Glass vs stone - better, worse or equal?
The glass theme in St. Petersburg's Lakhta Center is very curious, if only because glass performs the function of walls in the tower. It means that it must protect from the external environment and be resistant to destructive effects at least not worse than traditional materials. But can we say that behind the facade of the “Lakhta Center” - as if behind a stone wall?
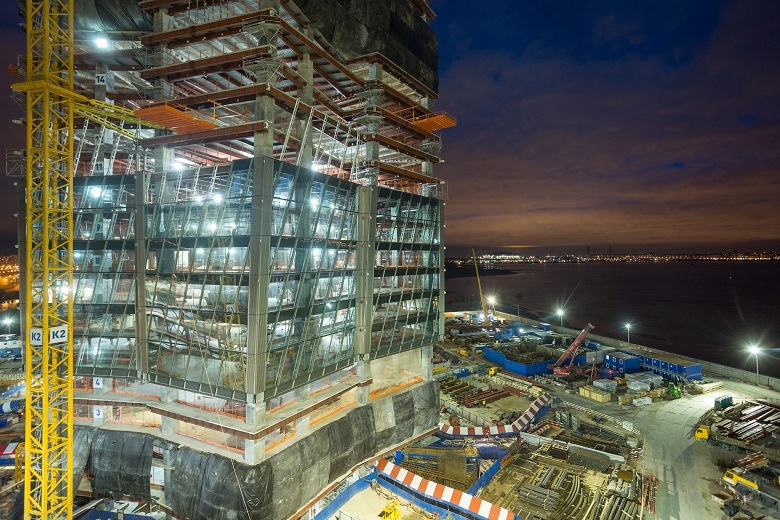

The question is not idle. After all, we all know from childhood how sad the stories about houses, where the walls are made of the wrong materials, end ...

Let us see!
Architects of skyscrapers often make a choice in favor of glass facades. Because it is:
A. Beautifully
B. The facade of glass is lighter than that of traditional materials. Although the weight of comparable volumes of glass and heavy concrete is approximately equal, glass material is needed less to build walls of the same quadrature.
C. Glass meets all the necessary requirements for walls - for durability, thermal insulation, protection from various external influences. We will talk about this below. So,
In the last post there was a separate discussion on the strength of the glass facade of a skyscraper. Somewhere on an intuitive level, it is clear that the facades in the tower must be reliable, but life experience at the same time suggests that glass is still fragile material. Even a frontal vehicle can be damaged due to temperature differences or a stone hit. What can we say about the glass wall - it is simply scary to lean against it, especially - somewhere on the 87th floor.
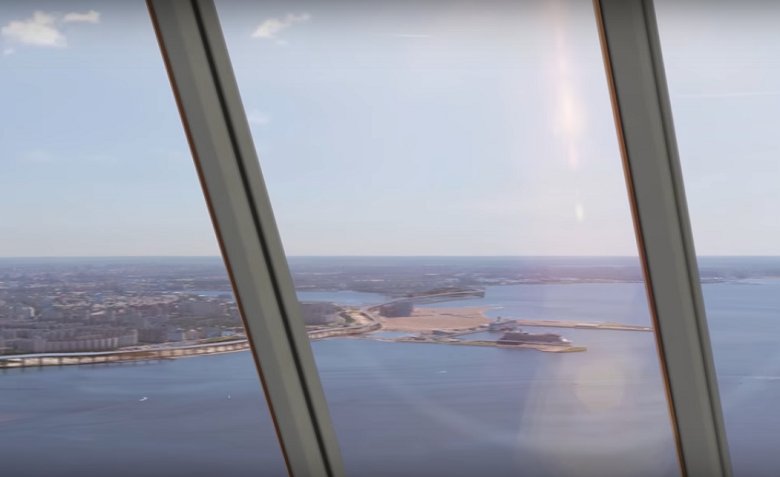

Visualization of the panorama from the top floor of the Lakhta Center. Would you come close to the glass?
However, the case under discussion is one in which life experience is wrong. Similar to the fact that the earth is still round, the plane flies without flapping its wings, the modern front glass with dignity withstands the ingress of stone into it, the temperature shock and damage does not give fragments, thus violating the usual, obtained by experienced observations, the world.
Moreover, today engineers use glass as a constructive element, that is, as supporting structures. The first building with glass constructions was built in the last century - in 1951. Now the translucent roofs with glass beams and arches have the building of the People's Bank in Hanover, the dining room of the Dresden University of Technology, glass columns, each of which has a carrying capacity of 6 tons - under the roof of the courtyard of the city administration building in Saint-Germain-en-Laye.
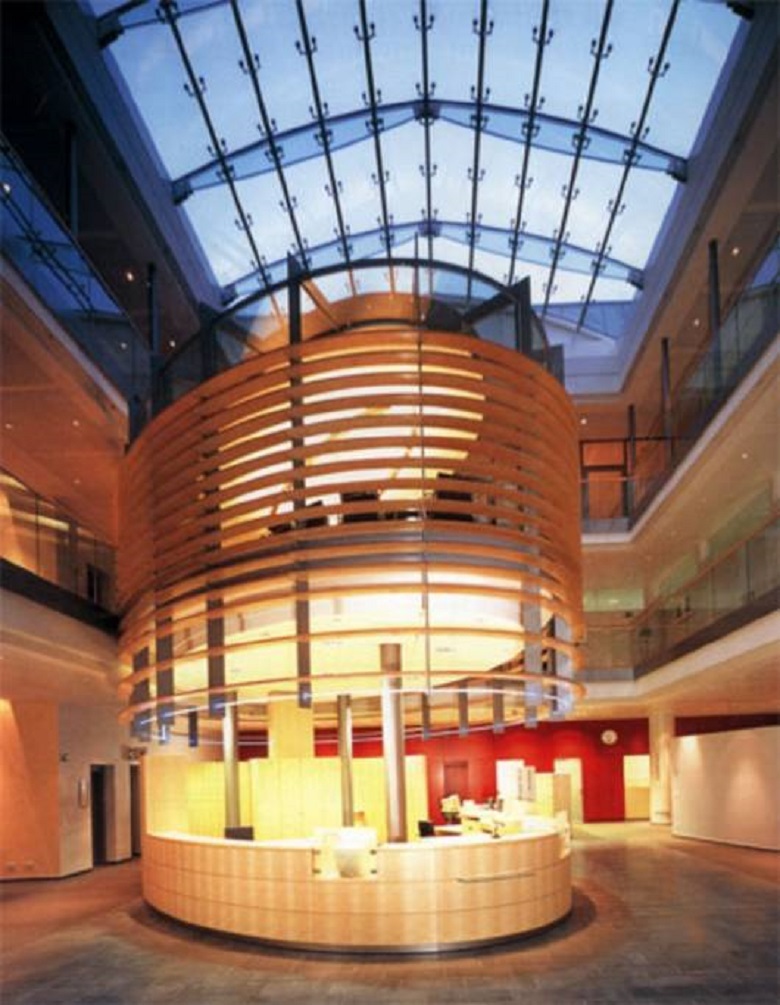

