About business processes humanly
That just did not write on Habré about business processes: about the general philosophy, about programming of processes, about numerous BPM systems, about notations, etc. In principle, the vendor understands everything: he took the process, cleaned it of cleanings, modeled, automated and run the instances when necessary. Business something. Meanwhile, the business to which the articles are addressed often does not understand the main thing - why do they need these business processes? After all, he is not Gazprom or the Kalashnikov concern. Here, the main things would be solved: so that the deadlines would not be broken, the employees would not lose documents and would not blame each other, otherwise one could not see any profit among this mess ...
We decided to rectify the situation and talk about business processes as simply as possible - so that everyone could understand whether they were good for the business or, well, they sat normally. Therefore, today without notations, complex schemes and advertising reviews. So, the introduction: “Everything is a process”, “Everyone has processes”, “If you don’t like business processes, you just don’t know how to prepare them.” Go. Pikabu.ru. Typical organization of the process in companies of any level: “The swan breaks into the clouds, Cancer backs up, and the Pike pulls into the water. Who is to blame for them, who is right, is not for us to judge; Yes, only things are there. ” The idea of this article was prompted by our own statistics. The fact is that in RegionSoft CRM

a module of business processes that we are proud of is built-in: a native graphical + logical editor, simple management, the ability to design the most complex processes without programming knowledge. But no.
About 12% -14% of customers use the functionality of business processes. This is not enough, it is incomprehensible, it is strange to have a reliable and simple tool and ignore it.
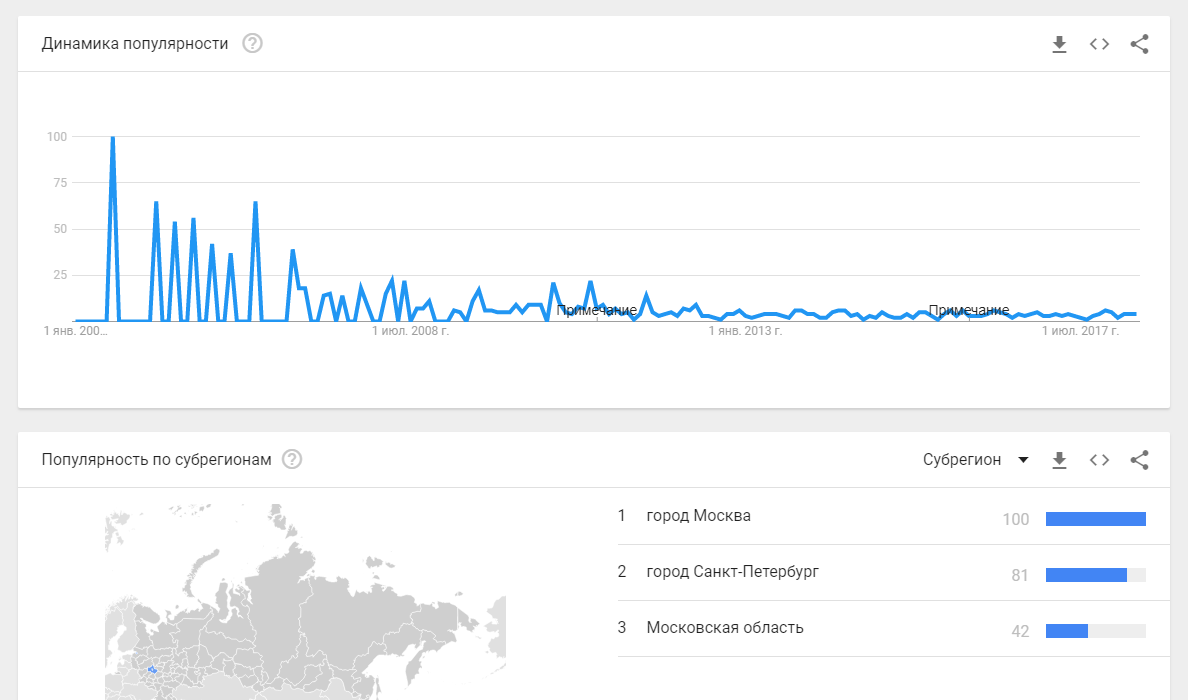
To test the hypothesis (in fact, we already know the situation, but still) go to Google Trends. Actually, this is all you need to know about the interest of Russian business in business processes:
Business processes are chains of actions and events that occur in a company and lead to an end result. Example: hiring and adapting an employee, purchasing and launching software, distribution, etc.
Processes can be single (for example, the development of a corporate website for a company) and cyclic, repeating (preparing mailings, manufacturing products, etc.). Also, processes can be enlarged (advertising campaigns) and fractional (banner design development). Fractional processes can be part of one-time projects or different processes (for example, developing banner designs can be for distribution, for context, for designing a widget on Habré, etc.).
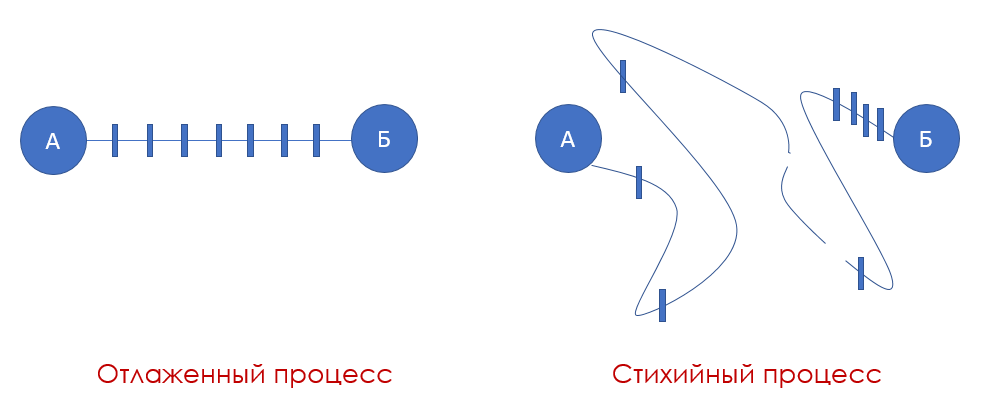
It turns out that every company has business processes and often they do not work as they would like. In the case of spontaneous, unattended, and non-automated processes, the goal is achieved in a rather complicated way, with problems and failures in communication. The implementation of the bulk of the tasks and stages occurs immediately before the deadline.
If the business processes in the company are not debugged, they lead to a loss of funds, strength, nerves and, ultimately, to lost competition - simply because all negative trends necessarily affect relations with customers. Such processes may be:
Surely, having read to this place, you already know at least some features of your company (sometimes several at once). And this is what happens with everyone - many factors influence business processes, from technological to psychological, so everything is as if by saying: there are no absolutely healthy companies, there are underexplored ones.
