LIDAR from Mazda. We test, we put on Lada

Hello.
This time I got a real LIDAR from the Mazda CX5, approximately 2012, into my hands. release. In this article I intend to disassemble the module and turn it on the table. And the funny thing is, I will install this LIDAR in Datsun Mido (Lada Kalina nee).
Although LIDAR is written on the device, in fact, it is such a laser car tape measure, which is capable of measuring the distance to the object in front of it. Main function — Providing automatic braking in the event of a dangerous approach to another vehicle, or, for example, a wall. The device is one of the main Mazda cars in the ADAS complex and is manufactured by Continental (they are not only tires made from rubber). The ADAS option is called CitySafety. The automatic braking system is called Mazda-SCBS. The obstacle detection range is 6 m, the system works at a speed of up to 40 km / h. According to the manufacturer, the system will help prevent an accident at speeds up to 15 km / h and reduce the severity of the accident at speeds up to 30 km / h.
Example of the system:
I note that the manufacturer’s website (link) was able to find sufficiently detailed documentation for the module. From the documentation it follows that the device was not designed for a specific brand of cars, it has a sufficiently developed internal software that allows to measure the distance to the object, as well as the speed of this object.
Here is an excerpt from the documentation on the main performance characteristics:
Purpose of the device:
- Collision Avoidance Sensor
- Measuring the distance to objects and measuring the speed of these objects in three independent channels. At a distance of 13.5 m
The device has an internal health monitoring system for IR laser and IR radiation receivers.
Characteristics declared by the manufacturer of the sensor:
- Range: 1.0-10m. Extended range up to 13.5 m
- Directional pattern 27 horizontally and 11 vertically
- Range resolution 1 mm
- The range of measured speeds of 2-160 km / h
- Accuracy of speed measurement + -2 km / h
- Measurement frequency 100 Hz
- Laser power 45 mW class 1 laser, 33 ns flash duration
- Wavelength 905 nm
- Work time 12000 hours or 15 years
The sensor has three measurement channels, one central and two lateral.
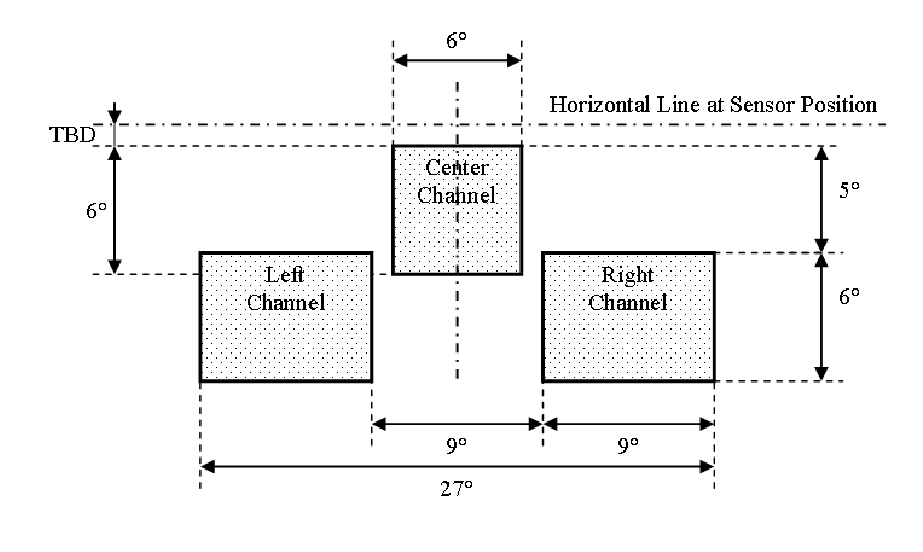

We proceed to the inspection and preparation.
The device is quite compact, has three glass "eyes". Two lenses for receiving the reflected radiation and one Fresnel lens for the formation of the necessary projection of the laser beam. Assembled in a plastic case without the use of screws. All on the clips.
Interiors from the bottom
Here is the radiating infrared element - quite unlike the laser. Under the emitter is an IR photodiode that controls the presence of radiation. The system is controlled by a 16-bit MC9S12XEG128 microcontroller, specialized for automotive applications. Also on this side are the elements of a pulsed power source.
Interiors from the top side
Here we see the mysterious microcircuit from ST, which, apparently, realizes the functions of a laser rangefinder. CAN transceiver, empty space for another CAN transceiver, two receiver lenses and an IR photocell board. Directly under the lenses are two IR LEDs that serve to verify the performance of the receiver. These elements can be seen in the photo with the lenses removed. The documentation for the device states that measurements are carried out on three independent channels; we can be sure of this by seeing three receiving elements.
