Function code integrity control
In the process of developing a multicomponent system for automated testing of a security scanner, we were faced with the problem of monitoring the integrity of the code of individual test functions and conducting revisions.
The number of written functional tests that the system launches has already exceeded several thousand and continues to increase. In our case, one functional test is one function. With this development method, after assigning the status of Ready to the test, it will be forgotten for a long time.
Meanwhile, in the process of developing other test functions, refactoring often becomes necessary. Moreover, this process, due to the carelessness of the tester-automation engineer, can also affect ready-made debugged tests.
Refactoring any program in itself, even if it affects many modules and functions, is a common and quite useful thing. However, with regard to test functions, this is not always the case. Each test is designed to implement a specific verification algorithm. The verification logic that the author laid down may be violated even with minor changes to the test code.
To avoid the negative consequences of such situations, we have developed a mechanism for revising the code of test functions, with which you can simultaneously control the integrity of functions and duplicate their code.
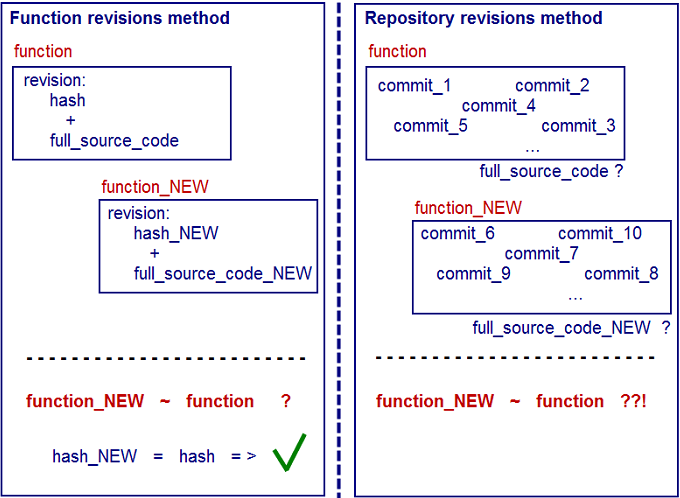
For each function, a revision, a set of a hash and a function code can be defined:
All critical functions can be added to the revision dictionary:
For us, for example, all functions with already developed tests are critical. All revisions can be stored in a special text file (revision file), which stores a list with the date of the last revision and the revision dictionary:
Before the next release of the testing system, the specialist responsible for revisions can track changes in the function code and, if necessary, restore the code of old tests in a short time, simply copying them from the revision.
Of course, there are alternative solutions to the problem, for example, code inspections and the use of tools in repositories (for example, GIT, SVN). However, inspections are useless if you make automatic changes to hundreds of tests, and tracking changes in the code using the repository tools after a few merges is a laborious and lengthy process. In addition, unit tests are usually not written to test functions, however, the need to control the quality and immutability of functions remains - this mechanism can also be solved by the revision mechanism.
To implement the idea described above, a small module FileRevision.py was written in Python. The Revision () class available in it can be imported into your project and add revisions for the functions you need.
Having slightly modified the module, you can additionally implement, for example, compressing the revision file, although this is not so critical for small projects.
The code is available at the link .
class Revision ():
To see examples of the use of this module, you just need to run it using Python 3.2.3:
python FileRevision.py
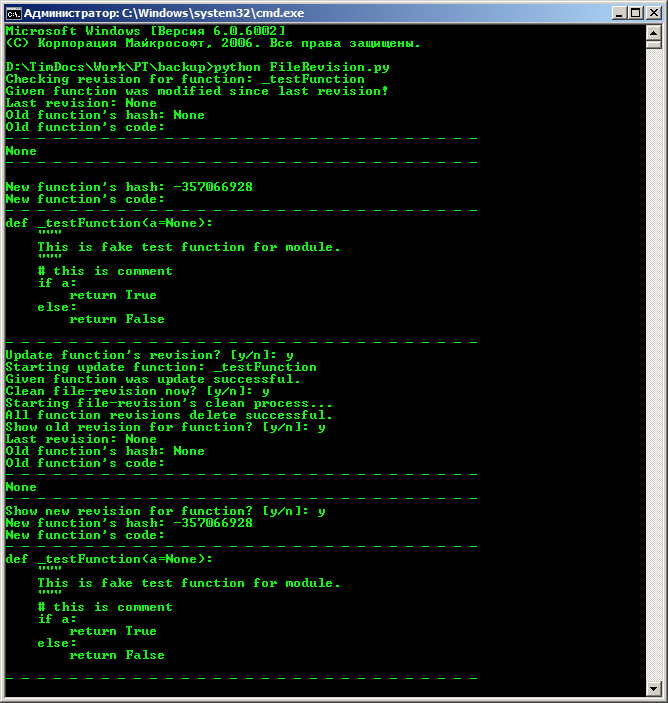
At the first start, the script will detect the absence of a revision for the fake function implemented in the example, offer to update information about it, clear the revision file, and also output information about previous and new revisions. Then, next to the .py file, a revision.txt file with revisions for examples will be created.
Thus, using our module and having an employee responsible for generating the code revision file, the degree of security of test functions will increase.
That's all for today. We look forward to your questions and suggestions in the comments. Thanks for attention!
Posted by Timur Gilmullin, Positive Technologies Automated Testing Group
The number of written functional tests that the system launches has already exceeded several thousand and continues to increase. In our case, one functional test is one function. With this development method, after assigning the status of Ready to the test, it will be forgotten for a long time.
Meanwhile, in the process of developing other test functions, refactoring often becomes necessary. Moreover, this process, due to the carelessness of the tester-automation engineer, can also affect ready-made debugged tests.
Refactoring any program in itself, even if it affects many modules and functions, is a common and quite useful thing. However, with regard to test functions, this is not always the case. Each test is designed to implement a specific verification algorithm. The verification logic that the author laid down may be violated even with minor changes to the test code.
To avoid the negative consequences of such situations, we have developed a mechanism for revising the code of test functions, with which you can simultaneously control the integrity of functions and duplicate their code.

Mechanism
For each function, a revision, a set of a hash and a function code can be defined:
(func_hash, func_source)
All critical functions can be added to the revision dictionary:
{"funcName1": (funcName1_hash, funcName1_source),
"funcName2": (funcName2_hash, funcName2_source), ...}
For us, for example, all functions with already developed tests are critical. All revisions can be stored in a special text file (revision file), which stores a list with the date of the last revision and the revision dictionary:
[revision's last date-n-time, {revisions}]
Before the next release of the testing system, the specialist responsible for revisions can track changes in the function code and, if necessary, restore the code of old tests in a short time, simply copying them from the revision.
Of course, there are alternative solutions to the problem, for example, code inspections and the use of tools in repositories (for example, GIT, SVN). However, inspections are useless if you make automatic changes to hundreds of tests, and tracking changes in the code using the repository tools after a few merges is a laborious and lengthy process. In addition, unit tests are usually not written to test functions, however, the need to control the quality and immutability of functions remains - this mechanism can also be solved by the revision mechanism.
The code
To implement the idea described above, a small module FileRevision.py was written in Python. The Revision () class available in it can be imported into your project and add revisions for the functions you need.
Having slightly modified the module, you can additionally implement, for example, compressing the revision file, although this is not so critical for small projects.
The code is available at the link .
Module implementation
class Revision ():
__init __ () # Parameter initialization
def __init__(self, fileRevision='revision.txt'):
self.fileRevision = fileRevision
self.mainRevision = self._ReadFromFile(self.fileRevision) # get main revision first
_ReadFromFile () # Getting revisions from a file
def _ReadFromFile(self, file=None):
"""
Helper function that parse and return revision from file.
"""
revision = [None, {}]
if file == None:
file = self.fileRevision
try:
if os.path.exists(file) and os.path.isfile(file):
with open(file) as fH:
revision = eval(fH.read())
except:
traceback.print_exc()
finally:
return revision
_WriteToFile () # Write revisions to a file.
def _WriteToFile(self, revision=[None, {}], file=None):
"""
Helper procedure than trying to write given revision to file.
"""
status = False
if file == None:
file = self.fileRevision
try:
with open(file, "w") as fH:
fH.write(str(revision))
status = True
except:
traceback.print_exc()
finally:
return status
_GetOld () # Get the previous revision for a function.
def _GetOld(self, func=None):
"""
Get old revision for given function and return tuple: (old_hash, old_source).
"""
funcHashOld = None # old code is None if function not exist in previous revision
funcSourceOld = None # old hash is None if function not exist in previous revision
try:
if func.__name__ in self.mainRevision[1]:
funcHashOld = self.mainRevision[1][func.__name__][0] # field with old hash of function
funcSourceOld = self.mainRevision[1][func.__name__][1] # field with old code of function
except:
traceback.print_exc()
finally:
return (funcHashOld, funcSourceOld)
_GetNew () # Get a new revision for a function.
def _GetNew(self, func=None):
"""
Get new revision for given function and return tuple: (new_hash, new_source).
"""
funcSourceNew = None # if function doesn't exist, its also doesn't have code
funcHashNew = None # hash is None if function not exist
try:
funcSourceNew = inspect.getsource(func) # get function's source
funcHashNew = hash(funcSourceNew) # new hash of function
except:
traceback.print_exc()
finally:
return (funcHashNew, funcSourceNew)
_Similar () # Comparison of two revisions.
def _Similar(self, hashOld, sourceOld, hashNew, sourceNew):
"""
Checks if given params for modified then return tuple with revision's diff:
(old_revision, new_revision), otherwise return None.
