Cloudy with a Chance of Non-Disableable Advertising in the Starry Sky
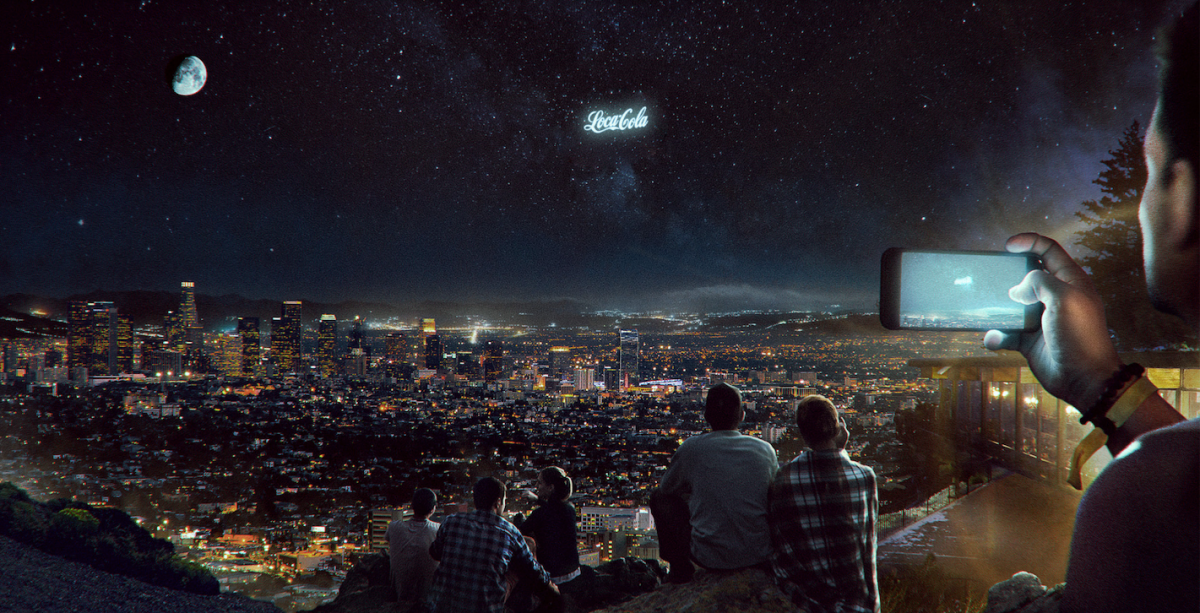

A difficult path must be walked from the idea of creation to the real creation of man-made stars and paintings in the night sky.
Man-made star
And it all started ... with a star from New Zealand.
On January 21, 2018 in New Zealand for the first time in the history of the country several satellites were successfully launched into space at once, it was also the first such mission completed in the southern hemisphere of our planet.
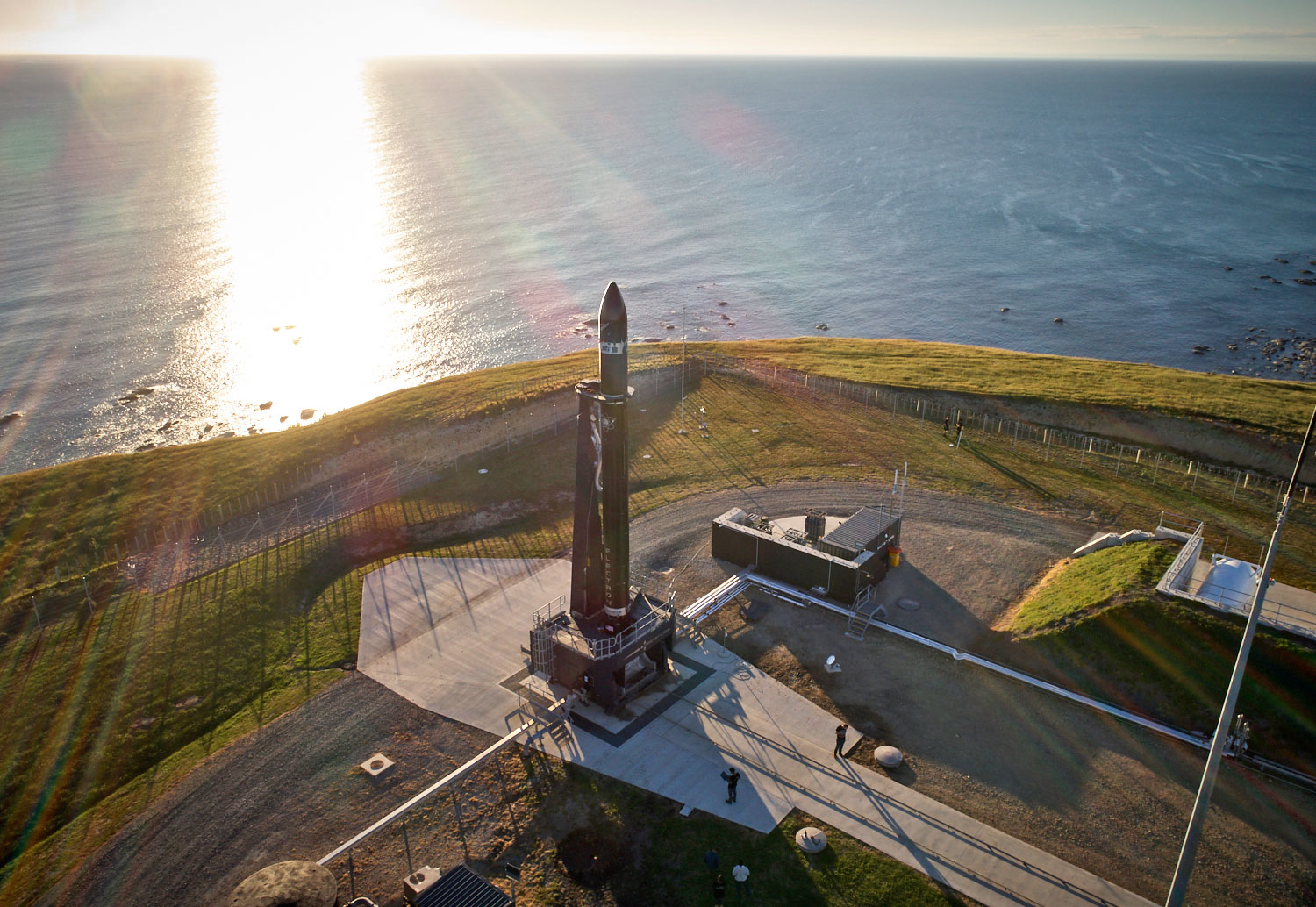
The Elektron rocket, called Still Testing, successfully launched the Planet Labs Dove Pioneer satellite and two Spire Global Lemur-2 satellites into orbit as the Rocket Lab’s Humanity Star satellite.
It turns out that in New Zealand there is a small spaceport "Rocket Lab Launch Complex 1", which was officially opened on September 26, 2016. This is a commercial spaceport located near Cape Ahuriri at the southern tip of the Mahia Peninsula, on the east coast of the North Island in New Zealand.

So what is this satellite star "Humanity Star"?
The project was initiated and implemented by Peter Beck, the founder of Rocket Lab, who called this unusual satellite the “Star of Humanity” (Humanity Star).