The first reason is that processes include a lot of human labor. If there is no automation, then almost everything is done by a person: writes out documents, makes calls, makes or does not make a task in the calendar, performs his main activity. Each employee has his own measure of responsibility, punctuality, conscientious attitude to work, etc. And since several people are involved in each process, errors accumulate and result in a disrupted process or in a completely different result that is needed.
For example, a software agency operates in Kazan. A customer from Vladivostok asks for the completion of, say, a CRM system in the shortest possible time, since a week later it launches a new product line. The revision is a real trifle; requirements and a signed ToR are needed. The manager from Kazan should contact the customer in the morning, interview him, agree on the details and receive documents. But she recalls this at 17:00. All, at least a day of downtime for the programmers on this project is provided - they now need to shift projects, reschedule time so that they can take the project to work as soon as specific requirements appear. The processes "went."
The second reason is poor control. We have already written a hundred times in our articles that we need to control not how the person works, but what indicators and what quality he gives out. Today, some kind of general fashion has gone to monitor every second of working time, and the result is still r ****. Do you know what the reason is? People a) are afraid b) imitate as the system pleases ( here I am sitting at the computer, I have a very important document open and I have been chasing a couple of lines in it for 2 hours / writing and rewriting the code of one function ). This is a bad control. Good control is the ability to set tasks and align motivation with them, so that the employee himself happily organizes his working time and performs tasks (this is just about delegation, development methodologies and the KPI system, if it comes to managers and businesses).
The third reason for the “diseases” of business processes is poor circulation of information within the company. There is nothing worse when all decisions are directively descending from above, and departments wage internecine wars to prove their importance and weight. Information in the company should pass freely along both the horizontal and vertical hierarchies, each employee has the right to request the data necessary for work from a neighboring department or manager and must provide data at the first request of colleagues. Of course, the most striking example of such a relationship is the eternal, almost holy war of marketing and sales. But there are worse stories, for example, when the development and testing department are at war.
Of course, depending on the field of activity and the features of the organizational structure, there may be other reasons for the failure of the processes, but these three are universal for everyone: from an advertising agency to a flight control center.
If you’ve been to different fast food chains, you probably noticed that McDonald’s in terms of speed, quality of service, availability of the entire assortment and accuracy of order fulfillment is bypassing its closest competitors. Although the principle is still the same: the franchise, young employees, managers above them, semi-finished products with a high degree of readiness, automated cash desks and sending an order to the kitchen (there are nuances, but not for this article). The reason is simple - it is at McDonald's that processes are perfectly debugged and as automated as possible. And the manager’s task is not to run to the cash desk to cancel the order, but to correct the subordinate at the first oversight, and not when the client noticed it. As a result, customers are satisfied, and it’s easier to work, because part of the responsibility lies with the process itself, you are only part of the chain.
And if you were at the same time, for example, at the large food courts of the shopping center, you could see how customers languishing with expectation sometimes change their location in the queue to the queue of a neighboring vendor and after a few minutes are removed to the place with the order received. Here we come to the main point. The business environment for most companies is the same food court, a cramped closed market for goods and services. If tomorrow RegionSoft employees do not provide a good service to a client who wants to buy RegionSoft CRM , he will not wait for the chief to push the back of the head and solve the problem - he will go to the competitors. And the client will not care that we are safe, functional, powerful, inexpensive and that our system is ultra fast. He will worry that the process has failed and is uncomfortable.
Improving business processes is your competitiveness and the key to survival in the market. Weak, unstructured processes, in addition to customer dissatisfaction, will entail an increase in costs, lower incomes and low motivation for employees (rush, vanity and abuse very quickly demotivate). If you want, the business process is a kind of flexible methodology for the entire company, and not just for development (this is an explanation for IT specialists).
Formal prescribed logic and clear execution. An automated process is a “programmed” model, available data and logging of all actions. The program is responsible for changing stages, notifications, documents, letters and some other attributes - it is from time to time that it starts everything at the right time and at specified intervals ( on April 17, start a process instance, on the 18th send a reminder to participants A and D, 19- on the basis of work A and D, form an invoice and send it in payment, send notifications E, reminders B, F, Z, on the 22nd, on the basis of all the work done, generate a report and send X ).
Validity of decisions.Business processes permeate all the activities of the company and when they are automated, accurate and relevant information about customers, deals, assortment, etc. is accumulated. That is, for example, if your BPM is embedded in some form in a CRM system (as, for example, it was done in RegionSoft CRM ), then all data during the process is distributed in its tables, which means that an information base appears for analysis and justification of decisions. By the way, in “pure BPM systems” all information is also accumulated, but not always in the context in which it is necessary for operational work.
Fast and high-quality team work.Since all stages and responsible ones are spelled out in the business process, the team works as a single mechanism, passing the baton from the employee to the employee. Everyone in their place knows what needs to be done and is sure that all previous work has been completed (otherwise the system will not continue the process, but will notify of violations of one of the links). It is very convenient to rely on a formal model and do the real work, that is, actually act according to a clear plan for the whole team and for each link separately.
Labor productivity growth.It's simple: part of the work is shifted to the program, so "robots are working hard, a person is happy." Most often, it is routine processes that are automated (that is, those that are cyclically repeated and require uniform work that can be formally described), so employees have more time to work aimed at communicating with customers, developing the product, etc.
For example, an article on Habré or Forbes in a large company. The author selects a topic, writes off with everyone, agrees, then writes, writes to everyone that he wrote, everyone reads, makes one hundred million edits, he writes again, everyone reads, etc., then someone masterfully makes up this business, searches for / draws pictures, etc. The sea of formal correspondence, which can be replaced by alerts on the action "File uploaded." And the freed up time can be spent on deeper work with the text.
The flexibility of the company in relation to change.Alas, in our time, changes can come from anywhere: employees quit, a new law was passed, sanctions were imposed, and now the business is forced to adapt to the changes. Even if they are very good, it is always stressful for the company. Automated processes easily change and are guided by new conditions - the business is quickly rebuilt on the right track. Today, flexibility and the ability to adapt is the key to successful business evolution in the market. Unfortunately, bureaucratic hulking dinosaurs will die out.
The effectiveness of remote employees, geographically distributed units.If you want all those who are further than 1 km from your office and work in your company to be integrated into the team, and not to carry out their monotonous work as outsourcers, business processes are important to you. Include employees in the process, assign roles, assign milestones, automate their work, and as a result, everyone will be involved in team work anyway, informed in time, and, most importantly, effective.
