Superhosted GhostMail service stops working with regular users
The company will only cooperate with corporate clients, as it does not want to take responsibility for the actions of criminals

GhostMail, a secure email service, announced that it will only work with corporate clients on September 1 . Ordinary users will not be able to work with this mail service. The company management made such a decision in order not to take responsibility for the possible actions of “bad people”. In other words, the creators of GhostMail are afraid that terrorists or other criminals who need to hide their correspondence from the authorities will work with the service.
An appeal to users published on the GhostMail homepage states the following: “Since the launch of our project, the world has changed for the worse, and we don’t want to take responsibility for supporting bad people - this is not a risk.”
“In general, we support the idea of the inviolability of private information, but we made a strategic decision to provide services only to corporate users. We hope that you understand our solution and offer a free alternative - ProtonMail. Users of paid accounts will receive their funds back, they will be contacted personally. ”
GhostMail began work in 2014. The founders of the service claim that the files deleted by the user are really deleted, and not stored on servers. The service description page says that the company is not American and does not collect user data. All information is encrypted.
“We are not interested in identifying you or in obtaining your personal data. When working with GhostMail, you are protected, and the risks of theft of personal information are minimized, ”the site says.
It is still unclear whether the service is being closed for ordinary users due to the requirements of the authorities of any country or countries, or whether the management of the company made this decision on its own, without pressure from the outside.
GhostMail is not the first hacked mail service to stop working (at least with regular users). A few years ago, the creator of the secure email service Lavabit had to liquidate the companyunder pressure from US authorities. Then Levinson received a court order to issue TLS keys. He decided to close the company, and instead of issuing the keys (as he said), he destroyed all the data, including files and keys. Lavabit was a popular service. At the time of closure, he totaled 410 thousand user accounts. Edward Snowden also worked with Lavabit, who considered this mailer to be safer than others.
It all started with the fact that the FBI agents came to the founder of the service and demanded access to the equipment to install tracking devices. The company owner had to agree, but after a while the FBI realized that agents did not have access to the contents of the letters. In order to read the letter, you need a TLS key. But the keys Ladar Levinson, the founder of Lavabit, refused to give out.
After that, litigation began, and Levinson was threatened with imprisonment. After weighing all the pros and cons, he decided to close his company.
One of the best known secure mail services is ProtonMail . It was created by several employees of the European Laboratory for Nuclear Research (CERN). This email service is one of the most secure in the world. For example, all information is encrypted on the client side, and all service servers are located in Switzerland. In this country, it is very difficult, if at all possible, to gain access to someone else’s private information.
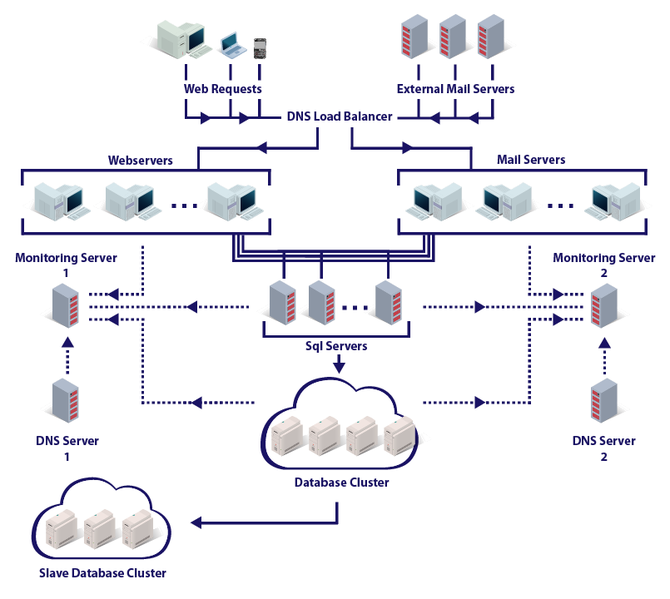
Protonmail System Architecture (2014)
Two-factor authentication with two passwords is used to authorize the user. One password is required to enter your own account and receive your own data in encrypted form. The second password gives access to the encryption key, with which all information is brought in a readable form. The second password cannot be restored - the support service will not help in case of loss. However, in order to be able to work with all the functions of the service, it is also necessary that the interlocutor is a ProtonMail user.
If desired, you can send a secure message to a third-party service user. When encrypting, the AES-256 algorithm is used. For decoding, you need a password that must be known to both the addressee and the sender. In the email received by the recipient, there is a link that directs to the ProtonMail server. In this case, the recipient will see a link to the letter, which can be read by entering the password.
