5 open-source security event management systems

How is a good IT security guard different from a regular one? No, not by the fact that at any given time he will recall from memory the number of messages that manager Igor sent yesterday to Maria’s colleague. A good security guard tries to identify possible violations in advance and catch them in real time, making every effort so that there is no continuation of the incident. Security event management systems (SIEM, from Security information and event management) greatly simplify the task of quickly recording and blocking any attempted violations.
Traditionally, SIEM systems combine an information security management system and a security event management system. An important feature of the systems is the analysis of security events in real time, which allows them to respond to existing damage.
The main tasks of SIEM systems:
- Data collection and normalization
- Data correlation
- Alert
- Visualization panels
- Organization of data storage
- Data Search and Analysis
- Reporting
Reasons for high demand for SIEM systems
Recently, the complexity and coordination of attacks on information systems have greatly increased. At the same time, the complex of information protection tools used is becoming more complicated — network and host intrusion detection systems, DLP systems, antivirus systems and firewalls, vulnerability scanners, and more. Each protection means generates a stream of events with different details and often an attack can only be seen by overlapping events from different systems.
A lot of things have been written about all kinds of commercial SIEM systems., but we offer a brief overview of free full-fledged open-source SIEM systems that do not have artificial restrictions on the number of users or the volumes of received / stored data, and are also easily scalable and supported. We hope this will help assess the potential of such systems and decide whether to integrate such solutions into the company's business processes.
AlienVault OSSIM
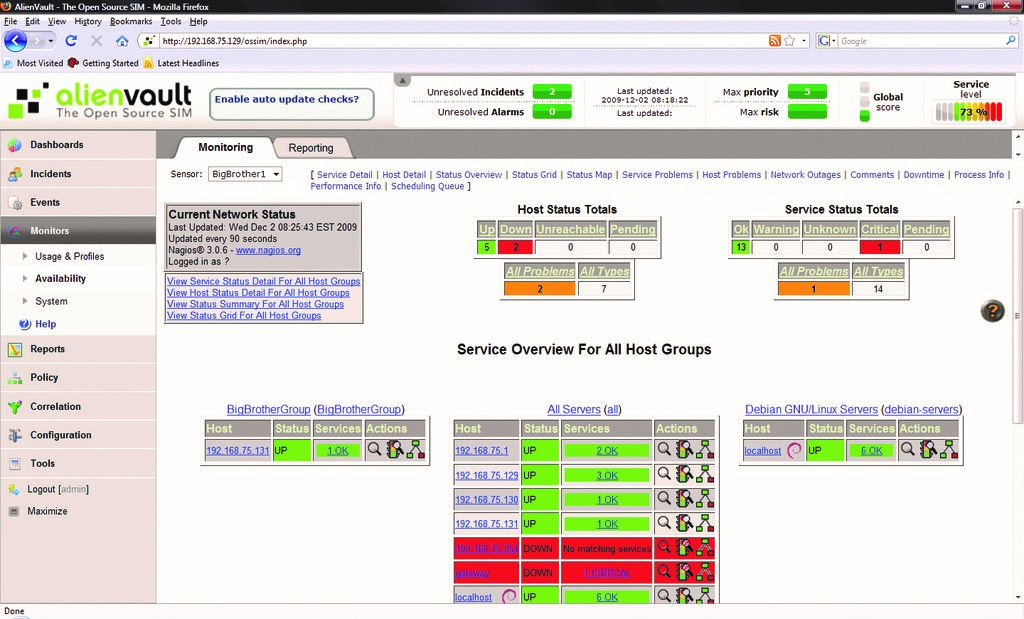
AlienVault OSSIM is an open-source version of AlienVault USM, one of the leading commercial SIEM systems. OSSIM is a framework consisting of several open source projects, including Snort intrusion detection network system, Nagios network and host monitoring system, OSSEC host intrusion detection system and OpenVAS vulnerability scanner.
For monitoring devices, the AlienVault Agent is used, which sends logs from the host in syslog format to the GELF platform or can be used by a plug-in for integration with third-party services, such as Cloudflare reverse proxy service or Okta multi-factor authentication system.
The USM version differs from OSSIM in terms of enhanced log management, cloud infrastructure monitoring, automation, and updated threat and visualization information.
Benefits
- Built on proven open-source projects;
- A large community of users and developers.
disadvantages
- Does not support monitoring of cloud platforms (for example, AWS or Azure);
- There is no log management, visualization, automation and integration with third-party services.