Three years ago, in one of the foreign analytical articles, I read a good explanation of the importance of processes using Wikipedia as an example. This project = a mega distributed team (the whole world) + mega routine tasks (texts, edits, fact checking) + mega debugged process with maximum automation. As a result, due to the constant improvement of regulations, forms, and communications, the so-called “joint anarchy” has acquired a cool and useful form.
Reducing risks and increasing the level of information security. We already wrote that automation itself plays an important role in strengthening information security, but business processes help to control every point of the implementation of tasks within the project, and in which case you can immediately detect a problem and begin to reduce the risks of an adverse outcome.
The openness and transparency of the process for all its participants is precisely the very security factor. Everyone can see who is currently the owner of the process and who the task is stuck on. When the company implements automated management of business processes (for example, in a CRM system), the human factor comes to almost zero, because it makes no sense to shift responsibility and be partisan in silence about a failure when you can see who wasted time in the program interface missed the task and did not complete the work on time.
Full subordination and coordination within the team , since all roles are distributed within the process and you can contact any participant in two clicks.
Protection of business continuity from personnel problems.HR problems happen all the time: illness, vacation, staff turnover (especially among salespeople, telemarketers, middle managers, etc.). When an employee drops out of the workflow, it is always a definite short-term (or not so) collapse in his area of responsibility. It is easy to reconfigure an automated business process by appointing a new employee - and the whole team will immediately understand who is responsible for what. Again, the collapse will be, but minimally short and without consequences from the organization of the process.
Accelerated adaptation of employees.In general, new employees today and 10 years ago are strikingly different. If earlier even the most brilliant employee was involved in the work for the first time and did not show himself in any way, today you can meet those who demonstrate activity on the first day. Of course, most often such activity is a headache for the whole team, but these guys do not want to beat their hands either. The inclusion of a novice in the business process that he can see helps him adapt as quickly as possible, and at the same time not go beyond his responsibilities. Subordination is observed, the project is at a glance, communication with colleagues is obvious - you can safely work. Another value of the processes is immediately revealed - the accumulation and translation of business knowledge.
Development of work culture and interaction culture.Again, I repeat that all employees are different and introverts and extroverts are especially distinguished, who find it difficult to converge and start working on a single result. A well-functioning process teaches employees a culture of communication and interaction, makes relationships comfortable and transparent. For example, the introvert tester Vasya does not need to ask all who are responsible for the design in fear in order to ask which of the 7 remote workers did the localization, because there is a typo in the interface translation. He opens the current process, looks at who specifically translated and writes his remark in any messenger.
Measurability and evaluation of the result.Automated processes accumulate a sea of information, can be measured (reports, KPI), log information and always eloquently demonstrate whether a result is achieved or not. If it seems to you that the reason for the failure was the non-optimal architecture of the process, you can always fix it by reconfiguring the parameters in the process editor.
BPM systems are like CRM, only BPM. Joke. This software is for modeling and running business processes. True, BPM systems are somewhat similar to CRM systems and belong to the corporate software class. Process models are created in the interface of such a system (most often using BPMN 2.0 notation or in a native editor), a graphical and logical representation appears, is stored on the server, and then process instances are launched on the desktop or in a web browser. The BPM system itself, unlike CRM or ERP, cannot provide end-to-end business automation, therefore it often requires integration (often vendors have several systems at once). Ultimately, BPM systems are quite expensive, difficult to manage and in their pure form are needed by companies with very complex processes (industry, government procurement, export, high-tech industries, etc. ) Frankly, it’s better than the picture below, and you won’t tell, they are often really anti-human and monstrous:
But even without business processes, a company at any level is very bad, so the vendors of CRM systems were not at a loss and included modules for modeling and process control in their systems. We won’t name specific brands, but let’s say frankly - everyone succeeded with varying degrees of success: someone dragged BPMN 2.0 for himself, someone took the notation elements and turned it into a completely miserable interface, and some of them turned out very well, distinct and businesslike. And this is the best option for most companies - a universal solution without the difficulties of integration and data exchange.
We introduced business processes back in RegionSoft CRM 5.0 release, collected data and reviews, worked on the system ourselves, understood our mistakes, estimated achievements in RegionSoft CRM 6.0 versionconducted a deep refactoring of the business process module, which migrated to later versions. Experience shows that in our editor you can configure and run the most complex processes.
A business process in itself is a route to accomplish one large task consisting of several stages. Based on this, we need to work on it.
When working with business processes, consider a couple of important points:
The answer to this question is concise: immediately, even if you just created a company. Let’s not pour water, but let’s take a look immediately at the example, what processes are even in the youngest company.
All of these processes are cyclical, some of them will become more complicated and develop, so the sooner you start, the faster and easier it will be to further reengineering.
And of course, if you have a bunch of established processes and you don’t know what to pull for, all the more it is worth looking towards automation.
Business process management is never without effect. According to the AIIM study, companies that turn to BPM receive up to 41% ROI growth. 62% note improved communication between company employees, 33% - reduced bureaucracy and levels of coordination, 42% - greater organizational flexibility.
Implement and automate business processes - this means stop solving business problems as tasks and go to the level of management by goals, work for the result. This means more freedom of hands and heads from routine and fuss, less conflict and corporate wars. Business processes are not a chip for the elite and great, not the prerogative of Gazprom or Rosatom, it is a transparent, convenient and affordable work tool for everyone, which significantly improves business in the company. So, if you have CRM (or are planning to be implemented), do not ignore the opportunities - use them. Be sure: after a short period of time, you will say “The process has begun” and will be happy to launch another instance of it.
Our site with absolutely desktop business software and our flagship RegionSoft CRM.
 Our live Telegram channel BizBreeze . Anything about CRM and business, wisely, without copy-paste and 90% without advertising. Subscribe.
Our live Telegram channel BizBreeze . Anything about CRM and business, wisely, without copy-paste and 90% without advertising. Subscribe.
We decided to rectify the situation and talk about business processes as simply as possible - so that everyone could understand whether they were good for the business or, well, they sat normally. Therefore, today without notations, complex schemes and advertising reviews. So, the introduction: “Everything is a process”, “Everyone has processes”, “If you don’t like business processes, you just don’t know how to prepare them.” Go. Pikabu.ru. Typical organization of the process in companies of any level: “The swan breaks into the clouds, Cancer backs up, and the Pike pulls into the water. Who is to blame for them, who is right, is not for us to judge; Yes, only things are there. ” The idea of this article was prompted by our own statistics. The fact is that in RegionSoft CRM

a module of business processes that we are proud of is built-in: a native graphical + logical editor, simple management, the ability to design the most complex processes without programming knowledge. But no.
