Curiosity - The First 50 Days on Mars
We decided to do reviews about current Curiosity research on Mars about once a week. But since two months have already passed, in the first posts we will go over quickly to catch up with the current moment.
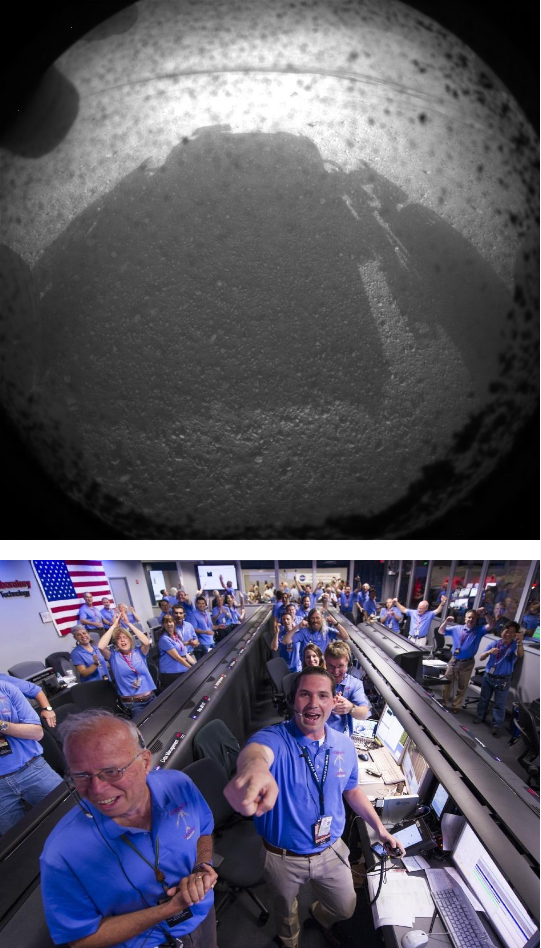
So, on August 6, 2012, the Mars rover MSL Curiosity successfully landed on the planet Mars. His first shot, transmitted to Earth, caused a wave of joy and enthusiasm among NASA experts:

Next, about the first 50 days of Curiosity on Mars, with photos, panoramas and illustrations.
But this was not the first frame made by Curiosity. Shooting with the MARDI camera began even at the moment when the rover was in the descent capsule.
The result of this shoot was finalized by director Bard Canning, who offered his work to the world:
After landing, the rover first examined itself with navigation cameras. It was necessary to understand whether the landing was flawless or with losses.
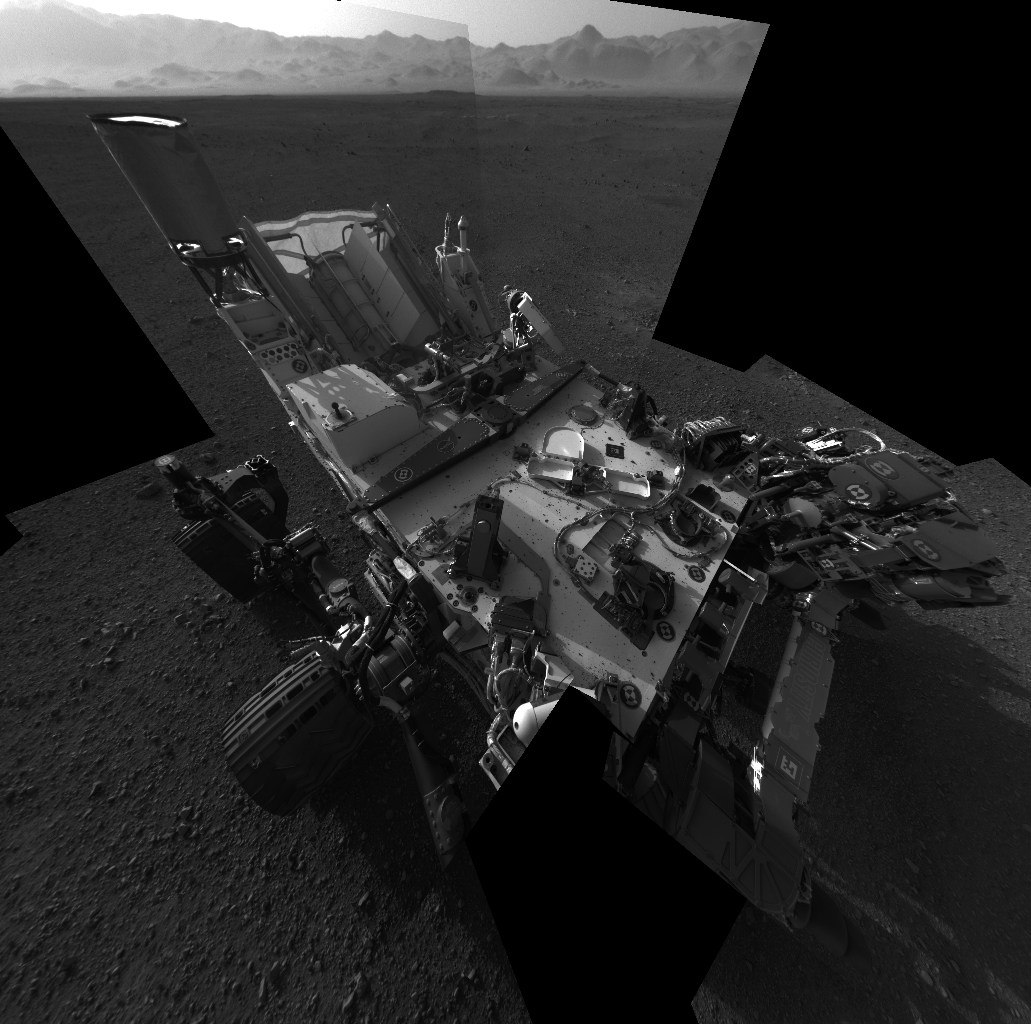

