Does Wi-Fi harm living organisms?

Mankind is increasingly gaining in technology, carrying more than one gadget in their pockets, which without stopping transmit and receive various electromagnetic signals. This also includes Wi-Fi technology, which has become the most popular in the world. It is difficult to find a building and a place in a large metropolis where such a method of data transfer would be common. Therefore, disputes about possible harm from electromagnetic pollution of the environment do not cease. In some cases, this even led to widespread public concern, as it was in the United States a few years ago, when many Americans moved from large cities to a village where there was no wifi signal. The reason for this migration was the so-called “allergy to wi-fi”.
If we discard diseases not confirmed by official science, but turn to research, it becomes clear that the constant exposure to strong microwave radiation on the human body does not pass without a trace for it and is fraught with health problems.
Due to the fact that the number of Wi-Fi devices in public places is growing steadily, and to increase the throughput, access points are placed close to each other, the signal level from all devices in total may exceed the permissible norms.
Wi-Fi devices operate in a non-ionizing radiation range that does not have such a harmful effect as ionizing radiation. The latter, in turn, is able to form ions in the substance it affects. There are several types of ionizing radiation: alpha, beta, gamma radiation, as well as neutron radiation.
However, non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation can also affect living organisms due to thermal and non-thermal effects, which can cause significant harm to health. Below are materials of some studies on the effect of Wi-Fi signal on the biochemical composition of blood and hematology.
Hematology is a branch of medicine that studies blood, blood-forming organs, and blood diseases. In addition, hematology includes the diagnosis, treatment, prognosis and prevention of blood diseases.
In the experiment, which will be described below to study the effect of Wi-Fi on the biochemical composition of blood, mice were used, since their biological characteristics are similar to humans.
At high signal strengths, Wi-Fi can cause a “thermal effect,” which can damage living cells. That is why there are sanitary standards that recommend the power of Wi-Fi routers 0.614 V / m (0.1 W / cm2) for access points installed in an open area and 0.19 V / m (0.01 W / cm2) for indoor use. When measuring the level of damage to cells from radiation, a Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) is used. It is measured in watts per kilogram of tissue (W / kg). SAR is a quantity that measures the body’s rate of absorption of energy by exposure to an electromagnetic field. SAR limits vary in the US and Europe. In Russia, radiation is measured in watts per square centimeter.
The scheme of the experiment conducted by the researchers was as follows. Antenna radiation with a signal generator operating at a frequency of 2.4 GHz is directed to cell “A”. The cell is located at a distance of a meter from the radiation of the antenna in its far field. It is worth knowing that the far zone of the antenna is the area where the angular distribution of the field is independent of the distance to the antenna.
In the cell "B" put 15 male mice. It was located near the signal generator, so the radiation should not have had almost any effect on them. The experiment lasted six months, during which experimental mice were irradiated for 8 hours daily.
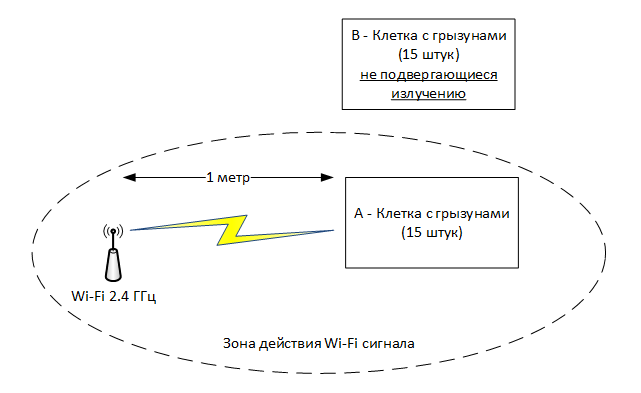
To determine the far zone of the antenna, it is first necessary to determine the wavelength

where c is the speed of light, f is the radiation frequency.
