The most antimagnetic watch in the world
The other day I attended an interesting presentation - Omega presented “the most antimagnetic watch in the world”: “for the first time in the history of the watch industry, a mechanism has been developed that can completely solve the problem of the effect of magnetic fields on the movement of a mechanical watch.” Honestly, until recently, I didn’t even think about why the watch needs anti-magnetic protection at all. Of course, everyone knows that if you bring a magnet to a mechanical watch, they will stop and forever, but it is unlikely that anyone will consciously deal with the damage of their watches, knowing about such a fact. But it is impossible to completely avoid the effect of magnets on the watch.
I don’t want to bore the details of the presentation, I’ll just share what I managed to learn about the effect of magnets on the watch, and a little about those “most anti-magnetic watches in the world”.
Have you thought about how many magnets around us? Cover for iPad, a women's handbag with a magnetic closure, an electric razor, a refrigerator door, a mobile phone, magnetic frames in supermarkets and airports, powerful studio speakers and others. Magnets are everywhere, and every year there are more and more of them.
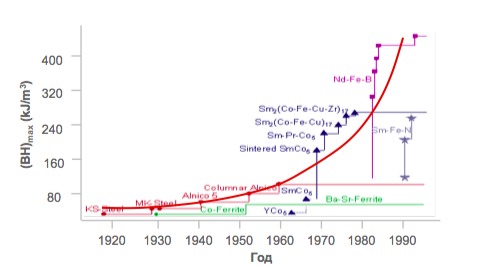

And this is one of the reasons that the reliability of modern mechanical watches, despite the efforts of manufacturers, is still not as close to absolute as we would like, because the parts of the clock mechanism are affected by magnets that surround us everywhere: at work, at home, in transport .
1. Under the influence of magnetic fields, the performance of the watch or the accuracy of movement is impaired, however, after the termination of this effect, the watch restores its characteristics. So household magnets act. If you suddenly want to refresh yourself at night and accidentally leave your watch on the refrigerator, then, of course, they will suffer from the influence of the magnet, with the help of which the refrigerator door closes, but will not fail at all.
2. Under the influence of magnetic fields, with increasing magnetic field strength (magnetic induction), the watch loses its performance, and they need demagnetization.
Strong magnetic fields arise from high currents: for example, during a short circuit or “lighting” a car. Moreover, you can magnetize the clock even when the call is triggered on your mobile phone: the current path in the phone’s battery is a small loop in which magnetic fields form. During a call, the current consumption from the battery can reach 10 amperes. The distance from the watch to the mobile is about 1 cm, and even a tension of 1 kA / m is enough for magnetization. Thus, it is enough to spend hours near any radiation object - they will remember this for a long time.

The problem of magnetization of watches is at the very heart of the watch movement, where there are two springs: a balance spring (hair spring) and a clockwork spring that provides the mechanism with energy. It is the hair spring that is attached to the pendulum that determines how often this pendulum swings. For most of the history of watchmaking, the balance spring was made of blued steel, and it is known to be magnetized like any other steel. When it is magnetized, the coils of the spring are attracted to each other, as a result of which the clock mechanism begins to “go crazy."
And although the production of most modern watches uses antimagnetic materials, they do not completely get rid of screening at the household level, providing protection only from short-term exposure to magnetic fields. So the problem of magnetization of watches remains very urgent, especially for those people of certain professions. Just this problem was solved by the engineers of Asulab, Nivarox and ETA, members of the Swatch Group.
In 2008, they created a Si14 silicon balancer spring. Why silicon? Because this element has extraordinary stability and resistance to magnetic fields.
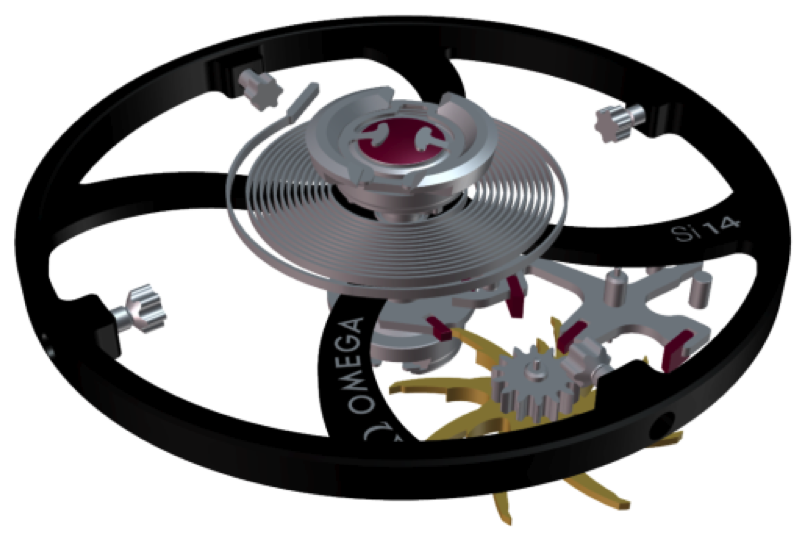
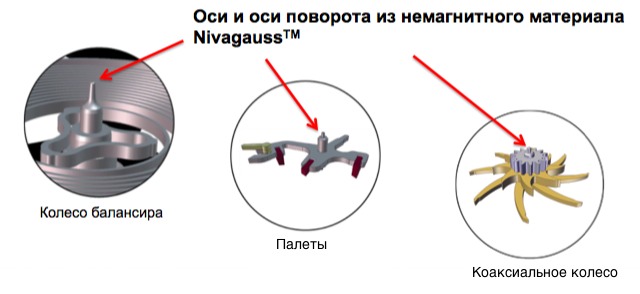
This was followed by the creation of the axles of the balancer wheel, pallets, coaxial wheels and rotation axes from the patented non-magnetic material Nivagauss ™ (an alloy of the combination of iron, neodymium and boron). Steel for coaxial mechanism plates has also been replaced with non-magnetic materials; shock absorbers spring made of amorphous metal. As a result, a completely new coaxial caliber 8508 mechanism was developed, completely made of iron-free materials.
So the Seamaster Aqua Terra watch was born, the revolutionary feature of which is the ability to withstand the influence of a magnetic field above 1.5 Tesla (15,000 gauss or 1,200,000 A / m). And this is 15 times ahead of all previous antimagnetic mechanisms.