The roof with glass arches - the building of Volksbank (Hannover) Photo from here . Five arches with a pitch of 2.5 m, glued together from 3 sheets of glass. Steel strips - “insurance” against collapse in case of beam failure. You can read more about the glass construction here , for example.
As another visual proof of the reliability of the glass, I will give an example of such a terrible but safe attraction: The
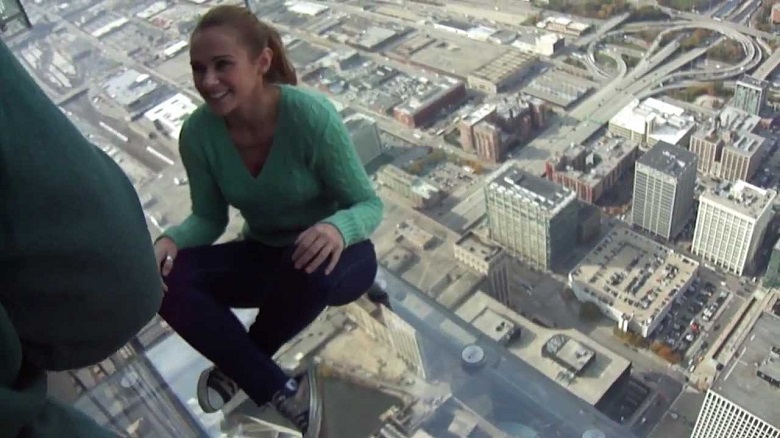

observation deck on the 103rd floor of the Willis Tower, Chicago. Made entirely of glass. You can not worry about the visitor - the floor under her is almost 4 cm thick, the balcony can withstand a load of 5 tons.
Facade glass in St. Petersburg "Lakhta Center" is even slightly thicker - 4.15 cm. The design load on the facades is 400 kg. on apt. m. It's like this:

Could Bruce Willis break it?

Most likely no. But Mike Theisson, with a stroke of 800 kg would have done well.
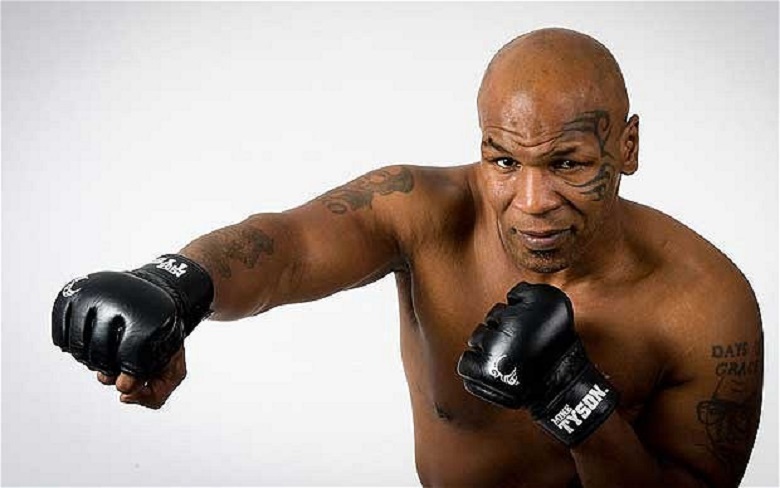

If you are not Mike, you can not only boldly lean against such a facade, but even slightly knock on it with a chair - as in the movie it will not work.
Nothing bad will happen.
First, the glass facade, although a wall, does not play a “role”. You can break as many glasses as you want - this does not affect the stability of the tower structures, where the load bearing forces are distributed between the core of reinforced concrete and the columns.
Secondly, glass designed for the facades of the Lakhta Center (and for the facades of other skyscrapers) is safe - if damaged, it does not give large or sharp fragments. It does not give fragments at all - instead, dents or cracks form on it. Damaged glass in such a "wrinkled", but mechanically holistic, waiting for his replacement.
This is because the glass consists of layers, one of which is a film.
This technology is called Triplex and, we think, is known to readers. For example, it is used for the manufacture of automotive front windows.
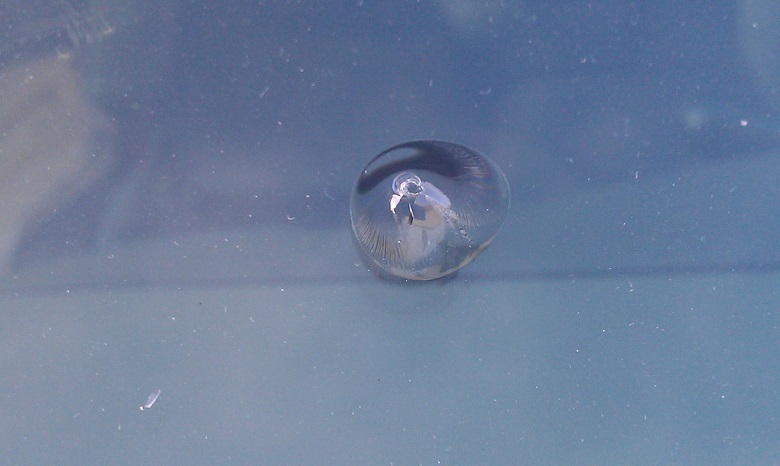