Then the far zone is determined by the formula
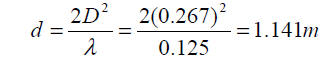
Where D is the antenna length (in the experiment it is 0.267 meters)
In order to exclude possible negative effects of water and food on the quality of the experiment, the mice were fed with diet food, purified water, and a constant room temperature was set in the room. Two weeks later, the first group of experimental mice, three from each cell, were sent for biological tests. Two weeks later, another group of mice was sent for testing, and so on, to the remaining rodents.
results
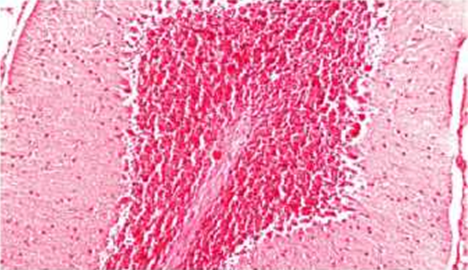
The first adverse biological effects from Wi-Fi began to appear after the first four months of testing. In particular, in experimental mice under irradiation, brain tissue and liver were inflamed, and an abscess of lung tissue was observed. In mice not exposed to radiation, the analysis showed no deviations.
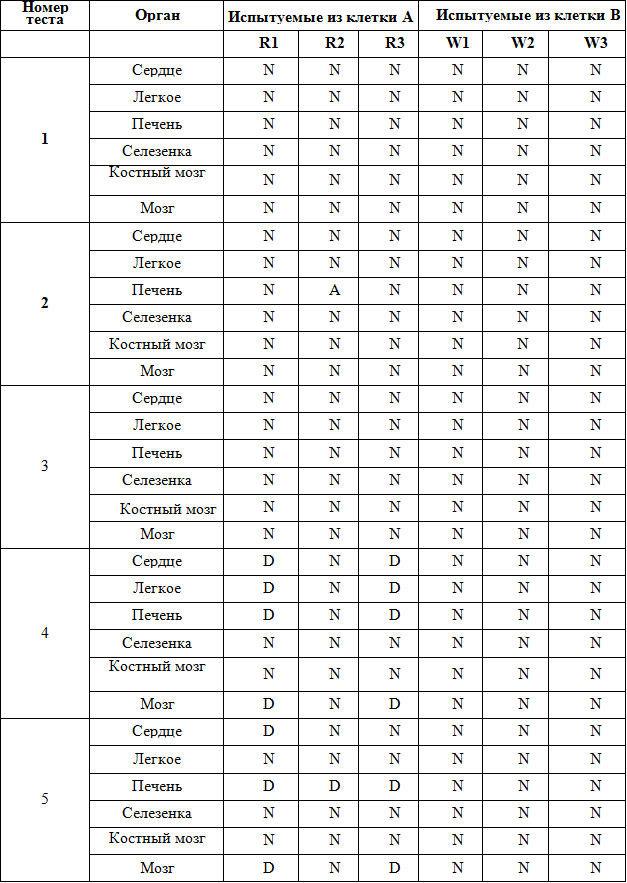
N = NORMAL; D = cell degeneration (cell is damaged).
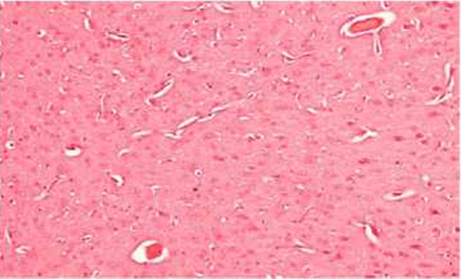
The appearance of normal and degraded tissues of various organs is shown in the figures. Observed organs: liver, brain, lungs.
