Cloud backup with vSphere Replication

For the vast majority of companies, having two or more of their own sites is still an inadmissible luxury. And what to do with ensuring the continuity of the provision of IT services in this situation? The conclusion is obvious: if for some reason it is not possible to use the public cloud as the main platform - it can be successfully used as a backup!
With the development of cloud technologies, an increasing number of organizations are ready to abandon their own infrastructure in favor of highly accessible services for hosting virtual machines in a public cloud .
However, there remain situations due to the specifics of the company, the presence of projects already completed to build a private cloud, specific requirements for performance, security, etc., which may be temporary, but do not allow you to use the public cloud to host your IT services.
Is there a technical possibility to place a backup site in a public cloud? What difficulties will you encounter when implementing the project? Such questions are increasingly arising both in the vastness of the network, and among potential consumers of cloud services. Service providers add to this questions about multi-tenancy, about resource efficiency, about compatibility, and about network infrastructure requirements.
Classic DRS Solutions
Classic solutions for creating backup sites or Data Recovery sites have always struck the layman's imagination with their complexity. First of all, this concerned data replication, which was supposed to be carried out by means of storage, which, in turn:
- greatly increased the bar for storage capabilities,
- imposed restrictions on the choice of storage manufacturers to ensure compatibility,
- required the purchase of expensive licenses.
And the software itself for managing backup and recovery had (and has at the moment) a significant cost. A striking example of such a solution is VMware Site Recovery Manager. However, technology does not stand still, and increasing competition in the market is forcing manufacturers to open up new opportunities for solving old problems.
New Approach - Hypervisor Replication
One of these new features was VMware vSphere Replication technology , which debuted as part of VMware Site Recovery Manager version 5.0, and then was included in the vSphere 5.1 virtualization platform, free of charge and in almost all editions!
This technology provided the ability to replicate data between sites at the hypervisor level , without using special storage capabilities. And almost immediately, the interest of companies with their own virtual infrastructure based on vSphere arose in the potential opportunity to organize a backup of their information systems with "little blood."
But the decoupling from storage did not only reduce the cost and simplification of replication systems - it provided an important opportunity for replication between "inconsistent" storage systems and independently managed infrastructures. And, in fact, it paved the way for the simple and effective implementation of a backup site in the cloud.
VSphere Replication Technology
VSphere Replication technology is very simple from a user perspective. Changes made to virtual machine disks on the main site are monitored by the hypervisor, and then, in accordance with the specified recovery point objective (RPO) policies, they are periodically synchronized with the backup site. In this case, synchronization is controlled by service virtual machines of the VR Appliance located in both sites, and data between sites is transferred from the hypervisor on the main site to the VR Appliance on the backup one.

At the same time, this technology is available both to ordinary users of the vSphere platform for organizing manual data replication and as part of the Site Recovery Manager, which allows flexible control of the failover and giveback process, with the corresponding automated network reconfiguration, periodic non-destructive testing, etc. .P.
Using vSphere Replication in practice
When another client contacted our company with a proposal to organize a backup site, less than a month has passed since the release of vSphere 5.1. But almost immediately, such replication technology became the main option considered in this project.
Using vSphere as a virtualization platform on both sides, differences in the storage systems used - all this determined the choice of replication technology, and the absence of the business need to implement automatic failover allowed to do without additional costs for using SRM.
The first stage of the project was the formation and implementation of a network scheme that provides secure and fast transfer of replicated data via dedicated channels, and in case of failover, a painless transition of users to work with a backup site.
The organization of the channels was carried out on the basis of the provider, which already provided the client with the services of combining the branches on the basis of the “virtual switch”, to which a new link to the service provider was added, to ensure routing and “embedding” of the backup site in the existing customer infrastructure.
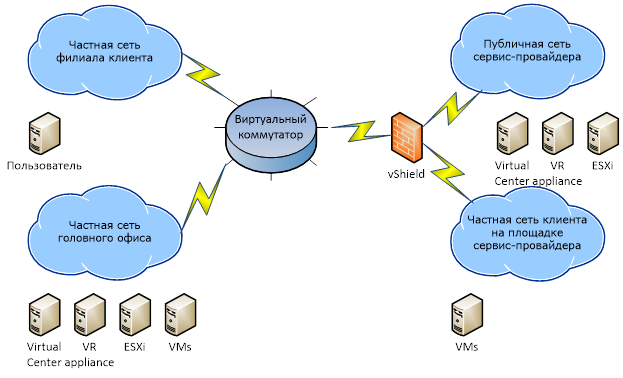
When replication is functioning (direct or reverse) in such a scheme, traffic using routers is sent to the service provider’s site or to the client’s head office, in case of failover, the gateways to the client’s server networks in which the virtual machines are located change at the client’s sites. Thus, the entire infrastructure appears to be working on the site of the service provider without reconfiguring the network in virtual machines.
The second stage of the project was the configuration and testing of vSphere Replication itself in relation to this task. I must say that the technology, which has survived essentially its second release, successfully functions “out of the box”, in standard configurations. However, the specifics of this implementation — independent infrastructures on both sides of the replication link, the need to differentiate user rights in the service provider's infrastructure — required considerable time to tinker with the settings and even make some changes to the infrastructure that made it possible for the previously unused technology to function.
During testing, attention was paid not only to functional testing of the circuit, but also to stress testing on real data - it was required to ensure compliance with RPO at the selected channel width. As a result, it was decided to expand the channel previously configured on 100 Mbit to 1 Gbit to provide a margin for replication speed during regular maintenance operations on client servers - for example, re-indexing and rebuilding a database that generate an increased volume of changes.
The third and final stage of the project was the initial replication of more than 10 TB of data to the site of the service provider and the launch of the system in industrial use. At the same time, to conduct periodic testing of the possibility of restoring the infrastructure, an additional routing scheme was created in which only an artificial group of users works with the infrastructure raised in the private network located at the service provider.
Conclusion
Is a backup site in the cloud currently possible ?
The fundamental answer is yes, it is possible.
So far, clients have to reckon with some assumptions - the incomplete correspondence of such solutions to the “cloud” ideology — for example, insufficient elasticity and the need to use the service provider support service instead of self-service interfaces in some cases. Service providers, in turn, have to reckon with the limited applicability of technologies in multi-tenant environments, while there are still limitations on the compatibility of various virtualization platforms.
However, the world does not stand still, and the first project is usually followed by new ones, and with the support of vendors, I am sure that the practice of organizing backup sites in the cloud will soon become widespread.