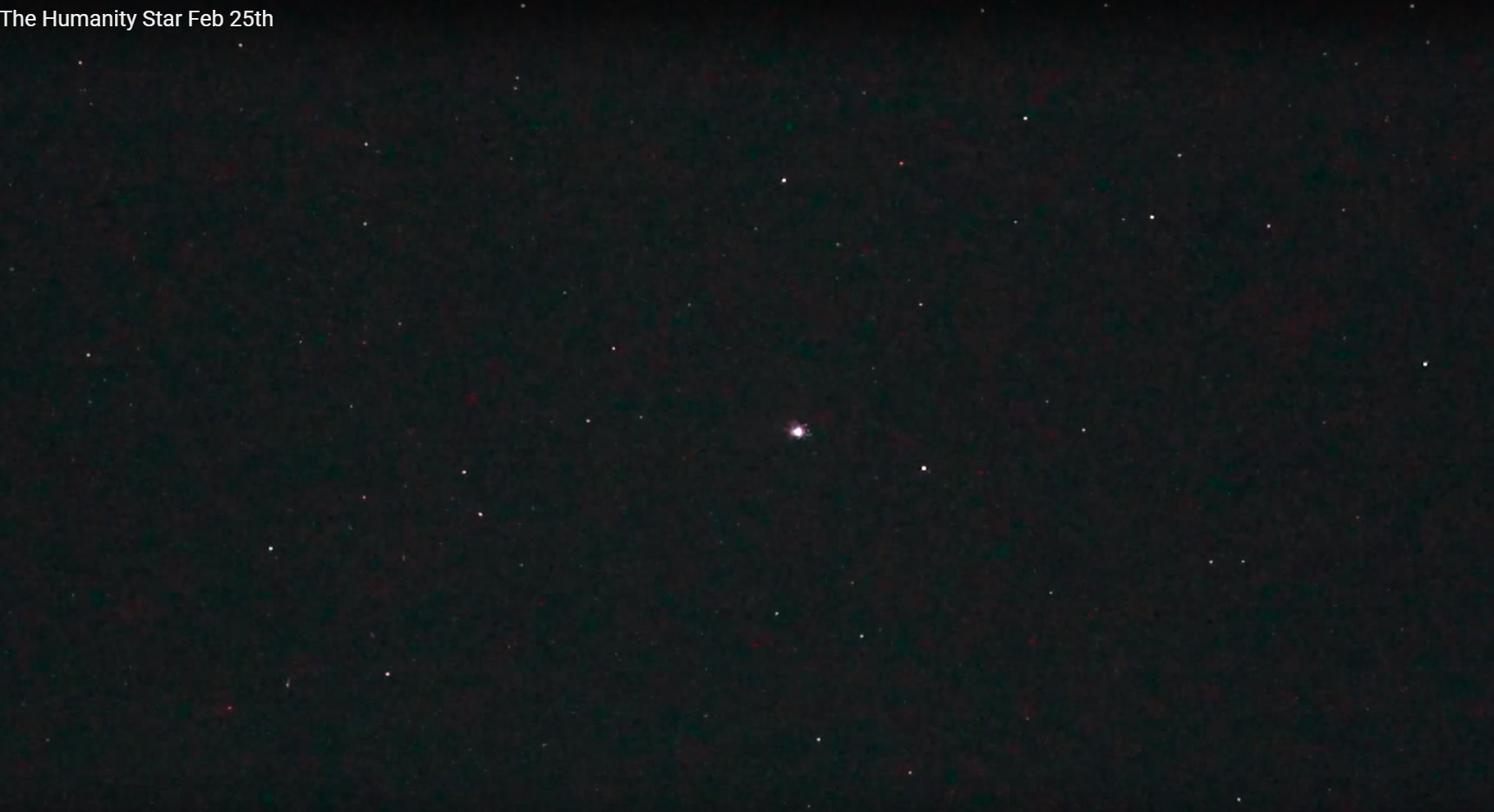
This is a faceted sphere with a diameter of just over 1 meter made of carbon fiber, which has 65 reflective panels that reflect sunlight from the body (according to estimates from a distance of 1000 km, with half illumination of the sphere) with an absolute magnitude of 7, although actually measured data after launch showed achieve brightness 1.6.

It was planned that the satellite-star in orbit of the Earth will be nine months and then burn in the atmosphere. But this term could not be maintained - only 2 months and 1 day, the “Star of Humanity” delighted the vault of heaven with its presence, entering the atmosphere on March 22, 2018.
A star satellite moved around the Earth in an elliptical orbit with perigee and apogee of approximately 292 and 529 kilometers, respectively, with an inclination of about 83 degrees and a period of 92 minutes.
It was assumed that due to such dimensions and contours of the reflecting surface, the satellite can be seen in the night sky even with the naked eye. Since the satellite is constantly rotating, it should blink in the sky, reflecting sunlight.
