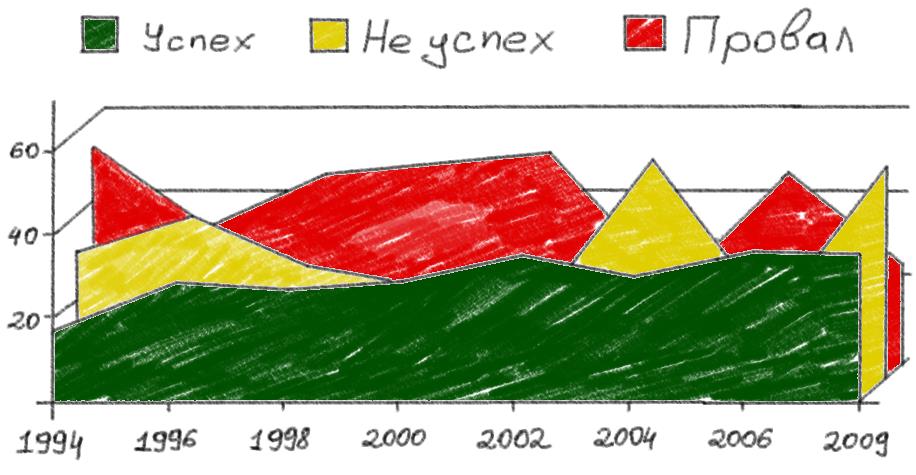
Let's recall how many research projects remained on paper before reaching the OCD, and how many more OCD ended with the closure of the topic. I believe that the percentage of innovations that have reached production of the total number of projects completed in industry research institutes will be comparable with the percentage of successful software projects. And this despite the fact that scientists at the research institute rely on fairly well-studied laws of mathematics, physics and chemistry, and in programming similar laws have not yet been discovered. And this is the second feature of programming.
Feature # 2. Lack of laws
Software development, IMHO, is mistakenly classified as engineering. Engineering is where the achievements of science and technology are applied, the laws of the natural sciences are used to solve specific problems and achieve goals.Newton’s laws have not yet been discovered in software development, there are no Lagrange equations, or at least a compromise, which would help us design and prove the correct architecture of the new non-trivial software system. The work of mathematicians in the field of logic, information theory, numerical methods, relational algebra, graph theory and some other disciplines does not cover the complexity of industrial programming problems.
Even prominent programmers will not take the liberty of claiming that the architecture of the new software system is successful. Although programming has already accumulated a certain experience of failures, which may allow the sophisticated programmer to see antipatterns in the architecture of the new system - sources of serious future problems. But no more than that.
The current state of Software Engineering resembles a large cookbook with numerous descriptions of recipes for once successfully prepared dishes from ingredients that will never be in the future. Tomorrow the new system will be other computers, technologies, programming languages, tools and surrounding software, new problems of interaction with which will have to be solved.
Corollary # 3. Programming is a craft.
And since this is a craft, a person who has learned to write programs in C ++ will also be far from a professional, as a third-grade student of high school who has learned to write in Russian from A.S. Pushkin or F.M. Dostoevsky. The path to mastery in the craft lies only through experience. You cannot learn how to develop software products by reading books.
Corollary # 4. Freedom is a prerequisite for the work of a programmer.
Due to the lack of open laws, most solutions to programming problems are found by trial and error. Programmers should have the right to make a mistake. This is a normal attribute of creative search. Learn from mistakes. The smart one is not the one who does not make mistakes, but the one who does not repeat them.
One of the elements of freedom is the lack of tight deadlines for the task. For professional managers, the lack of tight deadlines may sound like nonsense, but in creative activity this is one of the essential elements. It makes no sense to force programmers to work more, to arrange overtime rush jobs and subbotniks. Work more, it doesn’t mean at all - work more productively. Rather, the opposite. Excessive pressure and fuss lead to ill-conceived decisions and numerous subsequent processing.
Feature # 3.Lack of visualization tools
For software products have not yet come up with adequate visualization tools. Brookes spoke about this almost 40 years ago. Therefore, software developers are often likened to blind monks from a Buddhist parable .
Corollary # 5. The need for constant communication of development participants.
From experience. On average, each participant in a software development project takes 50% of the working time for all kinds of conversations. We call it “synchronization of mental models”. It is known that words, timbre and intonation transmit only slightly less than half of the information. Therefore, twice as much time is spent on transmitting information to a remote team member. The industry-specific COCOMO II methodology teaches that if a project is carried out by a distributed team, then its complexity should be multiplied by 1.5.
Corollary # 6. EQ is more important than IQ.
The ability to dialogue and effective interaction, the ability to reason, ask questions, analyze answers, seek a mutually beneficial solution in conflict situations, the mandatory quality of a team fighter. Creativity and effectiveness of a person is 80% dependent on the level of his emotional intelligence (EQ) and the activity of the right hemisphere, which is responsible for determination, will, empathy, intuition, and the ability to make heuristic judgments.
If you have insufficient EQ, do not despair. Unlike IQ, which is formed in early youth and then remains virtually unchanged, EQ can be increased throughout life.
Conclusion
For collective programmatic creativity, an analogy with the creation of a feature film or a theatrical performance is more likely to be appropriate. I believe that the number of failed projects in these areas is no less than in programming. God forbid, if at least a third of the films do not “go to the shelves” after the first screening.
And one more thing that makes software projects related to cinema. The presence of even the most stellar actors does not ensure the success of the film. Only a talented director is able to organize and inspire actors to create a masterpiece, discover new stars. And talented directors, as well as talented managers of software projects, unfortunately, are not as many as we would like.
