The Intel Core i7-8086K (Part 4)
- Transfer
Part 1 >> Part 2 >> Part 3 >> Part 4
We demonstrated our overclocking results, where we managed to achieve stable operation of the processor at a frequency of 5.1 GHz with a significant increase in voltage. However, work at a frequency of 5.1 GHz raised the working temperature dangerously high, so for our testing we went back to 5.0 GHz and again performed a series of tests at this increased speed. We also conducted some tests on the standard frequency, but with increased DRAM frequencies. We launched DRAM in our ASRock system on DDR4-3466, slightly overclocked beyond the limits indicated on its label: DDR4-3200.

On this (and the next) page, we will show the performance results of the Core i7-8086K using fast memory, as well as overclocking the processor to 5.0 GHz (with basic memory). For comparison, the results are displayed Core i7-8700K.







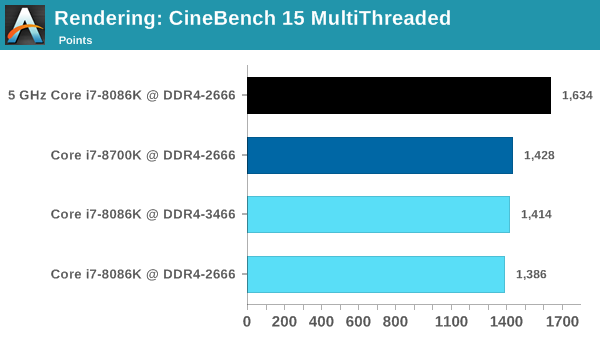




In all cases, except for single-threaded loads, overclocking 8086K to a pure 5GHz shows a very decent performance boost. You could already extrapolate these results on the basis of clock pulses, but it is customary to test theory with practice. The experiment clearly underlines the main drawback of the processor: a turbo single stream up to 5 GHz is almost useless. Very rarely will you load the system to the fullest. 8086K just screams about its desire to work at full 5GHz to make the most of its capabilities.
We managed to achieve stable operation of the processor at a frequency of 5.1 GHz with a significant increase in voltage. However, work at a frequency of 5.1 GHz raised the working temperature dangerously high, so for our testing we went back to 5.0 GHz and again performed a series of tests at this increased speed. We also conducted some tests on the standard frequency, but with increased DRAM frequencies. We launched DRAM in our ASRock system on DDR4-3466, slightly overclocked beyond the limits indicated on its label: DDR4-3200.
We show the results of the performance of the Core i7-8086K using fast memory, as well as overclocking the processor to 5.0 GHz (with basic memory). Core i7-8700K results are also displayed for comparison.




We have nothing to say about our testing of the GPU due to the use of the Radeon RX 580. When performance is limited by the processor, overclocking should help, but, alas, not in this case. Although at some point I wanted to delve into checking the duration of AI moves in Civilization 6 with 8086K, since overclocking could be effective here.
Intel, having released in honor of the 40th anniversary of the architecture, the jubilee Core i7-8086K took us by surprise. The paper processor is a higher binning version of the Core i7-8700K with a gain of +300 MHz at the base frequency and single-core turbo frequency, which allows Intel to announce the 8086K as the first 5 GHz Intel processor on the market.
We must once again voice BIG thanks to ASRock for getting the test system in Taipei in such a short time.
Our final analysis consists of three parts, depending on how you plan to use the processor.
Official specification changes are a bit unfair, to be honest. At stock frequencies, a single-core turbo new processor is identical to the i7-8700K when loading from two cores to full load. It is worth mentioning that the processor almost never gets out of the turbo and will not drop to an improved base frequency due to the wide possibilities of power and cooling of desktop PCs. This means that the only real performance advantage users will get is when the processor is under single-core heavy load.
Given the nature of computers that use multiple applications that open at once or run in the background, a completely isolated single-core load is practically unattainable. It turns out that the processor can run the core at a frequency of 5.0 GHz, if you use it as a single core. With that said, the Core i7-8086K is very limited, especially when it is offered at a premium price ($ 425) is much more expensive than the nearest competitor, who, moreover, often sells at a discount (8700K at a price of $ 350 or lower).