Her position could be tracked on thehumanitystar dot com.
Unfortunately, this site is currently not available.


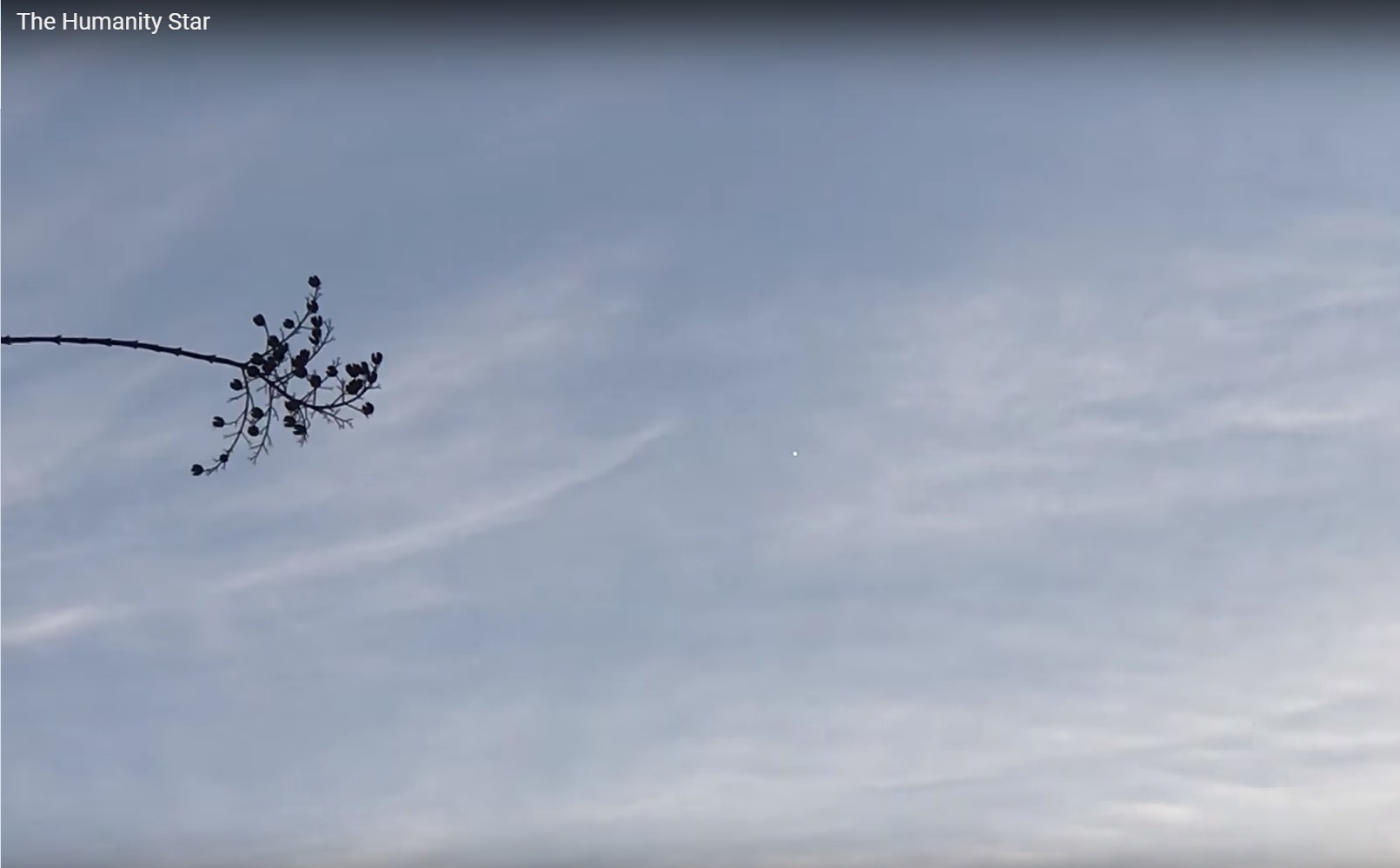
This is how the star-satellite was visible on the morning of January 25, 2018 - it was bright and constantly shining, but not blinking (the author of the video claims that it was really “Humanity Star”, as he checked the site with its coordinates):
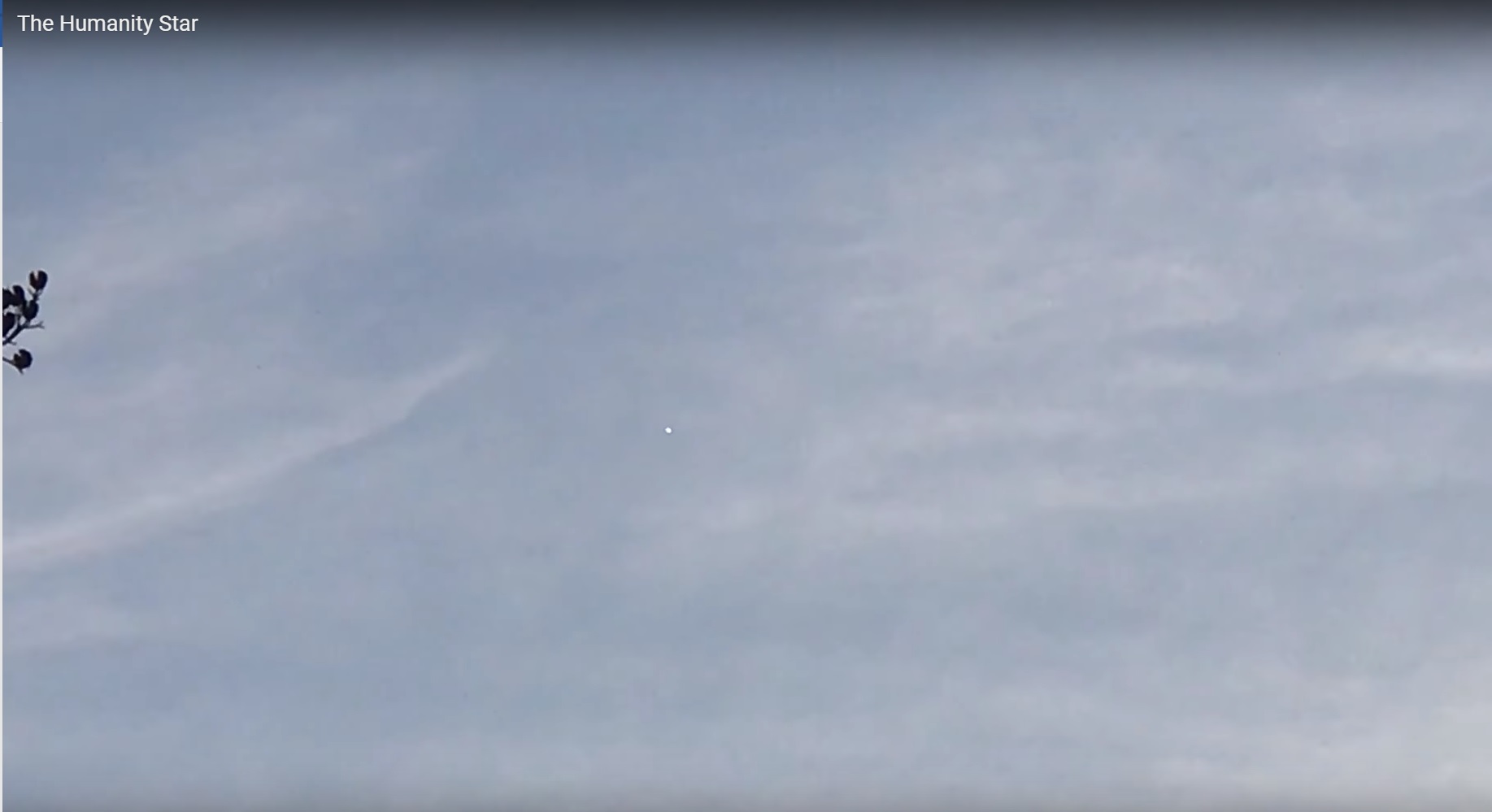



And so, a satellite-star in the night sky on February 25, 2018 blinked, but did not constantly shine:

As expected, the reaction of many astronomers to the appearance of the Humanity Star in the sky was negative, since such bright reflecting sunlight objects in orbit could interfere with astronomical observations.
As soon as this star was not called on the forums and in the press - the act of vandalism of the night sky, space graffiti, an advertising trick and sparkling space debris. Although, light flashes from existing satellites and the ISS are much brighter than from the "Star of Humanity."
In general, it is clear that the appearance of such objects in the orbit of the Earth is still expected, and the satellite "Star of Humanity" was only the first "private" ray.
