Granular recovery of virtualized application objects
An important function of modern backup products is the ability to granularly restore files, emails, documents in document management systems and other objects of various applications without the need to completely roll back the entire system to a certain control point in the past, when these objects still existed. When such a complete rollback is made, it is forced to “cast” all users of the system “into the past”, which creates a lot of business problems associated with “data loss over a period of time”.
There are two ways of such granular recovery when the system is not completely rolled back: " universal " (independent of the specific application, carried out by restoring the entire system to a test lab or "sandbox") and "specialized "(developed for a specific application, which allows you to extract data objects of a specific application directly from the application data file (s) without having to run the application (with all dependent components) in the sandbox).
The essence of these approaches will be shown using Veeam Backup & as an example Replication, which has the functionality to use both approaches, depending on what will be more optimal for the user in a particular case.
Veeam Universal Application Item Recovery The
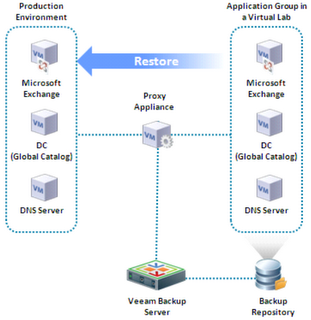
universal recovery mechanism is based on launching a set of interdependent virtual machines in a sandbox (an environment isolated from the productive network) directly from the backup repository, without having to unzip the disks of the selected virtual machine to a temporary location.
Speaking in terms of usage scenarios, the work process is schematically as follows:
Veeam Explorer for Microsoft Exchange
The product recovers deleted messages from Microsoft Exchange Server using the available backup copies of the virtual machine on which it is installed. Any type of backup can be used for recovery (full, incremental, compressed and / or deduplicated). Veeam Explorer for Microsoft Exchange allows you to open the Exchange server information database directly from the virtual machine’s disk and perform typical operations that are usually performed by the administrator when recovering messages: you can view the contents of Exchange mailboxes, search according to user-specified criteria, and restore the message in msg format or group letters in the form of a .pst file. The product uses a simple Explorer-like interface.
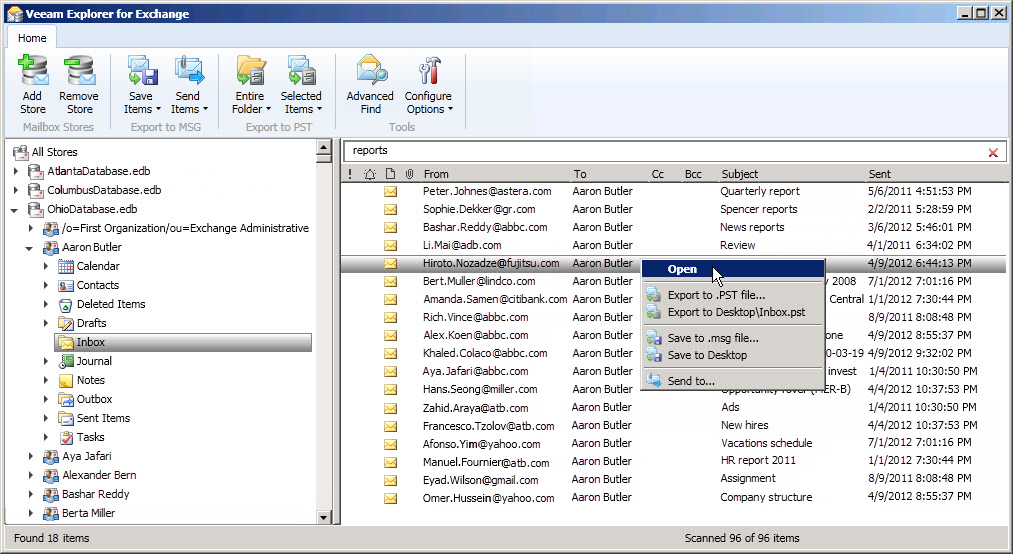
With this recovery method, no “farms” of interdependent virtual machines are started in the “sandbox”, since the Exchange server is not started in principle - instead, directly from the backup repository, the virtual machine’s drive is mounted on which the Exchange information storage file is located server, after which it is operated at a low level using a parser of the appropriate format.
In addition to the actual recovery operations of individual letters, Veeam Explorer for Microsoft Exchange allows you to perform compliance search (search in accordance with the requirements of the law) using various search criteria and the ability to export the result to a PST file.
Universal recovery can be applied in almost any case, but it may require running a large number of virtual machines with dependent services in the sandbox. For example, restoring an Exchange server may require (at least) restoring a virtual machine with a domain controller and (possibly separately installed) DNS server. During the launch of such a “farm,” network delays may occur in waiting for the start of virtual machines and services, on which the operability of the restored application server depends. The whole process of sequentially starting the server farm can take significantly more time than the specialized recovery that does not start the application server (it requires only the operating system to start with the application database file). But it should be noted
It is advisable to use products for "specialized recovery" :
It is advisable to use universal recovery tools:
There are two ways of such granular recovery when the system is not completely rolled back: " universal " (independent of the specific application, carried out by restoring the entire system to a test lab or "sandbox") and "specialized "(developed for a specific application, which allows you to extract data objects of a specific application directly from the application data file (s) without having to run the application (with all dependent components) in the sandbox).
The essence of these approaches will be shown using Veeam Backup & as an example Replication, which has the functionality to use both approaches, depending on what will be more optimal for the user in a particular case.
Universal recovery technology
Veeam Universal Application Item Recovery The
universal recovery mechanism is based on launching a set of interdependent virtual machines in a sandbox (an environment isolated from the productive network) directly from the backup repository, without having to unzip the disks of the selected virtual machine to a temporary location.

