How to beat the Petya virus
Following the sensational campaign of the WannaCry ransomware virus, which was recorded in May this year, on June 27, more than 80 companies in Russia and Ukraine fell victim to a new attack using the Petya ransomware. And this campaign turned out to be completely unrelated to WannaCry. Positive Technologies experts presented a detailed analysis of the new malware and made recommendations to combat it.
Ukrainian, Russian and international companies, in particular, Novaya Poshta, Zaporizhiaoblenergo, Dneproenergo, Oschadbank, media holding TRK Lux, Mondelēz International, TESA, Nivea, Mars, LifeCell, UkrTeleCom, Kyivstar and many other organizations, have already become victims of ransomware. In Kiev, some ATMs and cash registers in stores turned out to be infected. It was in Ukraine that the first attacks were recorded.
An analysis of the ransomware sample by our experts showed that Petya’s principle of operation is based on encrypting the master boot record (MBR) of the boot sector of the disk and replacing it with its own. This record is the first sector on the hard drive, it contains a partition table and a bootloader that reads from this table information about which partition of the hard drive will boot the system. The original MBR is stored in the 0x22nd sector of the disk and is encrypted using the XOR byte operation from 0x07.
After launching the malicious file, a task is created to restart the computer, delayed for 1-2 hours, at which time you can manage to run the bootrec / fixMbr commandto restore the MBR and restore the OS. Thus, it is possible to start the system even after it has been compromised, but the files cannot be decrypted. Each disk generates its own AES key, which exists in memory until encryption is completed. It is encrypted on the RSA public key and is deleted. Restoring content after completion requires knowledge of the private key, so without knowledge of the key, data cannot be restored. Presumably, the malware encrypts files to a maximum of 15 directories. That is, files embedded at great depths are safe (at least for this version of the encryptor).
If the disks were successfully encrypted after a reboot, a window appears with a message about the requirement to pay a ransom of $ 300 (as of June 27, 2017 - approximately 0.123 bitcoins) to obtain a file unlock key. To transfer money, the Bitcoin wallet 1Mz7153HMuxXTuR2R1t78mGSdzaAtNbBWX is indicated . A few hours after the start of the attack on the wallet, transactions are already multiples of the requested amount - some victims chose to pay the ransom, without waiting for the researchers to study the malware and try to find a file recovery tool.
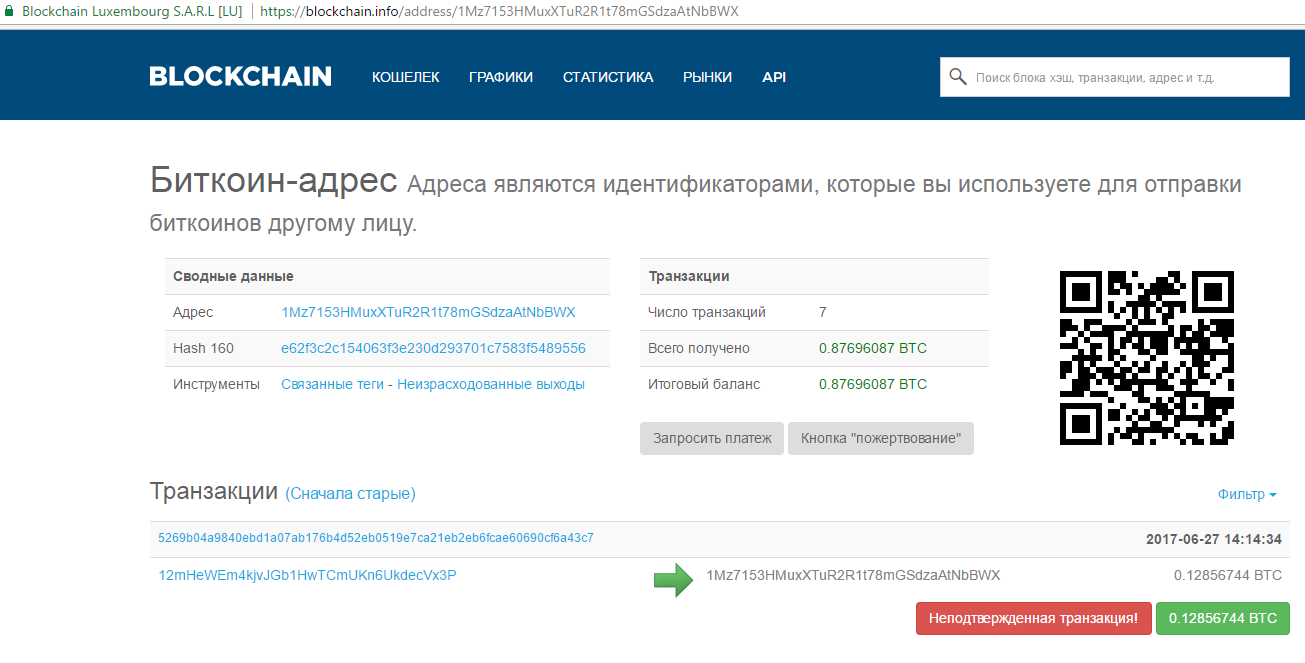
Currently, the number of transactions has increased to 45.