About 12% -14% of customers use the functionality of business processes. This is not enough, it is incomprehensible, it is strange to have a reliable and simple tool and ignore it.
To test the hypothesis (in fact, we already know the situation, but still) go to Google Trends. Actually, this is all you need to know about the interest of Russian business in business processes:
- the zone of interest is large megacities where large and advanced IT companies are concentrated
- clarification of interest (specific requests) - rather educational: “business process example”, “business processes”, “business process is”, etc.
- since 2008, a steady decline in interest (the impact of the crisis).

What are business processes?
Business processes are chains of actions and events that occur in a company and lead to an end result. Example: hiring and adapting an employee, purchasing and launching software, distribution, etc.
Processes can be single (for example, the development of a corporate website for a company) and cyclic, repeating (preparing mailings, manufacturing products, etc.). Also, processes can be enlarged (advertising campaigns) and fractional (banner design development). Fractional processes can be part of one-time projects or different processes (for example, developing banner designs can be for distribution, for context, for designing a widget on Habré, etc.).
It turns out that every company has business processes and often they do not work as they would like. In the case of spontaneous, unattended, and non-automated processes, the goal is achieved in a rather complicated way, with problems and failures in communication. The implementation of the bulk of the tasks and stages occurs immediately before the deadline.

If the business processes in the company are not debugged, they lead to a loss of funds, strength, nerves and, ultimately, to lost competition - simply because all negative trends necessarily affect relations with customers. Such processes may be:
- ineffective - at high labor costs, bring a minimally acceptable option, use too many resources;
- slow - due to the inconsistency of the participants in the process and the lack of clearly defined stages and deadlines allocated to each task;
- unreliable - such processes do not lead to the expected result, but to its partial implementation or to the complete absence of the final result;
- duplicating is not a bad option, but such processes overload workers and consume more resources than an optimized process does;
- redundant - too many stages, tasks and relationships overload the process, and as a result, achieving the goal is delayed or is too expensive;
- non-working - without comment, this is clearly a crisis (this happens, for example, when departments do not exchange information: techies developed new software, marketers came up with promotion, October 15th uploaded everything to the website and to the stores, and salespeople did not even hear about it therefore cannot answer customer questions and work in principle );
- superfluous - the company retains old processes or processes that have become irrelevant in the framework of current activities; the worst option is when such chains are binding.
Why so much trouble with business processes?
Surely, having read to this place, you already know at least some features of your company (sometimes several at once). And this is what happens with everyone - many factors influence business processes, from technological to psychological, so everything is as if by saying: there are no absolutely healthy companies, there are underexplored ones.
The first reason is that processes include a lot of human labor. If there is no automation, then almost everything is done by a person: writes out documents, makes calls, makes or does not make a task in the calendar, performs his main activity. Each employee has his own measure of responsibility, punctuality, conscientious attitude to work, etc. And since several people are involved in each process, errors accumulate and result in a disrupted process or in a completely different result that is needed.
For example, a software agency operates in Kazan. A customer from Vladivostok asks for the completion of, say, a CRM system in the shortest possible time, since a week later it launches a new product line. The revision is a real trifle; requirements and a signed ToR are needed. The manager from Kazan should contact the customer in the morning, interview him, agree on the details and receive documents. But she recalls this at 17:00. All, at least a day of downtime for the programmers on this project is provided - they now need to shift projects, reschedule time so that they can take the project to work as soon as specific requirements appear. The processes "went."
The second reason is poor control. We have already written a hundred times in our articles that we need to control not how the person works, but what indicators and what quality he gives out. Today, some kind of general fashion has gone to monitor every second of working time, and the result is still r ****. Do you know what the reason is? People a) are afraid b) imitate as the system pleases ( here I am sitting at the computer, I have a very important document open and I have been chasing a couple of lines in it for 2 hours / writing and rewriting the code of one function ). This is a bad control. Good control is the ability to set tasks and align motivation with them, so that the employee himself happily organizes his working time and performs tasks (this is just about delegation, development methodologies and the KPI system, if it comes to managers and businesses).
The third reason for the “diseases” of business processes is poor circulation of information within the company. There is nothing worse when all decisions are directively descending from above, and departments wage internecine wars to prove their importance and weight. Information in the company should pass freely along both the horizontal and vertical hierarchies, each employee has the right to request the data necessary for work from a neighboring department or manager and must provide data at the first request of colleagues. Of course, the most striking example of such a relationship is the eternal, almost holy war of marketing and sales. But there are worse stories, for example, when the development and testing department are at war.
Of course, depending on the field of activity and the features of the organizational structure, there may be other reasons for the failure of the processes, but these three are universal for everyone: from an advertising agency to a flight control center.
What to do with business processes?
If you’ve been to different fast food chains, you probably noticed that McDonald’s in terms of speed, quality of service, availability of the entire assortment and accuracy of order fulfillment is bypassing its closest competitors. Although the principle is still the same: the franchise, young employees, managers above them, semi-finished products with a high degree of readiness, automated cash desks and sending an order to the kitchen (there are nuances, but not for this article). The reason is simple - it is at McDonald's that processes are perfectly debugged and as automated as possible. And the manager’s task is not to run to the cash desk to cancel the order, but to correct the subordinate at the first oversight, and not when the client noticed it. As a result, customers are satisfied, and it’s easier to work, because part of the responsibility lies with the process itself, you are only part of the chain.
And if you were at the same time, for example, at the large food courts of the shopping center, you could see how customers languishing with expectation sometimes change their location in the queue to the queue of a neighboring vendor and after a few minutes are removed to the place with the order received. Here we come to the main point. The business environment for most companies is the same food court, a cramped closed market for goods and services. If tomorrow RegionSoft employees do not provide a good service to a client who wants to buy RegionSoft CRM , he will not wait for the chief to push the back of the head and solve the problem - he will go to the competitors. And the client will not care that we are safe, functional, powerful, inexpensive and that our system is ultra fast. He will worry that the process has failed and is uncomfortable.
Improving business processes is your competitiveness and the key to survival in the market. Weak, unstructured processes, in addition to customer dissatisfaction, will entail an increase in costs, lower incomes and low motivation for employees (rush, vanity and abuse very quickly demotivate). If you want, the business process is a kind of flexible methodology for the entire company, and not just for development (this is an explanation for IT specialists).
So, what are the benefits of automating business processes?