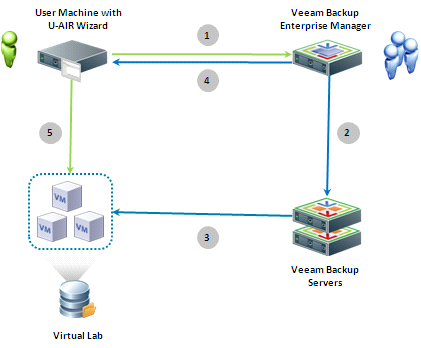
Speaking in terms of usage scenarios, the work process is schematically as follows:

- A user who needs to restore an application object (for example, an erroneously deleted Exchange server letter) starts the U-AIR universal recovery wizard and sends a request to restore objects of interest to him.
- The Backup Enterprise Manager administrator is notified by email of the registration of a new restore application.
- User rights to data requested for recovery are checked
- The user is informed of the result of checking his access rights, and, if there are rights, the Administrator starts the task of restoring virtual machines using the technology of automated testing of SureBackup backups. This technology allows you to run virtual machines directly from the backup repository, without requiring unpacking its disks to a temporary location.
- As soon as the set of virtual machines is restored and launched in the sandbox, the user receives a notification with a link to the prepared virtual machine with the application of interest.
- Using the received link, the user can independently restore the application objects of interest to him.
- At the end of the recovery procedure, the virtual machines shut down automatically or manually (by the administrator).
Specialized Granular Recovery Technology
Veeam Explorer for Microsoft Exchange
The product recovers deleted messages from Microsoft Exchange Server using the available backup copies of the virtual machine on which it is installed. Any type of backup can be used for recovery (full, incremental, compressed and / or deduplicated). Veeam Explorer for Microsoft Exchange allows you to open the Exchange server information database directly from the virtual machine’s disk and perform typical operations that are usually performed by the administrator when recovering messages: you can view the contents of Exchange mailboxes, search according to user-specified criteria, and restore the message in msg format or group letters in the form of a .pst file. The product uses a simple Explorer-like interface.

With this recovery method, no “farms” of interdependent virtual machines are started in the “sandbox”, since the Exchange server is not started in principle - instead, directly from the backup repository, the virtual machine’s drive is mounted on which the Exchange information storage file is located server, after which it is operated at a low level using a parser of the appropriate format.
In addition to the actual recovery operations of individual letters, Veeam Explorer for Microsoft Exchange allows you to perform compliance search (search in accordance with the requirements of the law) using various search criteria and the ability to export the result to a PST file.
Which way to choose?
Universal recovery can be applied in almost any case, but it may require running a large number of virtual machines with dependent services in the sandbox. For example, restoring an Exchange server may require (at least) restoring a virtual machine with a domain controller and (possibly separately installed) DNS server. During the launch of such a “farm,” network delays may occur in waiting for the start of virtual machines and services, on which the operability of the restored application server depends. The whole process of sequentially starting the server farm can take significantly more time than the specialized recovery that does not start the application server (it requires only the operating system to start with the application database file). But it should be noted
Thus, the following recommendations can be made:
It is advisable to use products for "specialized recovery" :
- if there is a complex configuration of the restored application server , consisting of a set of interconnected virtual servers (for example, a distributed Exchange organization) - for reasons of speed of the recovery operation;
- if necessary, perform specialized operations usually not available in universal recovery products, for example, “search in accordance with the requirements of laws”;
- if possible, delegate the restoration of the user document to the administrator . That is, if the user is ready to provide the administrator with a (potential) right to familiarize himself with the entire content of the document during the restoration process. Example of a recovery request: " Please restore a mistakenly deleted letter with a financial report for the 2nd quarter of this year ." It is clear that by executing such a request, the administrator will have to view all deleted letters for the period, even if they are previously selected by keywords.
It is advisable to use universal recovery tools:
- if the user must restore the letter on his own , as he does not want to give the administrator the right to familiarize himself with the contents of the document being restored
- if the application server is not very large in configuration complexity and size , since universal recovery will not require much time;
- (Obviously) If there is no specialized recovery tool for the required application server.
