The story of Oracle - the first commercially successful relational database engine
Until the mid-70s, information in databases was distributed according to the old hierarchical, or "tree-like" principle, which is still used in desktop operating systems.
The first prototypes of relational DBMSs existed already in the 70s of the XX century. However, few believed in the possibility of achieving effective implementation of such systems. However, by the end of the 1980s, relational systems had dominated the global DBMS market.
In this regard, many companies began to position their DBMS as “relational” for advertising purposes. But far from always they had enough reason for this. Therefore, the author of the relational data model, Edgar Codd, in 1985 published his famous “12 Codd Rules,” which every RDBMS must satisfy.
One of the first prototypes of relational databases was System R. This is an IBM project that appeared in 1976. He inspired the future founders of Oracle to create his own relational database management system, but he never received commercial success.
Chief among the creators of Oracle was Larry Ellison, who, along with Bob Miner and Ed Oates before Oracle, worked on a project for the CIA. A number of sources say that he was given the code name "Oracle". In 1977, a young programmer Larry Ellison dropped out of Yale to start his own business. At the disposal of Larry Ellison then it was only $ 1200. He persuaded two of the above friends to invest, but the starting capital from this grew by only $ 500.

On June 16, 1977, Software Development Laboratories was founded by Ed Oates, Bob Miner, and Larry Ellison in California (USA), soon renamed Relational Software Inc. Young programmers began to develop a database management system (DBMS), built on the principles of relational algebra.
Oracle 2
The first commercial version of the Oracle DBMS was called Oracle 2. This move was to make it clear to customers that the system is reliable and even passed the test of time.
In the late 70s, the main competitive advantage of Oracle DBMS was the high speed of processing huge amounts of information, which was noted by all experts. Unlike System R, which needed a powerful supercomputer - mainframe, Oracle 2 coped with the processing of information on more "miniature" machines. These and other advantages led to the fact that in the early 80s, the DBMS began to spread rapidly.
Ellison and colleagues had difficulty implementing compatibility with the IBM System R DBMS. IBM's reluctance to open source was a key issue. As a result of compatibility between the two systems, it was not possible to achieve.

Larry Ellison, Founder, Oracle
Oracle has historically been the first and one of the most advanced client / server implementations. Portability and scalability have always been a high priority for Oracle developers. This played a key role in achieving the success of the company in the DBMS market.
Oracle 2 ran the Digital Equipment PDP-11 mini-computer in the RSX-11 operating environment. Most of Oracle was written in PDP-11 assembler, and the individual components were written in the new C language for that time. Already in those days the system was portable and worked in other PDP-11 operating environments: IAS, RSTS and UNIX. Then it was decided to transfer Oracle to the new VMS. Due to this, Oracle DBMS has occupied a vast niche of corporate information systems in the rapidly growing VAX market.
Another important feature of the system is the full implementation of the capabilities of the new SQL query language - subqueries, join operation, and so on. Thanks to this, the productivity of SQL programmers has grown many times.
Standard SQL (IBM) has been extended with the CONNECT BY operation, which allows you to process tree structures, which becomes unique for SQL systems.Of course, it took a long time to work on the DBMS. In Oracle 2, for example, transactions were not supported: if a failure occurred during the database update process, it was almost impossible to restore the previous state of the database. Therefore, users were often forced to backup the database in order to avoid information loss.
On October 29, 1982, the company was renamed Oracle Systems.
Oracle 3 and 4
Oracle 3 entered the market in 1983. It was completely rewritten in C. This helped a lot to solve the problem of portability of Oracle to a wide range of platforms - there were at least 20 then. In addition, atomic transaction execution was implemented: the operation was either completed, either it didn’t execute at all, respectively, the transaction either completed successfully on all changes to the database, or rolled back all the changes it made.