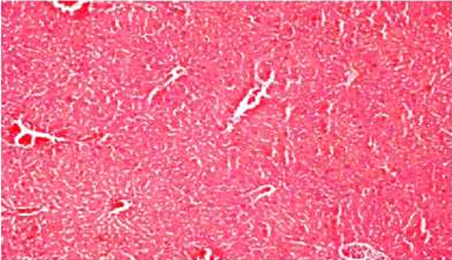
Normal tissue Liver with increasing x400
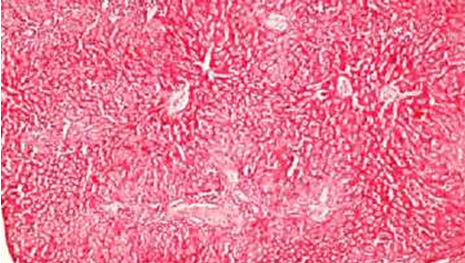
Degradation of liver tissue with increasing x400
Normal tissue of Brain with increasing x400
Degradation of brain tissue with increasing x400
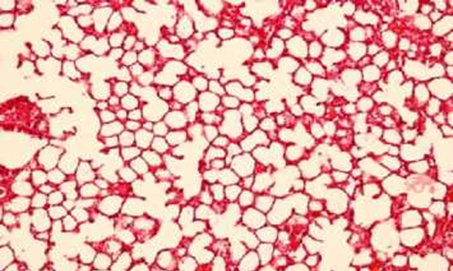
Normal tissue of the lung with increasing x400
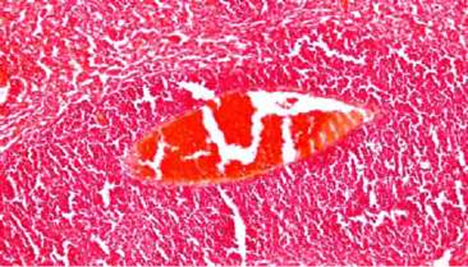
Degradation of lung tissue with an increase of x400
Blood changes
The results of a full blood test and hematological analysis showed no significant deviations from the norm, except for PCV (Packed Cell Volume - hematocrit, hematocrit, hematocrit, erythrocyte sedimentation volume), hemoglobin (Hb), and red blood cells (erythrocytes).
Detailed blood tests are shown in the graphs below:
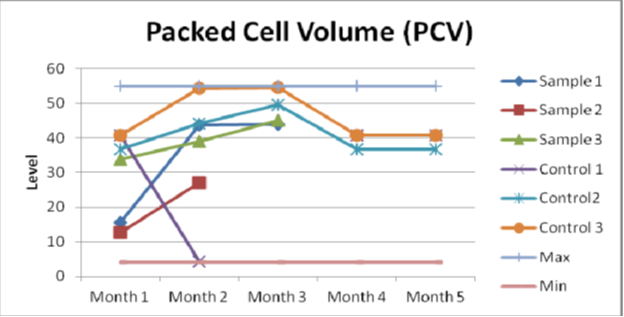
Hematocrit
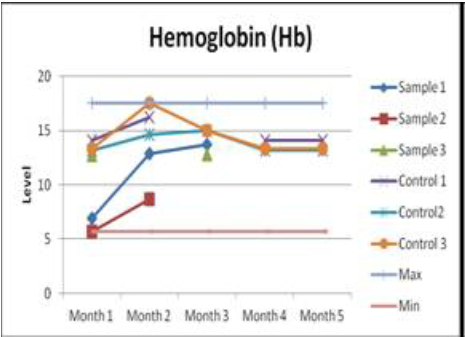
Hemoglobin
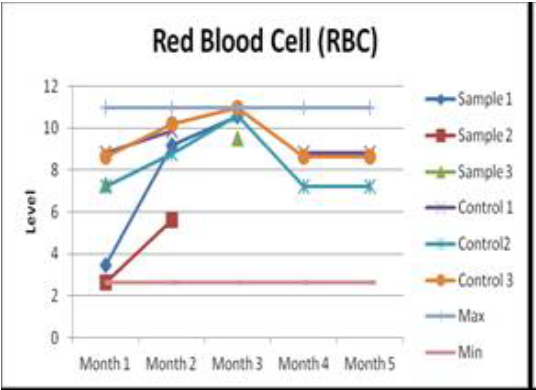
Blood Cell
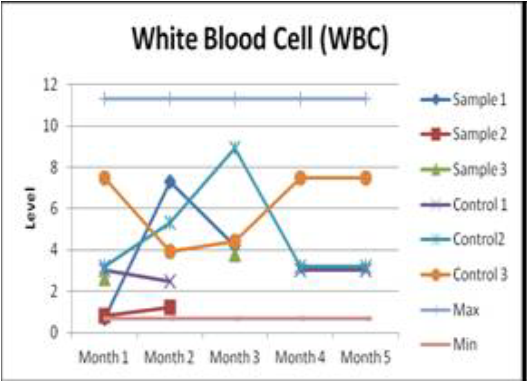
Level White
Blood Cell Level
These graphs show the results of blood biochemical composition analysis:
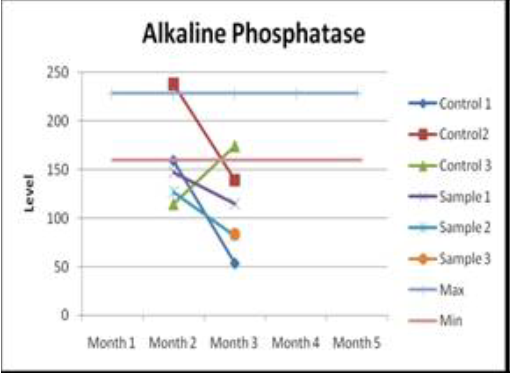
Hydrolase enzyme
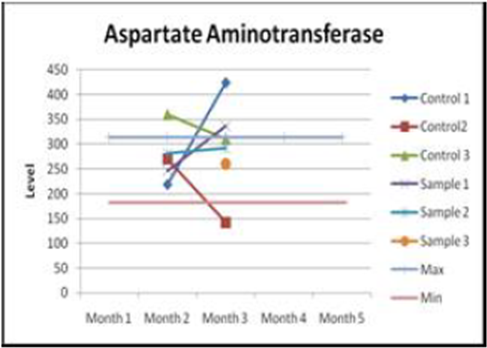
Aspartate aminotransferase
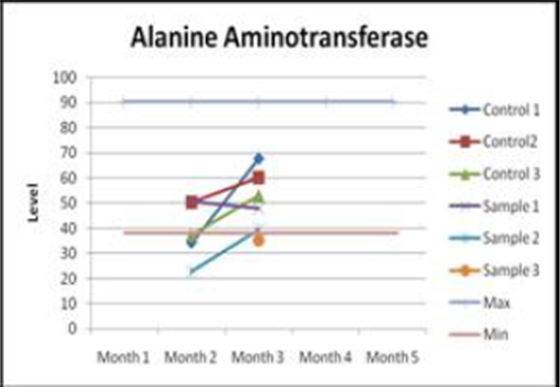
Alanine aminotransferase Glutamyl transferase
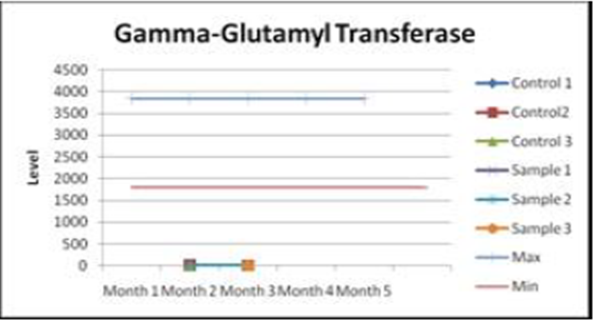
enzyme
Judging by the graphs, it becomes clear that the content of Alkaline Phosphatase - the enzyme hydrolase (alkaline phosphatase) drops below normal. In turn, aspartate aminotransferase shows a tendency to increase. As a rule, similar changes can result in liver injury. That is, changes in AST and ALT confirm the presence of degradation of liver cells.
