Because of a mutation in the X chromosome, some women have 100 times more colors than ordinary people.
 A few years ago, the artist Concetta Antico (Concetta Antico) realized that the richness of colors that she sees in the world around her is inaccessible to the eyes of other people, but is the result of a genetic mutation. It turned out that this is a symptom of tetrachromatia - the perception of the visible range of the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation by combinations of four primary colors, and not three colors, like in normal people.
A few years ago, the artist Concetta Antico (Concetta Antico) realized that the richness of colors that she sees in the world around her is inaccessible to the eyes of other people, but is the result of a genetic mutation. It turned out that this is a symptom of tetrachromatia - the perception of the visible range of the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation by combinations of four primary colors, and not three colors, like in normal people.The eye of a normal person contains three types of opsin receptors that are sensitive in the area:
- long waves (Long Wavelength Sensitive, LWS, 560 nm, red);
- medium waves (Middle Wavelength Sensitive, MWS, 530 nm, green);
- short wavelengths (Short Wavelength Sensitive, SWS, 414 nm, purple, bluish), this receptor mutated from the ultraviolet receptor as a result of the evolution of primates about 30-90 million years ago.
The receptor, which perceives green color, is obtained as a result of duplication of the red receptor gene. Both genes encoding these receptors are on the X chromosome. Because of this coding, four-color vision may appear in some women. Since each receptor has two copies, replacing one will lead to the fact that not two, but three receptors will be encoded in the genome.
Some scientists suggest that tetrachromatia is peculiar to 2-3% of women or even more , but in order for it to actually manifest itself, it probably needs training. American artist Conchetta Antico became the first person in the world with scientifically proven functional tetrachromatism .

One of the paintings of Kacchety Antico, the world's first proven tetrachromate
In the past few years, Antico has passed a series of tests that confirmed her vision. To determine how Antico's innate tetrachromatism developed to the stage of functional ability, scientists from the University of Nevada compared her vision with another tetrachromat (not an artist), as well as with the vision of a trichromate artist and a trichromate that does not have artistic preparation. The research results are published in the journal GLIMPSE.

The tests compared the sensitivity of vision to flowers with different wavelengths. Antico showed increased sensitivity in reddish hues, which exactly coincides with the theoretically predicted result, based on the presence of an additional type of receptor. In particular, she distinguishes colors much better in low light conditions, for example, she sees bright color scenes at dusk.
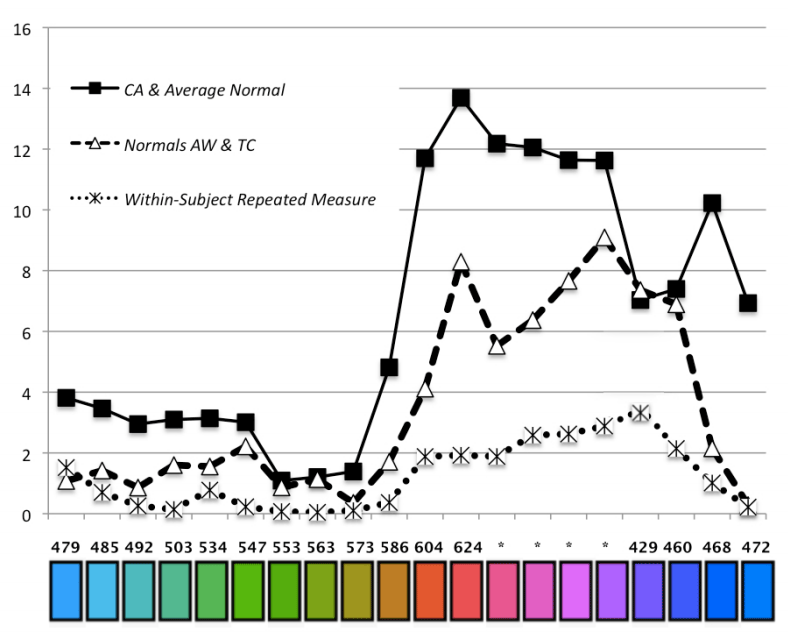
The vertical axis represents the difference of the Euclidean distance in the RGB color cube in the results between the participants. A value of 0 corresponds to the absence of a difference in the difference of colors.

As the scientists supposed, Antico showed a much better result than the other tetrahromat, not an artist. This may mean that many years of training are necessary for the manifestation of “supernormal abilities”.
To explain the features of tetrachromat view, the authors of the scientific work present a photograph with a display of the sites in which an additional fourth type of receptor is sensitive.

Here is another illustration that gives an opportunity to imagine what shades tetrachromat sees. Although we are not able to see it, but in his impressionistic paintings, Concette Antico somehow “strengthens” them so that the shades become accessible to our vision.

