Oracle Storage Cloud Services ─ Everything Enterprise Data Warehouse Need
Public cloud corporate data warehouses and related services have already been sufficiently verified by customers. They meet their needs for data storage, access and security. With Oracle, safe, flexible, and easy use of this data is available at any time and in any Internet-related IT environment.
Oracle develops and supplies data warehouses that can reduce storage costs, as well as provide minimum access time to data that is stored at any level ─ by optimizing their placement and a single access interface to them.
This article describes data storage services, their differences from other systems of this class, the structure of the solution architecture and a practical example of using Oracle Database Cloud Service.
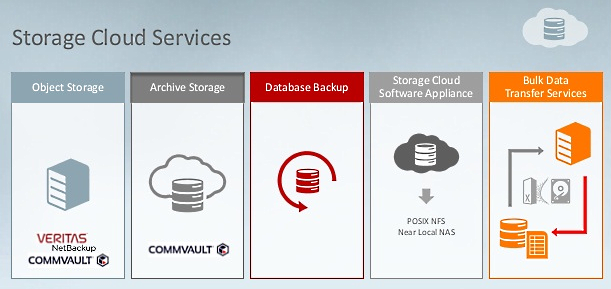
1. Oracle Storage Cloud Service ─ Object Storage
This solution provides storage of data sets of any type, including structured and unstructured data. A copy of the data can be stored in on-premise systems, moved to the cloud, or shared.
This approach simplifies the operation of the data center, scaling without the need for new hardware, reducing capital investment and operating costs due to less power consumption and requirements for cooling systems.
Common infrastructure allows for virtually infinite scalability. This eliminates the need for constant forecasting and long cycles of acquiring new capacities.
Simple management based on OpenStack and RESTful API simplifies integration, freeing up resources for other cloud projects. Pay-as-you-go payments and subscription models reduce costs compared to long-term contracts.
Client data encryption, combined with additional encryption in the Oracle data center, provides multi-level information protection. Client-side encryption is performed by the Oracle Storage Cloud Software Appliance and Java SDK. All roaming data is encrypted at the SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) level. The level of user and administrator access to data is carried out at the container level.
Integration with master backup and archive applications simplifies data deployment and recovery with minimal damage. It is possible to connect both through the public Internet and FastConnect, ─ for the most difficult workloads.
Georeplication technology is supported ─ automatic creation of a copy of data in a geographically remote data center. At the same time, data privacy rules are observed ─ stored data cannot be moved from the geographic areas specified by the administrator.
Development standards ─ RestAPI on Open Stack Swift, Java Applications (File Transfer Manager and Java API), Shell scripting (Upload CLI).
The solution has “eleven nines of reliability”, that is, 99.999999999% reliability is provided due to the support of several copies of each object on different devices. Periodic data integrity is verified by self-healing tools.
Oracle Storage Cloud Software Appliance ─ easy-to-use cloud storage with NFS compatible POSIX interface. It is a NAS gateway to the cloud.
2. Oracle Storage Cloud Service ─ Archive Storage
These are ─ the most cost-effective data warehouses in the industry. They are specifically designed for data that does not require frequent access, with enterprise-level security and flexible scalability.
A typical application is an archive in the cloud for large data sets and their long-term storage, as well as heterogeneous multimedia content, research results and digital copies of cultural heritage.
The main advantages of the solution include the maximum simplification of data center operations, low capital investments and operating costs due to lower power consumption and requirements for cooling systems. Pay-as-you-go and subscription models are also practiced, and the total archive storage fee is the lowest among peers ($ 12 / TB per year).
Client data is stored in encrypted form, traffic is encrypted with SSL, role-based access is carried out at the container level. Access, development standards, connectivity, reliability, geo-replication are the same as for Object Storage.
3. Oracle Database Backup Service
The data protection service is designed for the unique needs of Oracle Database clients, with direct integration with RMAN (Oracle Recovery Manager). Thus, you can take advantage of cloud-based data protection in IT processes.
Backups are encrypted directly in the data source, reliably transmitted and stored in the cloud. Data is always stored in the specified geographical regions. Built-in redundancy is used ─ mirroring is carried out in three ways, which ensures constant data availability. Backups are easily encrypted from RMAN. The data is constantly monitored, which prevents their degradation.
Backups are compressed before moving to the cloud. The capacity of the data warehouse is changed on demand by a simple click on the button. Data management includes role-based access control and automatic deletion of data according to specified criteria (after the preservation of time, etc.).