Connection on the table
Before connecting the device according to the datasheet, I determined the purpose of the connector pins on my own. The device turned out to be easy to connect, it took only a 12V power supply and a CAN bus. The CAN bus documentation was located on other pins, in my case they were not used and the empty space of the transceiver was meant just for them. The transfer rate in my CAN channel is 500 kbit \ s, unused, judging by the documents — 1Mbit \ s.
I connected the device to a typical standard laboratory source CAN bus to a Tektronix oscilloscope with a CAN decoder. Immediately after switching on, the current consumption was 90 mA, with bursts of up to 130 mA approximately once per second. Concluded that the lidar began to turn on the laser. The CAN bus also came to life immediately, a single packet appeared, which the oscilloscope easily recognized.
ID: 0x21D
DLC 8 byte
DATA: 0x7F 0x3F 0xFF 0x00 0x00 0x00 0xD2 0x94
Car installation and testing.
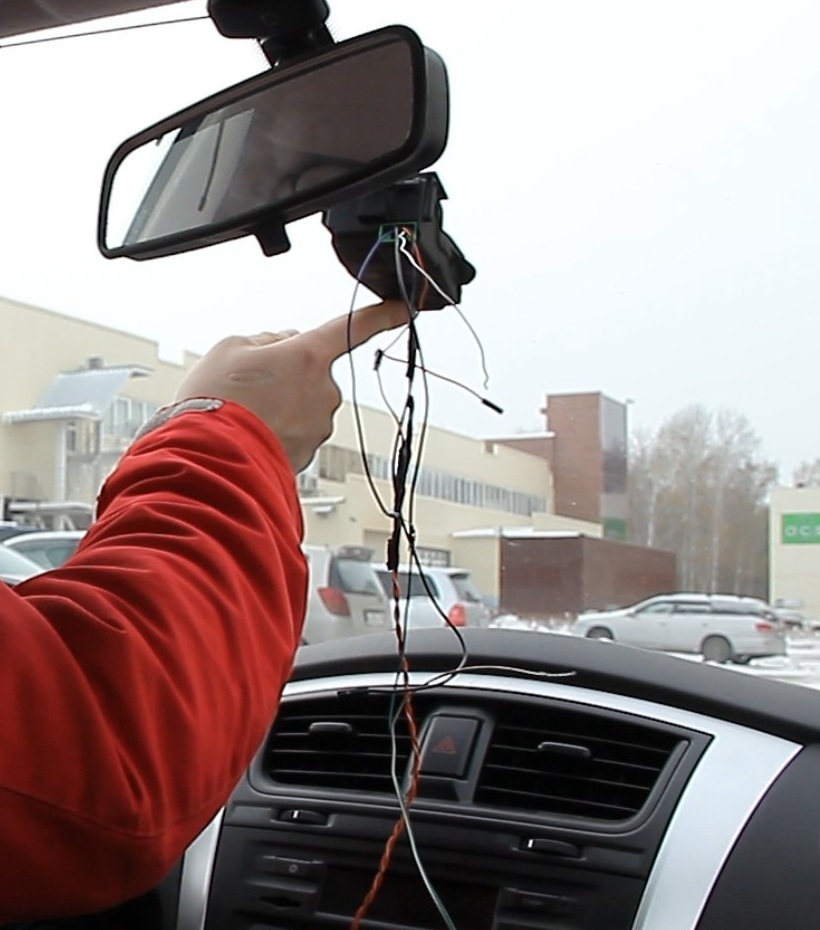
I began to install the “lidar” in my car by analogy with Mazda. Just stuck it on the double-sided tape on the windshield in the area of the rear-view mirror. Power supplied from the cigarette lighter socket.
I connected to CAN using an adapter made 10 years ago and compatible with the well-known program CAN-Hacker. Unlike the first inclusion on the table, the first byte of the packet began to change immediately, until the lidar was fixed on Lobovyk. Based on what I concluded that this byte is responsible for the measured distance.

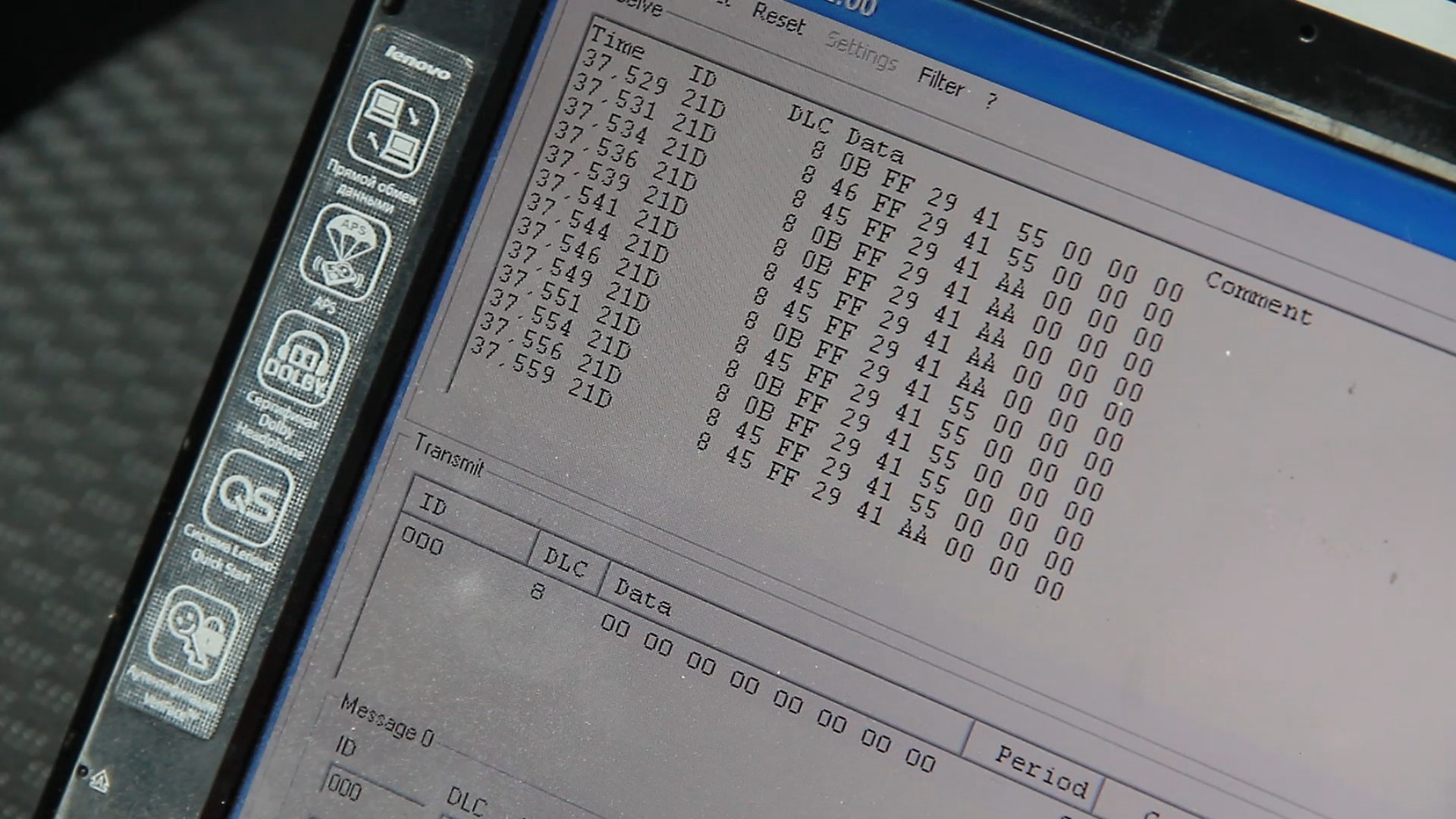
In the guide to the protocol of lidar communication with the outside world, quite a lot of transmitted parameters are described. In our case, it was possible to achieve only measurements of the distance to the object in front.
Testing
For testing, a friend's car was chosen as a target. The test was as follows:
- Approaching as close as possible to the target, fixing the first byte of the packet
- We measure the distance to the target using a laser tape measure
- We compare these roulettes with the data transmitted by the lidar.
The correspondence between the value of the first byte of the LIDAR packet and the value measured by a laser tape measure:
0x41 = 2.054 m
0x46 = 3.166 m
0x49 = 3.8 m
0x7F - target lost
It turned out that the lidar confidently measures the distance to the target no more than 4 meters. In my opinion, this is not the best result for an emergency braking sensor. It is possible that the device worked in some kind of simplified or test mode and on the car the device measures the distance in a wider range. We also conducted an experiment with a large glossy white board, in this case the distance was measured to 5 meters.
Summary
Continental's Mazda Short range LIDAR is an interesting device. I would like that the range of measuring the distance went beyond the 4-meter chapel. If possible, I will try to configure it in the mode described in the documentation and allows me to measure long distances and velocities of objects. Perhaps it will revive the second channel CAN. If suddenly there is someone who wants to pick it up in Novosibirsk, I will be glad to work together.
I will add that the device is easy enough to find on the analysis at a price of 3,000 to 6,000 rubles.
Catalog number: GHP9-67XD0
And finally, a movie about a device shot to the best of its capabilities.
Links:
→ Continental, documentation
→ MAZDA
→ User story
