Checking compliance with php coding standards through git
Developers of various levels often take part in the development of a project. This leads to the fact that there is no strict format for writing code. The quality of the code on the project has to be constantly monitored by senior developers and this takes them a lot of time.
In order topunish the govnokoders to alleviate the suffering of those who do code reviews, you can use automatic code verification tools that have long been known to everyone. These are PEAR and PHP Code Sniffer.
Most of the projects of the company where I work are made on Drupal, so an example of checking compliance with Drupal coding standards will be considered, although all the tools described below can be applied to other standards, for example Zend.
More recently, a set of rules has emerged to test Drupal coding standards through PHP Code Sniffer. Installing and configuring it is very simple, the most difficult part starts next. How to make everyone check their code? The influence of the human factor affects, the first forgot, the second did not want, and the third simply believes that his code cannot contain errors and, in general, all this is an waste of time.
The solution could beforcibly introducing code validation into the development process. In order for us not to have to stick with a stick over each programmer, we will use the git version control system. Thanks to git hooks, you can easily add your own scripts that will be executed during certain git operations, such as commit.
The first step is to add a code validation script to the pre-commit hook. When a developer commits his code, modified files will be automatically checked. If errors are found, the commit operation is aborted and a list of errors is displayed:
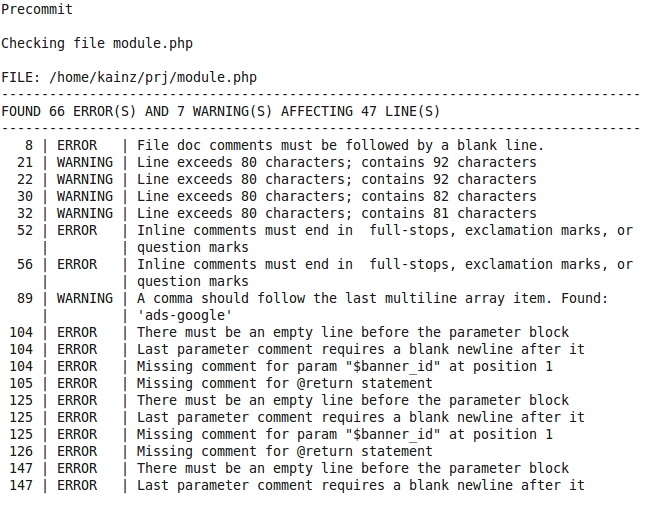
The code can be committed only when all errors have been fixed. Great, now we do not allow adding “bad” code to the project repository! But still the human factor remains. Again, someone forgets to add a verification script to the .git / hooks folder of his project, someone is too lazy to fix errors and he puts it off for later, etc., and the “smartest” just use git commit --no-verify because now they have no time for mistakes. In the latter case, git will not call the pre-commit hook and the modified files will go to the repository without checking.
In order to deal with this, we use the post-receive hook. This hook fires after adding code to the remote repository. The script that will be called in the post-receive hook checks the modified files for errors and sends a report to the mailbox of one or more senior developers who are responsible for the quality of the code on the project.
A report sent by mail looks like this:
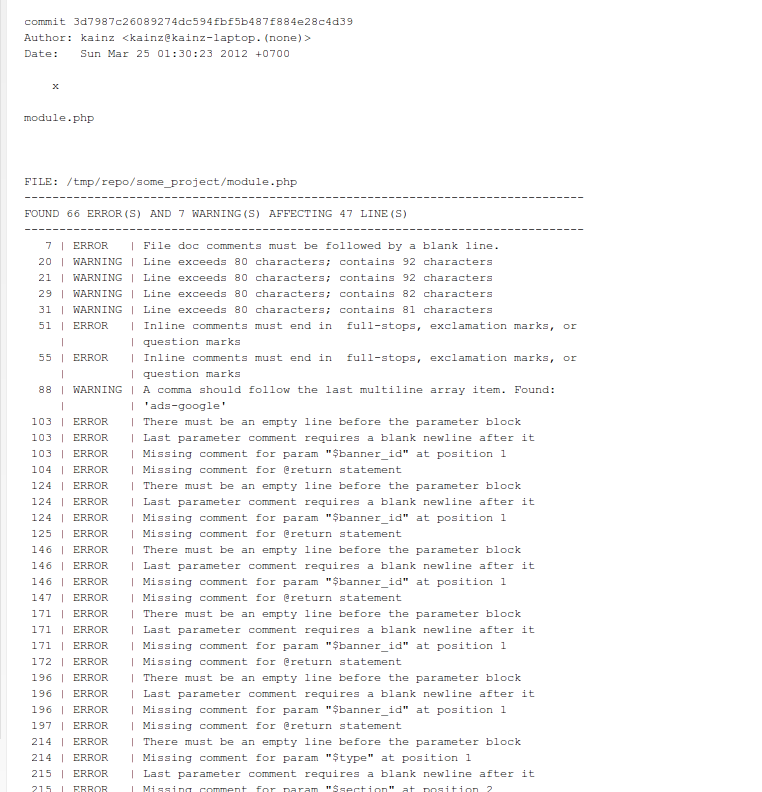
Thus, it is easy to automate the process of monitoring the quality of code on a project.
Strengths of this method:
Disadvantages:
Resources:
UPD 05/19/2012:
Added the ability to ignore file verification using the configuration file.
In order not to check some files and directories, you need to create a .hooks_ignore file in the project root. Then put in it the paths to files and directories that you do not want to check. This may be the core of the engine or third-party modules.
Example contents of the .hooks_ignore file The first two lines allow you to exclude from the scan the full directory with all the files inside, and the third excludes the specific file.
For greater convenience, the .hooks_ignore file should be made under version control so that it is also stored in the repository and is common to all developers on the project. And also so that the post-receive hook can use it when checking in the remote repository.
The source code on Drupal.org and GitHub has been updated.
I look forward to your wishes and comments on this small project.
In order to
Most of the projects of the company where I work are made on Drupal, so an example of checking compliance with Drupal coding standards will be considered, although all the tools described below can be applied to other standards, for example Zend.
More recently, a set of rules has emerged to test Drupal coding standards through PHP Code Sniffer. Installing and configuring it is very simple, the most difficult part starts next. How to make everyone check their code? The influence of the human factor affects, the first forgot, the second did not want, and the third simply believes that his code cannot contain errors and, in general, all this is an waste of time.
The solution could be
The first step is to add a code validation script to the pre-commit hook. When a developer commits his code, modified files will be automatically checked. If errors are found, the commit operation is aborted and a list of errors is displayed:

The code can be committed only when all errors have been fixed. Great, now we do not allow adding “bad” code to the project repository! But still the human factor remains. Again, someone forgets to add a verification script to the .git / hooks folder of his project, someone is too lazy to fix errors and he puts it off for later, etc., and the “smartest” just use git commit --no-verify because now they have no time for mistakes. In the latter case, git will not call the pre-commit hook and the modified files will go to the repository without checking.
In order to deal with this, we use the post-receive hook. This hook fires after adding code to the remote repository. The script that will be called in the post-receive hook checks the modified files for errors and sends a report to the mailbox of one or more senior developers who are responsible for the quality of the code on the project.
A report sent by mail looks like this:

Thus, it is easy to automate the process of monitoring the quality of code on a project.
Strengths of this method:
- Centralized control;
- Code verification cannot be completely avoided;
- Code verification scripts do not modify the source files and do not block the addition of code in case of a hotfix;
- Scripts are easy to install and configure;
- In addition to Drupal coding standard errors, functional errors are displayed. For example, that you forgot to use the t or check_plain function (which is already a security hole) when outputting data to a page.
Disadvantages:
- If you add this tool in the middle of development, all old errors will appear and at first it will be difficult to clear them.
Resources:
- Drupal code sniffer
- A set of scripts for automatically checking code through git
- Instructions for installing and configuring scripts in Russian
UPD 05/19/2012:
Added the ability to ignore file verification using the configuration file.
In order not to check some files and directories, you need to create a .hooks_ignore file in the project root. Then put in it the paths to files and directories that you do not want to check. This may be the core of the engine or third-party modules.
Example contents of the .hooks_ignore file The first two lines allow you to exclude from the scan the full directory with all the files inside, and the third excludes the specific file.
includes
sites/all/modules/contrib
sites/all/themes/garland/template.php
For greater convenience, the .hooks_ignore file should be made under version control so that it is also stored in the repository and is common to all developers on the project. And also so that the post-receive hook can use it when checking in the remote repository.
The source code on Drupal.org and GitHub has been updated.
I look forward to your wishes and comments on this small project.