In addition to small particles of soil on the body, external inspection did not reveal any problems.
On the third day on Mars, Curiosity shot the first full panorama with a Mast Cam left color camera with a focal length of 34 mm. A few days later, the photos were transferred to Earth, and brought together into a single 360 °. This allowed us to shut up the many-voiced chorus of conspiracy theorists around the world who lamented: "NASA hides the colored frames of Mars."

After the audience was satisfied, NASA was finally able to get down to business and sent Curiosity into hibernation one and a half weeks. During this time, the software was updated and all the scientific equipment was tested in passive mode. No irregularities were detected at this stage either.
Coming out of hibernation, the rover began to test the laser and the Chem Cam spectrograph. At first, test firing was carried out on special test targets located on the body of the rover:

Then the first sample was fired, which was first called “Stone No. 165”, and then Coronation.
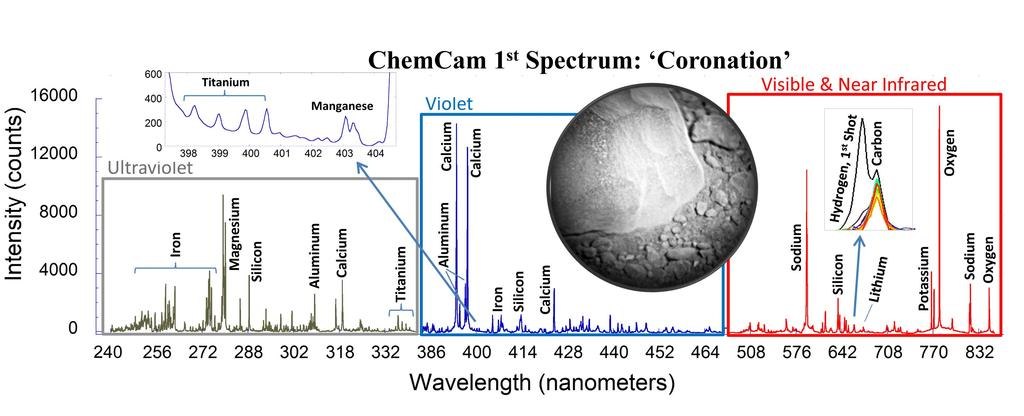
The result of the study showed that the laser effectively burns through a layer of dust covering the Martian stones, and reaches the sample itself. The chemical composition of Coronation turned out to be the closest to terrestrial basalt samples.
Then a new phase of equipment testing began - this time in practice.
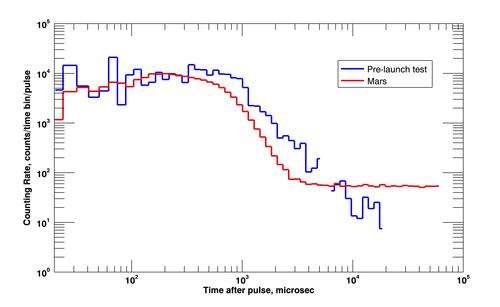
The Russian DAN instrument made the first study of the terrain for hydrogen in the ground. The graph showed the approximate water saturation of the Martian soil and the concrete floor of the laboratory where the preflight tests of the sensor were carried out:
The functionality of the manipulator was tested:
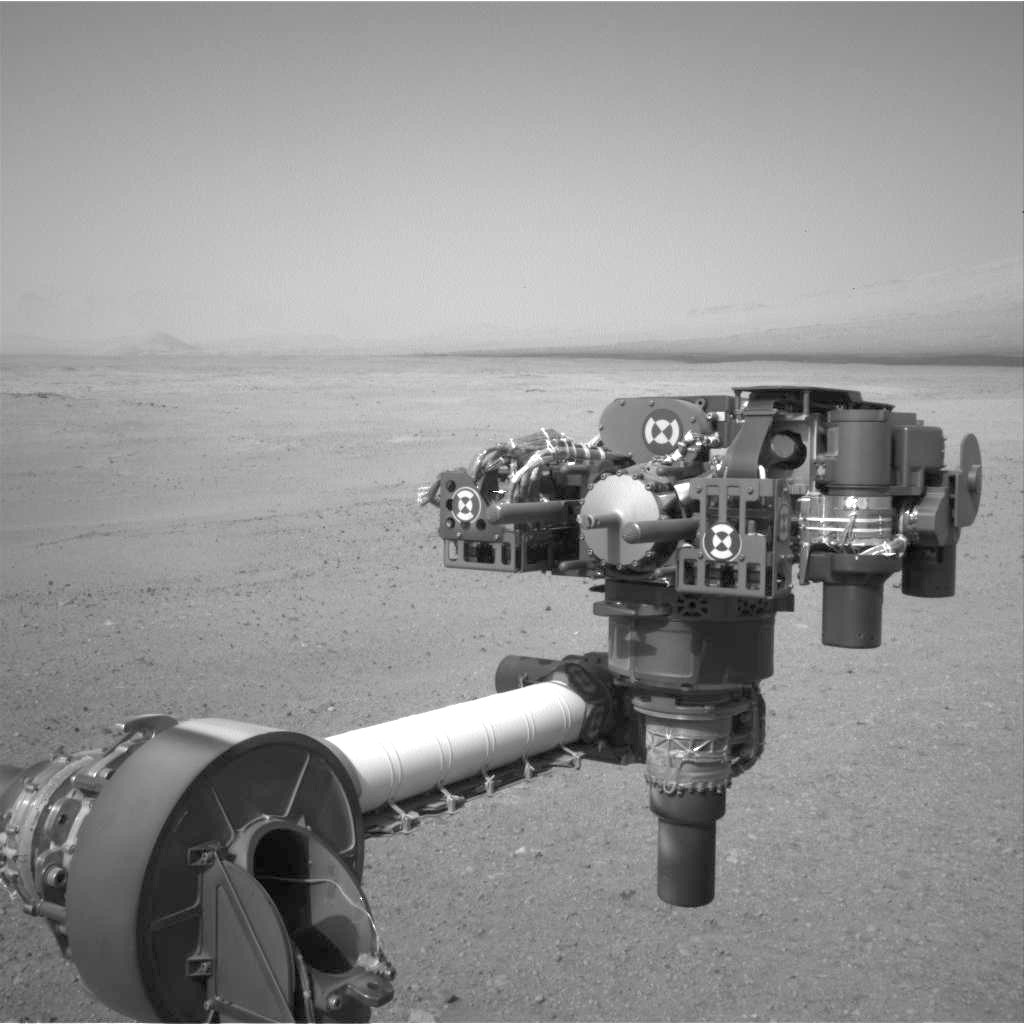