4. Oracle Storage Cloud Software Appliance
The solution provides role-based encryption, ensures data integrity by checking checksums, performs automatic conversion between files and objects, has performance at the local NAS level due to data caching and docker technology.
The solution has a familiar, well-understood interface. It provides application connectivity with NFS-based cloud storage, as well as compatibility with POSIX and Unix / Linux NFS clients. Implemented automatic data conversion, ─ the interface allows you to work with data as with files, while they are stored in the cloud as objects.
Information security tools are well developed. Before transmission, the data is encrypted. Possible encryption by the client, including granular (selective). A multi-level architecture with symmetric and asymmetric keys is used for maximum information security. The user can bring their own keys, or generate them immediately before encryption.
Data availability is ensured by regular backup of metadata to the cloud, and performance at the local NAS level is provided by buffer caching. The cache can be configured according to workloads. The Least Recently Used (LRU) algorithm caches up-to-date data and deletes unnecessary data.
For management, N-Way Management technology is used (N-Way ─ a telecommunication protocol for managing Ethernet network devices and user data). You can work from the Admin UI based on the browser, or the Command Line Interface (Command Line Interface). Scripts can be used for automation. REST APIs that provide multiple deployments from a single centralized location.
5. Oracle Public Cloud Data Transfer Services
Services provide fast transfer of the initial data set to the cloud and the formation of a data warehouse in the public Oracle cloud. This is the fastest way to get started with data in the cloud. The Storage Appliance Import service reliably transfers large data sets (historical archives, data lakes, large databases of inherited data). Up to 400 TB of data can be moved at a time.
At the same time, there is no need to pay for the construction of a faster network for one-time “wholesale” data transfer. Transmission is secure because traffic is encrypted using the AES-256 standard. A simple standard NFSv3 interface is used to load object or archive storage data. At the same time, a multi-row structure is formed. It is also possible to copy data inside the cloud to create a replica of the working base.
Oracle Storage Cloud Service and Traditional Solutions
Traditional storage solutions typically have certain problems with scalability, performance, and management. Oracle Storage Cloud Service helps overcome them.
1. In a system with a directly attached storage device (such as a regular hard drive in a desktop or laptop), the OS controls the storage of data, its search and organization through a file system.
Such a device provides low latency and fairly reliable long-term data storage. However, if you need a large capacity drive, it is distributed between individual disk devices, which makes scaling difficult and reduces performance.
2. In network-attached storage (NAS) storage devices, the hardware is physically separated from the servers on which the applications are running. Storage devices are available as network drives. Data storage, retrieval and sequencing is controlled by the Network File System (NFS). Applications running on different servers share a NAS for data storage. Management of storage resources in the local network is carried out centrally.
As with directly attached storage devices, NAS applications also rely on the main OS, ─ but also on the network file system. But such an architecture can only be implemented in a limited geographic area, and has limited scalability.
3. The block storage principle is used in applications such as OLTP databases with high Input / Output Operations per Second (IOPS). This allows you to effectively save and restore data bypassing the OS, directly interacting with virtual block devices.
Data fragments are stored in blocks, each with its own address, but without other metadata. Where the data is stored, applications decide. They restore data to the corresponding block addresses.
The block storage principle optimizes storage systems for IOPS and provides POSIX compatible file systems for Oracle Compute Cloud Service. However, this approach has limitations in terms of scalability and does not support granular metadata.
4. Object data storage provides the optimal combination of performance, scalability and manageability while storing large volumes of unstructured data. Multiple storage nodes (nodes) form a single common, horizontally scalable pool in which data is stored as objects (“data drops in the data pool”).
All object-stored data is associated with metadata and has a unique identifier. Thus, you can assign custom metadata to containers and objects, which greatly facilitates the search, analysis and management of data. Applications use object identifiers to directly access data through REST API calls.
Object storage is easy to use, does its job well and can scale virtually unlimited virtually.
Summing up the above, it should be noted that the Oracle Storage Cloud Service provides an inexpensive, reliable, secure, and scalable storage solution. This allows you to store unstructured data and access it anytime, anywhere.
This approach is ideal for backing up and archiving data, sharing files, and also for storing a large amount of unstructured data, such as logs, data received from sensors and images of virtual machines.
Architecture Overview
The architecture of the Oracle Storage Cloud Service is very affordable and redundant. It is well suited for external access, including user applications, Java SDKs, and REST clients.
When objects are stored in the Oracle Storage Cloud Service, data is replicated through multiple storage node nodes in the data center. This strategy ensures that stored object data can withstand hardware failure.