Petya uses 135, 139, 445 TCP ports for distribution (using SMB and WMI services). Propagation within the network to other nodes occurs by several methods: using Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) and PsExec , as well as using an exploit that uses the MS17-010 vulnerability ( EternalBlue) WMI is a technology for centralized management and monitoring of various parts of the computer infrastructure running the Windows platform. PsExec is widely used to administer Windows and allows processes to be run on remote systems. However, to use these utilities, you must have local administrator privileges on the victim’s computer, which means that the encryptor can continue to distribute only from devices whose user has the maximum OS privileges. The EternalBlue exploit allows you to obtain maximum privileges on a vulnerable system. The encryptor also uses the publicly available Mimikatz utility to obtain open credentials for all Windows users, including local administrators and domain users.Such a set of tools allows Petya to remain operational even in those infrastructures where the WannaCry lesson has been taken into account and the corresponding security updates have been installed, which is why the encryptor is so efficient .
As part of testing for penetration of modern corporate infrastructures, Positive Technologies experts regularly demonstrate the possibility of using the EternalBlue exploit (in 44% of works in 2017), as well as the successful use of the Mimikatz utility to develop an attack vector until full control over the domain (in each project).
Thus, Petya has functionality that allows it to spread to other computers, and this process is avalanche-like. This allows the ransomware to compromise, including the domain controller, and develop an attack before gaining control of all the domain nodes, which is equivalent to a complete compromise of the infrastructure.