Formal prescribed logic and clear execution. An automated process is a “programmed” model, available data and logging of all actions. The program is responsible for changing stages, notifications, documents, letters and some other attributes - it is from time to time that it starts everything at the right time and at specified intervals ( on April 17, start a process instance, on the 18th send a reminder to participants A and D, 19- on the basis of work A and D, form an invoice and send it in payment, send notifications E, reminders B, F, Z, on the 22nd, on the basis of all the work done, generate a report and send X ).
Validity of decisions.Business processes permeate all the activities of the company and when they are automated, accurate and relevant information about customers, deals, assortment, etc. is accumulated. That is, for example, if your BPM is embedded in some form in a CRM system (as, for example, it was done in RegionSoft CRM ), then all data during the process is distributed in its tables, which means that an information base appears for analysis and justification of decisions. By the way, in “pure BPM systems” all information is also accumulated, but not always in the context in which it is necessary for operational work.
Fast and high-quality team work.Since all stages and responsible ones are spelled out in the business process, the team works as a single mechanism, passing the baton from the employee to the employee. Everyone in their place knows what needs to be done and is sure that all previous work has been completed (otherwise the system will not continue the process, but will notify of violations of one of the links). It is very convenient to rely on a formal model and do the real work, that is, actually act according to a clear plan for the whole team and for each link separately.
Labor productivity growth.It's simple: part of the work is shifted to the program, so "robots are working hard, a person is happy." Most often, it is routine processes that are automated (that is, those that are cyclically repeated and require uniform work that can be formally described), so employees have more time to work aimed at communicating with customers, developing the product, etc.
For example, an article on Habré or Forbes in a large company. The author selects a topic, writes off with everyone, agrees, then writes, writes to everyone that he wrote, everyone reads, makes one hundred million edits, he writes again, everyone reads, etc., then someone masterfully makes up this business, searches for / draws pictures, etc. The sea of formal correspondence, which can be replaced by alerts on the action "File uploaded." And the freed up time can be spent on deeper work with the text.
The flexibility of the company in relation to change.Alas, in our time, changes can come from anywhere: employees quit, a new law was passed, sanctions were imposed, and now the business is forced to adapt to the changes. Even if they are very good, it is always stressful for the company. Automated processes easily change and are guided by new conditions - the business is quickly rebuilt on the right track. Today, flexibility and the ability to adapt is the key to successful business evolution in the market. Unfortunately, bureaucratic hulking dinosaurs will die out.
The effectiveness of remote employees, geographically distributed units.If you want all those who are further than 1 km from your office and work in your company to be integrated into the team, and not to carry out their monotonous work as outsourcers, business processes are important to you. Include employees in the process, assign roles, assign milestones, automate their work, and as a result, everyone will be involved in team work anyway, informed in time, and, most importantly, effective.
Three years ago, in one of the foreign analytical articles, I read a good explanation of the importance of processes using Wikipedia as an example. This project = a mega distributed team (the whole world) + mega routine tasks (texts, edits, fact checking) + mega debugged process with maximum automation. As a result, due to the constant improvement of regulations, forms, and communications, the so-called “joint anarchy” has acquired a cool and useful form.
Reducing risks and increasing the level of information security. We already wrote that automation itself plays an important role in strengthening information security, but business processes help to control every point of the implementation of tasks within the project, and in which case you can immediately detect a problem and begin to reduce the risks of an adverse outcome.
The openness and transparency of the process for all its participants is precisely the very security factor. Everyone can see who is currently the owner of the process and who the task is stuck on. When the company implements automated management of business processes (for example, in a CRM system), the human factor comes to almost zero, because it makes no sense to shift responsibility and be partisan in silence about a failure when you can see who wasted time in the program interface missed the task and did not complete the work on time.
Full subordination and coordination within the team , since all roles are distributed within the process and you can contact any participant in two clicks.
Protection of business continuity from personnel problems.HR problems happen all the time: illness, vacation, staff turnover (especially among salespeople, telemarketers, middle managers, etc.). When an employee drops out of the workflow, it is always a definite short-term (or not so) collapse in his area of responsibility. It is easy to reconfigure an automated business process by appointing a new employee - and the whole team will immediately understand who is responsible for what. Again, the collapse will be, but minimally short and without consequences from the organization of the process.
Accelerated adaptation of employees.In general, new employees today and 10 years ago are strikingly different. If earlier even the most brilliant employee was involved in the work for the first time and did not show himself in any way, today you can meet those who demonstrate activity on the first day. Of course, most often such activity is a headache for the whole team, but these guys do not want to beat their hands either. The inclusion of a novice in the business process that he can see helps him adapt as quickly as possible, and at the same time not go beyond his responsibilities. Subordination is observed, the project is at a glance, communication with colleagues is obvious - you can safely work. Another value of the processes is immediately revealed - the accumulation and translation of business knowledge.
Development of work culture and interaction culture.Again, I repeat that all employees are different and introverts and extroverts are especially distinguished, who find it difficult to converge and start working on a single result. A well-functioning process teaches employees a culture of communication and interaction, makes relationships comfortable and transparent. For example, the introvert tester Vasya does not need to ask all who are responsible for the design in fear in order to ask which of the 7 remote workers did the localization, because there is a typo in the interface translation. He opens the current process, looks at who specifically translated and writes his remark in any messenger.
Measurability and evaluation of the result.Automated processes accumulate a sea of information, can be measured (reports, KPI), log information and always eloquently demonstrate whether a result is achieved or not. If it seems to you that the reason for the failure was the non-optimal architecture of the process, you can always fix it by reconfiguring the parameters in the process editor.
What are BPM systems and which one to choose?
BPM systems are like CRM, only BPM. Joke. This software is for modeling and running business processes. True, BPM systems are somewhat similar to CRM systems and belong to the corporate software class. Process models are created in the interface of such a system (most often using BPMN 2.0 notation or in a native editor), a graphical and logical representation appears, is stored on the server, and then process instances are launched on the desktop or in a web browser. The BPM system itself, unlike CRM or ERP, cannot provide end-to-end business automation, therefore it often requires integration (often vendors have several systems at once). Ultimately, BPM systems are quite expensive, difficult to manage and in their pure form are needed by companies with very complex processes (industry, government procurement, export, high-tech industries, etc. ) Frankly, it’s better than the picture below, and you won’t tell, they are often really anti-human and monstrous:

But even without business processes, a company at any level is very bad, so the vendors of CRM systems were not at a loss and included modules for modeling and process control in their systems. We won’t name specific brands, but let’s say frankly - everyone succeeded with varying degrees of success: someone dragged BPMN 2.0 for himself, someone took the notation elements and turned it into a completely miserable interface, and some of them turned out very well, distinct and businesslike. And this is the best option for most companies - a universal solution without the difficulties of integration and data exchange.