Trail from hit the stone on the glass Triplex
Glasses for the Lakhta Center facades are made according to a multilayer formula: glass 8 mm + 1.5 mm film + 8 mm glass + 16 mm argon + 8 mm glass, in total - 4.15 cm thickness.
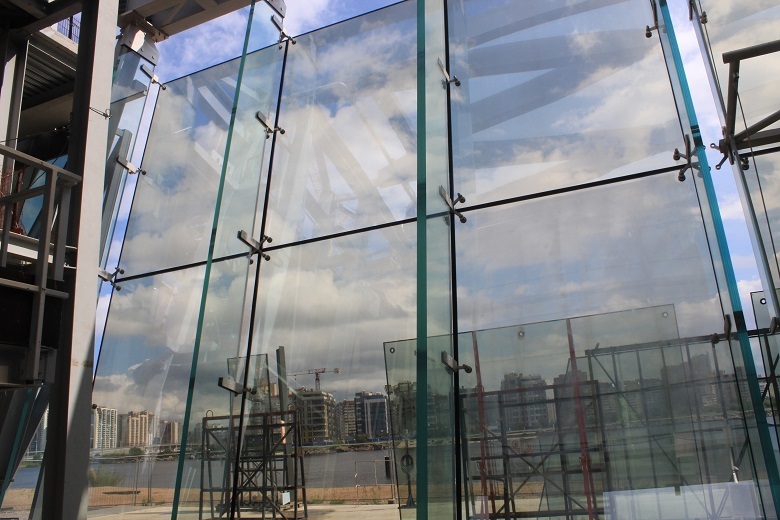

The thickness of the glass can be estimated by the rib part of the sheets. The
peculiarity of the outer layer of glass is thermo-reflective properties. To protect against excess solar radiation (even if such an assumption sounds strange for the climatic conditions of the northern capital), a special coating has been applied to the glass. It, by the way, also gives to a front covering a "metal", cold gray-blue shade.
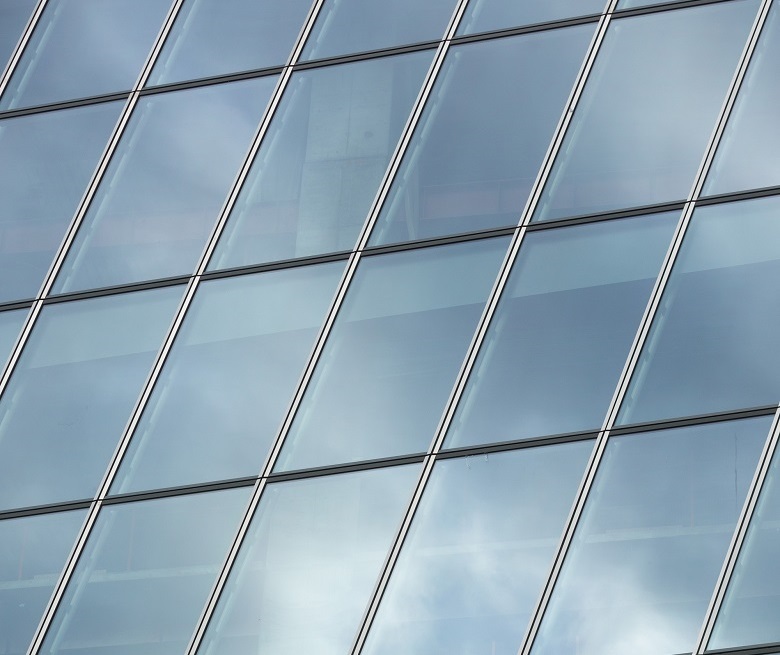