We reported on the existing threat of compromise more than a month ago in alerts about the WannaCry attack and gave recommendations on how to identify vulnerable systems, how to protect them and what to do if the attack has already occurred. We will give additional recommendations in this article. In addition, our company has developed a free utility WannaCry_Petya_FastDetectfor automated detection of vulnerabilities in the infrastructure. MaxPatrol detects this vulnerability in both Audit and Pentest modes. Detailed instructions are indicated in our recommendations . In addition, MaxPatrol SIEM has established correlation rules to detect Petya attacks.
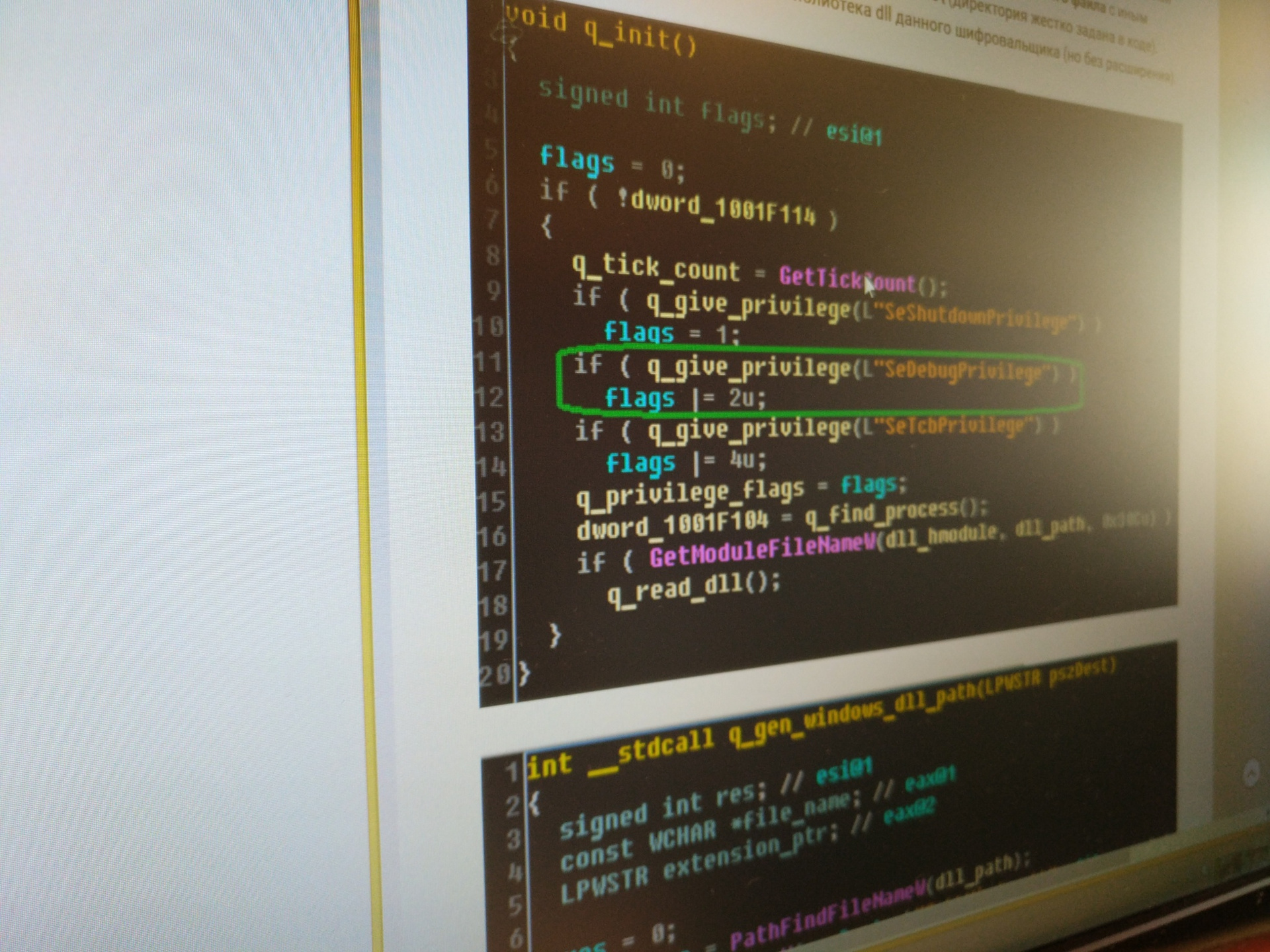
Positive Technologies experts revealed a “kill-switch” - the ability to locally disable the encryptor. If the process has administrative privileges in the OS, then before changing the MBR, the encryptor checks for the presence of the perfc file (or another empty file with a different name) without an extension in the C: \ Windows directory\ (the directory is hardcoded in the code). This file bears the same name as the dll library of this encryptor (but without the extension).
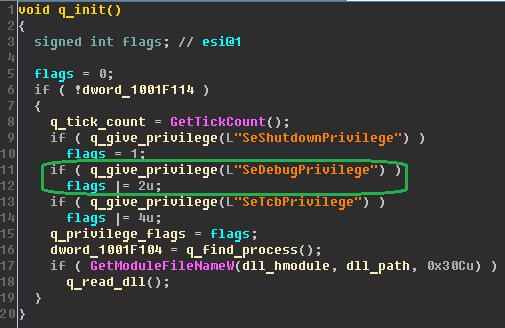
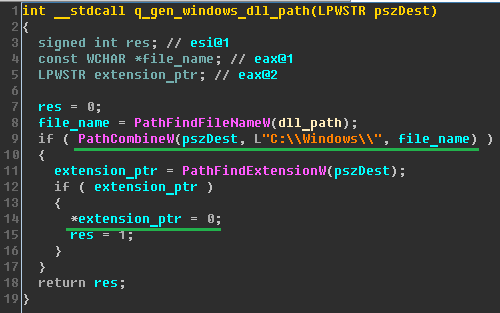
The presence of such a file in the specified directory may be one of the indicators of compromise. If the file is present in this directory, the malware execution process is completed, thus creating a file with the correct name can prevent MBR spoofing and further encryption.

If the encryptor does not detect such a file during verification, the file is created and the malware execution process starts. Presumably, this is to prevent the MBR spoofing process from restarting.
On the other hand, if the process does not initially have administrative privileges, then the encryptor will not be able to check for an empty file in the C: \ Windows \ directory, and the file encryption process will still start, but without replacing the MBR and restarting the computer.