With the release of Oracle 4, the system was ported to large computers running VM and MVS, as well as to a personal computer with 640 kilobytes of RAM.
A database access control model was also implemented, which ensured that the query result does not contradict the state of the database at the beginning of the query. Thanks to this, the well-known contradiction between the processes of reading and writing was eliminated.
Oracle 5
In 1985, Oracle launched version 5.0, which introduced the client / server architecture for the first time. In addition, the company released SQL * Net, a network product that provides a transparent connection between a client and a database or between two databases.
In version 5.1, distributed queries were first implemented - this made it possible to access data physically located in different nodes. Several interacting servers could create the illusion of a single logical database for the user of many physically spaced databases.
On March 12, 1986, the initial public offering of Oracle Corporation shares took place. High growth rates allowed Oracle to go public IPO with a profit of $ 55 million in 1986, and in just three years, ten times the profit to $ 584 million.
Oracle 6
The developers of version 6 sought to create a tool for building large-scale information systems focused on real-time transaction processing.
Sequence generators and write-level locking were introduced. At the same time, Oracle became the first multi-user network database server for OS / 2, Xenix, Banyan Vines, and Macintosh.
In version 6, fundamentally new features were incorporated, fully implemented later:
- SQL queries could be used in conjunction with the constructs of the PL / SQL procedural language and sent for execution to the server as anonymous procedures;
- PL / SQL has been used in SQL * Forms as an application programming tool;
- declarative definitions of referential integrity constraints were introduced into the description of the database schema at the syntactic level (in accordance with ANSI / ISO-standard).
The crisis
In 1990, the company was faced with serious problems, reporting significant losses. Allison had to lay off more than 400 employees to reduce costs. He also dismissed almost all of the top management, among which were people close to Larry, who for 10 years increased the fame and fortune of Oracle along with him. Larry left in the company of Bob Miner, whom he always considered a gifted programmer and just a good, kind person.
Such tough methods Larry explained as follows:
“We were the fastest growing company in the history of the computer industry, but we suddenly reached a dead end and started banging our heads against the wall,” he said. - We have reached billions in revenue, but we have faced practically insoluble management problems. The fact is that the people who managed the billionth company remained the same as at the time when our company was worth $ 15 million. I felt an incredible sense of gratitude to everyone who worked with me, to everyone with whom we created Oracle. But I had no choice. I had to fire them, realizing that if this is not done, then soon there will simply be no Oracle. First of all, I felt responsibility to the whole company, to all staff, all shareholders and customers.In addition, due to errors in registering sales and accounting for transactions that have not yet been completed in accounting documents, Oracle has encountered difficulties with regulators in the local market.
As a result, Oracle was close to bankruptcy, and competitors such as Informix and Sybase began to slowly increase their market share.
At that time, competition between major market players reached its climax - the 90s could be remembered by many, like the period of the Oracle and Informix advertising war. So, the latter bought a billboard near the office of Oracle and posted on it the inscription "Caution, dinosaurs cross the road", hinting at outdated Oracle technologies.

However, Larry still found a solution: he formed a new management staff, which was “trained” on the huge production volumes and fierce competition. As a result, after a certain time, Oracle returned to its former heights.
And in 1992, the release of Oracle 7 finally changed the situation for the better.
Oracle 7
In addition to a general increase in the efficiency of I / O, the use of a central processor and working with memory, the Oracle 7 DBMS version had a number of innovative architectural solutions:
- shared SQL cache on the server: the server recognizes SQL queries sent by clients that were previously analyzed and compiled and are currently in the cache, thereby saving analysis, optimization and translation time, as well as the memory required for storage SQL queries
- a shared server process pool instead of a separate process for each client, which saves a significant amount of memory.
In the field of database administration, a number of innovations were also introduced: a mirror transaction log, dynamic creation of data logs, the ANALYZE command, which allows you to collect statistics on the use of tables, indexes and other physical objects, user profiles for the use of system resources - CPU, input / output, and so on. Further.
In version 7, declarative referential integrity restrictions were fully implemented in accordance with ANSI / ISO standards. Within the framework of these restrictions (primary and foreign keys), the user could specify the cascading deletion of entries associated with a certain primary key. PL / SQL procedures could be described at the database schema level (stored procedures) and called by any application, other procedures, and triggers.
Another important innovation is database triggers.
A trigger is a pair (event + action), where the event is the deletion / entry / update of table entries, and the action (trigger body) is the PL / SQL procedure that is executed when the event occurs.Security and integrity management has been greatly simplified by the introduction of roles.
Triggers can be defined at the operation level (DELETE, INSERT, UPDATE) or at the level of individual rows (FOR-EACH-ROW triggers, which, in addition, can work with old and new row values). Using triggers, you can implement complex rules for controlling integrity, access rights, value output, and more.
A role is a set of access rights to database objects (INSERT, UPDATE, SELECT, and others) and system rights (CREATE TABLE, ALTER SYSTEM, and so on). Having defined the role, the database administrator can give the user privileges to work with some application with one command.In 1994, the company released a version of Oracle 7.1, including for the IBM PC. Previously, Oracle did not consider this platform as a server platform, but limited itself to creating client parts for its DBMS for it.
Oracle 7.1 introduced the parallel query option, as well as the ability to determine the number of server processes required to execute an SQL query based on the results of the query optimizer. In this version, full integration of PL / SQL and SQL was achieved, the built-in package DBMS_SQL and asynchronous symmetric data replication along with asynchronous call of remote procedures were introduced.
In 1994, the first Oracle official representative, Andreas Hart, appeared in Russia. Then, Oracle customers in Russia became such powerful structures as the FSB, the Cabinet of Ministers, Mosprivatization, Ministry of Railways, RAO UES and so on.
Oracle 8 and 9
In 1997, version 8 was released, in which the object model, new properties, and administrative tools appeared. Oracle 8.0 was more reliable than the previous version, had greater resistance to high loads. In addition, it implemented the ability to partition tables.
In 1998, the company announced Oracle 8i Release 1 (8.1.5). The letter "i" means that the version has Internet support.
Starting with Oracle 8.1.5, in subsequent versions, the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) built into the DBMS appears. Next came the version of Oracle 8i Release 2 (8.1.6), which supported XML, and also contained certain innovations related to the creation of data warehouses.
In 2001, Oracle 9i Release 1 (9.0.1) appeared, in which more than 400 changes were made compared to the previous one. Among them - the "intellectualization" of automated systems and the expansion of opportunities for analytics.
The new version includes tools for processing XML documents, Oracle RAC (Real Application Clusters) technology - as a replacement for Oracle Parallel Server (OPS), Oracle Streams replication creation mechanism, a scrollable cursor for C and C ++ programs, OLAP and Data support built into the DBMS Mining, renaming columns and integrity constraints, support for Java 1.3.1 and Unicode 3.1.
Best financial years
According to the Giga Information Group (The RDBMS Market: An Update, April 2001), the total database market in 2000 increased by 20% compared to 1999 and amounted to $ 8.8 billion in monetary terms. Key development factors: e-commerce support, data warehouse support, and server consolidation.
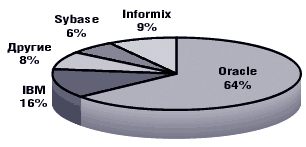
An approximate division of the database market for the Unix platform.

An approximate division of the database market for the Windows NT platform.
In 2004, Oracle 10g Release 1 (10.1.0) was released. The letter "g" in the name means "Grid" ("network") and symbolizes support for Grid-computing.
This year was one of the most successful in the history of the company - the profit margin was 38% (the highest rate for the entire existence of the corporation), annual turnover increased to 7% ($ 10.2 billion), revenue from software sales rose 12% ($ 8 , 1 billion), net income grew 16% ($ 2.7 billion).

The Oracle office in Russia and the CIS was included in the top three Oracle representative offices in terms of growth in the EMEA region (Europe, the Middle East and Africa), and for the fifth year in a row - among the top five among 145 Oracle representative offices in the world.
To the present day
In 2005, Oracle 10g Release 2 (10.2.0.1) was announced. And in 2007 - Oracle 11g Release 1 (11.1.0.6).

DBMS Market Status for 2007
In 2009, the company released Oracle 11g Release 2 (11.2.0.1). A new feature for Oracle was introduced into the version that allows for “hot” (without stopping the server) modification of metadata and business logic on PL / SQL - this was made possible thanks to the mechanism of simultaneous support of several versions of the scheme and logic called editions.
2013 - version 12c (12.1.0.1) was released, the main innovation is support for pluggable databases, which provides multi-tenancy and live database migration properties, the suffix “c” in the name stands for cloud.
April 24, 2015 it became known about Oracle’s plans to transfer almost all of its products to the cloud. Thus, the American company decided to change its business model to match changes in the market.

In September 2016, Larry Ellison announced the creation of second-generation IaaS data centers at Oracle and said that Amazon’s leadership in the cloud market is coming to an end. The company's goal is to offer Oracle customers a package of services where IaaS, PaaS and SaaS (“Software as a Service”) will be combined.