We introduced business processes back in RegionSoft CRM 5.0 release, collected data and reviews, worked on the system ourselves, understood our mistakes, estimated achievements in RegionSoft CRM 6.0 versionconducted a deep refactoring of the business process module, which migrated to later versions. Experience shows that in our editor you can configure and run the most complex processes.
Here's what we got (screenshots + explanations)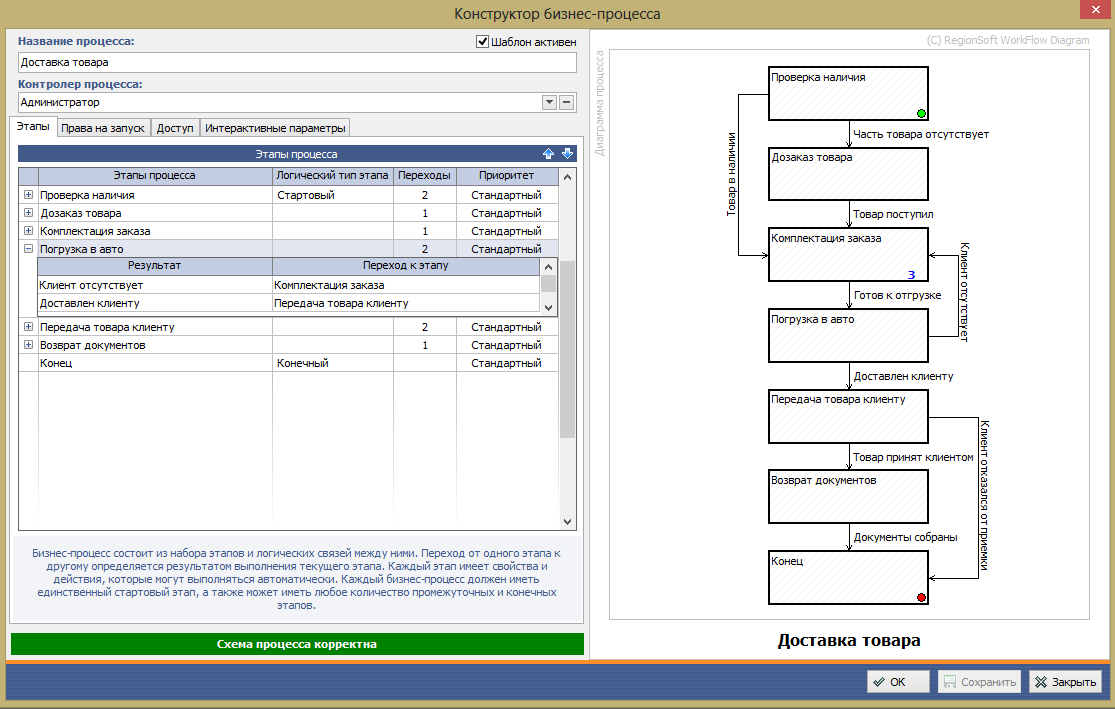
The final model of the finished process: on the left is a list of stages, transition rules and parameters, on the right is a visual graphic representation of the process (process diagram, aka workflow).
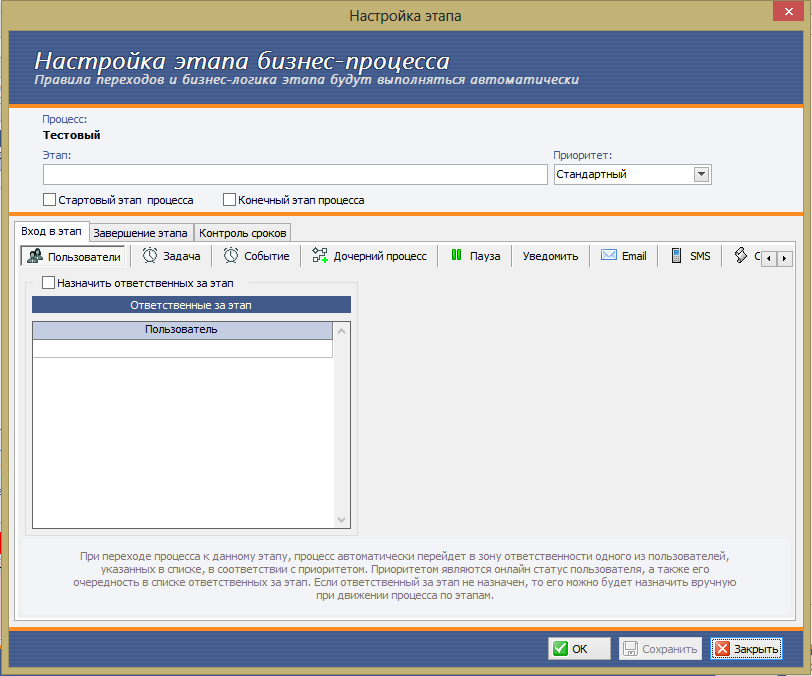
Setting up each stage of the process includes specifying those responsible, automatically creating tasks, managing deadlines, the possibility of a pause inside the process, various ways of notifying users and clients, etc. Each stage is also given priority.
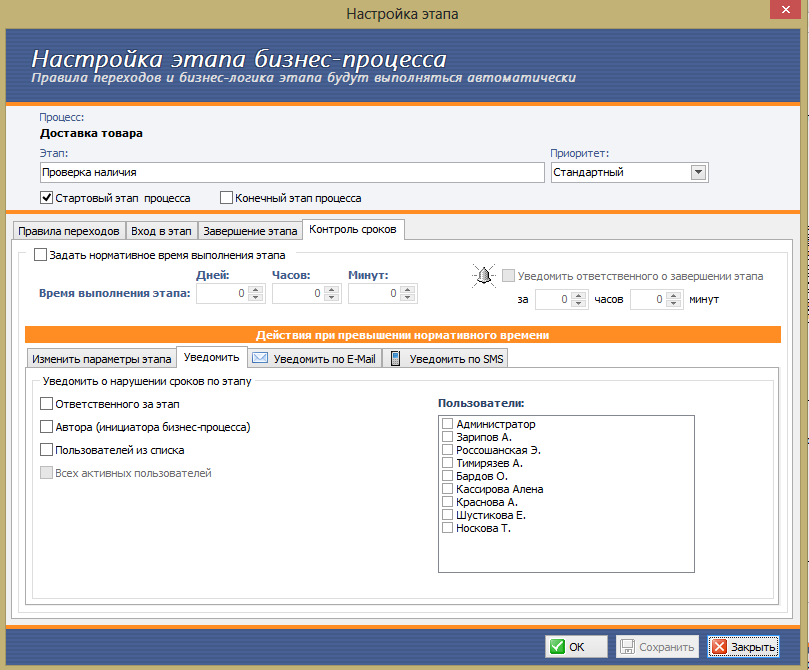
An example of what the action settings window looks like when the stage is overdue - it is possible to notify any interested parties, you can immediately evaluate the causes of the problem and an approximate shift of the deadlines.