In our tests of the “stock” processor, this analysis has borne fruit. In most tests, the 8086K was on par with the 8700K. In some, such as the CineBench R15 ST, he took the lead and set a new record because of the high frequency, but in other tests the results were worse, for example, in Blender and WinRAR, probably because of the thermal performance and reactions of our particular chip
Those who want to buy a Core i7-8086K, to run it at their native frequencies, hold their money. There are better suggestions.
In our testing, confirmed by extreme overclocker Alva Jonathan, the Core i7-8086K is a good choice if you want all six cores to work at 5.0 GHz. Our chip successfully worked with the full frequency of 5.0 GHz, and we achieved such a result only by adjusting the processor multiplier, and the motherboard coped with the other issues. With a few precautions, we were able to get 5.1 GHz in our Blender benchmark.
High performance is great, and the Core i7-8086K with a clock speed of 5.0 GHz provides a good level of performance. You can get a good Core i7-8700K for overclocking. If getting rid of excess risk costs an extra $ 65 +, then Core i7-8086K should be on the list of applicants.

As Alva showed, going beyond 1.3 volts can benefit from disassembling the processor (and replacing the heat transfer material) because it uses the same thermal conductor as the previous Coffee Lake processors. Intel made no changes to the thermal interface, and this, as I know, is not what enthusiasts want to hear. Intel constantly declares its commitment to its enthusiasts, and switching from a mediocre temperature interface will be the easiest way to demonstrate this commitment.
The reverse side of performance improvements up to 5.0 GHz - increased power consumption. Overclocking to 5.0 GHz improved performance by 16% in scenarios with a CPU reference due to a corresponding increase in frequency, but this increased the chip's power consumption by 68%. The Intel 14 ++ production process can really be the beginning of Skylake cores capable of such high frequencies, if we don’t consider the processor’s “+” power efficiency. But after all, few people care about energy efficiency during overclocking, you will gain in performance, and coolers of the highest class can cope with increased voltage and power - that’s what they were created for.
Intel will only release 50,000 of these processors, so this is probably a necessary purchase for each collector, and your orders are probably already in place. Or, fingers crossed, waiting for victory in the lottery.
Ultimately, Intel did not need to run a 40-year jubilee processor. Although the number is a multiple of ten, the 40th anniversary is not particularly remarkable for corporations. Nevertheless, as for the product, which, it would seem, appeared thanks to a joke from Twitter, 8086K is not completely without merit.
Intel is currently between the hammer and the anvil: the Core i7-8700K competes directly with the Ryzen 7 2700X, winning in single-threaded tasks and games at low resolution, but losing in multi-threaded performance and remaining on a par with high-resolution GPU games. We know that the 8-core Coffee Lake processor will be released later this year. During this time, AMD will release a 32-core Threadripper 2, available to everyone. As for the current launches, it is more likely to hold positions.
Intel had many options for the new Coffee Lake processor, and according to the Core i7-8086K specifications, it doesn’t look very good compared to the Core i7-8700K. The best thing that Intel could do in this situation is to give the top-end SKU an additional TDP, which would allow it to raise the frequencies on all the cores and get a significant boost. Of course, when switching to 105W it might seem that Intel was copying AMD, but processor performance should speak for itself. Otherwise, users pay + $ 75 for the best selected 8700K.