Mover functionality:

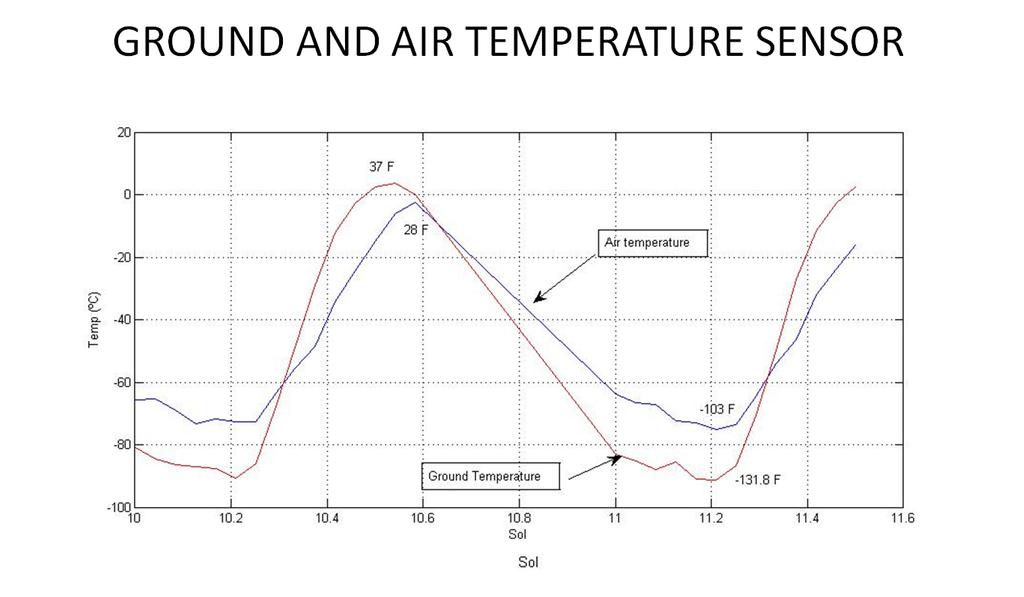
When testing the climate equipment, the first breakdown was revealed - one of the two REMS wind direction sensors failed. Apparently, it was damaged by a particle of soil during planting. However, this did not stop the rover from starting work in climate monitoring mode and transmitting regular weather reports from Gale Crater:

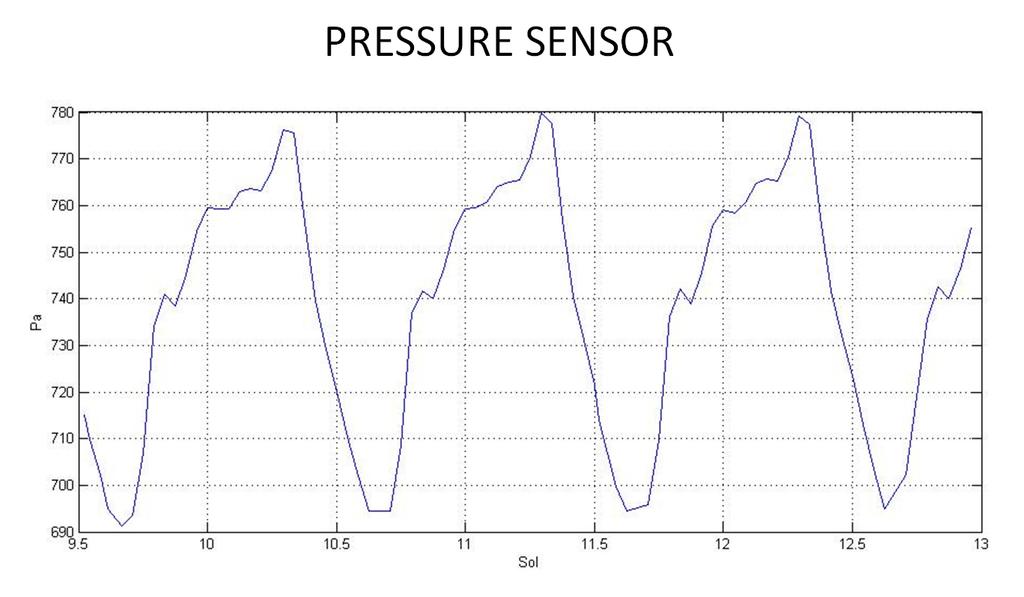
From that moment, research began on the temperature of the atmosphere and the surface of the planet:
and atmospheric pressure:
Finally, movement started at 21 sol (Martian day):
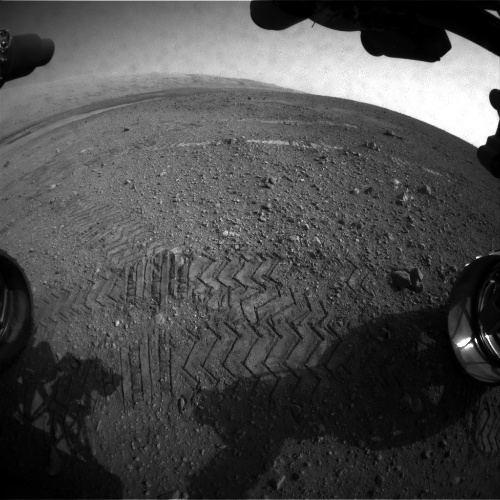

