SD-WAN “on the fingers”: pros, cons, pitfalls
A few days ago I was once again asked: “SD-WAN - is this pure marketing or is it really effective technology?”. Distrust is understandable: the market is eyeing with suspicion everything new - and technology has only been a couple of years old.
I’ll try to talk about what SD-WAN is, to whom and why such solutions are needed, as well as what are their pros and cons.
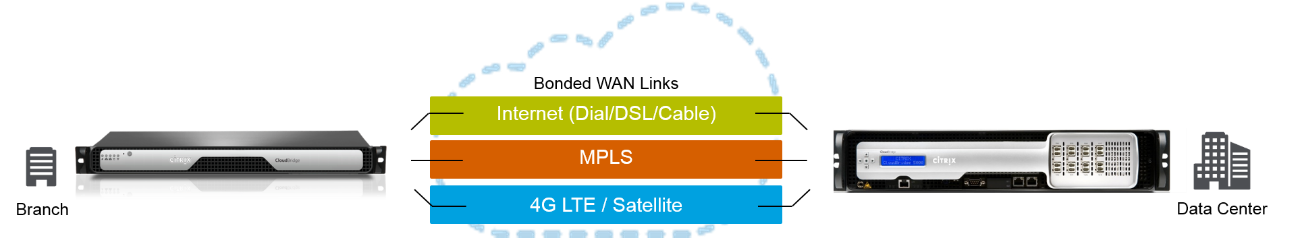
When we talk about SD-WAN - software-defined distributed networks - we mean solutions for network management and data transfer between the center and branches.
As for the main characteristics and tasks that are usually set for the SD-WAN, it is, as a rule, the intelligent traffic management, which is transmitted from the center to the branch and back. Also, software-defined networks are characterized by a single point of management of the entire infrastructure and monitoring.
Usually it looks like this: there is a certain central platform, there are branches. Everywhere must be installed devices that will work with the technology of software-defined networks. The entire configuration of this distributed wealth comes from a single point - the controller. With some configuration changes, the controller, at the request of the administrator, distributes updates to other devices located in branches.
In the case of a large number of branches, any typical configuration change procedures usually take a fairly large amount of time. In the case of SD-WAN, it will be different: just configure one device, and transfer all this over the network further. Hence, we have reduced operating costs for infrastructure management.
In addition to configuration management tasks, the controller also assumes the role of a monitoring point. He monitors the distributed network. The administrator does not need to go to each device in case of any changes in the network.
If a monitoring reveals a problem: a drop in the communication channel, deterioration of the channel’s characteristics, an increase in the signal delay, etc., this is immediately monitored and displayed in the corresponding panel. You can see both the current and historical channel load, track bursts of load of a particular branch. Everything is pretty clear.

It is rare when in large organizations - banks, retail, etc. - there is only one communication channel. Usually there are two or more. This serves as a guarantee of branch resiliency.
I think any retail employee can be raised at night and ask: how much does an hour of store downtime cost. And he will clearly answer - these are mandatory numbers that are easily counted. Or a bank branch. What will happen if it goes unconnected? Probably, many remember the recent failure on the network of one of the largest Russian operators. So, one of the main problems for people was the inability to confirm payments and transfers. There was no connection for only half a day, and the victims are still complaining.
The presence of more than one channel requires appropriate administration - there are certain difficulties associated with this: how you can reach this branch, how we will allow traffic to it.
For example, we need to intelligently distribute application traffic - let’s say, voice traffic is only allowed on the channel with the best characteristics, through an operator’s VPN. Less demanding traffic - mail - is allowed through a cheaper channel with a smaller SLA. It will take quite a long time to set up here, and if you multiply it by the number of branches, then this becomes a serious task.
SD-WAN solves this problem and allows you to dynamically, in real time check all available communication channels in the branch, and, based on the requirements of a particular application - for example, voice communication - direct traffic in the best way. This is one of the main concepts of such products, which is implemented not only by Citrix. But what distinguishes our solution is the packet data transfer.
The traffic of any application is presented to us as a certain set of packets that are transmitted to the channel, depending on the conditions that exist here and now. If there is voice traffic, the carrier channel is available and everything is fine with it, then the packet will go there (where we configured it). If something goes wrong with the operator’s network, the packet will go through a different channel within the same conversation. The user will not notice at all that something happened - only the administrator will know about it when he reads the logs. The application and the user will not suffer.
Any organization with a large number of branches. When the branch infrastructure becomes more complex and there are problems with the stability of the communication channels, the solution may be SD-WAN
The main advantage, in my opinion, is the ability to combine several communication channels into one logical one. And, accordingly, the intelligent redistribution of traffic depending on the type of application between these channels.
For the company, which is going to update the fleet of its branch network equipment, I do not see any cons. SD-WAN is the most advanced solution for managing branch operations and traffic distribution. There are no contraindications, as such. But if you have already managed to purchase classic equipment - then alas. Abrupt changes will entail certain difficulties. Which, however, depends only on the organization’s budget.
I’ll try to talk about what SD-WAN is, to whom and why such solutions are needed, as well as what are their pros and cons.