In order not to become a victim of such an attack, it is necessary first of all to update the software used to the latest versions, in particular, install all the latest MS Windows updates. In addition, you must minimize user privileges on workstations.
If the infection has already occurred, we do not recommend paying money to attackers. Intruders mailing address wowsmith123456@posteo.netwas blocked, and even in the case of payment of the ransom, the key for decrypting the files will probably not be received. To prevent the encryptor from spreading over the network, it is recommended that you turn off other computers that were not infected, disconnect infected nodes from the network, and take images of compromised systems. If researchers find a way to decrypt files, locked data can be restored in the future. In addition, this image can be used to conduct cryptographic analysis, which will help researchers in their work.
In the long run, it is recommended to develop a system of regular trainings for employees in order to increase their awareness of information security issues, based on the demonstration of practical examples of potential attacks on the company's infrastructure using social engineering methods. It is necessary to regularly check the effectiveness of such trainings. It is also necessary to install anti-virus software on all computers with a self-defense function that provides for entering a special password to disable or change settings. In addition, it is necessary to ensure regular software and OS updates on all nodes of the corporate infrastructure, as well as an effective process for managing vulnerabilities and updates. Regularly conducting IS audits and penetration testing will allow timely identification of existing security weaknesses and systems vulnerabilities. Regular monitoring of the perimeter of the corporate network will allow you to control the interfaces of network services available from the Internet and make timely adjustments to the configuration of firewalls. For the timely detection and suppression of an already occurred attack, it is necessary to monitor the internal network infrastructure, for which it is recommended to use a class SIEM system.
The following indicators can be used to identify a Petya attack in the infrastructure:
IDS / IPS rules triggering:
Signatures:

An analysis of the ransomware sample by our experts showed that Petya’s principle of operation is based on encrypting the master boot record (MBR) of the boot sector of the disk and replacing it with its own. This record is the first sector on the hard drive, it contains a partition table and a bootloader that reads from this table information about which partition of the hard drive will boot the system. The original MBR is stored in the 0x22nd sector of the disk and is encrypted using the XOR byte operation from 0x07.
After launching the malicious file, a task is created to restart the computer, delayed for 1-2 hours, at which time you can manage to run the bootrec / fixMbr commandto restore the MBR and restore the OS. Thus, it is possible to start the system even after it has been compromised, but the files cannot be decrypted. Each disk generates its own AES key, which exists in memory until encryption is completed. It is encrypted on the RSA public key and is deleted. Restoring content after completion requires knowledge of the private key, so without knowledge of the key, data cannot be restored. Presumably, the malware encrypts files to a maximum of 15 directories. That is, files embedded at great depths are safe (at least for this version of the encryptor).
If the disks were successfully encrypted after a reboot, a window appears with a message about the requirement to pay a ransom of $ 300 (as of June 27, 2017 - approximately 0.123 bitcoins) to obtain a file unlock key. To transfer money, the Bitcoin wallet 1Mz7153HMuxXTuR2R1t78mGSdzaAtNbBWX is indicated . A few hours after the start of the attack on the wallet, transactions are already multiples of the requested amount - some victims chose to pay the ransom, without waiting for the researchers to study the malware and try to find a file recovery tool.

Currently, the number of transactions has increased to 45.
Petya uses 135, 139, 445 TCP ports for distribution (using SMB and WMI services). Propagation within the network to other nodes occurs by several methods: using Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) and PsExec , as well as using an exploit that uses the MS17-010 vulnerability ( EternalBlue) WMI is a technology for centralized management and monitoring of various parts of the computer infrastructure running the Windows platform. PsExec is widely used to administer Windows and allows processes to be run on remote systems. However, to use these utilities, you must have local administrator privileges on the victim’s computer, which means that the encryptor can continue to distribute only from devices whose user has the maximum OS privileges. The EternalBlue exploit allows you to obtain maximum privileges on a vulnerable system. The encryptor also uses the publicly available Mimikatz utility to obtain open credentials for all Windows users, including local administrators and domain users.Such a set of tools allows Petya to remain operational even in those infrastructures where the WannaCry lesson has been taken into account and the corresponding security updates have been installed, which is why the encryptor is so efficient .
As part of testing for penetration of modern corporate infrastructures, Positive Technologies experts regularly demonstrate the possibility of using the EternalBlue exploit (in 44% of works in 2017), as well as the successful use of the Mimikatz utility to develop an attack vector until full control over the domain (in each project).