By the way, here's what they wrote here about this ambitious project earlier.
Man-made constellation picture
And then in 2018, there appears ... a startup called StartRocket, whose project goal is to create a certain recognizable picture (half the size of the moon) in the sky, clearly visible on Earth with the naked eye, with the possibility of changing its light state to display any logo or word.
That is, they have already swung to a larger sector in the sky than a small dot in the "Star of Humanity."
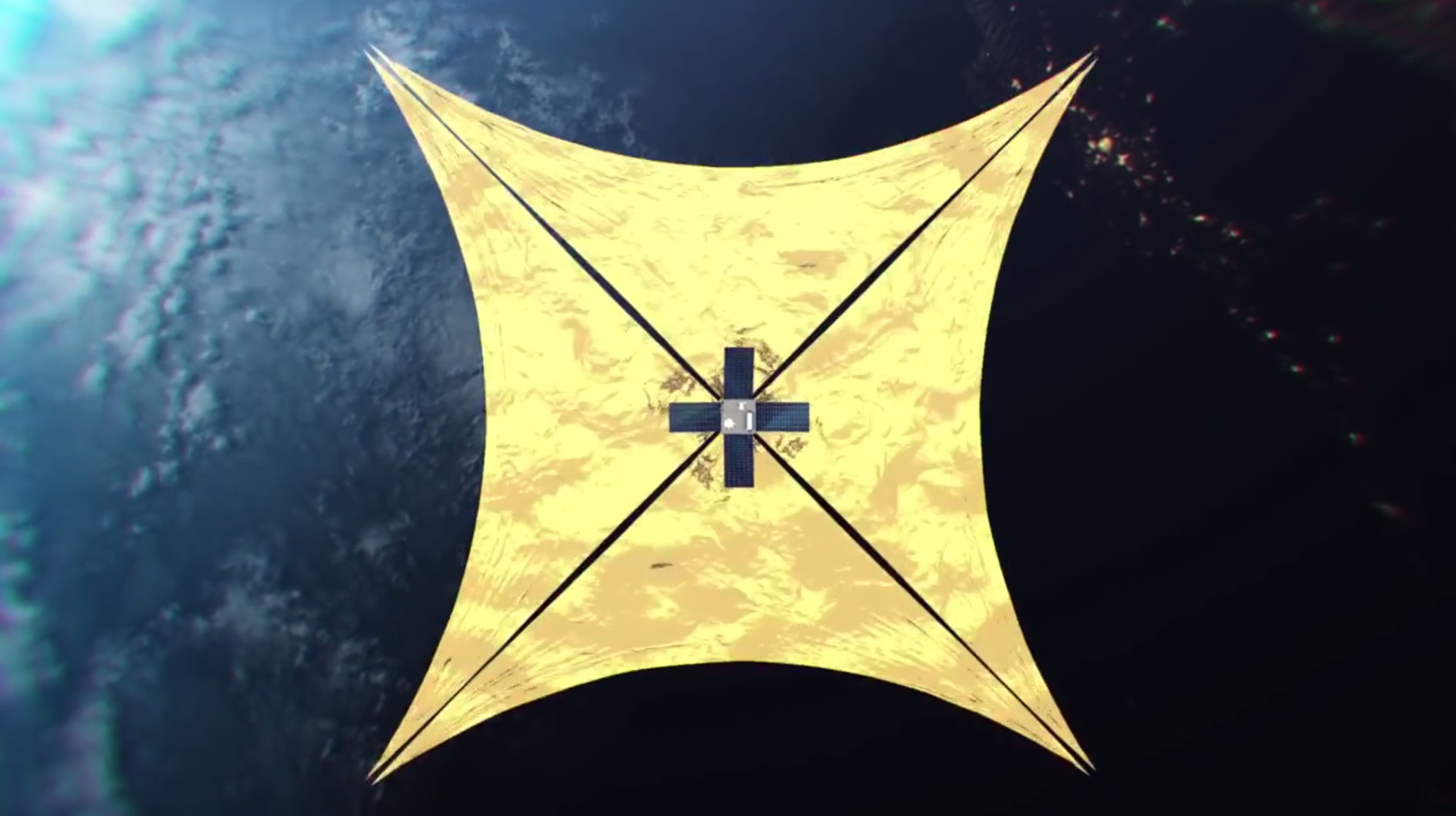
A multi-point image (picture) in the sky will be formed by a swarm of small satellites (cubesats) equipped with large reflective elements (it is planned that this will be a deployable sail from Mylar with a diameter of 10 meters), turning which (as well as changing the location of the satellites in the formation) can be changed the amount of reflected sunlight and receive different images.
Here is an example photo of a similar sail with a width of 20 meters:

Estimated number of satellites in one swarm (for a string of 5 letters): 20 x 5 = 100 pcs.