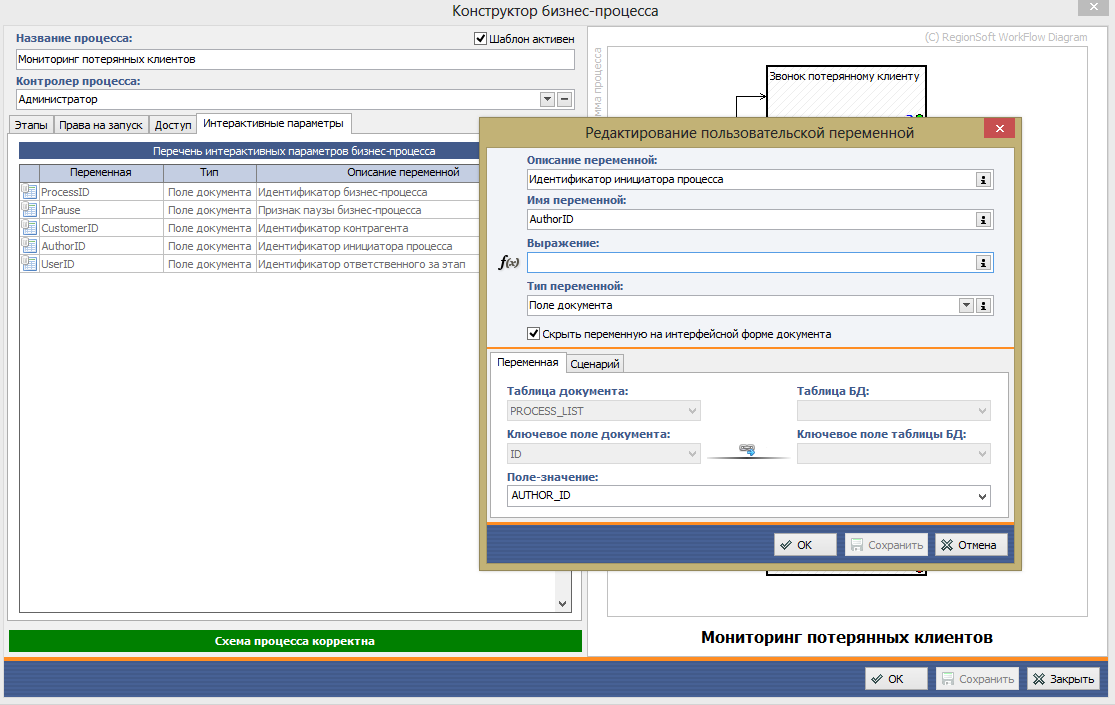
You can also create custom variables and use them in process modeling. Variable values can be initialized using software scripts written in the open programming language PascalScript.
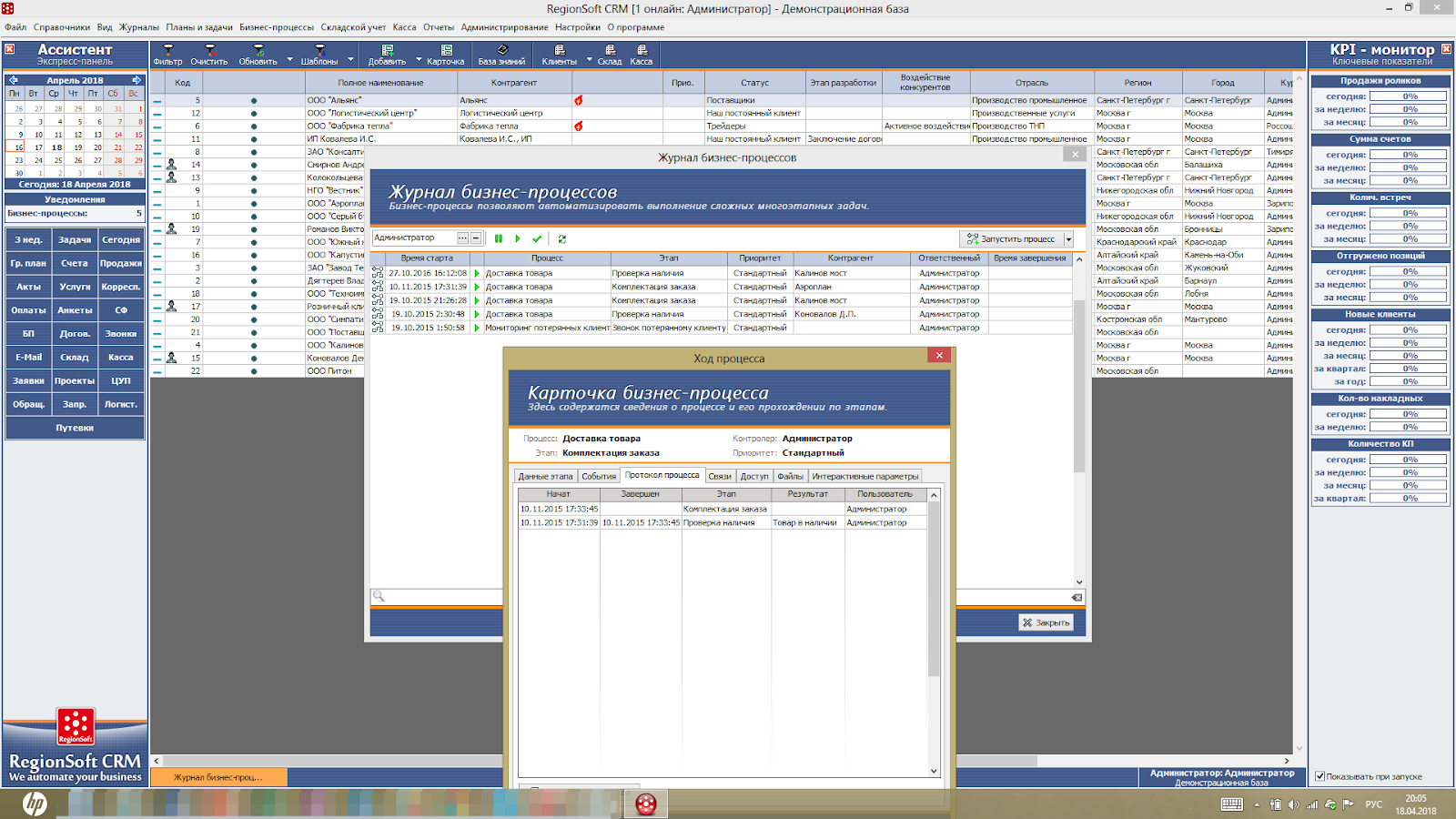
All actions inside process instances and state of processes are logged, in the logs you can see the status of the process, stage, open a card with details. The number of running process instances is also displayed in the "Assistant" panel (on the left side of the system interface. By the way, in this screenshot you can see the log opened on top of the RegionSoft CRM desktop.

The final model of the finished process: on the left is a list of stages, transition rules and parameters, on the right is a visual graphic representation of the process (process diagram, aka workflow).

Setting up each stage of the process includes specifying those responsible, automatically creating tasks, managing deadlines, the possibility of a pause inside the process, various ways of notifying users and clients, etc. Each stage is also given priority.

An example of what the action settings window looks like when the stage is overdue - it is possible to notify any interested parties, you can immediately evaluate the causes of the problem and an approximate shift of the deadlines.

You can also create custom variables and use them in process modeling. Variable values can be initialized using software scripts written in the open programming language PascalScript.

All actions inside process instances and state of processes are logged, in the logs you can see the status of the process, stage, open a card with details. The number of running process instances is also displayed in the "Assistant" panel (on the left side of the system interface. By the way, in this screenshot you can see the log opened on top of the RegionSoft CRM desktop.
Well, ok, the system is, what's next, how to design business processes?
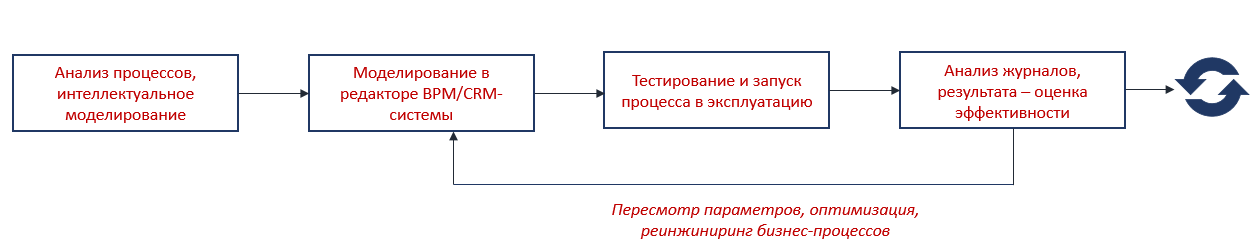
If we are talking about a small company with trivial processes, modeling is implemented quite simply even by managers who do not have programming skills. In the general case, business process modeling can be represented in the form of such a scheme:
A business process in itself is a route to accomplish one large task consisting of several stages. Based on this, we need to work on it.
- Analyze the existing processes, isolate the main thing, exclude unnecessary and try to sketch the diagram on paper. A small life hack: if you don’t know how to approach this procedure, record it yourself and ask employees to write down everything that they do during the day - this way it will be possible to identify routine tasks and proceed with their formal description.
- Fix the goals of the process - indicate why it is needed, what tasks it will solve and what part of the activity it will cover. Consider the criteria for successful completion of a particular business process.
- Make a process plan - steps leading to the result. Highlight the major milestones and detailed milestones within these milestones. Write down responsible, approximate deadlines and interim results for each stage.
- Make a detailed diagram on paper with all the parameters, discuss the final version with the responsible, make the final changes.
- Create a business process model in a CRM or BPM system, save.
- Run a test instance of the process, run it on the test data, make corrections.
- Run the process in real operating mode.
- After the business process is completed, analyze the result, progress, deadlines, process logs. Optimize the model if necessary.
- Run instances of business processes as needed.
- In case of changes, do not be afraid to reengineer all existing processes.
When working with business processes, consider a couple of important points:
- The business process should be repeating (cyclical) and final, that is, aimed at achieving a result. Failure is also a result. Modeling a business process for one-time use is almost always impractical (in such cases it is better to create a project).
- Each process should have a mandatory set of attributes: initial and final stages, human (responsible, calls) and automatic (add a task to the calendar, generate a report, send a notification or reminder) components, dates.
When to start automating business processes?
The answer to this question is concise: immediately, even if you just created a company. Let’s not pour water, but let’s take a look immediately at the example, what processes are even in the youngest company.
- Acceptance of the buyer's order and its processing;
- Ordering goods from suppliers; Work with contractors;
- Delivery of the order to the buyer;
- Processing of circulation, service desk, acceptance of goods for warranty repair or service;
- The work of telemarketing services and bringing the client to a deal in cold sales;
- Coordination of documents by different departments or employees within the company;
- Processes in information technology: input and maintenance of a PC, administration, incidents, etc.
All of these processes are cyclical, some of them will become more complicated and develop, so the sooner you start, the faster and easier it will be to further reengineering.
And of course, if you have a bunch of established processes and you don’t know what to pull for, all the more it is worth looking towards automation.
Business process management is never without effect. According to the AIIM study, companies that turn to BPM receive up to 41% ROI growth. 62% note improved communication between company employees, 33% - reduced bureaucracy and levels of coordination, 42% - greater organizational flexibility.
Implement and automate business processes - this means stop solving business problems as tasks and go to the level of management by goals, work for the result. This means more freedom of hands and heads from routine and fuss, less conflict and corporate wars. Business processes are not a chip for the elite and great, not the prerogative of Gazprom or Rosatom, it is a transparent, convenient and affordable work tool for everyone, which significantly improves business in the company. So, if you have CRM (or are planning to be implemented), do not ignore the opportunities - use them. Be sure: after a short period of time, you will say “The process has begun” and will be happy to launch another instance of it.
If you are an intelligent IT manager or want to become one and live in Nizhny Novgorod
If you are an intelligent manager in the IT field (implementation, system integration, development) or worked in an enterprise and want to become one, we are looking for guys for a full day in the office in Nizhny Novgorod - to work on complex and interesting CRM integration projects. We don’t have hammocks, board games on Fridays, burger parties and sunbeds - we have powerful PCs, thoughtful software and a lot of interesting work. We promise the growth of professionalism, pumped experience, adequate leadership. Send a resume to contact@regionsoft.ru or call, we will arrange an interview. We do not consider a remote woman and candidates without any experience. There will be no HRs at the interview, immediately hardcore.
Our site with absolutely desktop business software and our flagship RegionSoft CRM.