The first "steps" were a few meters - the rover moved to the spot left when landing with a Sky Crane jet. Her research was done by the DAN.
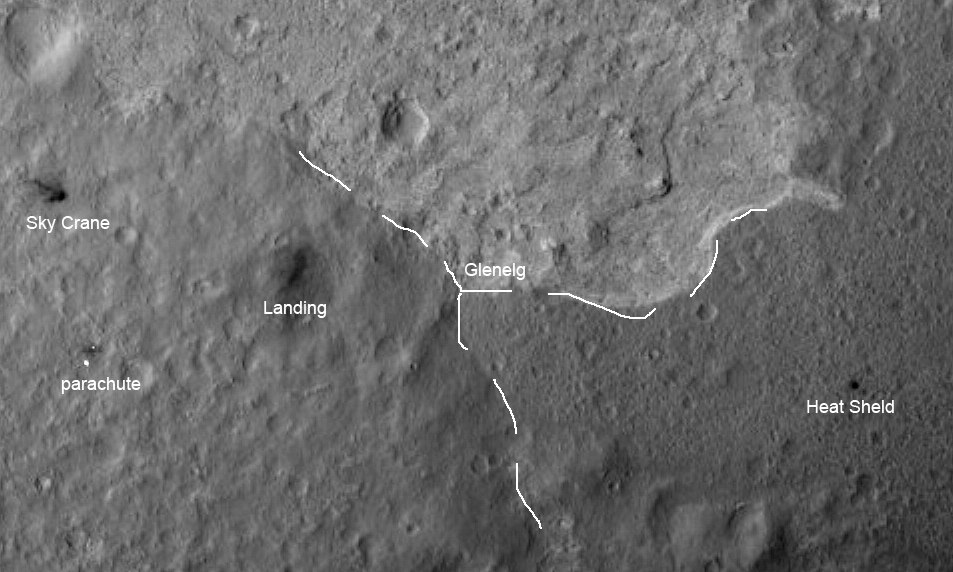
A few days later, Curiosity headed for Glenelg, a piece of the surface of Mars 400 meters east of the landing site. This place attracted the attention of NASA in that it converges three types of soil, apparently formed at different times and in different conditions.

