The collapse of IPv4, myths about the need to use dedicated IP
It's no secret that the Internet is developing very rapidly, because it is not at all surprising that the last free blocks of address / 8 (IPv4) were distributed by the administration of the Internet address space (IANA) between the needing regional registrars on February 3, 2011. The last block / 8 was distributed by the Regional Internet Registrar of Europe (RIPE) in September 2012. Only the existing local registrar, which has previously received IPv6 addresses, can apply for the / 22 block, consisting of 1024 addresses. A thousand addresses is the only thing he can claim. The distribution of provider-independent IPv4 addresses has ceased altogether. In this regard, getting the / 24 block or even an individual ip-address is becoming increasingly difficult.

There are two outputs:
- the transition to a new version of the Internet protocol IPv6, in which 2 128 degrees of free addresses (which is impossible in the coming years due to the use of equipment that does not support IPv6 by most providers);
- redistribution of existing IP addresses.
At the dawn of the development of the Internet, in September 1981, when they just introduced Internet Protocol (version 4), it seemed that the addresses would be enough forever and they were “endless”. After all, IPv4 uses 32-bit (four-byte) addresses, limiting the address space of 4,294,967,296 (2 to 32 degrees) to possible unique addresses. The real boom in the assignment of IP addresses began in 1993 as a result of a significant increase in the number of personal computers and intensified in 2005, when the number of mobile devices increased.
Over the years, schemes have been developed to "save" the use of addresses, for example, the use of private ranges of IP addresses that are unique within the same network, access to the Internet for which is through a gateway that already has an "external" IP address, which allowed a large number of users use only 1 or more addresses to access the Internet. Now this solution has become obsolete and represents a big complication on the way to transition to IPv6.

The graph shows the decrease in the number of unallocated blocks / 8 over time
Although the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 has been expected for a long time, many organizations are not ready to implement it. In addition, you must maintain a presence in both address spaces until the transition to IPv6 is complete. However, some organizations are beginning to provide their new services more and more often in only one address space. For example, Microsoft's DirectAccess is only available in IPv6, as manufacturers found presence in IPv4 too costly.
By August 2010, only 5% of unallocated addresses remained (12 blocks / 8 out of 256, about 16.7 million addresses in each). IPv4 was a victim of its own success.
The growing demand for IP addresses leads to the emergence of a "black market", which sharply increases the cost of getting the opportunity to "presence" on the Internet today. After the distribution of the last block of addresses / 8, the only way to obtain addresses will be the black market, where prices for addresses will rise to a level that will be acceptable for a business that needs addresses. If the survival of your business depends on obtaining IPv4 addresses, you will be ready to pay for them, even if you have to circumvent the rules.
Contributed to the development of the black market and hosting providers. In the past decade, once hosting became publicly available, providers had many free blocks of IP addresses. And as this often happens, the idea arose to earn additional funds for them by renting IP addresses. However, there was simply no one to sell such an amount of IP, because not all users need VDS, SSL, etc. The solution was found - to come up with myths according to which ordinary webmasters just need dedicated IP addresses for their sites and it is simply impossible to do without them.
Selling IP addresses in hundreds at $ 0.5-1 / month for the address, the providers received a good profit. So a subnet with 256 addresses cost the provider a maximum of $ 100 / year, and income from it sometimes exceeded $ 2500 per year. And such subnets sold out in dozens. The fact that the use of addresses was not entirely targeted was of little concern to anyone. The beginning of the shortage of IP addresses in the market of hosting services increased profit from their sale even more, some did not hesitate to offer a price of $ 5 per address or more. True, not all were thirsty for profit, some, raising prices, simply tried to unsuccessfully reduce demand, as their supply of addresses was coming to an end, and it was expensive / impossible to take new ones.