Thus, Petya has functionality that allows it to spread to other computers, and this process is avalanche-like. This allows the ransomware to compromise, including the domain controller, and develop an attack before gaining control of all the domain nodes, which is equivalent to a complete compromise of the infrastructure.
We reported on the existing threat of compromise more than a month ago in alerts about the WannaCry attack and gave recommendations on how to identify vulnerable systems, how to protect them and what to do if the attack has already occurred. We will give additional recommendations in this article. In addition, our company has developed a free utility WannaCry_Petya_FastDetectfor automated detection of vulnerabilities in the infrastructure. MaxPatrol detects this vulnerability in both Audit and Pentest modes. Detailed instructions are indicated in our recommendations . In addition, MaxPatrol SIEM has established correlation rules to detect Petya attacks.
Positive Technologies experts revealed a “kill-switch” - the ability to locally disable the encryptor. If the process has administrative privileges in the OS, then before changing the MBR, the encryptor checks for the presence of the perfc file (or another empty file with a different name) without an extension in the C: \ Windows directory\ (the directory is hardcoded in the code). This file bears the same name as the dll library of this encryptor (but without the extension).


The presence of such a file in the specified directory may be one of the indicators of compromise. If the file is present in this directory, the malware execution process is completed, thus creating a file with the correct name can prevent MBR spoofing and further encryption.

If the encryptor does not detect such a file during verification, the file is created and the malware execution process starts. Presumably, this is to prevent the MBR spoofing process from restarting.
On the other hand, if the process does not initially have administrative privileges, then the encryptor will not be able to check for an empty file in the C: \ Windows \ directory, and the file encryption process will still start, but without replacing the MBR and restarting the computer.
In order not to become a victim of such an attack, it is necessary first of all to update the software used to the latest versions, in particular, install all the latest MS Windows updates. In addition, you must minimize user privileges on workstations.
If the infection has already occurred, we do not recommend paying money to attackers. Intruders mailing address wowsmith123456@posteo.netwas blocked, and even in the case of payment of the ransom, the key for decrypting the files will probably not be received. To prevent the encryptor from spreading over the network, it is recommended that you turn off other computers that were not infected, disconnect infected nodes from the network, and take images of compromised systems. If researchers find a way to decrypt files, locked data can be restored in the future. In addition, this image can be used to conduct cryptographic analysis, which will help researchers in their work.
In the long run, it is recommended to develop a system of regular trainings for employees in order to increase their awareness of information security issues, based on the demonstration of practical examples of potential attacks on the company's infrastructure using social engineering methods. It is necessary to regularly check the effectiveness of such trainings. It is also necessary to install anti-virus software on all computers with a self-defense function that provides for entering a special password to disable or change settings. In addition, it is necessary to ensure regular software and OS updates on all nodes of the corporate infrastructure, as well as an effective process for managing vulnerabilities and updates. Regularly conducting IS audits and penetration testing will allow timely identification of existing security weaknesses and systems vulnerabilities. Regular monitoring of the perimeter of the corporate network will allow you to control the interfaces of network services available from the Internet and make timely adjustments to the configuration of firewalls. For the timely detection and suppression of an already occurred attack, it is necessary to monitor the internal network infrastructure, for which it is recommended to use a class SIEM system.
The following indicators can be used to identify a Petya attack in the infrastructure:
- C: \ Windows \ perfc
- Task in Windows Scheduler with an empty name and action (reboot)
- "% WINDIR% \ system32 \ shutdown.exe / r / f"
IDS / IPS rules triggering:
- msg: "[PT Open] Unimplemented Trans2 Sub-Command code. Possible ETERNALBLUE (WannaCry, Petya) tool"; sid: 10001254; rev: 2;
- msg: "[PT Open] ETERNALBLUE (WannaCry, Petya) SMB MS Windows RCE"; sid: 10001255; rev: 3;
- msg: "[PT Open] Trans2 Sub-Command 0x0E. Likely ETERNALBLUE (WannaCry, Petya) tool"; sid: 10001256; rev: 2;
- msg: "[PT Open] Petya ransomware perfc.dat component"; sid: 10001443; rev: 1
- msg: "[PT Open] SMB2 Create PSEXESVC.EXE"; sid: 10001444; rev: 1
Signatures:
