Google FalseStart 30% faster SSL “handshake”
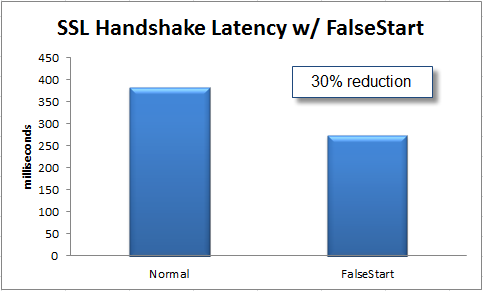
On a Chromium blog, Google developers talked about their success in implementing SSL FalseStart (RFC). This is a client technology for the browser, which does not require any changes on the server side, but at the same time speeds up confirmation of SSL communication by 30% (the delay is measured as the time between the initial TCP SYN packet and the end of the TLS procedure).
Thanks to FalseStart, the Chrome browser since the ninth version establishes an SSL connection 30% faster than other browsers. If you study the specifications , it seems that the main advantage in speed is achieved due to the fact that, subject to other conditions, the sending of data via a secure connection begins even before the confirmation of the connection is completed (see page 3).
After implementing this feature, the developers found that for some reason it does not work on all sites, although it fully complies with the official specifications of SSL and TLS.
To investigate the problem, a list of all HTTPS sites from the Google index was compiled and FalseStart was checked for them. It turned out that 0.4% were unable to establish a secure session. A more thorough study revealed that these sites work with load balancers from a limited number of vendors (for example, F5 and A10). They all received notifications from Google. Many have already solved the problem, others will do so soon. Thus, now Chromium sources contain a list of domainson which FalseStart is not supported. On these domains, the function is simply disabled. The list will be gradually reduced and eventually should disappear altogether.
Perhaps with an increase in SSL performance, more sites will start working in secure mode. As you know, now the biggest delay in SSL is given by the procedure for confirming the connection .