Source
MozDef (Mozilla Defense Platform)
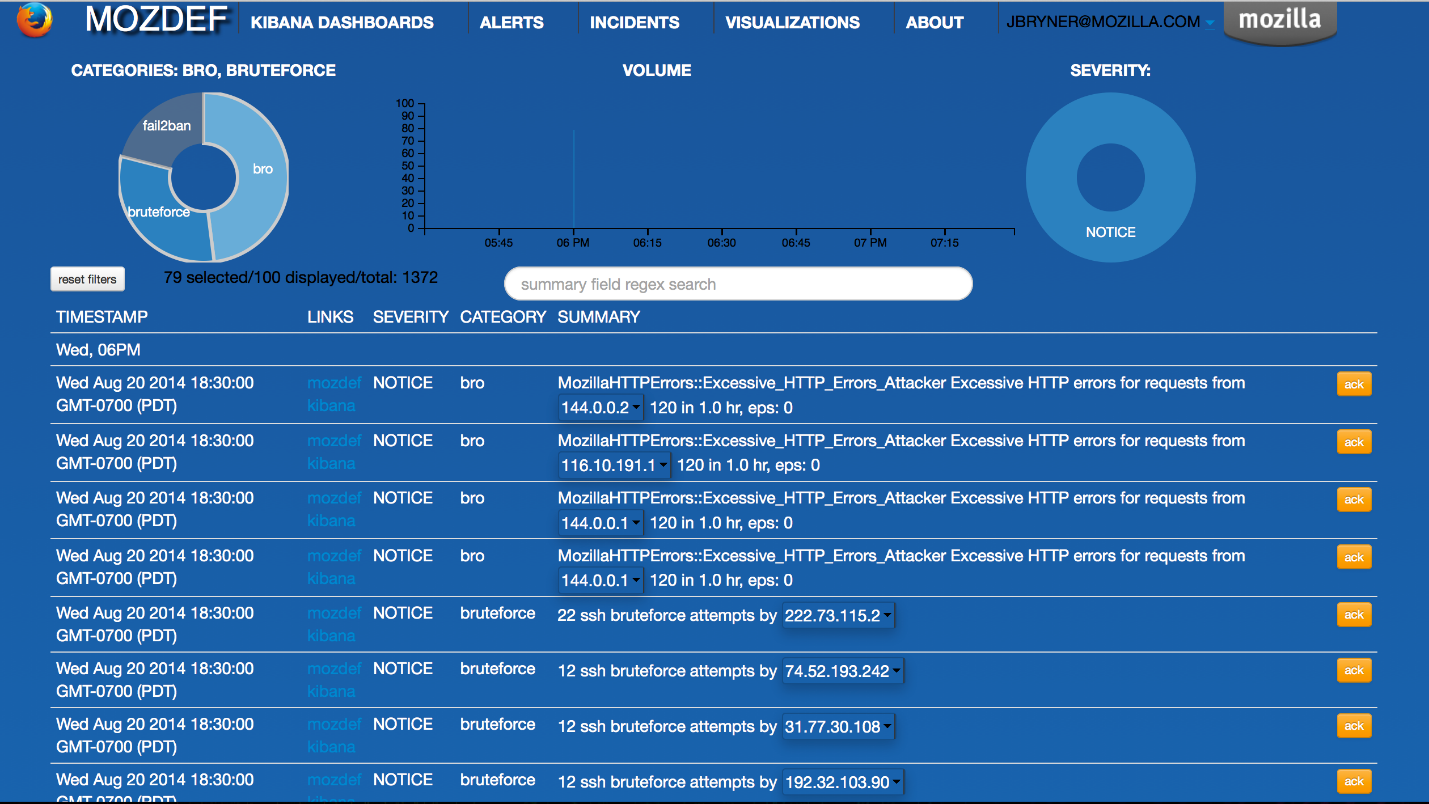
Mozilla’s MozDef SIEM system is used to automate security incident handling. The system is designed from the ground up for maximum performance, scalability and fault tolerance, with a microservice architecture - each service runs in a Docker container.
Like OSSIM, MozDef is built on time-tested open source projects, including the Elasticsearch logging and search indexing module, the Meteor platform for building a flexible web interface, and the Kibana plugin for visualization and graphing.
Event correlation and notification are performed using the Elasticsearch request, which allows you to write your own rules for event processing and alerts using Python. According to Mozilla, MozDef can handle more than 300 million events per day. MozDef only accepts events in JSON format, but there is integration with third-party services.
Benefits
- It does not use agents - it works with standard JSON logs;
- Easy to scale thanks to microservice architecture;
- Supports cloud service data sources, including AWS CloudTrail and GuardDuty.
disadvantages
- New and less established system.
Source
Wazuh
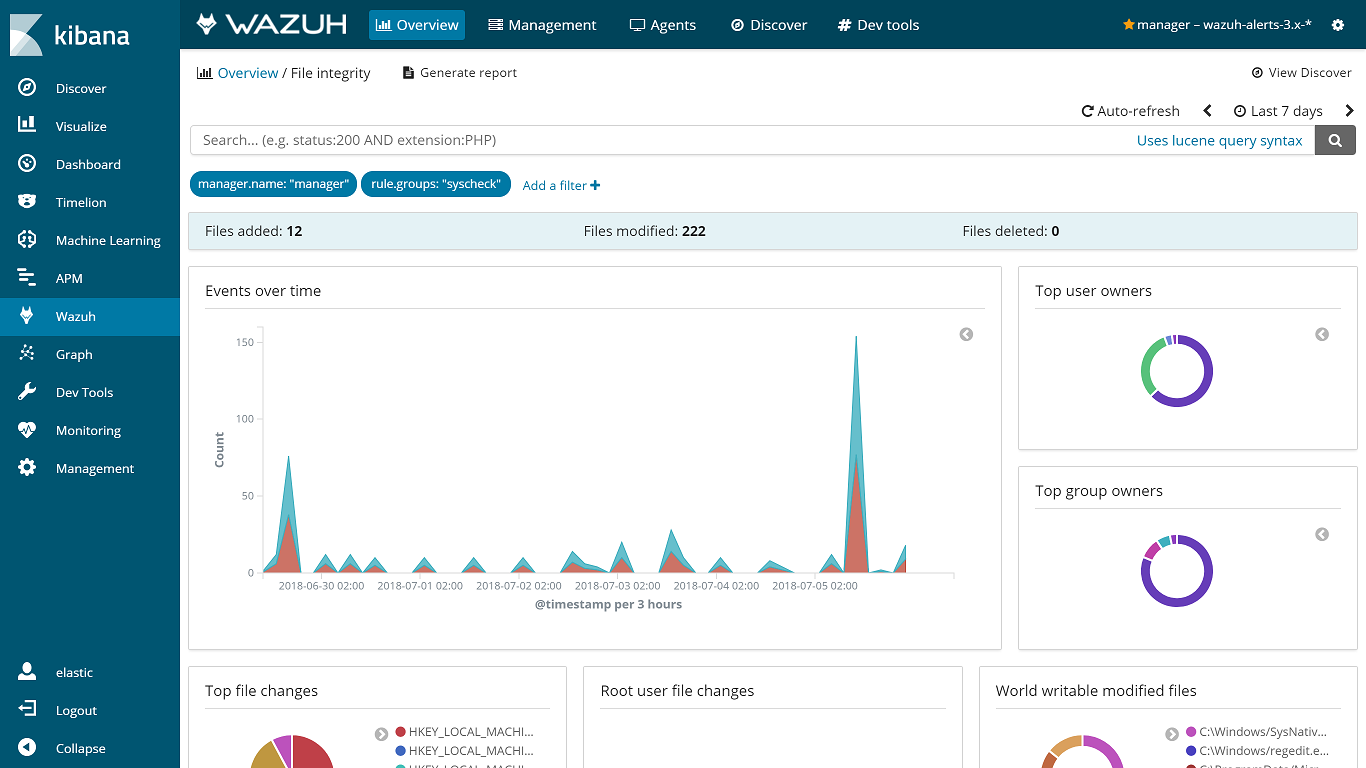
Wazuh began to evolve as a fork of OSSEC, one of the most popular open source SIEMs. And now this is its own unique solution with new functionality, bug fixes and optimized architecture.
The system is built on the ElasticStack stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) and supports both agent-based data collection and reception of system logs. This makes it effective for monitoring devices that generate logs but do not support agent installation — network devices, printers, and peripherals.
Wazuh supports existing OSSEC agents and even provides guidance on migrating from OSSEC to Wazuh. Although OSSEC is still actively supported, Wazuh is seen as a continuation of OSSEC due to the addition of a new web interface, REST API, a more complete set of rules, and many other improvements.
Benefits
- Founded and compatible with the popular SIEM OSSEC;
- Supports various installation options: Docker, Puppet, Chef, Ansible;
- Supports monitoring of cloud services, including AWS and Azure;
- It includes a comprehensive set of rules for detecting many types of attacks and allows you to match them in accordance with PCI DSS v3.1 and CIS.
- Integrates with Splunk log storage and analysis system for event visualization and API support.
disadvantages
- Sophisticated architecture - requires the full deployment of Elastic Stack in addition to the Wazuh server components.
Source
Prelude OSS
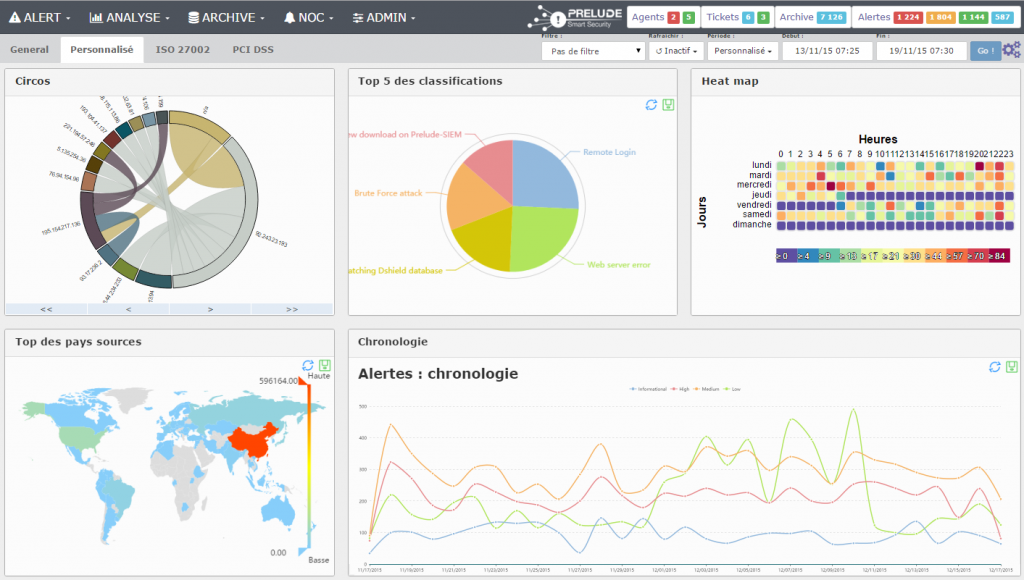
Prelude OSS is an open-source version of the commercial Prelude SIEM, developed by the French company CS. The solution is a flexible modular SIEM system that supports many log formats, integration with third-party tools such as OSSEC, Snort and Suricata network detection system.
Each event is normalized to a message in IDMEF format, which simplifies the exchange of data with other systems. But there is a fly in the ointment - Prelude OSS is very limited in performance and functionality compared to the commercial version of Prelude SIEM, and is intended more for small projects or for studying SIEM solutions and evaluating Prelude SIEM.
Benefits
- A time-tested system developed since 1998;
- Supports many different log formats;
- Normalizes data to IMDEF format, which makes it easy to transfer data to other security systems.
disadvantages
- Significantly limited in functionality and performance compared to other open-source SIEM systems.
Source
Sagan

Sagan is a high-performance SIEM that emphasizes Snort compatibility. In addition to supporting rules written for Snort, Sagan can write to the Snort database and can even be used with the Shuil interface. Essentially, it is a lightweight multi-threaded solution that offers new features while remaining user friendly for Snort.
Benefits
- Fully compatible with Snort database, rules, and user interface;
- Multi-threaded architecture provides high performance.
disadvantages
- A relatively young project with a small community;
- A complex installation process, including the assembly of the entire SIEM from the source.
Source
Conclusion
Each of the described SIEM systems has its own characteristics and limitations, therefore they cannot be called a universal solution for any organization. However, these solutions have open source code, which allows you to deploy, test and evaluate them without undue cost.
What else can you read on the Cloud4Y blog
→ VNIITE of the whole planet: how they came up with the “smart home” system in the USSR
→ How neural interfaces help humanity
→ Cyber insurance on the Russian market
→ Light, camera ... cloud: how clouds change the film industry
→ Football in the clouds - fashion or need?
Subscribe to our Telegram-channel, so as not to miss another article! We write no more than twice a week and only on business.