Such technology in StartRocket was called "Orbital Display", it is based on the management of a flotilla of cubesat, at an altitude of 400-500 km. It is planned that such a matrix of cubsats will be in orbit of the Earth and move at a constant speed, allowing the picture of the reflected solar candle to remain in the observer's field of view for only a few minutes.





It is planned to control the constellation of such satellites in its MCC from the Earth to quickly change their trajectory in order to avoid collision with other satellites in orbit of the Earth or with space debris.
The following technical restrictions are stated in the project:
- to change the image - a maximum of up to three different pictures per day;
- the visibility of the image - the image will be visible only during the morning / evening twilight.
It is likely that with the help of such pictures it will be possible to display informational warnings in case of danger.
Perhaps in the future such space screens will become a backup part of the global warning system.
Estimated timelines for the implementation of the stages of the project:
- 2019: production of system components and software development;
- 2020: first launch of a satellite constellation into orbit;
- 2020-2021: testing in orbit and refinement of the functional;
- 2020: commissioning, full demonstration of the system.
According to StartRocket, its specialists, with the help of the Skolteha Space Center staff (Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology), have already completed a project to scientifically substantiate the possibility of using sunlight to output messages on Earth orbit.
Also, according to information from StartRocket, they managed to solve the first technical problems associated with orienting and controlling the joint flight of elements of their small satellite constellation.
It seems to me that this is not a very viable project, since a lot of not only technical issues need to be resolved, but also from the legal side to agree with different countries on the possibility of such a broadcast, and get approval from many space agencies and their structures in the world to launch and placement in a particular orbit of a swarm of satellites.
If they get to the assembly of the prototype system and launch into space a small swarm of small satellites modernized for this task - this will be incredible luck.
The battle of two satellite advertising groups for a place under the Sun will probably look futuristic in the starry sky.
So far, I see such difficulties in the process of implementing this project:
- the need to use special small satellites modified for this task with a deployable sail from Mylar, where there is a high probability of damage to the sail with the failure of its components, so “broken pixels” can appear in the overall picture, which will be difficult to quickly eliminate, in general, how in any complex and multicomponent system, and even more so remote from the operator by thousands of kilometers;
- the concept of performing multiple turns of some satellites (or their sails separately) to change the picture will be difficult to implement, especially since these turns will need to be done often and many times (so far 3 times a day voiced), what is the actual life of such a launched screen it will not be clear in the end (most likely less than a year):
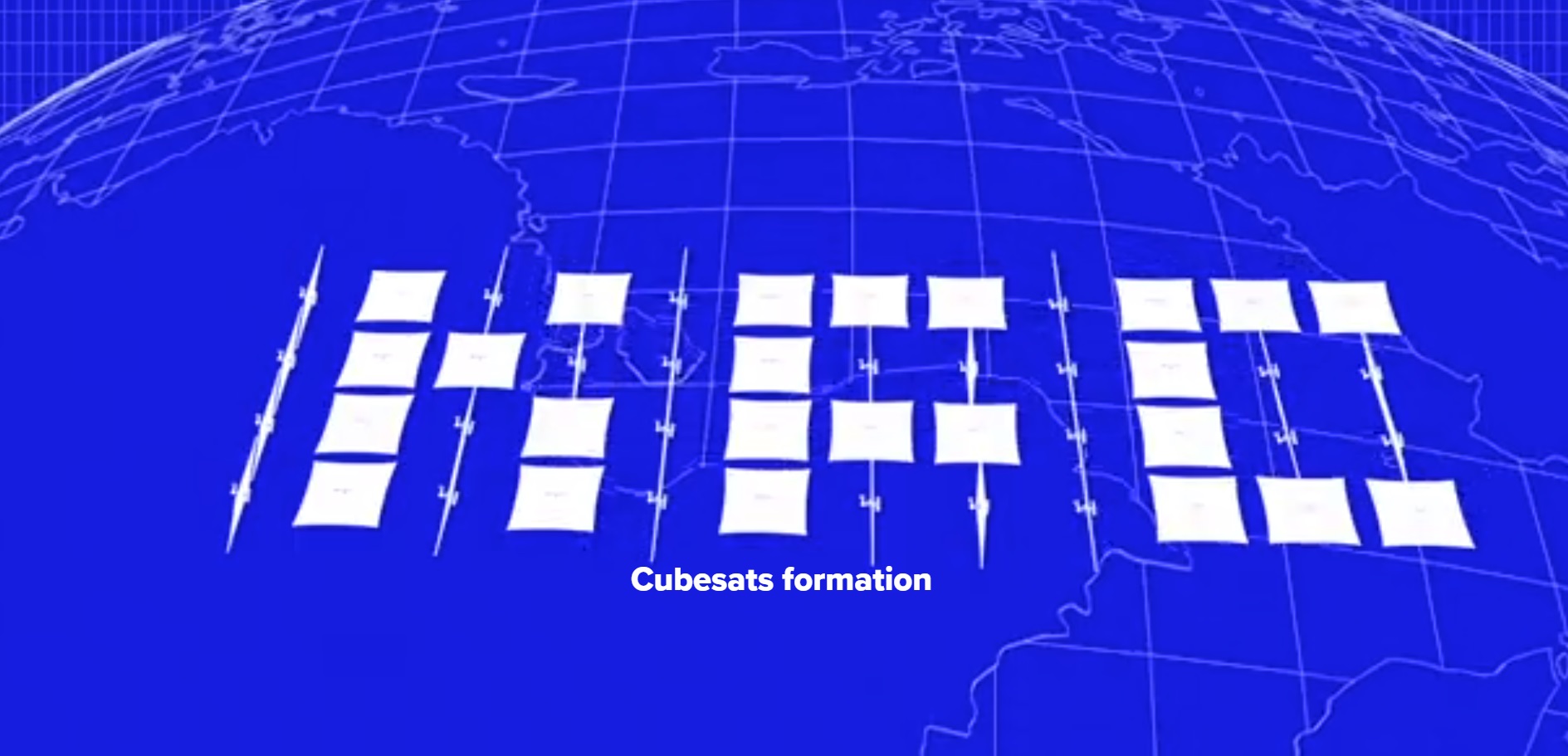
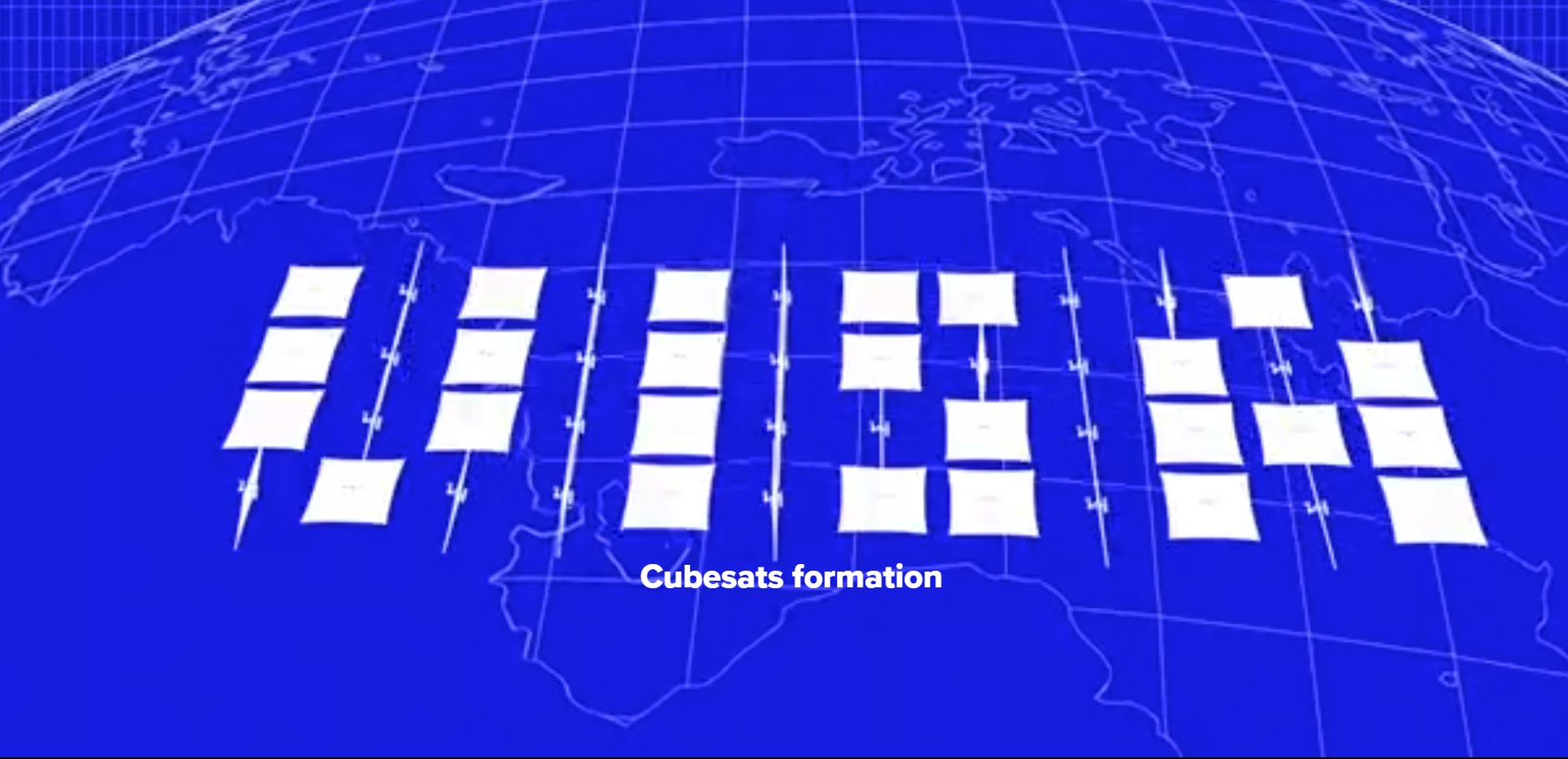
- it is not clear how the different image direction will be compensated for when flying over the eastern and western hemispheres, since if you can’t change the image (invert, flip when the satellites cross the Earth’s pole), then the picture will be normal in one hemisphere and inverted in the other that, since everything moves in the video of concepts of a solution in only one direction;
- Also, the estimated orbit height and image size do not guarantee these actual values after the satellites are launched, it will still be necessary to select the optimal altitude already in orbit and also adjust the distance between the satellites for a clearer and more understandable picture, when they are close, everything will merge, and at too great a distance from each other there will simply be dots white in the sky;
- it is possible that there will still be a light effect on the picture of even turned sails, so that in their place there will also be extraneous solar illumination with a thin strip;
- the weather in the world is changeable and more often clouds with clouds we see, not a clear sky, and this will greatly affect the visibility of their grouping and the perception of pictures as just a light haze behind the clouds;