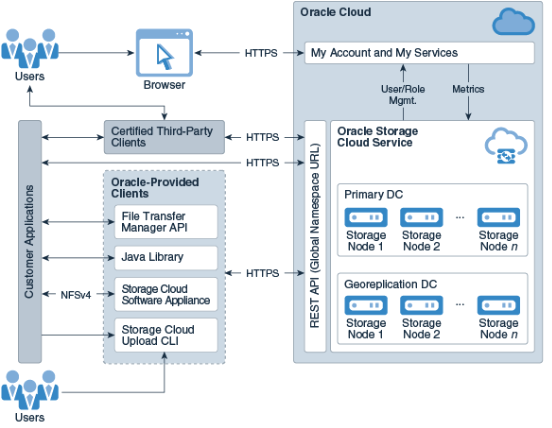
Typical Oracle Cloud Storage Service Architecture

Oracle develops and supplies data warehouses that can reduce storage costs, as well as provide minimum access time to data that is stored at any level ─ by optimizing their placement and a single access interface to them.
This article describes data storage services, their differences from other systems of this class, the structure of the solution architecture and a practical example of using Oracle Database Cloud Service.
1. Oracle Storage Cloud Service ─ Object Storage
This solution provides storage of data sets of any type, including structured and unstructured data. A copy of the data can be stored in on-premise systems, moved to the cloud, or shared.
This approach simplifies the operation of the data center, scaling without the need for new hardware, reducing capital investment and operating costs due to less power consumption and requirements for cooling systems.
Common infrastructure allows for virtually infinite scalability. This eliminates the need for constant forecasting and long cycles of acquiring new capacities.
Simple management based on OpenStack and RESTful API simplifies integration, freeing up resources for other cloud projects. Pay-as-you-go payments and subscription models reduce costs compared to long-term contracts.
Client data encryption, combined with additional encryption in the Oracle data center, provides multi-level information protection. Client-side encryption is performed by the Oracle Storage Cloud Software Appliance and Java SDK. All roaming data is encrypted at the SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) level. The level of user and administrator access to data is carried out at the container level.
Integration with master backup and archive applications simplifies data deployment and recovery with minimal damage. It is possible to connect both through the public Internet and FastConnect, ─ for the most difficult workloads.
Georeplication technology is supported ─ automatic creation of a copy of data in a geographically remote data center. At the same time, data privacy rules are observed ─ stored data cannot be moved from the geographic areas specified by the administrator.
Development standards ─ RestAPI on Open Stack Swift, Java Applications (File Transfer Manager and Java API), Shell scripting (Upload CLI).
The solution has “eleven nines of reliability”, that is, 99.999999999% reliability is provided due to the support of several copies of each object on different devices. Periodic data integrity is verified by self-healing tools.
Oracle Storage Cloud Software Appliance ─ easy-to-use cloud storage with NFS compatible POSIX interface. It is a NAS gateway to the cloud.
2. Oracle Storage Cloud Service ─ Archive Storage
These are ─ the most cost-effective data warehouses in the industry. They are specifically designed for data that does not require frequent access, with enterprise-level security and flexible scalability.
A typical application is an archive in the cloud for large data sets and their long-term storage, as well as heterogeneous multimedia content, research results and digital copies of cultural heritage.
The main advantages of the solution include the maximum simplification of data center operations, low capital investments and operating costs due to lower power consumption and requirements for cooling systems. Pay-as-you-go and subscription models are also practiced, and the total archive storage fee is the lowest among peers ($ 12 / TB per year).
Client data is stored in encrypted form, traffic is encrypted with SSL, role-based access is carried out at the container level. Access, development standards, connectivity, reliability, geo-replication are the same as for Object Storage.
3. Oracle Database Backup Service
The data protection service is designed for the unique needs of Oracle Database clients, with direct integration with RMAN (Oracle Recovery Manager). Thus, you can take advantage of cloud-based data protection in IT processes.
Backups are encrypted directly in the data source, reliably transmitted and stored in the cloud. Data is always stored in the specified geographical regions. Built-in redundancy is used ─ mirroring is carried out in three ways, which ensures constant data availability. Backups are easily encrypted from RMAN. The data is constantly monitored, which prevents their degradation.
Backups are compressed before moving to the cloud. The capacity of the data warehouse is changed on demand by a simple click on the button. Data management includes role-based access control and automatic deletion of data according to specified criteria (after the preservation of time, etc.).
4. Oracle Storage Cloud Software Appliance
The solution provides role-based encryption, ensures data integrity by checking checksums, performs automatic conversion between files and objects, has performance at the local NAS level due to data caching and docker technology.
The solution has a familiar, well-understood interface. It provides application connectivity with NFS-based cloud storage, as well as compatibility with POSIX and Unix / Linux NFS clients. Implemented automatic data conversion, ─ the interface allows you to work with data as with files, while they are stored in the cloud as objects.
Information security tools are well developed. Before transmission, the data is encrypted. Possible encryption by the client, including granular (selective). A multi-level architecture with symmetric and asymmetric keys is used for maximum information security. The user can bring their own keys, or generate them immediately before encryption.
Data availability is ensured by regular backup of metadata to the cloud, and performance at the local NAS level is provided by buffer caching. The cache can be configured according to workloads. The Least Recently Used (LRU) algorithm caches up-to-date data and deletes unnecessary data.
For management, N-Way Management technology is used (N-Way ─ a telecommunication protocol for managing Ethernet network devices and user data). You can work from the Admin UI based on the browser, or the Command Line Interface (Command Line Interface). Scripts can be used for automation. REST APIs that provide multiple deployments from a single centralized location.
5. Oracle Public Cloud Data Transfer Services
Services provide fast transfer of the initial data set to the cloud and the formation of a data warehouse in the public Oracle cloud. This is the fastest way to get started with data in the cloud. The Storage Appliance Import service reliably transfers large data sets (historical archives, data lakes, large databases of inherited data). Up to 400 TB of data can be moved at a time.
At the same time, there is no need to pay for the construction of a faster network for one-time “wholesale” data transfer. Transmission is secure because traffic is encrypted using the AES-256 standard. A simple standard NFSv3 interface is used to load object or archive storage data. At the same time, a multi-row structure is formed. It is also possible to copy data inside the cloud to create a replica of the working base.
Oracle Storage Cloud Service and Traditional Solutions
Traditional storage solutions typically have certain problems with scalability, performance, and management. Oracle Storage Cloud Service helps overcome them.
1. In a system with a directly attached storage device (such as a regular hard drive in a desktop or laptop), the OS controls the storage of data, its search and organization through a file system.
Such a device provides low latency and fairly reliable long-term data storage. However, if you need a large capacity drive, it is distributed between individual disk devices, which makes scaling difficult and reduces performance.
2. In network-attached storage (NAS) storage devices, the hardware is physically separated from the servers on which the applications are running. Storage devices are available as network drives. Data storage, retrieval and sequencing is controlled by the Network File System (NFS). Applications running on different servers share a NAS for data storage. Management of storage resources in the local network is carried out centrally.
As with directly attached storage devices, NAS applications also rely on the main OS, ─ but also on the network file system. But such an architecture can only be implemented in a limited geographic area, and has limited scalability.
3. The block storage principle is used in applications such as OLTP databases with high Input / Output Operations per Second (IOPS). This allows you to effectively save and restore data bypassing the OS, directly interacting with virtual block devices.
Data fragments are stored in blocks, each with its own address, but without other metadata. Where the data is stored, applications decide. They restore data to the corresponding block addresses.
The block storage principle optimizes storage systems for IOPS and provides POSIX compatible file systems for Oracle Compute Cloud Service. However, this approach has limitations in terms of scalability and does not support granular metadata.
4. Object data storage provides the optimal combination of performance, scalability and manageability while storing large volumes of unstructured data. Multiple storage nodes (nodes) form a single common, horizontally scalable pool in which data is stored as objects (“data drops in the data pool”).
All object-stored data is associated with metadata and has a unique identifier. Thus, you can assign custom metadata to containers and objects, which greatly facilitates the search, analysis and management of data. Applications use object identifiers to directly access data through REST API calls.
Object storage is easy to use, does its job well and can scale virtually unlimited virtually.
Summing up the above, it should be noted that the Oracle Storage Cloud Service provides an inexpensive, reliable, secure, and scalable storage solution. This allows you to store unstructured data and access it anytime, anywhere.
This approach is ideal for backing up and archiving data, sharing files, and also for storing a large amount of unstructured data, such as logs, data received from sensors and images of virtual machines.
Architecture Overview
The architecture of the Oracle Storage Cloud Service is very affordable and redundant. It is well suited for external access, including user applications, Java SDKs, and REST clients.
When objects are stored in the Oracle Storage Cloud Service, data is replicated through multiple storage node nodes in the data center. This strategy ensures that stored object data can withstand hardware failure.

Typical Oracle Cloud Storage Service Architecture