"""
similar = True # old and new functions are similar, by default
if hashNew != hashOld:
if sourceOld != sourceNew:
similar = False # modified if hashes are not similar and functions not contains similar code
return similar
Update () # Update the revision for the specified function.
def Update(self, func=None):
"""
Set new revision for function.
revision = [revision date-n-time,
{"funcName1": (funcName1_hash, funcName1_source),
{"funcName2": (funcName2_hash, funcName2_source), ...}]
"""
status = False
if func:
try:
funcSourceNew = inspect.getsource(func) # get function's source
funcHashNew = hash(funcSourceNew) # new hash of function
revisionDateNew = datetime.now().strftime('%d.%m.%Y %H:%M:%S') # revision's date
funcRevisionNew = {func.__name__: [funcHashNew, funcSourceNew]} # form for function's revision
self.mainRevision[0] = revisionDateNew # set new date for main revision
self.mainRevision[1].update(funcRevisionNew) # add function's revision to main revision
if self._WriteToFile(self.mainRevision): # write main revision to file
status = True
except:
traceback.print_exc()
finally:
return status
DeleteAll () # Delete all revisions from a file.
def DeleteAll(self):
"""
Helper function that parse and return revision from file.
"""
status = False
try:
self.mainRevision = [None, {}] # clean revision
if self._WriteToFile(self.mainRevision): # write main revision to file
status = True
except:
traceback.print_exc()
finally:
return status
ShowOld () # Displays information about the previous revision for a function.
def ShowOld(self, func=None):
"""
Function return old revision for given function.
"""
funcHashOld, funcSourceOld = self._GetOld(func) # get old revision for given function
dateStr = "Last revision: " + str(self.mainRevision[0])
hashStr = "\nOld function's hash: " + str(funcHashOld)
codeStr = "\nOld function's code:\n" + "- " * 30 + "\n" + str(funcSourceOld) + "\n" + "- " * 30
oldRevision = dateStr + hashStr + codeStr
return oldRevision
ShowNew () # Display information about a new revision for a function.
def ShowNew(self, func=None):
"""
Function return old revision for given function.
"""
funcHashNew, funcSourceNew = self._GetNew(func) # get old revision for given function
hashStr = "New function's hash: " + str(funcHashNew)
codeStr = "\nNew function's code:\n" + "- " * 30 + "\n" + str(funcSourceNew) + "\n" + "- " * 30
newRevision = hashStr + codeStr
return newRevision
Diff () # Compare revisions and output diff for function if necessary.
def Diff(self, func=None):
"""
Checks if given function modified then return tuple with revision's diff:
(old_revision, new_revision), otherwise return None.
"""
funcHashOld, funcSourceOld = self._GetOld(func) # get old revision for given function
funcHashNew, funcSourceNew = self._GetNew(func) # get new revision for given function
# check old and new revisions:
if self._Similar(funcHashOld, funcSourceOld, funcHashNew, funcSourceNew):
diff = None # not difference
else:
diff = ("Last revision: " + str(self.mainRevision[0]) +
"\nOld function's hash: " + str(funcHashOld) +
"\nOld function's code:\n" + "- " * 30 + "\n" +
str(funcSourceOld) + "\n" + "- " * 30,
"\nNew function's hash: " + str(funcHashNew) +
"\nNew function's code:\n" + "- " * 30 + "\n" +
str(funcSourceNew) + "\n" + "- " * 30) # if new function not similar old function
return diff
_testFunction () # Fake function for checking module operation
def _testFunction(a=None):
"""
This is fake test function for module.
"""
# this is comment
if a:
return True
else:
return False
if __name__ == '__main__' :() # Examples of using the module when it is launched separately.
func = _testFunction # set function for review in revision
revision = Revision('revision.txt') # init revision class for using with revision.txt
# how to use this module for review revision of function:
print(MSG_CHECK, func.__name__)
funcModified = revision.Diff(func) # get function's diff as tuple (old_revision, new_revision)
if funcModified:
print(MSG_MODIFIED)
print(funcModified[0]) # old revision
print(funcModified[1]) # new revision
else:
print(MSG_NOT_MODIFIED)
# how to use this module for update revision:
action = input("Update function's revision? [y/n]: ")
if action == 'y':
print(MSG_UPDATE, func.__name__)
if revision.Update(func):
print(MSG_UPDATED)
else:
print(MSG_UPDATE_ERROR)
# how to use this module for clean file-revision:
action = input("Clean file-revision now? [y/n]: ")
if action == 'y':
print(MSG_DELETE)
if revision.DeleteAll():
print(MSG_DELETED)
else:
print(MSG_DELETE_ERROR)
# how to use this module for show old review:
action = input('Show old revision for function? [y/n]: ')
if action == 'y':
print(revision.ShowOld(func))
# how to use this module for show new review:
action = input('Show new revision for function? [y/n]: ')
if action == 'y':
print(revision.ShowNew(func))
To see examples of the use of this module, you just need to run it using Python 3.2.3:
python FileRevision.py

At the first start, the script will detect the absence of a revision for the fake function implemented in the example, offer to update information about it, clear the revision file, and also output information about previous and new revisions. Then, next to the .py file, a revision.txt file with revisions for examples will be created.
Thus, using our module and having an employee responsible for generating the code revision file, the degree of security of test functions will increase.
That's all for today. We look forward to your questions and suggestions in the comments. Thanks for attention!
Posted by Timur Gilmullin, Positive Technologies Automated Testing Group