- the project already has opponents before its implementation: “This is a threat to astronomical research from Earth. Each of these moving light flares in the night sky can interfere with the collection of photons from space objects, ” are the words of the astronomer and head of the non-profit organization International Association of the Dark Sky John Barentine;
- will be a threat and a hindrance for large space orbital objects, for example, the ISS flight altitude is slightly lower than the estimated height of the planned swarm of satellites;
- it is necessary to have one or two large satellites in orbit above the swarm plane of satellites to monitor the status and orbit parameters of each kubsat and the possibility of autonomous swarm control in case of loss of communication with the Earth, that is, an already managed orbiting satellite constellation will be obtained;
- you need to implement a special system of protection against unauthorized changes in the picture, because intercepting control and the ability to illuminate certain symbols and signals in the sky are unacceptable in this system and it will be necessary to have an operational counteraction plan to prevent such intrusions, up to the destruction of the swarm by controlled combustion of its elements in the atmosphere;
- its commercial part and dependence on investments, since if it were possible to use such satellites scientifically, it would be more useful, but at the same time to fulfill their demonstrative responsibilities and conduct certain space research and transmit their data - this will be difficult to achieve.

However, I was pleased that their site is developing and adjusting, for example, I found such comments there directly in the site code a month ago (in Russian, of course):
// this line drops when embedding in an iframe
// maybe it’s here add statistics collection for such projects and say so do not
startrocket dot me
Now the code on the site has already been finalized and these lines have been removed.