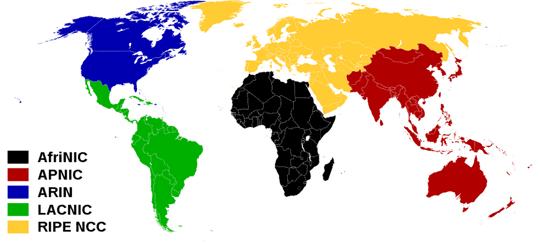
Areas of influence of responsible regional registrars trying to control fair distribution of addresses
More and more providers are beginning to realize that soon even for dedicated servers free addresses may not remain at all, and the server can’t do without its IP. In addition, the rental income of the server is ten times higher than the income from inappropriate sale of the address. Large companies such as LeaseWeb, where more than a hundred new servers are installed daily, were forced not only to raise prices to reduce demand, but even to introduce a limit on the maximum possible number of IPs provided for one server.
Will it help? I don’t think ... But it will definitely give some time.
For many years, webmasters have been encouraged to use dedicated IP addresses for their projects. Now the situation is reversed. More and more hosting providers are trying to prove that the client does not need an address, not only because everyone has suddenly become honest, more likely because the majority has nothing more to offer, and the client can go where else he is looking for ... Alas, people were zombified so that sometimes they simply cannot convince, even with the best intentions. People continue to believe in what they have been told ...
Let's look at the most common myths:
- SEO (search engine optimization), the myth that placing a site on a dedicated IP address increases its PR (page rank), but this is not so.
- The negative influence of neighboring sites when placed on the same ip-address is another invention. Placing hundreds or even thousands of sites on a single address is common practice, for example, most Google services use a common IP address. There can be no shortcomings in this, if only because there are more sites on the Internet than there are ip addresses.
- The need for a second address on the server to create DNS is also doubtful. You can always use the DNS-s of registrars, hosting providers, moreover, when placing the primary and secondary DNS on one server - the necessary redundancy is lost, to ensure which there is at least two ns-servers.
- Dedicated IP for SSL certificate. Although SSL sites cannot share the same IP address with other SSL sites, you can still host one such site on an IP address together with regular websites or any services (DNS, ftp, email, etc.).
- Dedicated IP to monitor traffic consumption. Another common myth is the assignment of different IP addresses to sites in order to control the traffic consumed by each site. In fact, for the same apache web server, you can install additional modules, such as mod_logio and mod_watch, with the help of which you can freely control traffic consumption by individual sites located at the same address.
- Only IPv4 addresses can be used. If you have sites / servers that are used for testing or just for you - it is advisable to assign them an IPv6 address, this can even lead to increased security, since you will make them inaccessible to the Internet IPv4.
- VPN access. You do not need a separate ip address for each virtual channel. If you use Network Address Translation (NAT), you can connect as many virtual channels as you want, and you will not be limited by the number of IP addresses, while all your virtual channel users will have one “external” address.
- Virtual servers (VDS). Yes, you really need dedicated IP addresses for them, if you want to sell them to different customers, but if you use virtualization as a security measure to isolate various services (databases, file storage), you should consider assigning, according to at least some virtual machines with private ("internal") IP addresses and make them available only from other virtual machines on this server.
- Black SEO. Sites promoted by black methods still have a sad fate. Search engines are advanced, able to recognize your doorways and more, even if they will be on different IP addresses.
In conclusion, I would like to ask especially webmasters involved in black SEO - do not litter the Internet with trash, make useful, unique projects for people, not for search engines. The online community will appreciate it and the addresses will be saved.

There are two outputs:
- the transition to a new version of the Internet protocol IPv6, in which 2 128 degrees of free addresses (which is impossible in the coming years due to the use of equipment that does not support IPv6 by most providers);
- redistribution of existing IP addresses.
A bit of history
At the dawn of the development of the Internet, in September 1981, when they just introduced Internet Protocol (version 4), it seemed that the addresses would be enough forever and they were “endless”. After all, IPv4 uses 32-bit (four-byte) addresses, limiting the address space of 4,294,967,296 (2 to 32 degrees) to possible unique addresses. The real boom in the assignment of IP addresses began in 1993 as a result of a significant increase in the number of personal computers and intensified in 2005, when the number of mobile devices increased.
Over the years, schemes have been developed to "save" the use of addresses, for example, the use of private ranges of IP addresses that are unique within the same network, access to the Internet for which is through a gateway that already has an "external" IP address, which allowed a large number of users use only 1 or more addresses to access the Internet. Now this solution has become obsolete and represents a big complication on the way to transition to IPv6.

The graph shows the decrease in the number of unallocated blocks / 8 over time
Although the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 has been expected for a long time, many organizations are not ready to implement it. In addition, you must maintain a presence in both address spaces until the transition to IPv6 is complete. However, some organizations are beginning to provide their new services more and more often in only one address space. For example, Microsoft's DirectAccess is only available in IPv6, as manufacturers found presence in IPv4 too costly.
By August 2010, only 5% of unallocated addresses remained (12 blocks / 8 out of 256, about 16.7 million addresses in each). IPv4 was a victim of its own success.
Black market
The growing demand for IP addresses leads to the emergence of a "black market", which sharply increases the cost of getting the opportunity to "presence" on the Internet today. After the distribution of the last block of addresses / 8, the only way to obtain addresses will be the black market, where prices for addresses will rise to a level that will be acceptable for a business that needs addresses. If the survival of your business depends on obtaining IPv4 addresses, you will be ready to pay for them, even if you have to circumvent the rules.
Contribution of hosting providers to the development of the black market
Contributed to the development of the black market and hosting providers. In the past decade, once hosting became publicly available, providers had many free blocks of IP addresses. And as this often happens, the idea arose to earn additional funds for them by renting IP addresses. However, there was simply no one to sell such an amount of IP, because not all users need VDS, SSL, etc. The solution was found - to come up with myths according to which ordinary webmasters just need dedicated IP addresses for their sites and it is simply impossible to do without them.
Selling IP addresses in hundreds at $ 0.5-1 / month for the address, the providers received a good profit. So a subnet with 256 addresses cost the provider a maximum of $ 100 / year, and income from it sometimes exceeded $ 2500 per year. And such subnets sold out in dozens. The fact that the use of addresses was not entirely targeted was of little concern to anyone. The beginning of the shortage of IP addresses in the market of hosting services increased profit from their sale even more, some did not hesitate to offer a price of $ 5 per address or more. True, not all were thirsty for profit, some, raising prices, simply tried to unsuccessfully reduce demand, as their supply of addresses was coming to an end, and it was expensive / impossible to take new ones.

Areas of influence of responsible regional registrars trying to control fair distribution of addresses
More and more providers are beginning to realize that soon even for dedicated servers free addresses may not remain at all, and the server can’t do without its IP. In addition, the rental income of the server is ten times higher than the income from inappropriate sale of the address. Large companies such as LeaseWeb, where more than a hundred new servers are installed daily, were forced not only to raise prices to reduce demand, but even to introduce a limit on the maximum possible number of IPs provided for one server.
Will it help? I don’t think ... But it will definitely give some time.
Myths
For many years, webmasters have been encouraged to use dedicated IP addresses for their projects. Now the situation is reversed. More and more hosting providers are trying to prove that the client does not need an address, not only because everyone has suddenly become honest, more likely because the majority has nothing more to offer, and the client can go where else he is looking for ... Alas, people were zombified so that sometimes they simply cannot convince, even with the best intentions. People continue to believe in what they have been told ...
Let's look at the most common myths:
- SEO (search engine optimization), the myth that placing a site on a dedicated IP address increases its PR (page rank), but this is not so.
- The negative influence of neighboring sites when placed on the same ip-address is another invention. Placing hundreds or even thousands of sites on a single address is common practice, for example, most Google services use a common IP address. There can be no shortcomings in this, if only because there are more sites on the Internet than there are ip addresses.
- The need for a second address on the server to create DNS is also doubtful. You can always use the DNS-s of registrars, hosting providers, moreover, when placing the primary and secondary DNS on one server - the necessary redundancy is lost, to ensure which there is at least two ns-servers.
- Dedicated IP for SSL certificate. Although SSL sites cannot share the same IP address with other SSL sites, you can still host one such site on an IP address together with regular websites or any services (DNS, ftp, email, etc.).
- Dedicated IP to monitor traffic consumption. Another common myth is the assignment of different IP addresses to sites in order to control the traffic consumed by each site. In fact, for the same apache web server, you can install additional modules, such as mod_logio and mod_watch, with the help of which you can freely control traffic consumption by individual sites located at the same address.
- Only IPv4 addresses can be used. If you have sites / servers that are used for testing or just for you - it is advisable to assign them an IPv6 address, this can even lead to increased security, since you will make them inaccessible to the Internet IPv4.
- VPN access. You do not need a separate ip address for each virtual channel. If you use Network Address Translation (NAT), you can connect as many virtual channels as you want, and you will not be limited by the number of IP addresses, while all your virtual channel users will have one “external” address.
- Virtual servers (VDS). Yes, you really need dedicated IP addresses for them, if you want to sell them to different customers, but if you use virtualization as a security measure to isolate various services (databases, file storage), you should consider assigning, according to at least some virtual machines with private ("internal") IP addresses and make them available only from other virtual machines on this server.
- Black SEO. Sites promoted by black methods still have a sad fate. Search engines are advanced, able to recognize your doorways and more, even if they will be on different IP addresses.
In conclusion, I would like to ask especially webmasters involved in black SEO - do not litter the Internet with trash, make useful, unique projects for people, not for search engines. The online community will appreciate it and the addresses will be saved.
