What does modern usability laboratory look like?

Many people imagine the usability laboratory as a space where prototypes of products are shown to people, everything is recorded and based on the data received, changes are made to the interface. Yes, this is in the laboratory, but at the same time - this is only the tip of the iceberg. Testing itself is already a spectacular finale. Before the development of the first prototype of the product begins, a huge number of different things must be done.
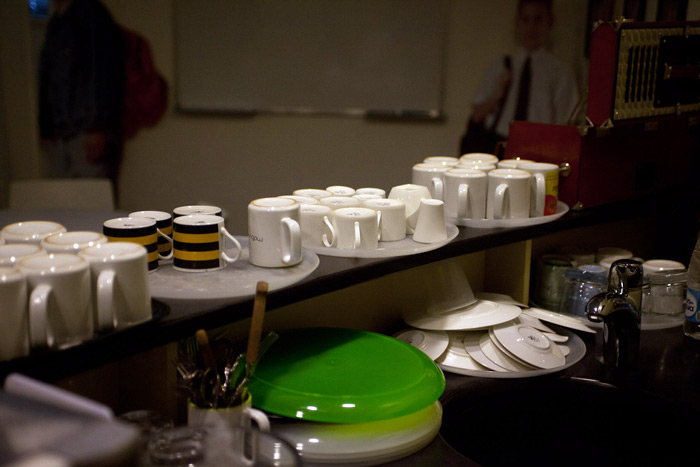
Usability laboratory- These are several rooms in which various contexts of using Beeline services are simulated. We have three zones: office, house and cafe. All three zones are equipped with recording equipment that allows specialists to accurately see and record what and how the user does. In all three zones “windows” go out from the hall where the observers are sitting - for the study participants they look like mirrors, for the members of the working group who came to observe the study, they are transparent.
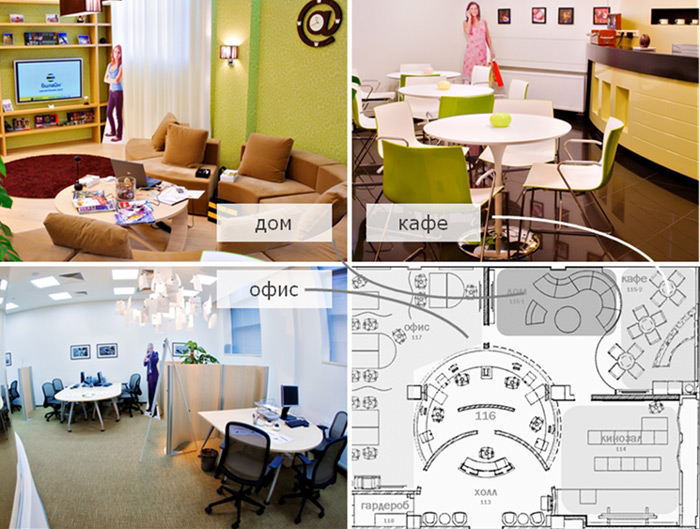

Laboratory premises
Another laboratory room is a conference room with a large screen, where presentations on the results of the study are held. It also contains design teams for the joint development of design solutions. If necessary, the Cinema Hall test zone is created in the same conference room.

Cinema Hall
Researchers and observers see user screens, and the respondent’s face and voice are also captured and transmitted. In parallel, using a special infrared camera, the eye movement of the study participant is recorded. During subsequent processing, you can view the “heat map”, on which noticeable and “blind” interface elements are clearly visible.

Aitreker

He is on the side. The
entrance to the laboratory is located before the office security turnstiles.
How is the work with the new product going?
We join the process of creating products at the earliest stages. At the very beginning, we get an idea formulated literally in the form of two sentences.
Work begins with the analysis of user tasks. First of all, you need to determine who will be interested in the product (for example, if we are talking about the loyalty program, then these are people with discount cards, if we are talking about parental control, these are parents whose children have the opportunity to access the Internet independently and so on). Several representatives of this audience are invited to the laboratory. A kind of brainstorming begins, the main purpose of which is to understand what people want from a ready-made solution. There are special methods that allow you to get fairly accurate wishes from the audience. At the end of the discussion, respondents select the tasks that are most important to them.
Usually from 5 to 9 groups take part in one study. Knowing the frequency of mentioning tasks in different groups and assessing their importance, we can calculate the priority of each task. After that, the project working group can determine what will be included in the first release of the product and what will be added at the next stages of development. ”
A lot depends on the skills and personality of the moderator. The moderator should be able to successfully behave and switch between several professional roles in time. Firstly, he is a hospitable host who knows how to establish emotional contact with a respondent or group, arouse trust, relieve stress, and do everything possible so that participants say “with their own voice and about what is important to them.” Secondly, the moderator is a strong leader responsible for everything that happens during the study. He must quickly and orderly respond to all emerging issues, manage the pace and quality of work of respondents. Thirdly, the moderator is an impartial observer who tries to contribute as little as possible his own experience, opinions and ratings to the results of the participants' work. And finally the moderator has all responsibility for recording research data, for the sake of which, in fact, the laboratory was organized. As a rule, researchers come to us from professions related to social research - psychology, sociology, marketing research. There were experiments with moderators from technical departments, but they often do not understand how you can not understand the work of the product. Where the psychologist sees the problem in the interface, for example, of software, the technical specialist sees the problem in people who cannot understand something extremely obvious to him. That is why people with a liberal education or former interface designers become the best researchers. related to social research - psychology, sociology, marketing research. There were experiments with moderators from technical departments, but they often do not understand how you can not understand the work of the product. Where the psychologist sees the problem in the interface, for example, of software, the technical specialist sees the problem in people who cannot understand something extremely obvious to him. That is why people with a liberal education or former interface designers become the best researchers. related to social research - psychology, sociology, marketing research. There were experiments with moderators from technical departments, but they often do not understand how you can not understand the work of the product. Where the psychologist sees the problem in the interface, for example, of software, the technical specialist sees the problem in people who cannot understand something extremely obvious to him. That is why people with a liberal education or former interface designers become the best researchers. who cannot understand something extremely obvious to him. That is why people with a liberal education or former interface designers become the best researchers. who cannot understand something extremely obvious to him. That is why people with a liberal education or former interface designers become the best researchers.
Data from users is not the only source of information about the functionality of a future product. In addition, we conduct a study of world and industry practice, most often there is an opportunity to look at an analogue in the Western market and take into account already known problems.
In parallel, data is requested from experts in this field within the company or from suppliers of technical solutions. Thus, information from customers is checked and updated.
How are customer requirements specified?
The task list for creating a product interface is often not enough.
If the product turns out to be functionally or content-loaded, as, for example, it happens with corporate portals, you need to understand what sections should be divided into content and how to name these sections so that customers do not have problems finding information in the future. The method of card sorting helps in creating information architecture.
During a group discussion, several people should agree among themselves and explain to the moderator which groups they want to divide the content they offer, according to what criteria the groups are selected, as the resulting groups would like to name. There are special analytical tools for processing this kind of data, their principle of operation is to take into account the “distance” between individual units of content, it is calculated which of them often end up in the same group and which always diverge into different categories.
From the names of groups proposed by customers, you can choose the most successful. Subsequently, this will not only facilitate the search for information, but also, for example, help SEO, because the section names are formulated in the language of the clients.

Card sorting in progress
In some cases, other studies may be required. For example, we find out what steps and in what sequence in their normal lives customers take if they have a specific task. This information can be obtained in various ways, including by listening to several dozen calls to the call center.
Research results are taken into account when creating prototypes. To prototype web interfaces and software, standard tools such as Axure Pro are used, prototypes for mobile devices are made using software specially developed for these purposes, and paper prototyping is also used in some cases.
All these methods have one simple goal - until the start of development, have detailed user interface requirements tested on real clients. It is known that the later a problem is discovered, the more expensive it is to fix it. You may feel that research is dragging out the project, but in fact there is no better way to avoid the numerous alterations and the “war of opinions” that accompany the creation of products in any large company.
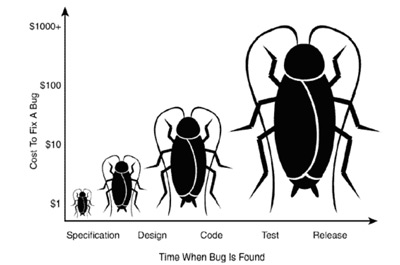
The later the corrections, the worse.
Design
Usually, up to three design iterations are carried out, each of which is tested on users using usability tests. This is just the most famous and familiar stage for many. Here it is important to check not the quality of individual buttons, filters and pages, but the success of custom tasks. Tasks are set for the respondent in the most neutral, natural, simple manner. For example, a task can be formulated as follows: “Find the tune of Peter Nalich“ Kam Tu May Boudoir ”, order it and set yourself instead of beeps of waiting. The option is not very successful, as we give the respondent a sequence of steps. Such a wording would be much better: “You called a friend and heard this tune (we give the number on which the beep with the song Nalicha is set, we don’t call the performer). Make the same melody play with you. ”
During the tests, a study protocol is maintained. All words and actions of respondents are recorded and processed. Data is collected on the success of the work, the time spent, the emotional assessment of what is happening, and also about the problems that arise.
For problems, ratings are calculated depending on their frequency and impact on the result. The results of the work are graphs on the effectiveness, productivity and user satisfaction, as well as detailed descriptions of usability problems.

There is usability testing.
Then a working group is assembled, which includes a product manager, project manager, technologist, sometimes a representative of technical services involved in implementation. At the meeting, a change plan is drawn up and the next iteration begins.
It is clear that the process of iterative design and research is quite laborious, now our resources are far from enough for all products of the company.
Both technical interfaces (WAP, USS, WEB, IVR, and so on) and advertising layouts, for example, promotional flyers, from which users learn about the procedure for using the services, and sites where users search for information and decide on purchase. Even television and outdoor advertising in its own way is a user interface, and studies of its perception can greatly increase its effectiveness.
What research brings companies?
Now the average level of convenience of services being brought to the market without involving usability works in them is at the level of 45-60%. This means that no more than this share of users of services is able to use them independently, without outside assistance and support. The rest are forced to experience difficulties, call technical support, make additional attempts that load our network to get the desired service, ask questions to relatives and friends, or even refuse too complex services. All this is measured in money. At the same time, in a service where the convenience factor is observed, the proportion of successful users rises to 75-85%.
Good examples of successfully implemented usability design are the Beeline WAP portal, the Hello service, Mobile commerce services, updated navigation on the Beeline main voice portal - 0611, as well as a number of services that accompany voice communications.
Photo
A piece of office space, here for convenience - a payment terminal for tests:

This is the “home” zone, here products and services for the home are checked:
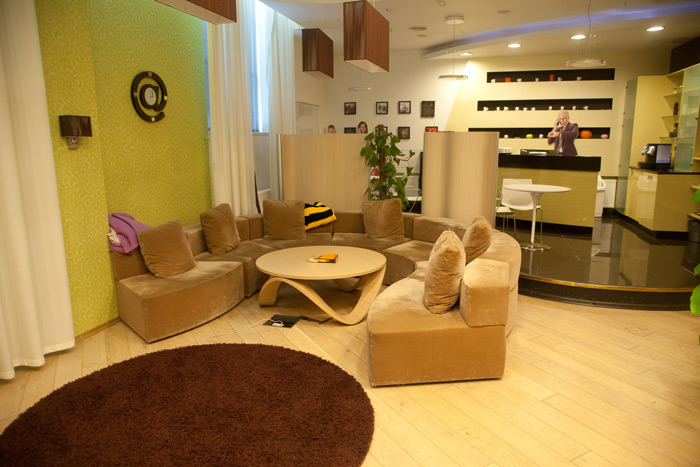

Here, for example, tests of IPTV services are carried out:
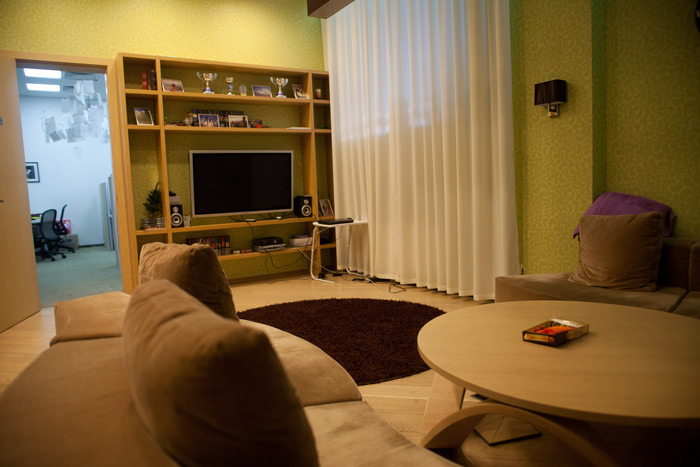

Hardware, where specialists are sitting. From it you can see other rooms of the laboratory:

Rack with iron:

Cafe area:

