Sleep is the main resource for the brain of a programmer
You can use this post as an argument in negotiations.

You have probably already heard this thoughtful phrase that was said by Reed Hastings, CEO of Netflix, speaking about the development of the company: "Our main competitor is a dream." He logically argues that from the point of view of the profitability of his business, sleep, which occupies a third of all time, is a huge resource for which you can compete. But if we value our health, beauty and life, then he should not receive a minute from us from our sleep. We still underestimate sleep so much that this fact is surprising in itself. Why do we consider a dream to be something to sacrifice, to squeeze, to mock? Even the simplest popular idea of biology tells us that nature would not demand from us a third of life for something unimportant.
What is the value of your first 25 years of life, from the moment you first opened your eyes and burst into tears, and while you realized that adulthood is already in full swing? The value of sleep is even absurd to measure, and yet it takes about the same amount of time in our lives.
Meanwhile, we really do not know why we are sleeping. Yes, we have explanations - about the consolidation of memory, training, recovery, and more. The question itself remains open and is asked again and again, because we suspect that this is not all that we know about sleep.
All animals sleep, provided that they live at least a few days. There are exceptions, but they can be purely methodological: until recently, scientists did not have enough data to call sleep periods in some animals (insects) sleep.
There is not a single function of the body that would not depend to one degree or another on sleep. Sleep is the most effective, free and powerful tool for rebooting our brain and health that happens every day. In addition, sleep is a legal means to improve athletic performance and recovery. Federer is said to sleep 12 hours, Usain Bolt is also a lover of sleep, and just before the most important competitions: once he won important competitions half an hour later when he woke up.

Matthew Walker, author of the book Why We Sleep, already in Russian, says he sleeps 8 hours, not because he is a model for others, but because “if you knew as much about sleep as I do, you would understood how important he is. ” As they say, if someone presented a medicine that does as much for the body as it does a dream, it would be the greatest product in the world. In fact, a dream is like a Swiss knife, says Matthew: he has some kind of tool for any disease.
It so happened that millions of years of evolution led to about 8 hours of sleep. And from these millions of years, over the past few hundred years, we have begun to capture darkness with artificial light, intruding into the domain of sleep. Previously, we slept very differently than today ( Dream that we lost ).
Already in 1940, on average in England, sleep took 7.9 hours. Now - 6.5 hours, this is a loss of almost 20 percent of sleep! We, perhaps for the first time in history, began to experience problems with sleep, and problems from its lack.
Sleeping less than 6 or 7 hours a day on a regular basis leads to an increase in cancer risk by 50%. Even one night without sleep or less than 5 hours of sleep leads to a 70% drop in the number of NK cells, natural killer cells of cancer cells.
Lack of sleep leads to increased appetite and worsened saturation signaling, that is, a double increase in the likelihood of accumulating excess weight. If against this background, you start to engage in diet, then it, first of all, will begin to reduce muscle mass, and not fat. But thank God this is a two-way connection: it’s worth a dream, as everything starts to improve.
The number of fatal accidents caused by lack of sleep is much greater than those where the cause is alcohol or drug intoxication of drivers. In the United States, according to the most conservative estimates, sleeping at the wheel kills 10,000 people a year . We do not know the number of aviation accidents caused by fatigue and lack of sleep for pilots, because there are no standards for assessing lack of sleep.
If you take a healthy person and make him sleep no more than 6 hours, within a week, then the regulation of glucose in the blood is disrupted so much that a doctor unfamiliar with his situation will diagnose him with prediabetes.
In countries where the clock is still moving to summer time, in the spring, when people lose an hour of sleep, this leads to a 24% increase in heart attacks. In the fall, when an hour of sleep is added, a 21% reduction in heart attacks occurs.
People who sleep 5 hours are 4 times more likely to have colds and other common viral diseases, compared to people who sleep 8 hours.
Not a single mental illness was found in which there would be a normal sleep. Bad sleep can be a predictor of many psychiatric conditions. 10 times higher risk of depression. Lack of sleep is associated with suicidal ideation (9 times higher than normal sleep people), attempted (7.5 times higher), and successful suicide.
With a chronic lack of sleep, the somatosensory cortex, which processes the signals of pain and touch, becomes hypersensitive. As a result, pain sensations intensify. In addition, another region of the brain that modulates information on what to do with signals about pain, which, normally, can evaluate the situation and say: “okay, it hurts us, but there’s nothing to worry about” - now it becomes less active. Thus, pain that could pass unnoticed, with lack of sleep, may look exaggeratedly strong.
As you can see, lack of sleep is a very dangerous factor, and we should seek full sleep.
There is nothing more predictable in the world than sunrise. And there is nothing in the world that loves predictability more than our brains. Therefore, the brain is attached to the sun in building work cycles. And not just the brain: a recent study found its own rhythms in the liver and skin, rhythms, again, dependent on light. You can be sure that in the near future we will learn a lot.
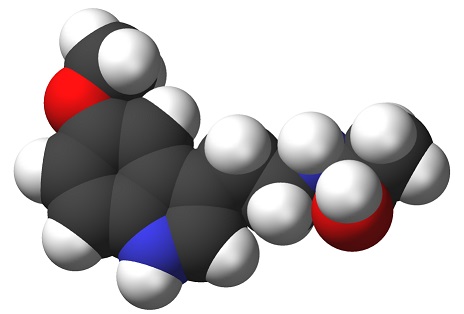
C 13 H 16 N 2 O 2
When evening comes, our brain begins to produce melatonin. Melatonin is not a sleeping pill, but, if you like, just a herald who rushes through the body and tells all organs that night falls and it's time to sleep. He does not participate in “closing windows” and “blowing out candles,” metaphorically speaking. It is very sensitive to light, and as soon as the light touches the retina, it gives the melatonin a signal to disappear, and its reminders to the organs of sleep cease.
Since melatonin is not a medicine, its production is not standardized, and this means that in melatonin tablets, its actual content can range from 0% to 500%indicated on the label. Given this, we can safely say that melatonin in tablets is perhaps a very effective placebo.
If melatonin tablets are not a solution, then can there be sleeping pills, real medicines made by reputable pharmaceutical companies that have spent hundreds of millions of dollars and many years on research?
But the word "sleeping pills" - in fact, an oxymoron, these drugs do not "create a dream", but simply cut down. What we get by swallowing a pill is definitely not a dream.
In the spring of 2018, Rosanna Barr, the host of the ABC show, made a couple of tweets with a racist bias. The next morning, the channel terminated the contract with her. In her defense, the former presenter said she tweeted in the middle of the night, not really thinking what she was doing, because she was under the influence of Ambien. A spokesperson for Sanofi, the manufacturer of this possibly the most popular sleeping pill, immediately caustically remarked: "Although all pharmaceuticals have side effects, racism is not one of the side effects of any of Sanofi's drugs." Sorry, but the medicine suppresses the central nervous system, acting almost like alcohol, and can in no way influence what you can control in your thoughts and speech? Everyone who ever drank in companies and carried a blizzard, and, therefore, committed terrible, stupid or idiotic actions under the influence of alcohol, for which the next morning was infinitely ashamed, know that alcohol can not stand by as if it had nothing to do with it. Nobody just wants to open the Pandora's box: recognizing that sleeping pills change behavior, and they certainly do, this is to enable people to avoid responsibility for their actions, explaining this with the actions of drugs.
There are quite solid studies based on the data of tens of thousands of people, on the effect of various sleeping pills , showing that they increase the likelihood of death and cancer .
The results are frightening: scientists observed people taking sleeping pills and people not taking such drugs, and compared mortality for two and a half years. Only 18 tablets per year increased mortality over this period by 3.6 times ! Those who take more than 132 tablets per year were at risk 5.3 times higher.
Scientists have also found out the main cause of death - an increased incidence of infectious diseases. If we remember that sleep is the best way to fight diseases, and sleeping pills do not create sleep, but rather spoil it, then this reduces the efficiency of the immune system. Other causes of death for people taking sleeping pills: again, an accident while driving (after sleeping pills, drowsiness persists after waking up), cardiovascular diseases and strokes. In addition, those who take sleeping pills have a 30–40% increased risk of cancer over 2.5 years .
These are all associative connections, correlations. It can not be argued that sleeping pills lead to death and cancer, and identifying a causal relationship is not an easy thing, especially when there are stakeholders and ethical barriers. Only Ambien brings Sanofi billions of dollars annually. And who will do the clinical trial, as a result of which people are likely to die? It is worth repeating again: these drugs have nothing to do with sleep, but simply suppress the brain.
What can help to get a full sleep?

Mammoth Cave.
In 1938, two experimenters from the University of Chicago, Professor Nathaniel Kleitman and his student Bruce Richardson, set offto Kentucky, to the Mammoth Cave, the largest explored underground system in the world. At a depth of 40 meters, where complete darkness reigns and a constant temperature of 12 degrees Celsius, they found ideal conditions, where they spent a month. They wanted to check what would happen if the influence of the sun was excluded. They used kerosene lamps and created their own every day and night cycle.
Scientists meticulously measured body temperature and the time taken to sleep and stay awake. Soon 20-year-old Richardson switched to 28 hours, and Kleitman, who was 43 years old, entered the rhythm lasting a little more than 24 hours. Thereby they made two important discoveries:
First- people generate an internal rhythm independent of the sun, as a source of change of day and night on Earth. This rhythm was, however, the same predictable and repetitive.
Second - this rhythm is approximately equal to 24 hours, and most often, a little longer, especially in youth. The sun adjusts our “hurrying” internal clock every day.
Only 20 years later, Franz Holberg gave this rhythm a name: circadian, from the Latin words “circus” - approximately, and “diam” - day. A modern estimate of the duration of the human circadian rhythm: 24 hours 15 minutes. That's just because the circadian rhythm is not exactly 24 hours, sleep phases tend to shift. Every morning, like a hand, adjusts a slightly hurrying internal clock.
In a recent issue of New Scientist, the main article in the issue.- just about the effect of light on life, health and sleep.
We spend an incredible amount of time indoors. Statistics say that in developed countries people spend 90% of their time indoors, and this is twice as much as 50 years ago. It is enough to recall our childhood - how much time we spent on the street and compare with modern children. If we take into account that our species in general was formed over the millions of years exclusively in the fresh air, then our transition to the “shade”, into enclosed spaces, could not but affect our behavior. Less oxygen, vitamin D, fewer movements. And, of course, less light and, as a result, sleep impairment.
In comparison, Amish, religious groups primarily engaged in agriculture and living almost without technology, spend much more time outside.
In summer, they receive about 4000 lux of sunlight on average, per hour, 7 times more than a typical European. In winter, the Amish quietly “take” 1,500 lux of sunlight, again 7 times more than a typical city dweller. In this evening, the illumination of their houses is only 10 lux, while in the cities in each apartment everything is flooded with artificial and bright light.

Scenery from the 5th season of the Black Mirror.
This is also confirmed by the experiments of the Danes, when they placed people for three days in a completely glass house. This allowed us to create the maximum possible approximation to the natural cycle in comfortable conditions. Morning light in the morning "correctly" awakens the brain, optimally synchronizing the work of all rhythms. Such “smart” glass houses are an ideal place for light lovers, and offer a different view of the world and housing. For example: www.thephotonspace.com .

In order to correct the “circulating rhythm” during the night, the morning rhythm should be bright enough. How bright? Ideally, at least 10 thousand lux. Such brightness will quickly “remove” melatonin and the brain will receive a charge of vivacity. Researchers from Berlin in 2017 found that receiving bright light in the morning increases the reaction rate and maintains it at a high level throughout the day.
But we often do not have the opportunity to get enough light. Try it yourself by installing one of the applications for smartphones (by measuring the brightness of the light, and you will see that even when sitting by the window in the summer, there will be much less light than when we go outside.
Therefore, the most optimal solution for restoring and maintaining a full sleep can be new developments - glasses that give bright light to the eyes. Only 30 minutes after waking up, the remnants of melatonin will be completely removed and energized. Half an hour in the morning is enough to restore circadian rhythms, and for vigor - more.
But the most interesting thing is that such a dose of light in the morning reduces the harmful effects of blue light in the evening before bedtime. It is believed that it is this light - from the screens of TVs, computers and phones that prevents us from falling asleep.
Having received a light charge in the morning, after lunch, on the contrary, we must strive to reduce the exposure to light. If sleep is disturbed, you can even wear sunglasses. Ideally, a couple of hours before bedtime, it is better not to eat, turn off the lights and not use gadgets. You can develop the habit of setting an alarm not to wake up, but to fall asleep. For example, a signal at 23:30 will remind you that at 12 you should already be in the crib and begin to fall asleep. This advice, by the way, is considered by Matthew Walker to be the most important among all concerning sleep hygiene.
You have noticed that most of the tips for establishing a healthy sleep are about falling asleep. Meanwhile, an understanding of the biology of sleep tells us that we can effectively restore it from the moment we wake up.
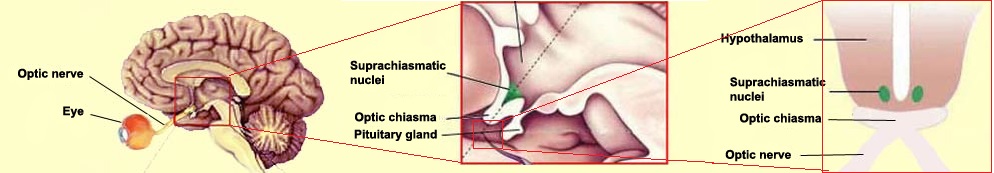
The location of the suprachiasmatic nucleus.
There is such a thing in the brain -the suprachiasmatic nucleus , the main generator of circadian rhythms in mammals, controls the secretion of melatonin in the pineal gland and synchronizes the work of the body’s “biological clock”. The activity of SCN neurons changes periodically during the day and adjusts to external light signals.
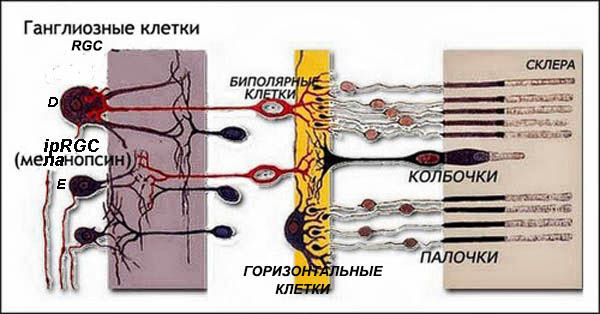
Photosensitive retinal cells ipRGC (intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells) are internal photosensitive retinal nerve cells in the eye. Their main functional role is not the creation of optical images at all, which is how they differ significantly from the rods and cones, which are located in the retina on the focal surface and form an optical image. Unlike rods and cones, they provide a stable idea of the surrounding light, color information - the magnitude of the intensity of the incident light flux. It is they who send information about the illumination through the retinohypothalamic tract directly to the main section of the circadian rhythms of the brain - to the suprachiasmatic nucleus.
These cells were discovered only in 1991., but they can become the basis for research, experimentation and the creation of technologies for normalizing circadian rhythms. Even NASA became interested in this method and conducted their research for NASA shiftworkers (staff and astronauts who worked on a shift schedule during Shuttle missions. Those NASA employees who “shone their eyes” (Light treatment) talked about better health compared with those who did not shine.
You do not need to shine a powerful LED flashlight myself in the eye or twist the brightness of the monitor to the full and watch the morning serialchik. Tehnogiki reforged "swords into plowshares», Google glasses in glasses for sleep.
There are projects and on Kickstarter - glasses with Pegasi took $ 116.695
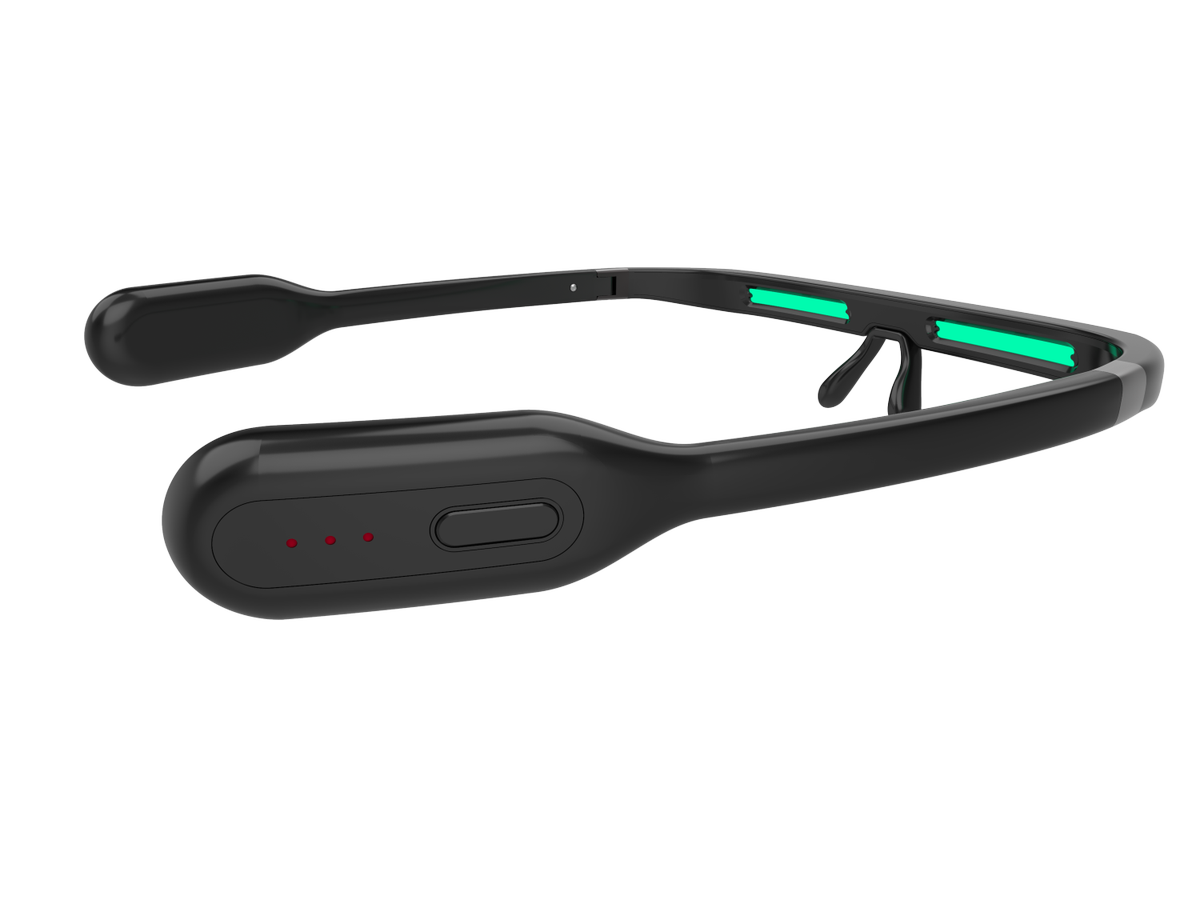
Smart glasses PEGASI - winner of the 2018 CES Asia.
Many researchers believe that blue and violet colors are optimal for ipRGC cells, but there are studies for green too .
If you are the person who "does not see the light of day" (in a secret bunker underground or simply in the office of a high-tech company), then in order to help the body restore sleep, you must wear these glasses in the interval from 7 to 9 in the morning. According to the developers, in 7 days there will be a noticeable effect, and in a month - happiness.
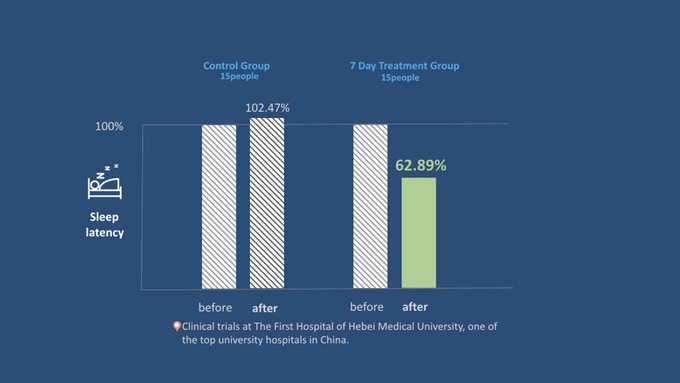
Glasses appeared in Russia and now, instead of chemicals (coffee, alcohol, sleeping pills), you can “wake up” more vigorously with cyberpunk methods and get enough sleep like Jimmy Wales.
The article was written in collaboration with Boris Zubkov.

You have probably already heard this thoughtful phrase that was said by Reed Hastings, CEO of Netflix, speaking about the development of the company: "Our main competitor is a dream." He logically argues that from the point of view of the profitability of his business, sleep, which occupies a third of all time, is a huge resource for which you can compete. But if we value our health, beauty and life, then he should not receive a minute from us from our sleep. We still underestimate sleep so much that this fact is surprising in itself. Why do we consider a dream to be something to sacrifice, to squeeze, to mock? Even the simplest popular idea of biology tells us that nature would not demand from us a third of life for something unimportant.
What is the value of your first 25 years of life, from the moment you first opened your eyes and burst into tears, and while you realized that adulthood is already in full swing? The value of sleep is even absurd to measure, and yet it takes about the same amount of time in our lives.
Meanwhile, we really do not know why we are sleeping. Yes, we have explanations - about the consolidation of memory, training, recovery, and more. The question itself remains open and is asked again and again, because we suspect that this is not all that we know about sleep.
All animals sleep, provided that they live at least a few days. There are exceptions, but they can be purely methodological: until recently, scientists did not have enough data to call sleep periods in some animals (insects) sleep.
There is not a single function of the body that would not depend to one degree or another on sleep. Sleep is the most effective, free and powerful tool for rebooting our brain and health that happens every day. In addition, sleep is a legal means to improve athletic performance and recovery. Federer is said to sleep 12 hours, Usain Bolt is also a lover of sleep, and just before the most important competitions: once he won important competitions half an hour later when he woke up.

Matthew Walker, author of the book Why We Sleep, already in Russian, says he sleeps 8 hours, not because he is a model for others, but because “if you knew as much about sleep as I do, you would understood how important he is. ” As they say, if someone presented a medicine that does as much for the body as it does a dream, it would be the greatest product in the world. In fact, a dream is like a Swiss knife, says Matthew: he has some kind of tool for any disease.
It so happened that millions of years of evolution led to about 8 hours of sleep. And from these millions of years, over the past few hundred years, we have begun to capture darkness with artificial light, intruding into the domain of sleep. Previously, we slept very differently than today ( Dream that we lost ).
Already in 1940, on average in England, sleep took 7.9 hours. Now - 6.5 hours, this is a loss of almost 20 percent of sleep! We, perhaps for the first time in history, began to experience problems with sleep, and problems from its lack.
Sleeping less than 6 or 7 hours a day on a regular basis leads to an increase in cancer risk by 50%. Even one night without sleep or less than 5 hours of sleep leads to a 70% drop in the number of NK cells, natural killer cells of cancer cells.
Lack of sleep leads to increased appetite and worsened saturation signaling, that is, a double increase in the likelihood of accumulating excess weight. If against this background, you start to engage in diet, then it, first of all, will begin to reduce muscle mass, and not fat. But thank God this is a two-way connection: it’s worth a dream, as everything starts to improve.
The number of fatal accidents caused by lack of sleep is much greater than those where the cause is alcohol or drug intoxication of drivers. In the United States, according to the most conservative estimates, sleeping at the wheel kills 10,000 people a year . We do not know the number of aviation accidents caused by fatigue and lack of sleep for pilots, because there are no standards for assessing lack of sleep.
If you take a healthy person and make him sleep no more than 6 hours, within a week, then the regulation of glucose in the blood is disrupted so much that a doctor unfamiliar with his situation will diagnose him with prediabetes.
In countries where the clock is still moving to summer time, in the spring, when people lose an hour of sleep, this leads to a 24% increase in heart attacks. In the fall, when an hour of sleep is added, a 21% reduction in heart attacks occurs.
People who sleep 5 hours are 4 times more likely to have colds and other common viral diseases, compared to people who sleep 8 hours.
Not a single mental illness was found in which there would be a normal sleep. Bad sleep can be a predictor of many psychiatric conditions. 10 times higher risk of depression. Lack of sleep is associated with suicidal ideation (9 times higher than normal sleep people), attempted (7.5 times higher), and successful suicide.
With a chronic lack of sleep, the somatosensory cortex, which processes the signals of pain and touch, becomes hypersensitive. As a result, pain sensations intensify. In addition, another region of the brain that modulates information on what to do with signals about pain, which, normally, can evaluate the situation and say: “okay, it hurts us, but there’s nothing to worry about” - now it becomes less active. Thus, pain that could pass unnoticed, with lack of sleep, may look exaggeratedly strong.
As you can see, lack of sleep is a very dangerous factor, and we should seek full sleep.
There is nothing more predictable in the world than sunrise. And there is nothing in the world that loves predictability more than our brains. Therefore, the brain is attached to the sun in building work cycles. And not just the brain: a recent study found its own rhythms in the liver and skin, rhythms, again, dependent on light. You can be sure that in the near future we will learn a lot.

C 13 H 16 N 2 O 2
When evening comes, our brain begins to produce melatonin. Melatonin is not a sleeping pill, but, if you like, just a herald who rushes through the body and tells all organs that night falls and it's time to sleep. He does not participate in “closing windows” and “blowing out candles,” metaphorically speaking. It is very sensitive to light, and as soon as the light touches the retina, it gives the melatonin a signal to disappear, and its reminders to the organs of sleep cease.
Since melatonin is not a medicine, its production is not standardized, and this means that in melatonin tablets, its actual content can range from 0% to 500%indicated on the label. Given this, we can safely say that melatonin in tablets is perhaps a very effective placebo.
If melatonin tablets are not a solution, then can there be sleeping pills, real medicines made by reputable pharmaceutical companies that have spent hundreds of millions of dollars and many years on research?
But the word "sleeping pills" - in fact, an oxymoron, these drugs do not "create a dream", but simply cut down. What we get by swallowing a pill is definitely not a dream.
In the spring of 2018, Rosanna Barr, the host of the ABC show, made a couple of tweets with a racist bias. The next morning, the channel terminated the contract with her. In her defense, the former presenter said she tweeted in the middle of the night, not really thinking what she was doing, because she was under the influence of Ambien. A spokesperson for Sanofi, the manufacturer of this possibly the most popular sleeping pill, immediately caustically remarked: "Although all pharmaceuticals have side effects, racism is not one of the side effects of any of Sanofi's drugs." Sorry, but the medicine suppresses the central nervous system, acting almost like alcohol, and can in no way influence what you can control in your thoughts and speech? Everyone who ever drank in companies and carried a blizzard, and, therefore, committed terrible, stupid or idiotic actions under the influence of alcohol, for which the next morning was infinitely ashamed, know that alcohol can not stand by as if it had nothing to do with it. Nobody just wants to open the Pandora's box: recognizing that sleeping pills change behavior, and they certainly do, this is to enable people to avoid responsibility for their actions, explaining this with the actions of drugs.
There are quite solid studies based on the data of tens of thousands of people, on the effect of various sleeping pills , showing that they increase the likelihood of death and cancer .
The results are frightening: scientists observed people taking sleeping pills and people not taking such drugs, and compared mortality for two and a half years. Only 18 tablets per year increased mortality over this period by 3.6 times ! Those who take more than 132 tablets per year were at risk 5.3 times higher.
Scientists have also found out the main cause of death - an increased incidence of infectious diseases. If we remember that sleep is the best way to fight diseases, and sleeping pills do not create sleep, but rather spoil it, then this reduces the efficiency of the immune system. Other causes of death for people taking sleeping pills: again, an accident while driving (after sleeping pills, drowsiness persists after waking up), cardiovascular diseases and strokes. In addition, those who take sleeping pills have a 30–40% increased risk of cancer over 2.5 years .
These are all associative connections, correlations. It can not be argued that sleeping pills lead to death and cancer, and identifying a causal relationship is not an easy thing, especially when there are stakeholders and ethical barriers. Only Ambien brings Sanofi billions of dollars annually. And who will do the clinical trial, as a result of which people are likely to die? It is worth repeating again: these drugs have nothing to do with sleep, but simply suppress the brain.
What can help to get a full sleep?

Mammoth Cave.
In 1938, two experimenters from the University of Chicago, Professor Nathaniel Kleitman and his student Bruce Richardson, set offto Kentucky, to the Mammoth Cave, the largest explored underground system in the world. At a depth of 40 meters, where complete darkness reigns and a constant temperature of 12 degrees Celsius, they found ideal conditions, where they spent a month. They wanted to check what would happen if the influence of the sun was excluded. They used kerosene lamps and created their own every day and night cycle.
Scientists meticulously measured body temperature and the time taken to sleep and stay awake. Soon 20-year-old Richardson switched to 28 hours, and Kleitman, who was 43 years old, entered the rhythm lasting a little more than 24 hours. Thereby they made two important discoveries:
First- people generate an internal rhythm independent of the sun, as a source of change of day and night on Earth. This rhythm was, however, the same predictable and repetitive.
Second - this rhythm is approximately equal to 24 hours, and most often, a little longer, especially in youth. The sun adjusts our “hurrying” internal clock every day.
Only 20 years later, Franz Holberg gave this rhythm a name: circadian, from the Latin words “circus” - approximately, and “diam” - day. A modern estimate of the duration of the human circadian rhythm: 24 hours 15 minutes. That's just because the circadian rhythm is not exactly 24 hours, sleep phases tend to shift. Every morning, like a hand, adjusts a slightly hurrying internal clock.
In a recent issue of New Scientist, the main article in the issue.- just about the effect of light on life, health and sleep.
We spend an incredible amount of time indoors. Statistics say that in developed countries people spend 90% of their time indoors, and this is twice as much as 50 years ago. It is enough to recall our childhood - how much time we spent on the street and compare with modern children. If we take into account that our species in general was formed over the millions of years exclusively in the fresh air, then our transition to the “shade”, into enclosed spaces, could not but affect our behavior. Less oxygen, vitamin D, fewer movements. And, of course, less light and, as a result, sleep impairment.
In comparison, Amish, religious groups primarily engaged in agriculture and living almost without technology, spend much more time outside.
In summer, they receive about 4000 lux of sunlight on average, per hour, 7 times more than a typical European. In winter, the Amish quietly “take” 1,500 lux of sunlight, again 7 times more than a typical city dweller. In this evening, the illumination of their houses is only 10 lux, while in the cities in each apartment everything is flooded with artificial and bright light.

Scenery from the 5th season of the Black Mirror.
This is also confirmed by the experiments of the Danes, when they placed people for three days in a completely glass house. This allowed us to create the maximum possible approximation to the natural cycle in comfortable conditions. Morning light in the morning "correctly" awakens the brain, optimally synchronizing the work of all rhythms. Such “smart” glass houses are an ideal place for light lovers, and offer a different view of the world and housing. For example: www.thephotonspace.com .

In order to correct the “circulating rhythm” during the night, the morning rhythm should be bright enough. How bright? Ideally, at least 10 thousand lux. Such brightness will quickly “remove” melatonin and the brain will receive a charge of vivacity. Researchers from Berlin in 2017 found that receiving bright light in the morning increases the reaction rate and maintains it at a high level throughout the day.
But we often do not have the opportunity to get enough light. Try it yourself by installing one of the applications for smartphones (by measuring the brightness of the light, and you will see that even when sitting by the window in the summer, there will be much less light than when we go outside.
Therefore, the most optimal solution for restoring and maintaining a full sleep can be new developments - glasses that give bright light to the eyes. Only 30 minutes after waking up, the remnants of melatonin will be completely removed and energized. Half an hour in the morning is enough to restore circadian rhythms, and for vigor - more.
But the most interesting thing is that such a dose of light in the morning reduces the harmful effects of blue light in the evening before bedtime. It is believed that it is this light - from the screens of TVs, computers and phones that prevents us from falling asleep.
Having received a light charge in the morning, after lunch, on the contrary, we must strive to reduce the exposure to light. If sleep is disturbed, you can even wear sunglasses. Ideally, a couple of hours before bedtime, it is better not to eat, turn off the lights and not use gadgets. You can develop the habit of setting an alarm not to wake up, but to fall asleep. For example, a signal at 23:30 will remind you that at 12 you should already be in the crib and begin to fall asleep. This advice, by the way, is considered by Matthew Walker to be the most important among all concerning sleep hygiene.
You have noticed that most of the tips for establishing a healthy sleep are about falling asleep. Meanwhile, an understanding of the biology of sleep tells us that we can effectively restore it from the moment we wake up.

The location of the suprachiasmatic nucleus.
There is such a thing in the brain -the suprachiasmatic nucleus , the main generator of circadian rhythms in mammals, controls the secretion of melatonin in the pineal gland and synchronizes the work of the body’s “biological clock”. The activity of SCN neurons changes periodically during the day and adjusts to external light signals.

Photosensitive retinal cells ipRGC (intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells) are internal photosensitive retinal nerve cells in the eye. Their main functional role is not the creation of optical images at all, which is how they differ significantly from the rods and cones, which are located in the retina on the focal surface and form an optical image. Unlike rods and cones, they provide a stable idea of the surrounding light, color information - the magnitude of the intensity of the incident light flux. It is they who send information about the illumination through the retinohypothalamic tract directly to the main section of the circadian rhythms of the brain - to the suprachiasmatic nucleus.
These cells were discovered only in 1991., but they can become the basis for research, experimentation and the creation of technologies for normalizing circadian rhythms. Even NASA became interested in this method and conducted their research for NASA shiftworkers (staff and astronauts who worked on a shift schedule during Shuttle missions. Those NASA employees who “shone their eyes” (Light treatment) talked about better health compared with those who did not shine.
You do not need to shine a powerful LED flashlight myself in the eye or twist the brightness of the monitor to the full and watch the morning serialchik. Tehnogiki reforged "swords into plowshares», Google glasses in glasses for sleep.
There are projects and on Kickstarter - glasses with Pegasi took $ 116.695

Smart glasses PEGASI - winner of the 2018 CES Asia.
Many researchers believe that blue and violet colors are optimal for ipRGC cells, but there are studies for green too .
If you are the person who "does not see the light of day" (in a secret bunker underground or simply in the office of a high-tech company), then in order to help the body restore sleep, you must wear these glasses in the interval from 7 to 9 in the morning. According to the developers, in 7 days there will be a noticeable effect, and in a month - happiness.

Glasses appeared in Russia and now, instead of chemicals (coffee, alcohol, sleeping pills), you can “wake up” more vigorously with cyberpunk methods and get enough sleep like Jimmy Wales.
“How many hours a day does Jimmy Wales sleep at all?” Less than the average adult? I always thought that really successful people just do not need so much sleep to remain vigilant and highly functional.
- I sleep for 8 hours approximately every night. When I can, I sleep more. I believe in a dream. I think the big mistake that young people make when they want to be successful is to deprive themselves of sleep. This is terribly stupid.
How does sleep deprivation affect mental abilities? Do great people like Einstein, Feynman and Ramanujan have any way to sleep less? If not, how did they do their job?
I think it’s possible to deceive a dream, but I think that the bulk of the evidence points to the opposite of what you seem to be thinking and the opposite of what most people think. But it should be so, and this should be a cool deception of sleep. :-) The
best way to fool a dream is not to pursue some kind of bizarre regime that, we hope, will fool our body to sleep less. You can train to sleep less - but you will be cognitively weakened and less productive, so what's the point?
So deceive your dream according to the system of one of the greatest sleep cheaters of all time, Benjamin Franklin. "Early retirement and early awakening makes a person healthy, rich and wise."
Go to bed and make sure your sleep is effective. No caffeine in the afternoon. No luminous screens and lights in the evenings. Go to bed early. Get up naturally, but much earlier than if you were socialized and watched TV until midnight.
In case someone asks a question, I don’t do it all myself. But I have very productive periods in my life, and now I have to become even better.
[ source ]
Sources
- Kripke, DF (2013). The Dark Side of Sleeping Pills: Mortality and Cancer Risks, Which Pills to Avoid & Better Alternatives, March 2013, accessed at www.darksideofsleepingpills.com .
- Erland, LA, & Saxena, PK (2017). Melatonin natural health products and supplements: presence of serotonin and significant variability of melatonin content, Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 13 (2): 275–81.
- Gedes, L. (2019). Living daylight. New Scientist, No. 3232.
- Kushida, C. Encyclopedia of Sleep, Volume 1 (Elsever, 2013).
- Leschziner, G. (2019). The Nocturnal Brain: Nightmares, Neuroscience, and the Secret World of Sleep. St. Martin's Press: London.
- Walker, M. (2017). Why We Sleep: The New Science of Sleep and Dreams. Penguin Books Limited: New York.
- Wong, Kwoon Y .; Dunn, Felice A .; Berson, David M. (December 22, 2005). Photoreceptor Adaptation in Intrinsically Photosensitive Retinal Ganglion Cells (HTML: Full text). Neuron 48: 1001-1010. doi: 10.1016 / j.neuron.2005.11.016. www.neuron.org/content/article/fulltext?uid=PIIS0896627305009645
- Joshua J. Gooley1,2,3, Shantha MW Rajaratnam1,2,4, George C. Brainard5, Richard E. Kronauer1,2,6, Charles A. Czeisler (2010) Spectral Responses of the Human Circadian System Depend on the Irradiance and Duration of Exposure to Light. Science translational medicine
Read more
The article was written in collaboration with Boris Zubkov.
Only registered users can participate in the survey. Please come in.
Are you satisfied with your sleep?
- 33.5% yes 476
- 60.8% no 864
- 5.5% other 79
How many hours do you sleep?
- 9.9% less than 6 hours 191
- 37.1% 6-7 hours 717
- 35.3% 7-8 hours 682
- 14.1% 8-9 hours 272
- 3.4% more than 9 hours 66
