Asynchronous programming (full course)
- Tutorial
Asynchronous programming has recently become no less developed than classical parallel programming, and in the world of JavaSript, both in browsers and in Node.js, an understanding of its techniques has taken one of the central places in shaping the worldview of developers. I bring to your attention a holistic and most comprehensive course with an explanation of all the widespread methods of asynchronous programming, adapters between them and auxiliary openings. Now it consists of 23 lectures, 3 reports and 28 repositories with many sample code on github. Only about 17 hours of video: link to the playlist .
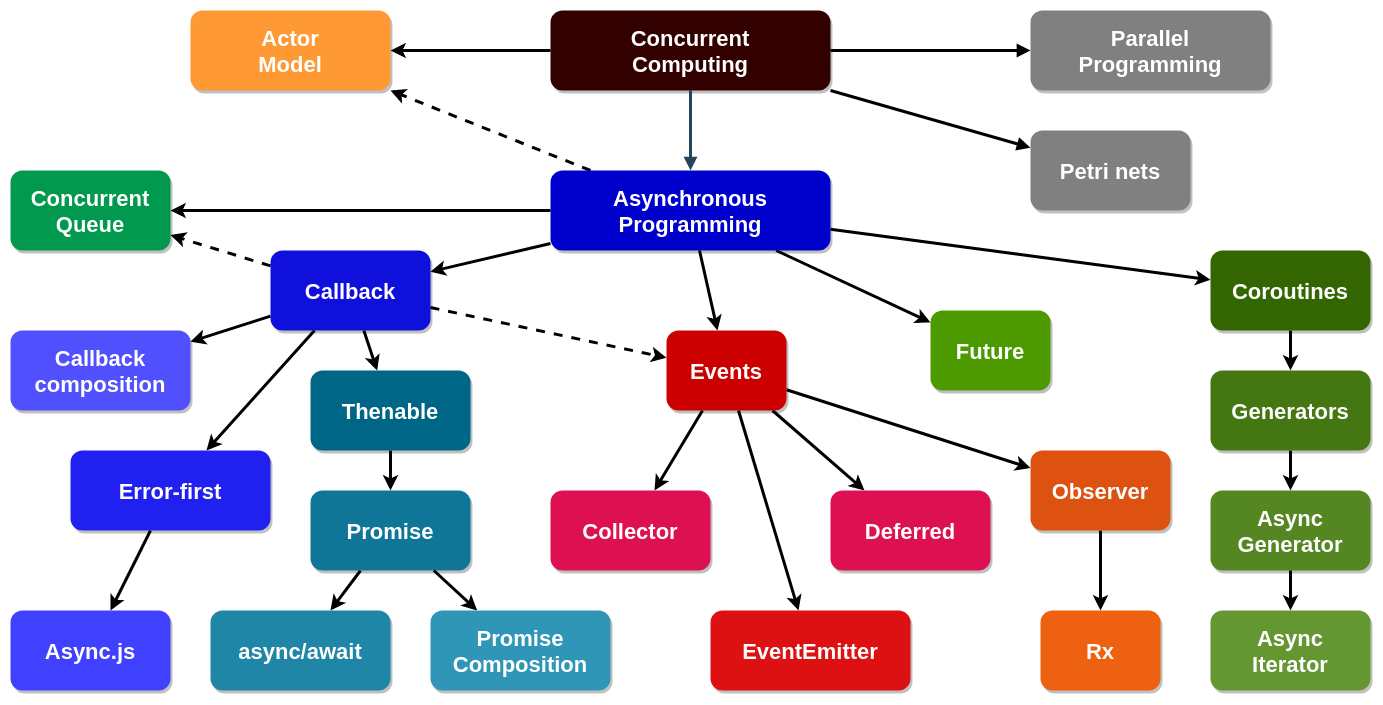
Explanations for the scheme
The diagram (above) shows the connections between different ways of working with asynchrony. Colored blocks refer to asynchronous programming, while b / w shows parallel programming methods (semaphores, mutexes, barriers, etc.) and petri nets, which, like asynchronous programming and the actor model, are different approaches to the implementation of parallel computing (they are given in the diagram only to more accurately determine the location of asynchronous programming). The actor model is associated with asynchronous programming because the implementation of actors without multithreading also has a right to exist and serves to structure asynchronous code. The dashed lines of events and the competitive queue are associated with callbacks because these abstractions are based on callbacks, but still form qualitatively new approaches.
Lecture topics
1. Asynchronous programming (overview)
2. Timers, timeouts and EventEmitter
3. Asynchronous programming on callbacks
4. Non-blocking asynchronous iteration
5. Asynchrony with async.js library
6. Asynchrony on promises
7. Asynchronous functions and error handling
8. Asynchronous adapters: promisify, callbackify, asyncify
9. Asynchronous data collectors
10. Raw errors in promises
11. Asynchronous stack trace problem
12. Generators and asynchronous generators
13. Iterators and asynchronous iterators
14. Cancellation of asynchronous operations
15. Asynchronous composition function th
16. Thenable and lightweight await
17. Competitive asynchronous queue
18. Revealing Constructor
19. Future: Asynchrony on stateless futures
20. Deferred: Asynchrony on state differs
21. Actor Model
22. Observer + Observable
23. Asynchrony on RxJS and event streams
Under each video, there are links to repositories with code examples that understand the video. I tried to show that it is not necessary to reduce everything to one abstraction of asynchrony. A universal approach to asynchrony does not exist, and for each case, you can choose those methods that will allow you to write code more naturally for this specific task. Of course, this course will be supplemented and I ask everyone to suggest new topics and contribute to code examples. The main objective of the course is to show how to build abstractions of asynchrony from the inside, and not just to teach how to use them. Almost all abstractions are not taken from libraries, but are given in their simplest implementation and their work is step-by-step sorted.
Only registered users can participate in the survey. Please come in.
What is your attitude to the course?
- 58.2% I will see the entire course 176
- 37.7% I will look selectively 114
- 0.6% One approach is enough for me 2
- 0.6% I will contribute to course 2
- 2.6% not interested in async 8