It seemed there was a danger in releasing a significantly more high-performance processor. He may be a cannibal of future sales. If the 9th generation "i7-9700K" will not have 105 W TDP, the new product may not be sold. But Intel promises that the 8086K processors are limited in circulation, which means that Intel controls the flow of the product on the market. If there are no 8086K processors available, 9700K will take the best place. Intel could take this into account and make the Core i7-8086K the best step worthy of the jubilee release, but the company did not use the opportunity. It is clear why Intel did not use the press to start the processor, given the slight increase in frequencies.
Is this processor designed for everyday use? Intel's binning process means that if one core can operate at 5.0 GHz at a reasonable voltage, all other cores are guaranteed to do the same. This means that this chip is ideally matched for overclocking up to 5.0 GHz. In fact, there is a suspicion that Intel really wanted to release a true full-scale 5-GHz processor - and spit on increased consumption - but at the last moment was frightened and decided to require the end users to press the magic button to unlock the full potential of the processor.
it's hard to imagine a person who is well versed in processors and will not overclock this chip to full 5.0 GHz. This means that the dignity of the 8086K is in its proper application. Is a new product one of those processors whose performance gain is too small, or is it a hidden attempt by Intel to provide high-performance and high-voltage Coffee Lake for customers who need an Intel processor with the highest clock speed?
Ultimately, the main question is whether it makes sense to buy a Core i7-8086K or not. The Core i7-8086K is, without a doubt, the most productive desktop Intel processor for desktops, and it shows superiority in some tests due to the increased single-core turbo frequency. The best advantages of the processor are manifested during overclocking, and both processors mentioned in this review can easily operate at 5.0 GHz on all cores. This is a good performance, and if you want to use the best, you should pay an extra price (or win the lottery), but this is an expensive purchase for most users.
My advice? If you really choose between the Core i7-8700K and Core i7-8086K, then take the i7-8700K. Although the commemorative edition can make you proud for a while, it will give you the opportunity to show it in your forum signature or show off on Reddit for several years, or a higher number on the box makes you smile, the final difference is minimal until the placebo effect. Spend extra on a larger SSD or additional memory. It is a good processor, but Intel could do more.
Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending to your friends, a 30% discount for Habr's users for a unique analogue of the entry-level servers that we invented for you:The whole truth about VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps from $ 20 or how to share the server? (Options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).
Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper? Only we have 2 x Intel Dodeca-Core Xeon E5-2650v4 128GB DDR4 6x480GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 249 in the Netherlands and the USA! Read about How to build an infrastructure building. class c using servers Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 worth 9000 euros for a penny?
Overclocking performance: CPU tests
We demonstrated our overclocking results, where we managed to achieve stable operation of the processor at a frequency of 5.1 GHz with a significant increase in voltage. However, work at a frequency of 5.1 GHz raised the working temperature dangerously high, so for our testing we went back to 5.0 GHz and again performed a series of tests at this increased speed. We also conducted some tests on the standard frequency, but with increased DRAM frequencies. We launched DRAM in our ASRock system on DDR4-3466, slightly overclocked beyond the limits indicated on its label: DDR4-3200.

On this (and the next) page, we will show the performance results of the Core i7-8086K using fast memory, as well as overclocking the processor to 5.0 GHz (with basic memory). For comparison, the results are displayed Core i7-8700K.
FCAT Processing

3DPM v2.1

Dolphin v5

DigiCortex v1.20

Blender

Pov ray

Cinebench R15 ST

Cinebench R15 MT

7-zip

Truecrypt

GeekBench 4 ST

GeekBench 4 MT

In all cases, except for single-threaded loads, overclocking 8086K to a pure 5GHz shows a very decent performance boost. You could already extrapolate these results on the basis of clock pulses, but it is customary to test theory with practice. The experiment clearly underlines the main drawback of the processor: a turbo single stream up to 5 GHz is almost useless. Very rarely will you load the system to the fullest. 8086K just screams about its desire to work at full 5GHz to make the most of its capabilities.
Overclocking performance: GPU tests
We managed to achieve stable operation of the processor at a frequency of 5.1 GHz with a significant increase in voltage. However, work at a frequency of 5.1 GHz raised the working temperature dangerously high, so for our testing we went back to 5.0 GHz and again performed a series of tests at this increased speed. We also conducted some tests on the standard frequency, but with increased DRAM frequencies. We launched DRAM in our ASRock system on DDR4-3466, slightly overclocked beyond the limits indicated on its label: DDR4-3200.
We show the results of the performance of the Core i7-8086K using fast memory, as well as overclocking the processor to 5.0 GHz (with basic memory). Core i7-8700K results are also displayed for comparison.
Civilization 6