On the half-way to Glenelg, the rover stopped and again began checking the functionality of the manipulator:
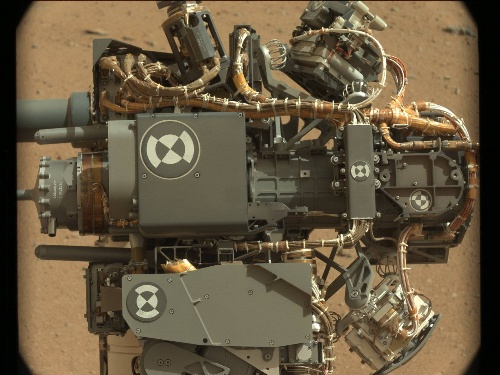
The camera on the MAHLI manipulator took the first pictures without a dust cap and transmitted high-quality

and detailed images :
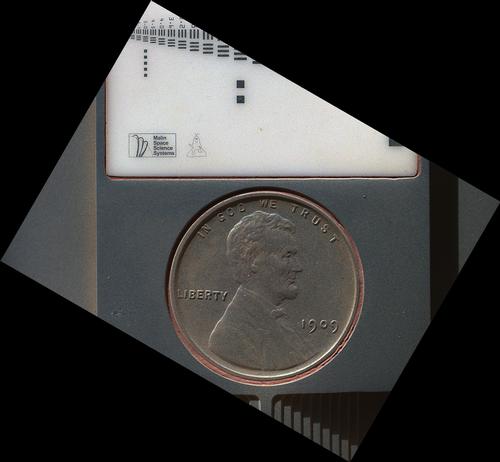

Read more about where the coin and children's drawing of an alien come from on the rover .
The find of Curiosity on 43 sols again forced the conspiracy theorists of all stripes to become excited. Still, the rover found the pyramid:
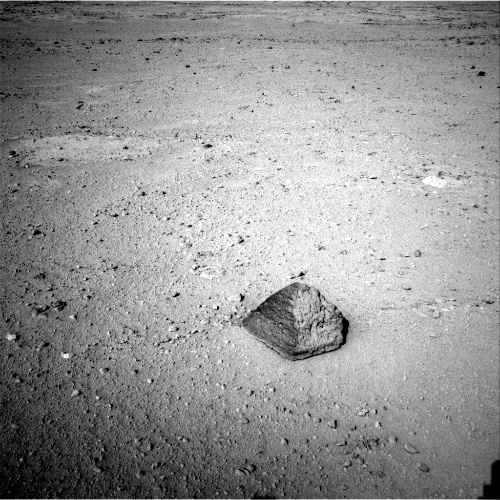

True, a little. To the surprise of many, NASA not only did not try to hide the find, but studied it in the most thorough way, so that no one had any doubts about the naturalness of this stone, named in memory of one of the engineers: Jake Matievich.

Using this stone as an example, it’s convenient to understand what type of rover cameras what images it transmits:

(hashtags for contact are indicated)
While the manipulator was studying the “pyramid”, the right 100 mm Mast Cam shot a huge panorama of more than 70 frames with a view of Mount Sharpe:

(do not ask about color and the sky is “in paint” inserted).
You can admire the option Medium 6.5 mb or Fullsize 43 mb .
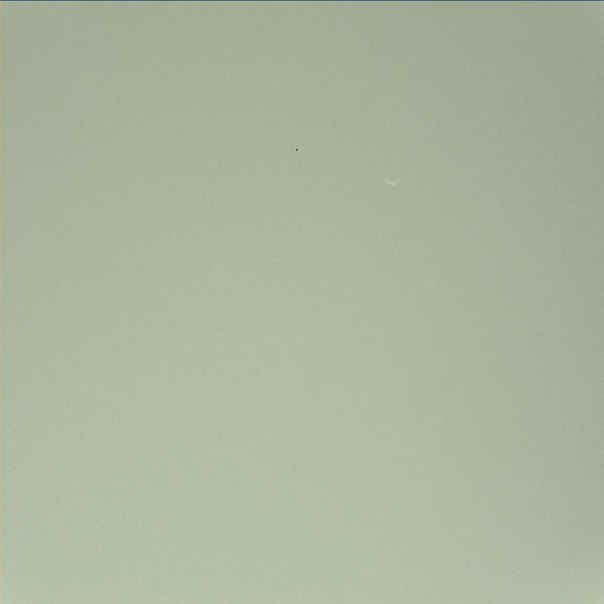
In the following days, Curiosity tested the role of a solar astronomer and removed Phobos’s transit from the Sun’s disk from two attempts:

Then Deimos:

Then just a spot on the Sun:

It turned out to capture the Martian “Moon” in the daylight:

And then he still arrived in Glenelg :

And this is a completely different story, to be continued.
Post co-written with Zelenyikot
So, on August 6, 2012, the Mars rover MSL Curiosity successfully landed on the planet Mars. His first shot, transmitted to Earth, caused a wave of joy and enthusiasm among NASA experts:

Next, about the first 50 days of Curiosity on Mars, with photos, panoramas and illustrations.
But this was not the first frame made by Curiosity. Shooting with the MARDI camera began even at the moment when the rover was in the descent capsule.
The result of this shoot was finalized by director Bard Canning, who offered his work to the world:
After landing, the rover first examined itself with navigation cameras. It was necessary to understand whether the landing was flawless or with losses.

In addition to small particles of soil on the body, external inspection did not reveal any problems.
On the third day on Mars, Curiosity shot the first full panorama with a Mast Cam left color camera with a focal length of 34 mm. A few days later, the photos were transferred to Earth, and brought together into a single 360 °. This allowed us to shut up the many-voiced chorus of conspiracy theorists around the world who lamented: "NASA hides the colored frames of Mars."

After the audience was satisfied, NASA was finally able to get down to business and sent Curiosity into hibernation one and a half weeks. During this time, the software was updated and all the scientific equipment was tested in passive mode. No irregularities were detected at this stage either.
Coming out of hibernation, the rover began to test the laser and the Chem Cam spectrograph. At first, test firing was carried out on special test targets located on the body of the rover:

Then the first sample was fired, which was first called “Stone No. 165”, and then Coronation.

The result of the study showed that the laser effectively burns through a layer of dust covering the Martian stones, and reaches the sample itself. The chemical composition of Coronation turned out to be the closest to terrestrial basalt samples.
Then a new phase of equipment testing began - this time in practice.
The Russian DAN instrument made the first study of the terrain for hydrogen in the ground. The graph showed the approximate water saturation of the Martian soil and the concrete floor of the laboratory where the preflight tests of the sensor were carried out:

The functionality of the manipulator was tested:

Mover functionality:

When testing the climate equipment, the first breakdown was revealed - one of the two REMS wind direction sensors failed. Apparently, it was damaged by a particle of soil during planting. However, this did not stop the rover from starting work in climate monitoring mode and transmitting regular weather reports from Gale Crater:

From that moment, research began on the temperature of the atmosphere and the surface of the planet:

and atmospheric pressure:

Finally, movement started at 21 sol (Martian day):

The first "steps" were a few meters - the rover moved to the spot left when landing with a Sky Crane jet. Her research was done by the DAN.
A few days later, Curiosity headed for Glenelg, a piece of the surface of Mars 400 meters east of the landing site. This place attracted the attention of NASA in that it converges three types of soil, apparently formed at different times and in different conditions.

On the half-way to Glenelg, the rover stopped and again began checking the functionality of the manipulator:

The camera on the MAHLI manipulator took the first pictures without a dust cap and transmitted high-quality

and detailed images :

Read more about where the coin and children's drawing of an alien come from on the rover .
The find of Curiosity on 43 sols again forced the conspiracy theorists of all stripes to become excited. Still, the rover found the pyramid:

True, a little. To the surprise of many, NASA not only did not try to hide the find, but studied it in the most thorough way, so that no one had any doubts about the naturalness of this stone, named in memory of one of the engineers: Jake Matievich.

Using this stone as an example, it’s convenient to understand what type of rover cameras what images it transmits:

(hashtags for contact are indicated)
While the manipulator was studying the “pyramid”, the right 100 mm Mast Cam shot a huge panorama of more than 70 frames with a view of Mount Sharpe:

(do not ask about color and the sky is “in paint” inserted).
You can admire the option Medium 6.5 mb or Fullsize 43 mb .
In the following days, Curiosity tested the role of a solar astronomer and removed Phobos’s transit from the Sun’s disk from two attempts:

Then Deimos:

Then just a spot on the Sun:

It turned out to capture the Martian “Moon” in the daylight:

And then he still arrived in Glenelg :

And this is a completely different story, to be continued.
Post co-written with Zelenyikot