The inner layer of glass is hardened. Toughened glass is the second type of extremely durable and, at the same time, safety glass, which does not give sharp or large fragments in case of damage.
Argon layer is used to improve energy efficiency.
The thermal conductivity of this gas is approximately 1.5 times lower than that of air (0.68 of the thermal conductivity of air). Although the figure is not so great, but it becomes quite significant in the scale of the glazing area of the building - 72.5 thousand square meters.
There are other pleasant "little things" - for example, a high viscosity of the noble gas, which reduces the speed of convection, and, consequently, heat transfer between the layers of glass.
Due to the multi-layered and argon interlayer, the package in the “Lakhta Center” is single-chamber and the single-glazed string, with the exception of some special sections, which will be discussed later. The weight of the glass part of the facade is about 13 thousand tons. In the case of multi-chamber glass solutions, the weight would have increased significantly. This, in turn, would affect the design parameters - we probably would not have seen the tower as it is being built now.
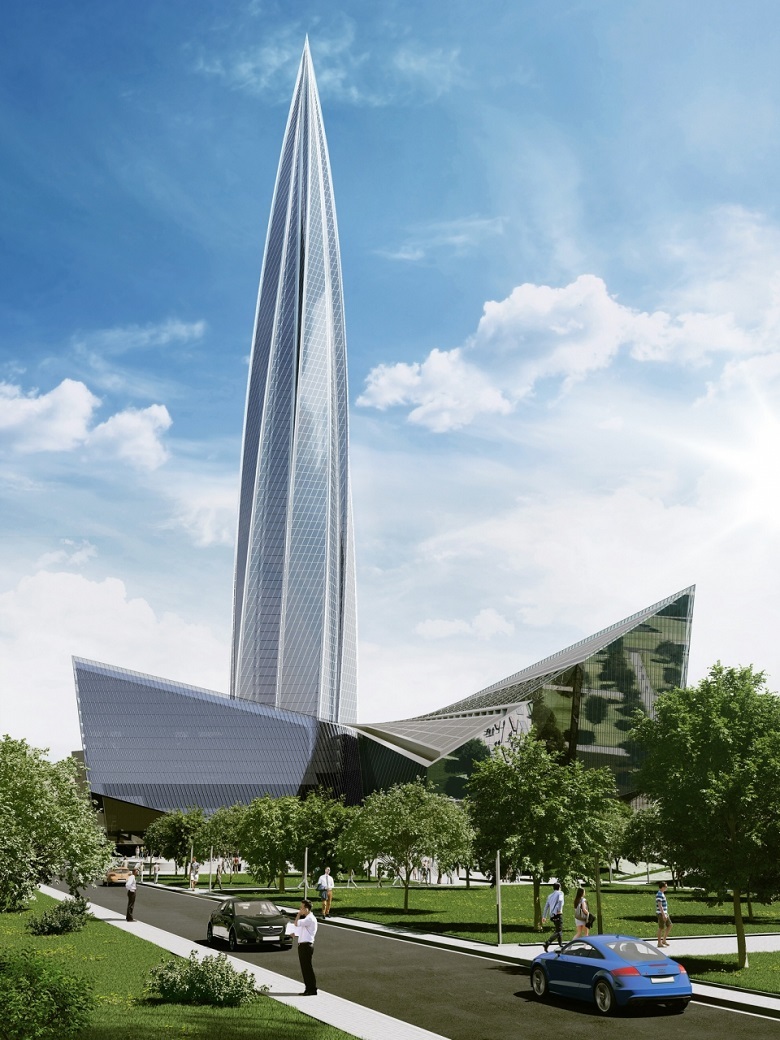

Engineering group "Lakhta Center" refers to glass without any reverence. Some readers are aware that the glass has been frozen and blown, but this is not all. He was also drowned, set on fire and spied on him day and night.
Tests on the integrity of facades - at the site of the company Gartner (Germany). With the help of various instruments, testers will imitate different types of heavy rain and their effect on glass packs.
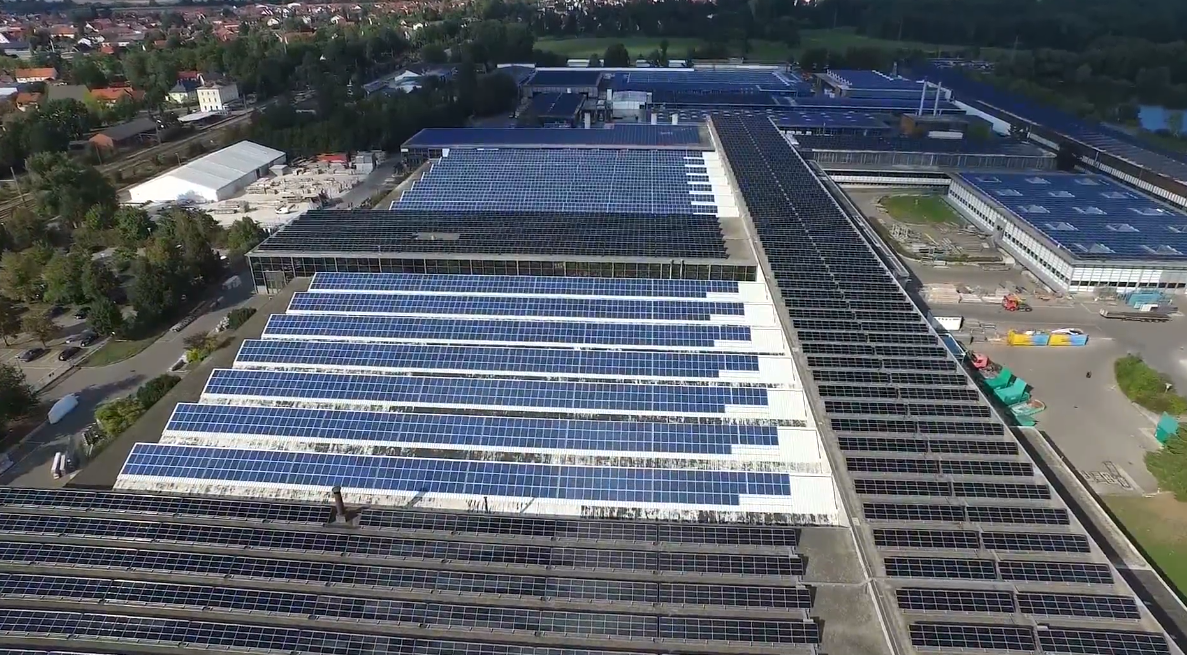

Laboratory site where the passage was carried out. Pay attention to light metal scaffolding. Behind them is a full-scale model of the facade - several glass packs in the form of a parallelogram.