Due to the fact that this watch does not have a traditional protective container, the watch does not look bulky and heavy. Their back cover is completely transparent, so that the mechanism itself and its finish are visible through it. By 2014, all coaxial watches will be equipped with such an anti-magnetic mechanism.
I wonder how soon other watch manufacturers will be pulled to a given bar? And how much will such a watch be in demand?
I don’t want to bore the details of the presentation, I’ll just share what I managed to learn about the effect of magnets on the watch, and a little about those “most anti-magnetic watches in the world”.
Have you thought about how many magnets around us? Cover for iPad, a women's handbag with a magnetic closure, an electric razor, a refrigerator door, a mobile phone, magnetic frames in supermarkets and airports, powerful studio speakers and others. Magnets are everywhere, and every year there are more and more of them.
Magnetic energy density evolution


And this is one of the reasons that the reliability of modern mechanical watches, despite the efforts of manufacturers, is still not as close to absolute as we would like, because the parts of the clock mechanism are affected by magnets that surround us everywhere: at work, at home, in transport .
Under the influence of magnetic fields on the watch, two scenarios can be realized:
1. Under the influence of magnetic fields, the performance of the watch or the accuracy of movement is impaired, however, after the termination of this effect, the watch restores its characteristics. So household magnets act. If you suddenly want to refresh yourself at night and accidentally leave your watch on the refrigerator, then, of course, they will suffer from the influence of the magnet, with the help of which the refrigerator door closes, but will not fail at all.
2. Under the influence of magnetic fields, with increasing magnetic field strength (magnetic induction), the watch loses its performance, and they need demagnetization.
Strong magnetic fields arise from high currents: for example, during a short circuit or “lighting” a car. Moreover, you can magnetize the clock even when the call is triggered on your mobile phone: the current path in the phone’s battery is a small loop in which magnetic fields form. During a call, the current consumption from the battery can reach 10 amperes. The distance from the watch to the mobile is about 1 cm, and even a tension of 1 kA / m is enough for magnetization. Thus, it is enough to spend hours near any radiation object - they will remember this for a long time.

The problem of magnetization of watches is at the very heart of the watch movement, where there are two springs: a balance spring (hair spring) and a clockwork spring that provides the mechanism with energy. It is the hair spring that is attached to the pendulum that determines how often this pendulum swings. For most of the history of watchmaking, the balance spring was made of blued steel, and it is known to be magnetized like any other steel. When it is magnetized, the coils of the spring are attracted to each other, as a result of which the clock mechanism begins to “go crazy."
And although the production of most modern watches uses antimagnetic materials, they do not completely get rid of screening at the household level, providing protection only from short-term exposure to magnetic fields. So the problem of magnetization of watches remains very urgent, especially for those people of certain professions. Just this problem was solved by the engineers of Asulab, Nivarox and ETA, members of the Swatch Group.
In 2008, they created a Si14 silicon balancer spring. Why silicon? Because this element has extraordinary stability and resistance to magnetic fields.

This was followed by the creation of the axles of the balancer wheel, pallets, coaxial wheels and rotation axes from the patented non-magnetic material Nivagauss ™ (an alloy of the combination of iron, neodymium and boron). Steel for coaxial mechanism plates has also been replaced with non-magnetic materials; shock absorbers spring made of amorphous metal. As a result, a completely new coaxial caliber 8508 mechanism was developed, completely made of iron-free materials.

So the Seamaster Aqua Terra watch was born, the revolutionary feature of which is the ability to withstand the influence of a magnetic field above 1.5 Tesla (15,000 gauss or 1,200,000 A / m). And this is 15 times ahead of all previous antimagnetic mechanisms.

Due to the fact that this watch does not have a traditional protective container, the watch does not look bulky and heavy. Their back cover is completely transparent, so that the mechanism itself and its finish are visible through it. By 2014, all coaxial watches will be equipped with such an anti-magnetic mechanism.
I wonder how soon other watch manufacturers will be pulled to a given bar? And how much will such a watch be in demand?
