All nuclear explosions on one map
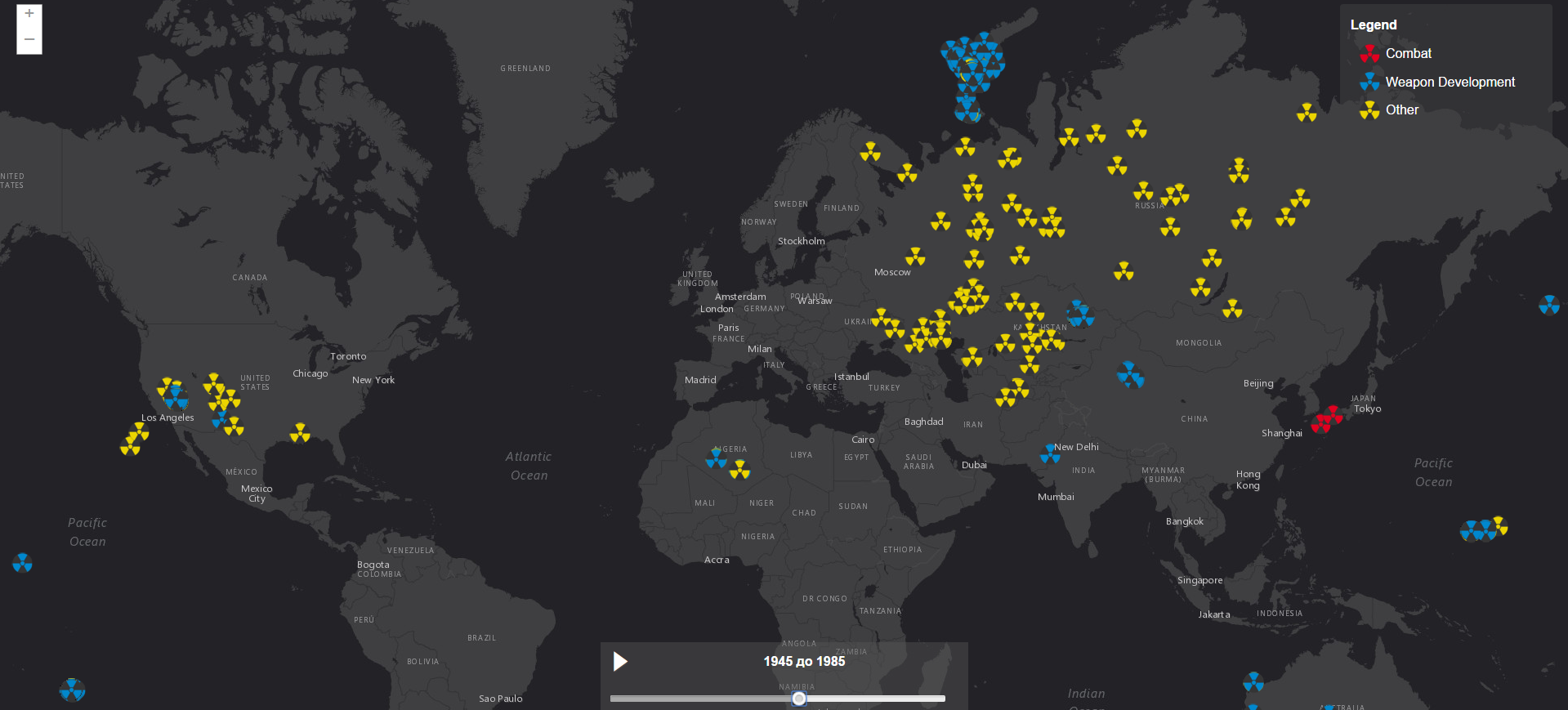
The American company Esri has developed an interactive map that shows all 2624 successful nuclear explosions since 1945, independent reports .
The first successful nuclear explosion in history was the Trinity test conducted by the US Army in July 1945.
The explosion energy of that bomb was equivalent to about 21 kilotons of TNT. One of the project managers, Robert Oppenheimer , an American theoretical physicist, said: “We knew that the world would not be the same. Someone laughed, someone cried, but most people were silent, and I remembered a line from the Hindu scripture: “I became Death, the destroyer of the Worlds.”
In August 1945, the United States dropped nuclear bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. A quarter of a million people died, all but 20 thousand of which were civilians. However, it is now known that the bombs dropped on the Japanese were not very powerful. In addition, they exploded before reaching the ground. The explosions in Hiroshima and Nagasaki are the only use of nuclear weapons in wartime, but at the same time they gave impetus to successful nuclear tests proliferating around the globe.
The first Soviet atomic bomb, tested on August 29, 1949 at the Semipalatinsk test site, was copied from the American model.
Great Britain followed the example of the USSR and on October 3, 1952 in the region of the Monte Bello Islands (northwest of Australia) made the first test of surface nuclear weapons. The result was an explosion with a capacity of about 25 kilotons. In 1960, France chose the Algerian desert to detonate a device three times the power of a bomb dropped on Nagasaki.
The most powerful nuclear weapon tested is the Tsar Bomb, developed in the USSR. The total energy of the explosion, according to various sources, ranged from 57 to 58.6 megatons in TNT equivalent. The bomb tests took place on October 30, 1961. Result: the fireball of the explosion reached a radius of about 4.6 kilometers, the nuclear mushroom rose to a height of 67 kilometers, the diameter of its two-tier “hat” reached (at the upper tier) 95 kilometers. The bomb was 1,500 more powerful than those dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
The largest nuclear weapon - Castle Bravo, was tested on March 1, 1954 on the Bikini Atoll (Republic of the Marshall Islands, associated with the United States). In addition, this weapon is the most powerful of all US nuclear tests. The explosion was three times stronger than scientists predicted. The cloud formed after the Castle Bravo blast carried to the inhabited atolls, which caused radiation sickness and birth defects. According to the Japanese Ministry of Health, as a result of the Castle Bravo test, 856 Japanese fishing vessels with a total number of crews of about 20 thousand were exposed to varying degrees of infection.
Over the next decades, China, India, and Pakistan have successfully tested nuclear devices. It is believed that Israel and South Africa may have secretly tested nuclear weapons. The DPRK ratified the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty in 2003, but later withdrew its signature and in 2006 may have tested a small nuclear device.
The map also contains pictograms of non-military explosions of nuclear devices, primarily conducted by the USSR. These include excavation of artificial harbors, geological exploration of gas and oil fields, as well as tests aimed at stimulating deposits and facilitating the production of natural gas.