Shadow of Mordor

Rise of the Tomb Raider

Grand theft auto v

We have nothing to say about our testing of the GPU due to the use of the Radeon RX 580. When performance is limited by the processor, overclocking should help, but, alas, not in this case. Although at some point I wanted to delve into checking the duration of AI moves in Civilization 6 with 8086K, since overclocking could be effective here.
Conclusions: save money
Intel, having released in honor of the 40th anniversary of the architecture, the jubilee Core i7-8086K took us by surprise. The paper processor is a higher binning version of the Core i7-8700K with a gain of +300 MHz at the base frequency and single-core turbo frequency, which allows Intel to announce the 8086K as the first 5 GHz Intel processor on the market.
We must once again voice BIG thanks to ASRock for getting the test system in Taipei in such a short time.
Our final analysis consists of three parts, depending on how you plan to use the processor.
For use on basic parameters
Official specification changes are a bit unfair, to be honest. At stock frequencies, a single-core turbo new processor is identical to the i7-8700K when loading from two cores to full load. It is worth mentioning that the processor almost never gets out of the turbo and will not drop to an improved base frequency due to the wide possibilities of power and cooling of desktop PCs. This means that the only real performance advantage users will get is when the processor is under single-core heavy load.
Given the nature of computers that use multiple applications that open at once or run in the background, a completely isolated single-core load is practically unattainable. It turns out that the processor can run the core at a frequency of 5.0 GHz, if you use it as a single core. With that said, the Core i7-8086K is very limited, especially when it is offered at a premium price ($ 425) is much more expensive than the nearest competitor, who, moreover, often sells at a discount (8700K at a price of $ 350 or lower).

In our tests of the “stock” processor, this analysis has borne fruit. In most tests, the 8086K was on par with the 8700K. In some, such as the CineBench R15 ST, he took the lead and set a new record because of the high frequency, but in other tests the results were worse, for example, in Blender and WinRAR, probably because of the thermal performance and reactions of our particular chip
Those who want to buy a Core i7-8086K, to run it at their native frequencies, hold their money. There are better suggestions.
For overclocking
In our testing, confirmed by extreme overclocker Alva Jonathan, the Core i7-8086K is a good choice if you want all six cores to work at 5.0 GHz. Our chip successfully worked with the full frequency of 5.0 GHz, and we achieved such a result only by adjusting the processor multiplier, and the motherboard coped with the other issues. With a few precautions, we were able to get 5.1 GHz in our Blender benchmark.
High performance is great, and the Core i7-8086K with a clock speed of 5.0 GHz provides a good level of performance. You can get a good Core i7-8700K for overclocking. If getting rid of excess risk costs an extra $ 65 +, then Core i7-8086K should be on the list of applicants.