After one month of exposure to radiation, the level of Globulin decreases. After another two months, an even greater downward trend is visible. Much lower than normal is the level of glutamyl transferase. On the contrary, the level of lactate dehydrogenase was above normal after. This enzyme has the property to be released when cells are damaged, and a high level of ammonia in the blood indicates that the liver is simply not able to convert ammonia into urea, which leads to hepatitis.
Indicators of the level of Globulin (whey protein) becomes much lower than the normal range after a month of exposure to microwave radiation, and this level is further reduced after another 2 months of research. The level of glutamyl transferase (enzymes) is significantly lower relative to the level, and the level of lactate dehydrogenase for all samples under the influence of microwave was significantly higher compared to the normal value. Note that this enzyme is released from cells into the bloodstream when cells are damaged. High levels of ammonia in the blood indicate that the liver is not able to convert ammonia into urea. This in turn can cause hepatitis.
The results of the study speak for themselves - microwave radiation has an adverse effect on biological organisms. When exposed to radiation over a long period, changes in the tissues of organs begin, as well as biochemical blood parameters deviate from the norm. This clearly shows that Wi-Fi radiation leads to the degradation of certain organs and tissues.
Sources:
1. http: //ieeexplore.ie...cument/5296279/
2. http: //ieeexplore.ie...cument/6944290/
3. http: //ieeexplore.ie...cument/1232183 /
4. http: //ieeexplore.ie...cument/6717901/