What is it and why
When we talk about SD-WAN - software-defined distributed networks - we mean solutions for network management and data transfer between the center and branches.
As for the main characteristics and tasks that are usually set for the SD-WAN, it is, as a rule, the intelligent traffic management, which is transmitted from the center to the branch and back. Also, software-defined networks are characterized by a single point of management of the entire infrastructure and monitoring.
Usually it looks like this: there is a certain central platform, there are branches. Everywhere must be installed devices that will work with the technology of software-defined networks. The entire configuration of this distributed wealth comes from a single point - the controller. With some configuration changes, the controller, at the request of the administrator, distributes updates to other devices located in branches.
In the case of a large number of branches, any typical configuration change procedures usually take a fairly large amount of time. In the case of SD-WAN, it will be different: just configure one device, and transfer all this over the network further. Hence, we have reduced operating costs for infrastructure management.
In addition to configuration management tasks, the controller also assumes the role of a monitoring point. He monitors the distributed network. The administrator does not need to go to each device in case of any changes in the network.
If a monitoring reveals a problem: a drop in the communication channel, deterioration of the channel’s characteristics, an increase in the signal delay, etc., this is immediately monitored and displayed in the corresponding panel. You can see both the current and historical channel load, track bursts of load of a particular branch. Everything is pretty clear.

Why else is it needed
It is rare when in large organizations - banks, retail, etc. - there is only one communication channel. Usually there are two or more. This serves as a guarantee of branch resiliency.
I think any retail employee can be raised at night and ask: how much does an hour of store downtime cost. And he will clearly answer - these are mandatory numbers that are easily counted. Or a bank branch. What will happen if it goes unconnected? Probably, many remember the recent failure on the network of one of the largest Russian operators. So, one of the main problems for people was the inability to confirm payments and transfers. There was no connection for only half a day, and the victims are still complaining.
The presence of more than one channel requires appropriate administration - there are certain difficulties associated with this: how you can reach this branch, how we will allow traffic to it.
For example, we need to intelligently distribute application traffic - let’s say, voice traffic is only allowed on the channel with the best characteristics, through an operator’s VPN. Less demanding traffic - mail - is allowed through a cheaper channel with a smaller SLA. It will take quite a long time to set up here, and if you multiply it by the number of branches, then this becomes a serious task.
SD-WAN solves this problem and allows you to dynamically, in real time check all available communication channels in the branch, and, based on the requirements of a particular application - for example, voice communication - direct traffic in the best way. This is one of the main concepts of such products, which is implemented not only by Citrix. But what distinguishes our solution is the packet data transfer.
The traffic of any application is presented to us as a certain set of packets that are transmitted to the channel, depending on the conditions that exist here and now. If there is voice traffic, the carrier channel is available and everything is fine with it, then the packet will go there (where we configured it). If something goes wrong with the operator’s network, the packet will go through a different channel within the same conversation. The user will not notice at all that something happened - only the administrator will know about it when he reads the logs. The application and the user will not suffer.
Who needs it
Any organization with a large number of branches. When the branch infrastructure becomes more complex and there are problems with the stability of the communication channels, the solution may be SD-WAN
What are the advantages of technology
The main advantage, in my opinion, is the ability to combine several communication channels into one logical one. And, accordingly, the intelligent redistribution of traffic depending on the type of application between these channels.
Cons and pitfalls
For the company, which is going to update the fleet of its branch network equipment, I do not see any cons. SD-WAN is the most advanced solution for managing branch operations and traffic distribution. There are no contraindications, as such. But if you have already managed to purchase classic equipment - then alas. Abrupt changes will entail certain difficulties. Which, however, depends only on the organization’s budget.
