Median Filter Generalization
annotation
This article talks about a unique filter, an article about which appeared in 1990: Maslov A.M., Sergeev V.V. Identification of a linear distorting system using rank signal processing // Computer Optics. - M., 1990. - Issue 6. - S.97-102. This algorithm is called the “Rank Processing Algorithm” and in fact is a generalization of the median filter.
The use of this filter is justified in two cases - to suppress noise and to reduce grease.
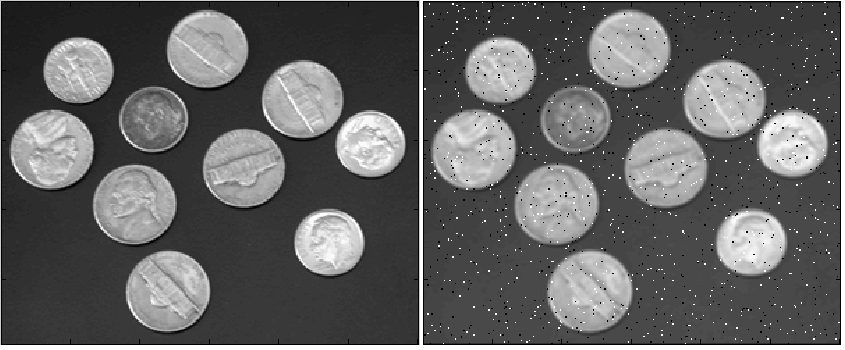
Figure 1 - the original image, 2 - blurry and noisy salt.
Signal Processing Algorithm - Extreme Filter
The algorithm consists in processing the image by a local window with recording the result of processing in a new image:
- Let us be at the image point with coordinates (I, J) - current count
- Around the current reference, we consider a local neighborhood of size NxN
- Using the values of points in a local neighborhood, a variational series is constructed , which we denote by p . The size of this row is N * N.
- In the resulting image, the current count takes on the following rule:
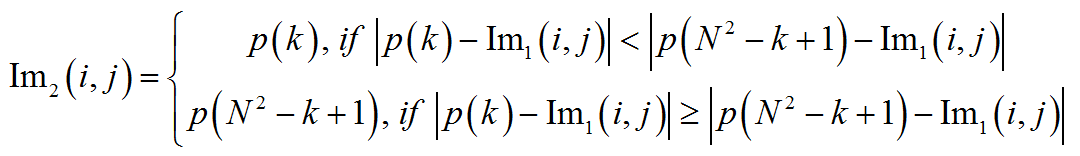
where k is the parameter of the algorithm, N is an odd number, Im1 is the original image, Im2 is the resulting image.
If k = (N ^ 2 + 1) / 2 - that is, the center of the variational series - this filter becomes a known median filter. In the future, this parameter will be called indentation .
Extreme Filter Properties
The properties of this filter are very useful in practice, since the filter allows you to compensate not only for noise but to eliminate (partially) the effects of image blur. The limiting case of this filter at k = (N ^ 2 + 1) / 2 is a median filter that only eliminates noise but does not touch the border, and if the image is blurry, the blur will remain.
At k <(N ^ 2 + 1) / 2, the noise is filtered slightly worse, but the image sharpness increases, and at k = 0, the noise is not filtered at all, but the grease will be eliminated in the strongest way.
In order not to bother readers with an elementary implementation of this algorithm, I will provide here the code in Matlab.
The testing script will read the image, blur it, and add noise. Then the image is restored by these extreme filters. Filter function code im2_rang_filter :
- I1 = imread('coins.png');
- h = ones(3,3) / 9;
- I2 = imfilter(I1,h) ;
- I3 = imnoise(I2,'salt & pepper',0.02);
- I4 = im2_rang_filter (I3, 1, 2);
-
- figure; imagesc(I1);
- colormap gray;
- figure; imagesc(I3);
- colormap gray;
- figure; imagesc(I4)
- colormap gray;
* This source code was highlighted with Source Code Highlighter.
- function outImage= im2_rang_filter (aImage, aHalfWindowSize, aOtsup)
- [ver,hor] = size(aImage);
- wsize = (aHalfWindowSize*2+1)^2;
- result = zeros(ver,hor);
- for i = aHalfWindowSize+1 : (ver - aHalfWindowSize)
- for j = aHalfWindowSize+1 : (hor - aHalfWindowSize)
-
- wind = aImage((i-aHalfWindowSize) : (i + aHalfWindowSize), (j-aHalfWindowSize) : (j + aHalfWindowSize));
- vec = reshape(wind,1,wsize);
- vec = sort(vec);
-
- if (abs(vec(aOtsup+1) - aImage(i,j)) < abs(vec(wsize - aOtsup) - aImage(i,j)) )
- result(i,j) = vec(aOtsup+1);
- else result(i,j) = vec(wsize - aOtsup);
- end;
-
- end;
- end;
- outImage = result;
* This source code was highlighted with Source Code Highlighter.
Experiments
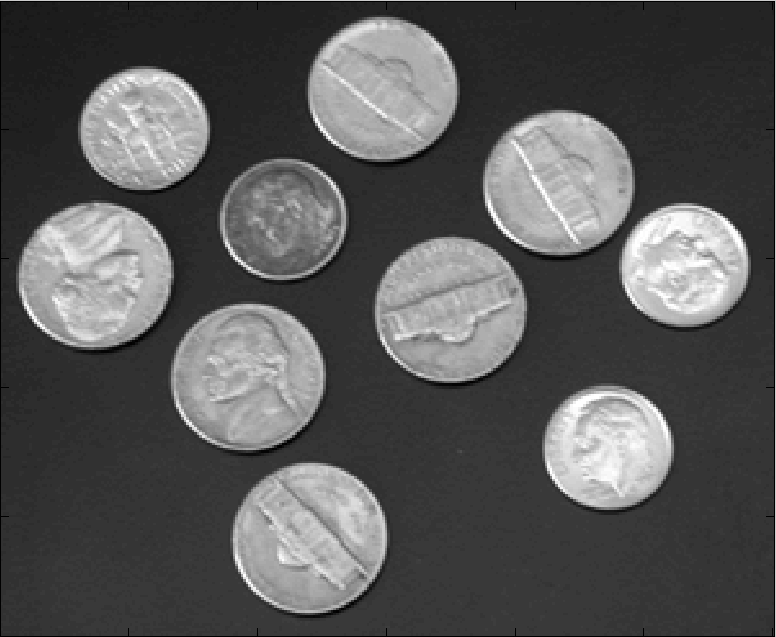
Shown below are the results of filtering with a 3 by 3 window by varying the parameter k = 1.2.5. The first picture is the original image, the second picture is distorted, followed by filtered ones at k = 1, 2, 5:
Original:

Distorted:
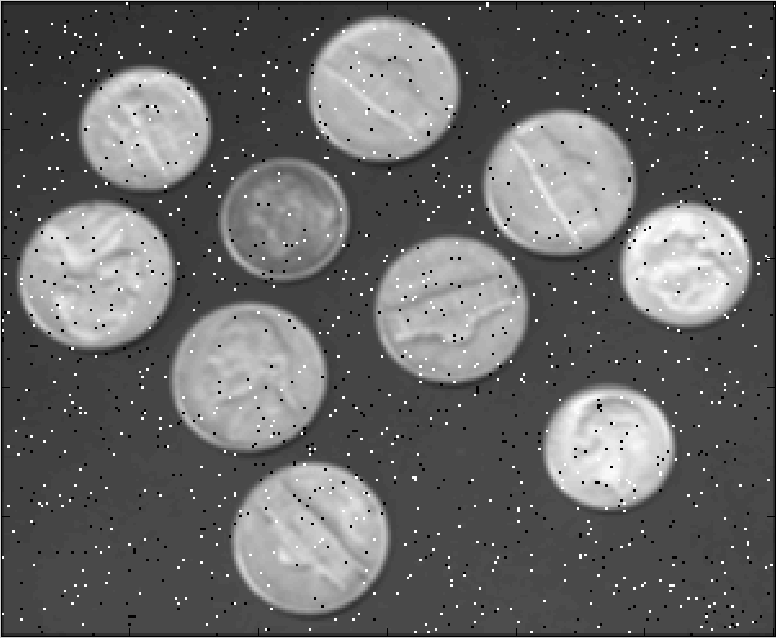
Recovered at k = 1:
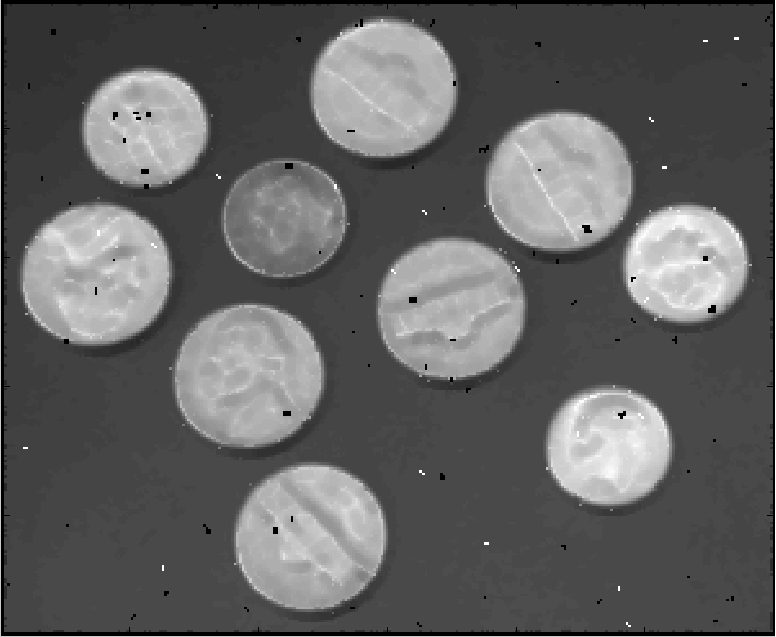
Recovered at k = 2:
Recovered at k = 5:

I have this I really like the filter and I actively use it in practice. Readers are interested in this filter.