Testing has begun. Double-glazed window is poured by a stream of water under strong pressure. Water comes from here such sprinklers:

The sprinkler is not single. What looked like forests, in fact - numerous rows of sprinklers:

The experiment revealed a side effect - a rainbow):
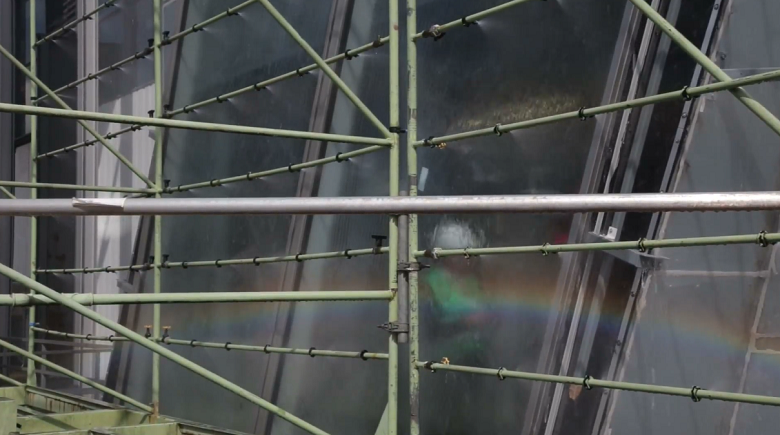
On this side of the glass - just a flood:

But this is not enough. After all, what is “rain” without “wind”? The following setup goes into battle:
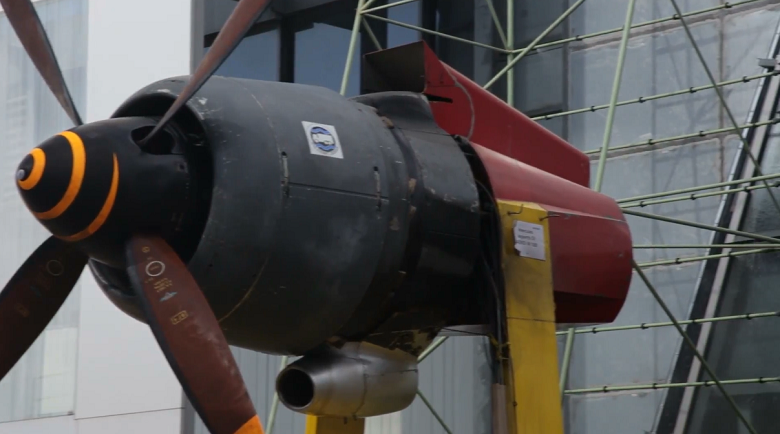

It will add a hurricane wind:
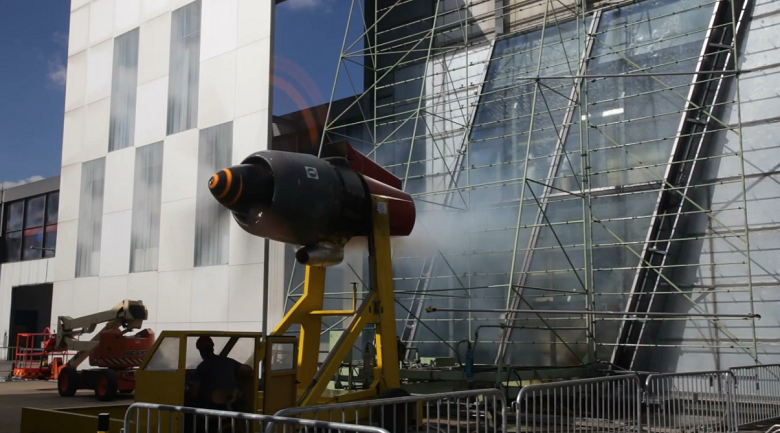

Now a whole storm is raging behind the facade:

Testers from the opposite side, dry to the skin, unlike their colleagues outside, collect indicators and record the response of the facade to different “weather” conditions, stability of the glass unit to various types of rain, the tightness of the "covering" of the full-scale model.

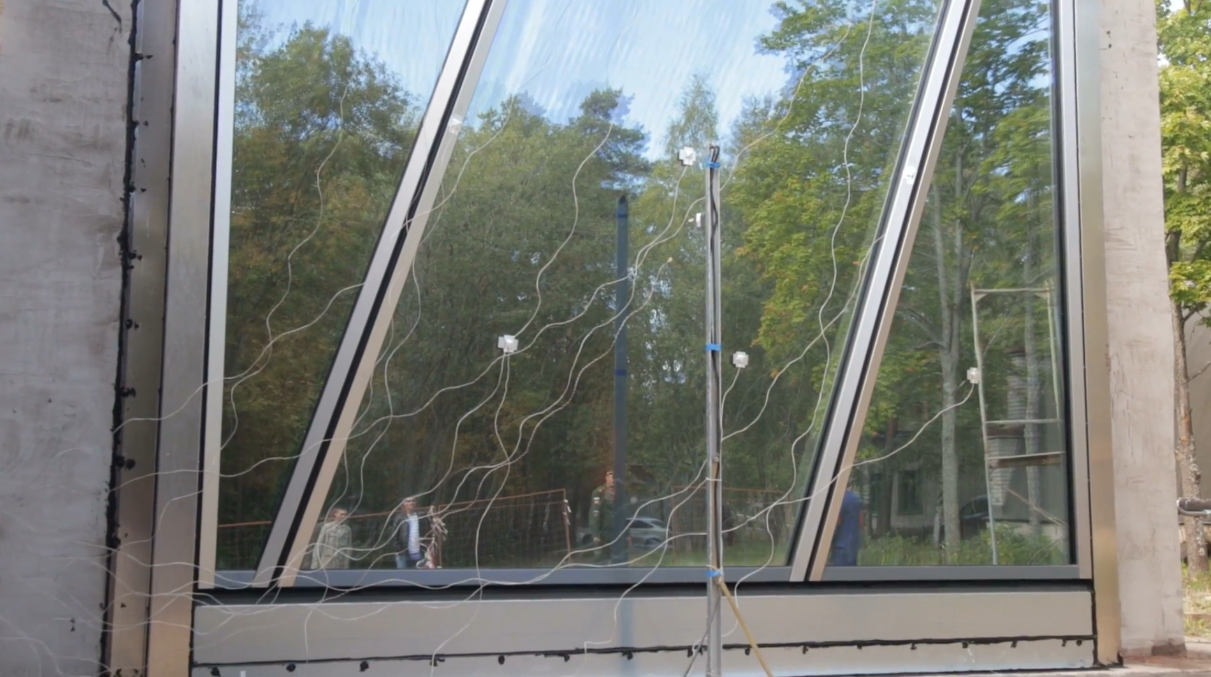
But another series of tests - fire. Here the glass will be set on fire. Full-scale fire tests are carried out in a surface concrete bunker, one of the walls of which is replaced by an experimental glass on which sensors are fixed:

During the first part, they will test the response of the glass to a fire with a fire extinguishing system running. Indoors, everything is ready for arson:

These sprinklers will protect the facade:

Let's go!
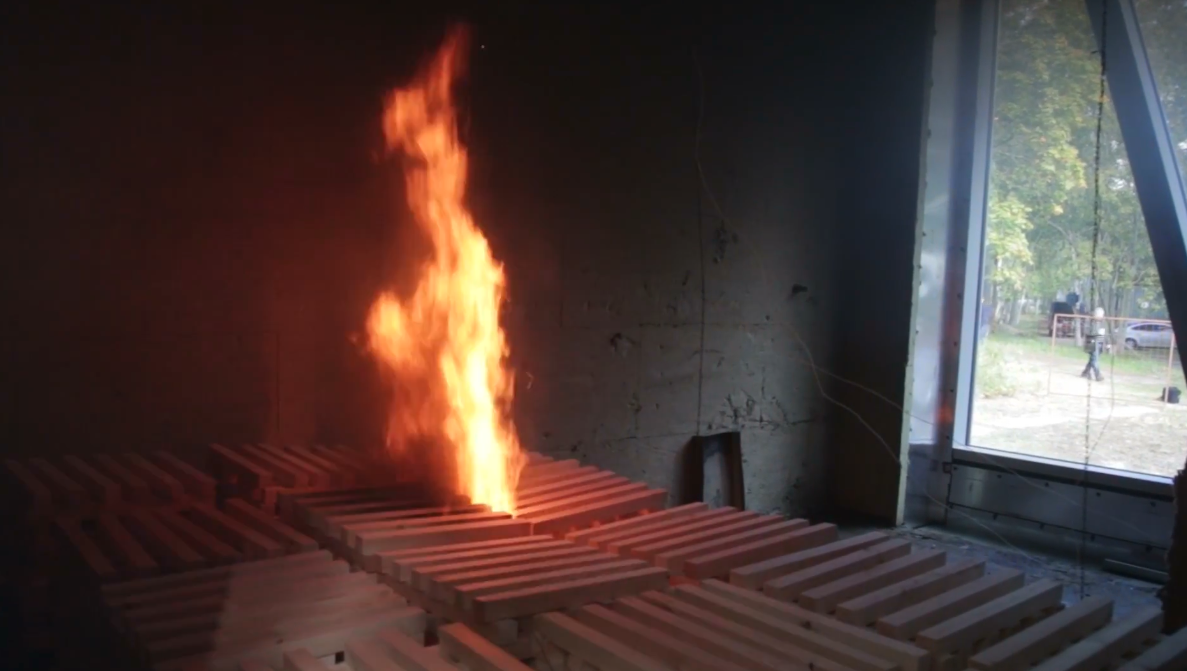

Within a few minutes a fire rages inside the concrete cabin ...

And the water ... Sprinklers work - in the photo you can see the accumulation of moisture on the frame:
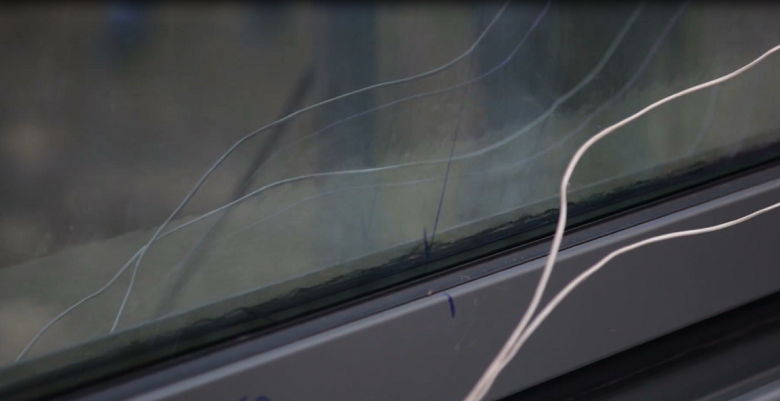

But the temperature of the facade when the fire extinguishing system is working. Different sensors at different time points record 18-20 degrees on the outer surface of the glass, the temperature does not rise higher. The result is very good.

The second part of the test is to confirm the thermal stability limit of the glasses. Here, the fire extinguishing system turns off and fixes the maximum temperatures at which the glass retains its integrity, as well as other properties without irreversible changes:

Over 600 degrees is a good indicator. Approximately the same - in a specialized fireplace glass.
Finally, another full-scale modeling was carried out in order to evaluate the aesthetic properties of the facade. Today, the modeling site, which is located next to the construction site, is not overwhelmed - there are grids, samples of paving coverings, and variants of the planetarium shell ... But this layout:

... appeared on the site the very first, almost a year and a half ago. Different glass samples were inserted and changed into it. A group of designers observed how the glass looks and how it behaves in different weather conditions, in different seasons and time of day - day and night.
Due to the dusting and the fact that the glass on the facades is “enlightened”, i.e. with the lowest possible content of "yellowing" iron oxide (less than 0.015 versus the usual 0.6-0.8), the tower looks different in a cold range under different lighting conditions. Shades depend on light. For example, in the daytime with bright sun and reflection of the sky - blue glass:

In cloudy weather, the edges of the facade may look gray and bronze:

In full bloom and sunset in clear, cloudless weather, observers may catch another unusual shade - red-violet:
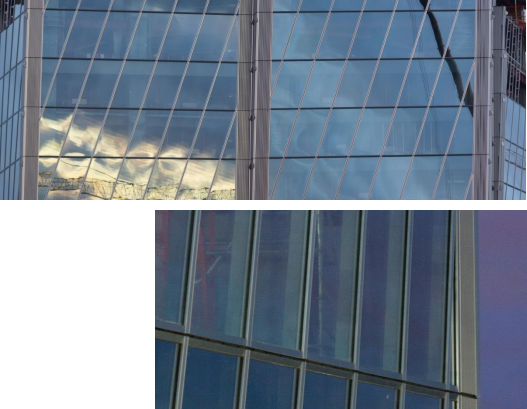

And yet most of the tower of time is gray-blue in color, organically merging with our northern sky and the smoothness of the cold Gulf of Finland.
All these series of tests - on fire, water and beauty, confirmed the compliance of the facade structures with the specified design parameters.
As you can see, glass facades can be strong, safe, warm and beautiful walls. Our opinion is better than stone.

In the next post we will talk about how the aesthetic effect of glazing without edges is achieved, and how the facades of the tower are mounted.

The question is not idle. After all, we all know from childhood how sad the stories about houses, where the walls are made of the wrong materials, end ...

Let us see!
Architects of skyscrapers often make a choice in favor of glass facades. Because it is:
A. Beautifully
B. The facade of glass is lighter than that of traditional materials. Although the weight of comparable volumes of glass and heavy concrete is approximately equal, glass material is needed less to build walls of the same quadrature.
C. Glass meets all the necessary requirements for walls - for durability, thermal insulation, protection from various external influences. We will talk about this below. So,
Do I need to be a tough nut to break the facade of the tower
In the last post there was a separate discussion on the strength of the glass facade of a skyscraper. Somewhere on an intuitive level, it is clear that the facades in the tower must be reliable, but life experience at the same time suggests that glass is still fragile material. Even a frontal vehicle can be damaged due to temperature differences or a stone hit. What can we say about the glass wall - it is simply scary to lean against it, especially - somewhere on the 87th floor.

Visualization of the panorama from the top floor of the Lakhta Center. Would you come close to the glass?
However, the case under discussion is one in which life experience is wrong. Similar to the fact that the earth is still round, the plane flies without flapping its wings, the modern front glass with dignity withstands the ingress of stone into it, the temperature shock and damage does not give fragments, thus violating the usual, obtained by experienced observations, the world.
Moreover, today engineers use glass as a constructive element, that is, as supporting structures. The first building with glass constructions was built in the last century - in 1951. Now the translucent roofs with glass beams and arches have the building of the People's Bank in Hanover, the dining room of the Dresden University of Technology, glass columns, each of which has a carrying capacity of 6 tons - under the roof of the courtyard of the city administration building in Saint-Germain-en-Laye.

The roof with glass arches - the building of Volksbank (Hannover) Photo from here . Five arches with a pitch of 2.5 m, glued together from 3 sheets of glass. Steel strips - “insurance” against collapse in case of beam failure. You can read more about the glass construction here , for example.
As another visual proof of the reliability of the glass, I will give an example of such a terrible but safe attraction: The

observation deck on the 103rd floor of the Willis Tower, Chicago. Made entirely of glass. You can not worry about the visitor - the floor under her is almost 4 cm thick, the balcony can withstand a load of 5 tons.
Facade glass in St. Petersburg "Lakhta Center" is even slightly thicker - 4.15 cm. The design load on the facades is 400 kg. on apt. m. It's like this:

Could Bruce Willis break it?

Most likely no. But Mike Theisson, with a stroke of 800 kg would have done well.

If you are not Mike, you can not only boldly lean against such a facade, but even slightly knock on it with a chair - as in the movie it will not work.
Mike broke the glass. What's next?
Nothing bad will happen.
First, the glass facade, although a wall, does not play a “role”. You can break as many glasses as you want - this does not affect the stability of the tower structures, where the load bearing forces are distributed between the core of reinforced concrete and the columns.
Secondly, glass designed for the facades of the Lakhta Center (and for the facades of other skyscrapers) is safe - if damaged, it does not give large or sharp fragments. It does not give fragments at all - instead, dents or cracks form on it. Damaged glass in such a "wrinkled", but mechanically holistic, waiting for his replacement.
This is because the glass consists of layers, one of which is a film.
This technology is called Triplex and, we think, is known to readers. For example, it is used for the manufacture of automotive front windows.

Trail from hit the stone on the glass Triplex
Formula glass and alternative reality
Glasses for the Lakhta Center facades are made according to a multilayer formula: glass 8 mm + 1.5 mm film + 8 mm glass + 16 mm argon + 8 mm glass, in total - 4.15 cm thickness.

The thickness of the glass can be estimated by the rib part of the sheets. The
peculiarity of the outer layer of glass is thermo-reflective properties. To protect against excess solar radiation (even if such an assumption sounds strange for the climatic conditions of the northern capital), a special coating has been applied to the glass. It, by the way, also gives to a front covering a "metal", cold gray-blue shade.

The inner layer of glass is hardened. Toughened glass is the second type of extremely durable and, at the same time, safety glass, which does not give sharp or large fragments in case of damage.
Argon layer is used to improve energy efficiency.
The thermal conductivity of this gas is approximately 1.5 times lower than that of air (0.68 of the thermal conductivity of air). Although the figure is not so great, but it becomes quite significant in the scale of the glazing area of the building - 72.5 thousand square meters.
There are other pleasant "little things" - for example, a high viscosity of the noble gas, which reduces the speed of convection, and, consequently, heat transfer between the layers of glass.
Due to the multi-layered and argon interlayer, the package in the “Lakhta Center” is single-chamber and the single-glazed string, with the exception of some special sections, which will be discussed later. The weight of the glass part of the facade is about 13 thousand tons. In the case of multi-chamber glass solutions, the weight would have increased significantly. This, in turn, would affect the design parameters - we probably would not have seen the tower as it is being built now.

Experimental
Engineering group "Lakhta Center" refers to glass without any reverence. Some readers are aware that the glass has been frozen and blown, but this is not all. He was also drowned, set on fire and spied on him day and night.
Tests on the integrity of facades - at the site of the company Gartner (Germany). With the help of various instruments, testers will imitate different types of heavy rain and their effect on glass packs.

Laboratory site where the passage was carried out. Pay attention to light metal scaffolding. Behind them is a full-scale model of the facade - several glass packs in the form of a parallelogram.

Testing has begun. Double-glazed window is poured by a stream of water under strong pressure. Water comes from here such sprinklers:

The sprinkler is not single. What looked like forests, in fact - numerous rows of sprinklers:

The experiment revealed a side effect - a rainbow):
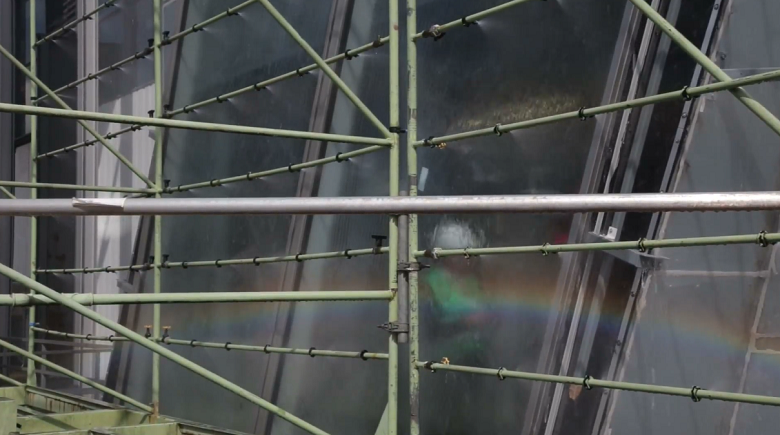
On this side of the glass - just a flood:

But this is not enough. After all, what is “rain” without “wind”? The following setup goes into battle:

It will add a hurricane wind:

Now a whole storm is raging behind the facade:

Testers from the opposite side, dry to the skin, unlike their colleagues outside, collect indicators and record the response of the facade to different “weather” conditions, stability of the glass unit to various types of rain, the tightness of the "covering" of the full-scale model.

But another series of tests - fire. Here the glass will be set on fire. Full-scale fire tests are carried out in a surface concrete bunker, one of the walls of which is replaced by an experimental glass on which sensors are fixed:

During the first part, they will test the response of the glass to a fire with a fire extinguishing system running. Indoors, everything is ready for arson:

These sprinklers will protect the facade:

Let's go!

Within a few minutes a fire rages inside the concrete cabin ...

And the water ... Sprinklers work - in the photo you can see the accumulation of moisture on the frame:

But the temperature of the facade when the fire extinguishing system is working. Different sensors at different time points record 18-20 degrees on the outer surface of the glass, the temperature does not rise higher. The result is very good.

The second part of the test is to confirm the thermal stability limit of the glasses. Here, the fire extinguishing system turns off and fixes the maximum temperatures at which the glass retains its integrity, as well as other properties without irreversible changes:

Over 600 degrees is a good indicator. Approximately the same - in a specialized fireplace glass.
Finally, another full-scale modeling was carried out in order to evaluate the aesthetic properties of the facade. Today, the modeling site, which is located next to the construction site, is not overwhelmed - there are grids, samples of paving coverings, and variants of the planetarium shell ... But this layout:

... appeared on the site the very first, almost a year and a half ago. Different glass samples were inserted and changed into it. A group of designers observed how the glass looks and how it behaves in different weather conditions, in different seasons and time of day - day and night.
Due to the dusting and the fact that the glass on the facades is “enlightened”, i.e. with the lowest possible content of "yellowing" iron oxide (less than 0.015 versus the usual 0.6-0.8), the tower looks different in a cold range under different lighting conditions. Shades depend on light. For example, in the daytime with bright sun and reflection of the sky - blue glass:

In cloudy weather, the edges of the facade may look gray and bronze:

In full bloom and sunset in clear, cloudless weather, observers may catch another unusual shade - red-violet:

And yet most of the tower of time is gray-blue in color, organically merging with our northern sky and the smoothness of the cold Gulf of Finland.
All these series of tests - on fire, water and beauty, confirmed the compliance of the facade structures with the specified design parameters.
As you can see, glass facades can be strong, safe, warm and beautiful walls. Our opinion is better than stone.

In the next post we will talk about how the aesthetic effect of glazing without edges is achieved, and how the facades of the tower are mounted.