As Alva showed, going beyond 1.3 volts can benefit from disassembling the processor (and replacing the heat transfer material) because it uses the same thermal conductor as the previous Coffee Lake processors. Intel made no changes to the thermal interface, and this, as I know, is not what enthusiasts want to hear. Intel constantly declares its commitment to its enthusiasts, and switching from a mediocre temperature interface will be the easiest way to demonstrate this commitment.
The reverse side of performance improvements up to 5.0 GHz - increased power consumption. Overclocking to 5.0 GHz improved performance by 16% in scenarios with a CPU reference due to a corresponding increase in frequency, but this increased the chip's power consumption by 68%. The Intel 14 ++ production process can really be the beginning of Skylake cores capable of such high frequencies, if we don’t consider the processor’s “+” power efficiency. But after all, few people care about energy efficiency during overclocking, you will gain in performance, and coolers of the highest class can cope with increased voltage and power - that’s what they were created for.
For processor collectors
Intel will only release 50,000 of these processors, so this is probably a necessary purchase for each collector, and your orders are probably already in place. Or, fingers crossed, waiting for victory in the lottery.
Is launching a new processor just a trick?
Ultimately, Intel did not need to run a 40-year jubilee processor. Although the number is a multiple of ten, the 40th anniversary is not particularly remarkable for corporations. Nevertheless, as for the product, which, it would seem, appeared thanks to a joke from Twitter, 8086K is not completely without merit.
Intel is currently between the hammer and the anvil: the Core i7-8700K competes directly with the Ryzen 7 2700X, winning in single-threaded tasks and games at low resolution, but losing in multi-threaded performance and remaining on a par with high-resolution GPU games. We know that the 8-core Coffee Lake processor will be released later this year. During this time, AMD will release a 32-core Threadripper 2, available to everyone. As for the current launches, it is more likely to hold positions.
Intel had many options for the new Coffee Lake processor, and according to the Core i7-8086K specifications, it doesn’t look very good compared to the Core i7-8700K. The best thing that Intel could do in this situation is to give the top-end SKU an additional TDP, which would allow it to raise the frequencies on all the cores and get a significant boost. Of course, when switching to 105W it might seem that Intel was copying AMD, but processor performance should speak for itself. Otherwise, users pay + $ 75 for the best selected 8700K.

It seemed there was a danger in releasing a significantly more high-performance processor. He may be a cannibal of future sales. If the 9th generation "i7-9700K" will not have 105 W TDP, the new product may not be sold. But Intel promises that the 8086K processors are limited in circulation, which means that Intel controls the flow of the product on the market. If there are no 8086K processors available, 9700K will take the best place. Intel could take this into account and make the Core i7-8086K the best step worthy of the jubilee release, but the company did not use the opportunity. It is clear why Intel did not use the press to start the processor, given the slight increase in frequencies.
Is this processor designed for everyday use? Intel's binning process means that if one core can operate at 5.0 GHz at a reasonable voltage, all other cores are guaranteed to do the same. This means that this chip is ideally matched for overclocking up to 5.0 GHz. In fact, there is a suspicion that Intel really wanted to release a true full-scale 5-GHz processor - and spit on increased consumption - but at the last moment was frightened and decided to require the end users to press the magic button to unlock the full potential of the processor.
it's hard to imagine a person who is well versed in processors and will not overclock this chip to full 5.0 GHz. This means that the dignity of the 8086K is in its proper application. Is a new product one of those processors whose performance gain is too small, or is it a hidden attempt by Intel to provide high-performance and high-voltage Coffee Lake for customers who need an Intel processor with the highest clock speed?
Ultimately, the main question is whether it makes sense to buy a Core i7-8086K or not. The Core i7-8086K is, without a doubt, the most productive desktop Intel processor for desktops, and it shows superiority in some tests due to the increased single-core turbo frequency. The best advantages of the processor are manifested during overclocking, and both processors mentioned in this review can easily operate at 5.0 GHz on all cores. This is a good performance, and if you want to use the best, you should pay an extra price (or win the lottery), but this is an expensive purchase for most users.
Intel can better
My advice? If you really choose between the Core i7-8700K and Core i7-8086K, then take the i7-8700K. Although the commemorative edition can make you proud for a while, it will give you the opportunity to show it in your forum signature or show off on Reddit for several years, or a higher number on the box makes you smile, the final difference is minimal until the placebo effect. Spend extra on a larger SSD or additional memory. It is a good processor, but Intel could do more.
Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending to your friends, a 30% discount for Habr's users for a unique analogue of the entry-level servers that we invented for you:The whole truth about VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps from $ 20 or how to share the server? (Options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).
Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper? Only we have 2 x Intel Dodeca-Core Xeon E5-2650v4 128GB DDR4 6x480GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 249 in the Netherlands and the USA! Read about How to build an infrastructure building. class c using servers Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 worth 9000 euros for a penny?
